Unlocking Engineering Excellence: The Ultimate CRM Guide for Small Engineering Firms
Introduction: Why Small Engineering Firms Need a CRM
In the dynamic world of engineering, where precision and collaboration are paramount, maintaining a competitive edge requires more than just technical expertise. It demands a robust system for managing client relationships, streamlining workflows, and maximizing efficiency. This is where a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system comes into play. For small engineering firms, the right CRM can be the difference between struggling to stay afloat and thriving in a competitive market.
Choosing the best CRM for a small engineering firm isn’t just about picking a software; it’s about investing in a strategic tool that can transform how you operate. It’s about empowering your team to focus on what they do best: engineering. This comprehensive guide will delve into the essential features, benefits, and considerations for selecting the perfect CRM to propel your firm towards success. We’ll explore the specific needs of small engineering companies, dissect the top CRM options available, and provide practical advice to ensure a smooth implementation process.
The Unique Challenges Faced by Small Engineering Firms
Small engineering firms face a unique set of challenges that often require tailored solutions. Unlike larger corporations, these firms typically operate with limited resources, a lean team, and a strong emphasis on personalized client interactions. Key challenges include:
- Client Relationship Management: Building and maintaining strong relationships with clients is critical. Small firms rely heavily on repeat business and referrals, making effective client communication and follow-up essential.
- Project Management: Engineering projects are complex and multifaceted. Managing timelines, budgets, and resources efficiently is crucial for profitability and client satisfaction.
- Lead Generation and Sales: Finding and converting new leads can be a significant hurdle. Small firms often lack dedicated sales teams, so they must rely on efficient lead management and conversion strategies.
- Collaboration and Communication: Effective communication among team members and with clients is vital. This includes sharing project updates, managing documentation, and facilitating feedback.
- Data Management and Security: Protecting sensitive client data and project information is paramount. Small firms need a secure and reliable system to store and manage their data.
A CRM system can address these challenges by providing a centralized platform for managing all aspects of the business, from lead generation to project completion. It can automate tasks, improve communication, and provide valuable insights into business performance.
Key Features to Look for in a CRM for Engineers
When selecting a CRM for a small engineering firm, it’s crucial to focus on features that directly address the specific needs of the industry. Here’s a breakdown of the essential features to consider:
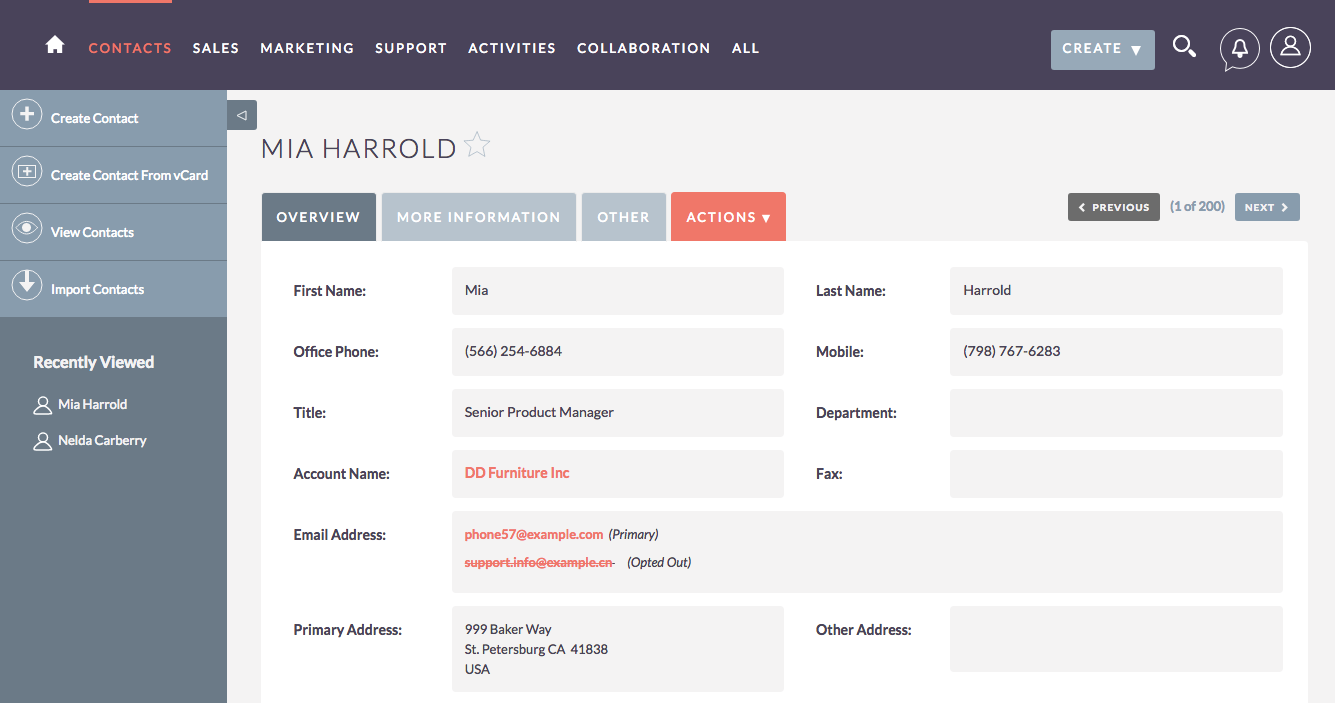
1. Contact and Lead Management
This is the foundation of any CRM. It allows you to store and organize client information, track interactions, and manage leads effectively. Look for features like:
- Contact Database: A centralized repository for storing client contact details, including names, addresses, phone numbers, email addresses, and other relevant information.
- Lead Tracking: The ability to track leads from initial contact through the sales pipeline, including lead source, status, and activity history.
- Segmentation: The ability to segment leads and contacts based on various criteria, such as industry, project type, or location, for targeted marketing and communication.
- Activity Tracking: Logging all interactions with clients and leads, including calls, emails, meetings, and notes.
2. Project Management Integration
Engineering projects are often complex, requiring detailed planning, resource allocation, and progress tracking. A CRM that integrates with project management tools or offers project management features can significantly streamline workflows. Consider these features:
- Task Management: The ability to create, assign, and track tasks related to specific projects.
- Timeline and Milestone Tracking: Visual representations of project timelines and milestones to ensure projects stay on schedule.
- Resource Allocation: The ability to allocate resources, such as team members and equipment, to specific tasks and projects.
- Budget Tracking: Tracking project budgets and expenses to monitor profitability.
3. Sales Pipeline Automation
Automating sales processes can save time and improve conversion rates. Look for CRM features that streamline the sales pipeline, such as:
- Automated Email Sequences: Sending pre-written email sequences to leads based on their stage in the sales pipeline.
- Sales Automation Workflows: Automating tasks such as follow-up calls, meeting scheduling, and proposal generation.
- Deal Tracking: Monitoring the progress of sales deals, including the probability of closing and the estimated revenue.
4. Reporting and Analytics
Data-driven decision-making is essential for business success. A good CRM provides valuable insights into business performance through reporting and analytics. Key features include:
- Customizable Dashboards: Displaying key performance indicators (KPIs) in a visually appealing and easy-to-understand format.
- Sales Reports: Tracking sales performance, including revenue, conversion rates, and deal closure rates.
- Project Performance Reports: Analyzing project profitability, timelines, and resource utilization.
- Lead Source Analysis: Identifying the most effective lead generation channels.
5. Communication and Collaboration Tools
Effective communication is crucial for both internal team members and external clients. Look for a CRM that offers communication and collaboration features, such as:
- Email Integration: Integrating with your email provider to send and receive emails directly from the CRM.
- Meeting Scheduling: Scheduling meetings with clients and team members directly from the CRM.
- Document Management: Storing and sharing project documents, such as proposals, contracts, and drawings.
- Collaboration Tools: Features that facilitate communication and collaboration among team members, such as internal messaging and task assignments.
6. Mobile Accessibility
In today’s fast-paced world, it’s important to have access to your CRM data on the go. Look for a CRM that offers a mobile app or a mobile-responsive interface.
7. Integration Capabilities
The CRM should integrate with other tools you use, such as accounting software, email marketing platforms, and project management software. This will streamline your workflows and eliminate the need for manual data entry.
Top CRM Systems for Small Engineering Firms
With a clear understanding of essential features, let’s examine some of the top CRM systems specifically suited for small engineering firms. Each CRM offers a unique set of strengths, so the best choice will depend on your firm’s specific needs and priorities.
1. HubSpot CRM
Overview: HubSpot CRM is a popular choice for small businesses, and for good reason. It offers a free version with a robust set of features, making it an excellent starting point for firms on a budget. Its user-friendly interface and comprehensive features make it easy to adopt and use.
Key Features for Engineers:
- Free Forever Plan: Offers a generous free plan with contact management, deal tracking, and email marketing features.
- Sales Pipeline Management: Intuitive sales pipeline visualization and deal tracking.
- Email Integration: Seamlessly integrates with popular email providers, allowing you to track email interactions.
- Reporting and Analytics: Provides basic reporting and analytics to track sales performance.
- Integrations: Integrates with a wide range of other tools, including project management software and accounting platforms.
Pros:
- Free plan is incredibly valuable.
- User-friendly interface.
- Excellent for sales and marketing automation.
- Large ecosystem of integrations.
Cons:
- The free plan has limitations on the number of contacts and features.
- More advanced features require paid plans.
- May not have all the project management features some engineering firms require.
2. Zoho CRM
Overview: Zoho CRM is a comprehensive CRM system that offers a wide range of features at a competitive price point. It’s a great option for small engineering firms looking for a powerful and customizable CRM solution.
Key Features for Engineers:
- Customization: Highly customizable to fit the specific needs of your engineering firm.
- Workflow Automation: Powerful workflow automation to streamline tasks and processes.
- Project Management Integration: Integrates with Zoho Projects and other project management tools.
- Sales Force Automation: Comprehensive sales force automation features, including lead management, opportunity management, and sales forecasting.
- Reporting and Analytics: Robust reporting and analytics capabilities.
Pros:
- Highly customizable.
- Feature-rich at a competitive price.
- Excellent workflow automation capabilities.
- Strong integration with other Zoho apps.
Cons:
- Can be overwhelming for new users due to the number of features.
- The user interface can feel cluttered.
- Learning curve can be steeper than some other options.
3. Pipedrive
Overview: Pipedrive is a sales-focused CRM that’s known for its simplicity and ease of use. It’s a great choice for small engineering firms that prioritize sales and lead management.
Key Features for Engineers:
- Visual Sales Pipeline: Intuitive visual sales pipeline for tracking deals and opportunities.
- Lead Management: Effective lead management features, including lead scoring and lead tracking.
- Email Integration: Seamless email integration with email tracking and reporting.
- Automation: Automated tasks and workflows to streamline sales processes.
- Reporting: Provides sales-focused reporting and analytics.
Pros:
- Easy to use and set up.
- Excellent visual sales pipeline.
- Focuses on sales productivity.
- Good value for the price.
Cons:
- May lack some of the advanced features of other CRMs.
- Less emphasis on project management features.
- Reporting is primarily focused on sales.
4. Monday.com
Overview: While not solely a CRM, Monday.com is a versatile work management platform that can be customized to serve as a CRM. It’s a good option for engineering firms that need a flexible and collaborative platform.
Key Features for Engineers:
- Customizable Workflows: Highly customizable workflows to manage projects, leads, and clients.
- Project Management: Strong project management features, including task management, timeline tracking, and resource allocation.
- Collaboration: Excellent collaboration tools, including team messaging and file sharing.
- Visual Interface: Intuitive and visually appealing interface.
- Integrations: Integrates with a variety of other tools.
Pros:
- Highly flexible and customizable.
- Excellent project management features.
- Strong collaboration tools.
- Visually appealing interface.
Cons:
- Can be more expensive than other CRMs.
- May require more setup and configuration.
- Not as sales-focused as some other options.
5. Freshsales (Freshworks CRM)
Overview: Freshsales, now part of Freshworks CRM, is another strong contender, particularly for firms wanting robust sales and marketing automation features. It’s known for its user-friendliness and affordability.
Key Features for Engineers:
- Built-in Phone and Email: Offers integrated phone and email functionalities, streamlining communication.
- AI-Powered Chatbots: Provides AI-powered chatbots for lead qualification and customer support.
- Sales Sequences: Allows you to create automated sales sequences to nurture leads.
- Reporting and Analytics: Offers comprehensive reporting and analytics.
- User-Friendly Interface: Easy to navigate and use.
Pros:
- User-friendly interface.
- Strong sales and marketing automation features.
- Affordable pricing.
- Integrated phone and email.
Cons:
- May lack some of the advanced project management features of other CRMs.
- Can feel slightly less customizable than some other options.
Implementing a CRM: A Step-by-Step Guide
Choosing the right CRM is only the first step. Successful implementation requires careful planning and execution. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you implement your new CRM effectively:
1. Define Your Goals and Objectives
Before you start, clearly define your goals and objectives for implementing a CRM. What do you want to achieve? Are you looking to increase sales, improve client satisfaction, streamline project management, or all of the above? Having clear goals will guide your implementation process and help you measure your success.
2. Assess Your Current Processes
Analyze your existing processes for client management, sales, and project management. Identify any inefficiencies or bottlenecks. This will help you determine which features of the CRM are most important to your firm and how to customize the system to fit your needs.
3. Choose the Right CRM
Based on your needs assessment, choose the CRM that best fits your requirements. Consider factors such as features, pricing, ease of use, and integration capabilities.
4. Plan Your Implementation
Develop a detailed implementation plan that includes timelines, responsibilities, and milestones. This will help you stay on track and ensure a smooth transition. Break down the implementation process into smaller, manageable steps.
5. Data Migration
Migrate your existing data from your spreadsheets, databases, or other systems into the CRM. Ensure that your data is accurate, complete, and well-organized. Clean up your data to avoid duplicates or errors. This is a critical step, so take the time to do it right.
6. Customize the CRM
Customize the CRM to fit your specific needs. This may involve configuring fields, creating custom workflows, and integrating with other tools. Tailor the system to match your engineering firm’s unique processes and terminology.
7. Train Your Team
Provide comprehensive training to your team on how to use the CRM. This should include both basic and advanced features. Offer ongoing support and training to ensure that your team is comfortable using the system and can take full advantage of its capabilities. Consider using video tutorials, online documentation, and in-person training sessions.
8. Test and Iterate
Test the CRM thoroughly before launching it. Make sure that all features are working correctly and that your team is comfortable using the system. Gather feedback from your team and make any necessary adjustments. Implement an iterative approach, continuously refining the system based on user feedback and changing business needs.
9. Monitor and Evaluate
Regularly monitor the performance of the CRM and evaluate whether it’s meeting your goals. Track key metrics, such as sales conversion rates, client satisfaction, and project profitability. Use the data to identify areas for improvement and make adjustments to your processes or the CRM configuration.
10. Provide Ongoing Support
Offer ongoing support to your team. This includes providing technical assistance, answering questions, and offering training. Ensure that your team has the resources they need to use the CRM effectively.
Maximizing the Benefits of Your CRM
Once your CRM is implemented, it’s time to maximize its benefits. Here are some tips for getting the most out of your CRM:
- Use the CRM consistently: Encourage your team to use the CRM daily to track interactions, manage leads, and update project information. Consistent use ensures that your data is accurate and up-to-date.
- Automate tasks: Leverage the CRM’s automation features to streamline your workflows and save time. Automate tasks such as email follow-ups, task assignments, and report generation.
- Segment your data: Use data segmentation to target your marketing and sales efforts. Create targeted campaigns based on client industry, project type, or other criteria.
- Analyze your data: Regularly review your CRM data to identify trends, measure performance, and make data-driven decisions. Use the reports and analytics to gain insights into your business.
- Integrate with other tools: Integrate your CRM with other tools, such as project management software, accounting software, and email marketing platforms, to create a seamless workflow.
- Regularly review and update your CRM: As your business grows and your needs change, regularly review and update your CRM. Add new features, customize workflows, and integrate with new tools.
- Foster a CRM-focused culture: Encourage a culture of CRM usage within your firm. Emphasize the importance of using the CRM and provide incentives for consistent and effective use.
Conclusion: Embracing CRM for Engineering Success
In conclusion, for small engineering firms, adopting the right CRM is not just a technological upgrade; it’s a strategic investment in future success. By choosing a CRM that aligns with their specific needs, implementing it effectively, and maximizing its benefits, engineering firms can significantly improve their client relationships, streamline their projects, and boost their overall efficiency. The right CRM provides a centralized hub for all client and project-related information, fostering better communication, collaboration, and decision-making. It empowers engineering teams to focus on what they excel at: creating innovative solutions. As the engineering landscape continues to evolve, embracing a CRM is no longer optional; it’s essential for staying competitive and achieving long-term success.
By taking the time to research, plan, and implement a CRM strategically, small engineering firms can unlock their full potential, drive growth, and thrive in the dynamic world of engineering.