Unlocking Growth: How CRM for Small Business Analytics Transforms Your Operations
In the dynamic landscape of modern business, small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) often find themselves navigating a complex web of customer interactions, sales pipelines, and operational intricacies. The ability to effectively manage and analyze this data is no longer a luxury; it’s a necessity for survival and sustainable growth. This is where a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system integrated with robust analytics capabilities steps in as a game-changer.
This comprehensive guide delves into the transformative power of CRM for small business analytics. We’ll explore how this powerful combination can revolutionize your business, streamline operations, and empower you to make data-driven decisions that propel your company forward. From understanding the fundamental concepts to implementing practical strategies, we’ll cover everything you need to know to leverage the full potential of CRM and analytics.
Understanding the Fundamentals: CRM and Business Analytics
Before diving into the specifics, let’s establish a solid foundation by defining the key components: CRM and Business Analytics.
What is CRM?
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) is more than just software; it’s a strategic approach to managing and nurturing your company’s interactions with current and potential customers. At its core, a CRM system serves as a centralized hub for all customer-related data, including contact information, communication history, purchase history, and more. This consolidated view allows businesses to gain a comprehensive understanding of their customers, enabling them to personalize interactions, improve customer service, and ultimately, drive sales.
Think of a CRM system as the central nervous system of your customer relationships. It collects, organizes, and disseminates vital information, ensuring that every interaction is informed and effective. This can include:
- Contact Management: Storing and managing customer contact details, including names, addresses, phone numbers, and email addresses.
- Lead Management: Tracking potential customers (leads) through the sales pipeline, from initial contact to conversion.
- Sales Automation: Automating repetitive sales tasks, such as email follow-ups and appointment scheduling, freeing up sales teams to focus on building relationships.
- Marketing Automation: Automating marketing campaigns, such as email blasts and social media posts, to nurture leads and promote products or services.
- Customer Service: Managing customer inquiries, complaints, and support requests, ensuring prompt and efficient resolution.
What is Business Analytics?
Business Analytics (BA) is the process of using data to gain insights into business performance and make informed decisions. It involves collecting, cleaning, analyzing, and interpreting data to identify trends, patterns, and anomalies. This information is then used to improve business processes, optimize resource allocation, and ultimately, drive profitability.
Business analytics transforms raw data into actionable intelligence. By applying various analytical techniques, such as statistical analysis, data mining, and predictive modeling, businesses can uncover hidden insights that would otherwise remain invisible. Key areas where business analytics can be applied include:
- Sales Analysis: Identifying top-performing products, sales trends, and customer segments.
- Marketing Analysis: Measuring the effectiveness of marketing campaigns, identifying target audiences, and optimizing marketing spend.
- Customer Analysis: Understanding customer behavior, identifying customer churn risks, and improving customer satisfaction.
- Operations Analysis: Optimizing operational efficiency, identifying bottlenecks, and reducing costs.
The Synergy: CRM for Small Business Analytics
The true power lies in the integration of CRM and business analytics. When combined, these two powerful tools create a synergistic effect that amplifies their individual strengths. A CRM system provides the data, while business analytics provides the tools to analyze it. This allows small businesses to gain a deeper understanding of their customers, sales processes, and overall business performance.
Here’s how CRM for small business analytics works:
- Data Collection: The CRM system collects and stores all customer-related data, creating a rich data repository.
- Data Integration: The CRM system integrates with other data sources, such as marketing platforms, sales tools, and financial systems, to provide a holistic view of the business.
- Data Analysis: Business analytics tools are used to analyze the data, identify trends, and generate insights.
- Reporting and Visualization: The insights are presented in the form of reports, dashboards, and visualizations, making it easy to understand and share information.
- Decision-Making: Based on the insights, businesses can make data-driven decisions to improve their performance.
Benefits of Implementing CRM for Small Business Analytics
The advantages of implementing CRM for small business analytics are numerous and far-reaching. By leveraging the power of data, small businesses can achieve significant improvements in various areas of their operations. Some of the most notable benefits include:
Improved Customer Understanding
A CRM system provides a 360-degree view of your customers, giving you a deeper understanding of their needs, preferences, and behaviors. This allows you to personalize interactions, tailor your products and services, and build stronger customer relationships. You can:
- Identify Customer Segments: Group customers based on demographics, purchase history, and other factors to create targeted marketing campaigns.
- Understand Customer Preferences: Track customer interactions, such as website visits and email opens, to gain insights into their interests.
- Personalize Customer Communication: Tailor your messaging and offers to resonate with individual customers.
- Improve Customer Service: Provide faster and more efficient support by having access to a complete customer history.
Enhanced Sales Performance
CRM for small business analytics helps you optimize your sales process, improve lead conversion rates, and increase revenue. You can:
- Track Sales Performance: Monitor sales metrics, such as sales revenue, deal size, and conversion rates, to identify areas for improvement.
- Improve Lead Management: Track leads through the sales pipeline, identify bottlenecks, and optimize lead nurturing strategies.
- Forecast Sales: Use historical data to predict future sales and make informed decisions about resource allocation.
- Increase Sales Efficiency: Automate repetitive sales tasks, such as email follow-ups and appointment scheduling, to free up sales teams to focus on selling.
Increased Marketing Effectiveness
By analyzing customer data and marketing campaign performance, you can optimize your marketing efforts, reach the right audience, and improve your return on investment (ROI). You can:
- Track Marketing Campaign Performance: Measure the effectiveness of your marketing campaigns, such as email marketing, social media marketing, and paid advertising.
- Identify Target Audiences: Use customer data to identify the most profitable customer segments and tailor your marketing messages accordingly.
- Optimize Marketing Spend: Allocate your marketing budget to the most effective channels and campaigns.
- Personalize Marketing Messages: Tailor your marketing messages to resonate with individual customers.
Improved Operational Efficiency
CRM for small business analytics helps you streamline your operations, reduce costs, and improve overall efficiency. You can:
- Automate Business Processes: Automate repetitive tasks, such as data entry and report generation, to free up employees to focus on more strategic activities.
- Identify Bottlenecks: Analyze your business processes to identify areas where efficiency can be improved.
- Reduce Costs: Optimize your resource allocation and reduce unnecessary expenses.
- Improve Decision-Making: Make data-driven decisions to improve your overall business performance.
Choosing the Right CRM System for Small Business Analytics
Selecting the right CRM system is crucial for maximizing the benefits of CRM for small business analytics. There are numerous CRM systems available, each with its own features, pricing, and target audience. Here are some key factors to consider when choosing a CRM system:
Features and Functionality
Ensure the CRM system offers the features and functionality you need to manage your customer relationships, sales process, and marketing campaigns. Consider the following features:
- Contact Management: Ability to store and manage customer contact details, including names, addresses, phone numbers, and email addresses.
- Lead Management: Ability to track leads through the sales pipeline, from initial contact to conversion.
- Sales Automation: Ability to automate repetitive sales tasks, such as email follow-ups and appointment scheduling.
- Marketing Automation: Ability to automate marketing campaigns, such as email blasts and social media posts.
- Reporting and Analytics: Ability to generate reports and dashboards to track key metrics and gain insights into your business performance.
- Integration: Ability to integrate with other tools and platforms, such as your website, email marketing software, and accounting system.
Ease of Use
Choose a CRM system that is easy to use and navigate. A user-friendly interface will ensure that your employees can quickly adopt the system and use it effectively. Look for a system with:
- Intuitive Interface: An interface that is easy to understand and navigate.
- Customization Options: Ability to customize the system to meet your specific needs.
- Training and Support: Access to training resources and customer support to help you get started and troubleshoot any issues.
Scalability
Choose a CRM system that can scale with your business. As your business grows, you’ll need a system that can handle an increasing number of customers, leads, and transactions. Consider the following:
- Storage Capacity: Ensure the system can store a sufficient amount of data.
- User Limits: Ensure the system can accommodate the number of users you need.
- Integration Capabilities: Ensure the system can integrate with other tools and platforms as your business grows.
Pricing and Budget
Consider your budget and choose a CRM system that offers a pricing plan that fits your needs. There are various pricing models available, including:
- Free Plans: Some CRM systems offer free plans with limited features.
- Subscription Plans: Most CRM systems offer subscription plans with monthly or annual fees.
- Custom Pricing: Some CRM systems offer custom pricing for larger businesses.
Integration Capabilities
Make sure the CRM system integrates with the other tools and platforms you use, such as your website, email marketing software, and accounting system. This will ensure that data flows seamlessly between your different systems and that you have a complete view of your business.
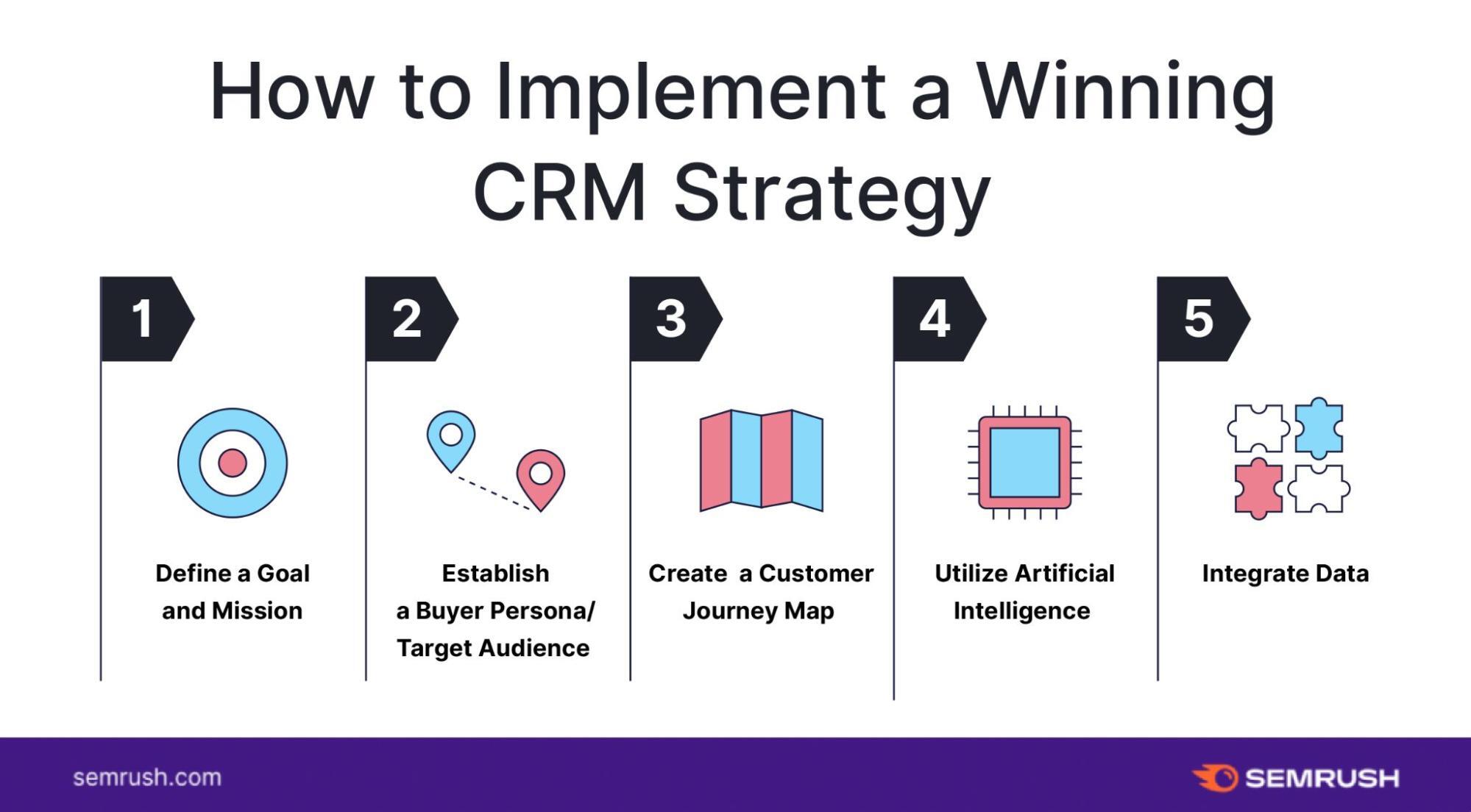
Implementing CRM for Small Business Analytics: A Step-by-Step Guide
Implementing CRM for small business analytics can seem daunting, but with a well-defined plan, you can ensure a smooth transition and maximize your chances of success. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you get started:
1. Define Your Goals and Objectives
Before you begin, clearly define your goals and objectives for implementing CRM. What do you want to achieve? Are you looking to improve customer satisfaction, increase sales, or streamline your operations? Having clear goals will help you choose the right CRM system and measure its success.
2. Assess Your Current Processes
Analyze your current customer relationship processes. Identify areas where you can improve efficiency and effectiveness. This will help you determine the features and functionality you need in your CRM system.
3. Choose the Right CRM System
Research different CRM systems and choose the one that best fits your needs and budget. Consider the factors discussed above, such as features, ease of use, scalability, and integration capabilities.
4. Plan Your Data Migration
If you’re migrating from an existing system, plan your data migration carefully. Ensure that all your data is transferred accurately and efficiently. Consider cleaning and organizing your data before migrating it to the new CRM system.
5. Customize Your CRM System
Customize the CRM system to meet your specific needs. Configure the system’s settings, create custom fields, and integrate it with other tools and platforms.
6. Train Your Employees
Provide training to your employees on how to use the new CRM system. Ensure that they understand how to enter data, manage customer relationships, and generate reports. Provide ongoing support and training as needed.
7. Implement the CRM System
Roll out the CRM system to your employees. Start with a pilot program to test the system and identify any issues. Then, gradually roll out the system to the rest of your organization.
8. Monitor and Evaluate
Monitor the performance of the CRM system and evaluate its effectiveness. Track key metrics, such as sales revenue, customer satisfaction, and lead conversion rates. Make adjustments as needed to optimize the system’s performance.
Best Practices for Maximizing the Value of CRM for Small Business Analytics
To get the most out of your CRM for small business analytics, it’s essential to follow some best practices. These practices will help you ensure that your CRM system is used effectively and that you’re able to leverage its full potential.
1. Data Accuracy and Consistency
Ensure that your data is accurate and consistent. This means entering data correctly and regularly updating it. Inaccurate data can lead to flawed insights and poor decision-making.
2. Data Segmentation and Targeting
Segment your customer data to create targeted marketing campaigns and personalize customer interactions. This will help you reach the right audience with the right message.
3. Automation and Efficiency
Automate repetitive tasks, such as email follow-ups and appointment scheduling, to save time and improve efficiency. This will free up your employees to focus on more strategic activities.
4. Reporting and Analysis
Regularly generate reports and analyze your data to gain insights into your business performance. Track key metrics, such as sales revenue, customer satisfaction, and lead conversion rates. Use these insights to make informed decisions.
5. Integration and Collaboration
Integrate your CRM system with other tools and platforms, such as your website, email marketing software, and accounting system. This will ensure that data flows seamlessly between your different systems and that you have a complete view of your business. Encourage collaboration between different departments to ensure that everyone is working with the same data.
6. Continuous Improvement
Continuously improve your CRM system and your business processes. Regularly review your CRM system and identify areas where you can improve efficiency and effectiveness. Stay up-to-date on the latest CRM trends and best practices.
Real-World Examples of CRM for Small Business Analytics in Action
Let’s explore some real-world examples of how small businesses are leveraging CRM for analytics to achieve remarkable results:
Example 1: E-commerce Business
An e-commerce business uses CRM to track customer purchase history, website behavior, and email interactions. By analyzing this data, they identify customers who are likely to churn and proactively offer them personalized discounts and promotions, significantly reducing churn rate and increasing customer lifetime value.
Example 2: Consulting Firm
A consulting firm uses CRM to manage their sales pipeline and track the progress of each lead. They analyze the data to identify the most effective lead generation channels and optimize their sales process, resulting in a significant increase in qualified leads and closed deals.
Example 3: Local Retail Store
A local retail store uses CRM to track customer purchase history and preferences. They send personalized email offers based on past purchases, driving repeat business and increasing customer loyalty. They also use the data to optimize their inventory and marketing efforts.
Challenges and Considerations
While CRM for small business analytics offers immense benefits, it’s crucial to be aware of potential challenges and considerations:
Data Privacy and Security
Protecting customer data is paramount. Ensure your CRM system complies with data privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA. Implement robust security measures to protect sensitive customer information.
Data Quality and Accuracy
Garbage in, garbage out. Ensure your data is clean, accurate, and up-to-date. Invest in data cleansing and validation processes to maintain data integrity.
Employee Adoption
Employee resistance to change can hinder CRM implementation. Provide adequate training and support to ensure employees understand the benefits of the system and adopt it effectively.
Integration Complexity
Integrating your CRM system with other tools and platforms can be complex. Carefully plan your integration strategy and seek expert assistance if needed.
Cost and Resources
Implementing and maintaining a CRM system requires investment in software, training, and ongoing support. Carefully consider your budget and allocate sufficient resources.
The Future of CRM for Small Business Analytics
The future of CRM for small business analytics is bright. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more sophisticated features and capabilities:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML will play an increasingly important role in CRM, enabling businesses to automate tasks, personalize customer interactions, and gain deeper insights into customer behavior. Expect to see more AI-powered chatbots, predictive analytics, and automated recommendations.
Mobile CRM
Mobile CRM will become even more prevalent, allowing businesses to access and manage customer data on the go. Expect to see more mobile-optimized CRM apps and features.
Integration with Emerging Technologies
CRM systems will continue to integrate with emerging technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and virtual reality (VR). This will enable businesses to gain even more insights into customer behavior and personalize their interactions.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Data
In conclusion, CRM for small business analytics is no longer a luxury; it’s a strategic imperative for success in today’s competitive landscape. By embracing the power of data, small businesses can gain a deeper understanding of their customers, optimize their sales processes, improve their marketing effectiveness, and streamline their operations. By following the best practices outlined in this guide, you can successfully implement CRM for small business analytics and unlock its transformative potential. Don’t just manage your customer relationships; cultivate them, analyze them, and watch your business flourish.
The journey to data-driven decision-making may seem challenging, but the rewards – increased sales, improved customer satisfaction, and sustainable growth – are well worth the effort. Start today, and embrace the power of data to transform your small business into a thriving enterprise.