Unlock Growth: Essential CRM Features for Small Businesses in 2024

Unlock Growth: Essential CRM Features for Small Businesses in 2024
Running a small business is a rollercoaster. There are highs, lows, moments of sheer panic, and incredible bursts of joy. One thing that can make the ride a whole lot smoother, and significantly increase your chances of success, is a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system. But with so many options out there, choosing the right CRM and understanding its features can feel overwhelming. This article will break down the essential CRM features for small businesses, equipping you with the knowledge to select the perfect tool to fuel your growth in 2024 and beyond.
What is a CRM and Why Does Your Small Business Need One?
Before diving into features, let’s clarify what a CRM actually *is*. At its core, a CRM is a software solution designed to manage all your interactions with current and potential customers. Think of it as your central hub for everything customer-related. It helps you organize, track, and analyze every touchpoint – from initial contact to post-sale support. A CRM isn’t just about storing contact information; it’s about building lasting relationships and driving revenue.
Why is a CRM so crucial for small businesses? Here are a few compelling reasons:
- Improved Customer Relationships: A CRM provides a 360-degree view of each customer, allowing you to personalize interactions and build stronger relationships.
- Increased Sales: By streamlining the sales process and providing sales teams with valuable insights, a CRM can significantly boost sales performance.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Automate repetitive tasks, freeing up your team to focus on higher-value activities.
- Better Data Analysis: Gain valuable insights into customer behavior, sales trends, and marketing campaign performance.
- Scalability: A CRM grows with your business, ensuring you have the tools you need as you expand.
Essential CRM Features for Small Businesses
Now, let’s delve into the core features that are essential for small business CRM success. These are the building blocks of a robust CRM system, providing the foundation for effective customer management and business growth.
1. Contact Management
At its heart, a CRM is about managing contacts. This feature allows you to store and organize all your customer information in one centralized location. Key aspects of contact management include:
- Contact Database: Store contact details such as names, email addresses, phone numbers, and physical addresses.
- Contact Segmentation: Group contacts based on various criteria, such as demographics, purchase history, or lead source. This allows for targeted marketing and personalized communication.
- Contact Import/Export: Easily import contact data from spreadsheets or other sources and export it for backup or analysis.
- Activity Tracking: Log all interactions with a contact, including emails, calls, meetings, and notes.
- Duplicate Detection: Prevent the creation of duplicate contact entries, ensuring data accuracy and consistency.
A well-organized contact database is the cornerstone of any successful CRM implementation. It provides a single source of truth for all customer information, making it easier to manage relationships and personalize interactions.
2. Lead Management
Lead management is the process of tracking and nurturing potential customers through the sales funnel. This feature helps you capture leads, qualify them, and guide them towards conversion. Key elements of lead management include:
- Lead Capture: Capture leads from various sources, such as website forms, landing pages, and social media.
- Lead Scoring: Assign scores to leads based on their engagement and demographics, helping you prioritize the most promising prospects.
- Lead Qualification: Determine whether a lead is a good fit for your business based on predefined criteria.
- Lead Nurturing: Automate email campaigns and other communication to nurture leads and move them through the sales funnel.
- Lead Assignment: Automatically assign leads to sales representatives based on criteria such as geography or product interest.
Effective lead management can significantly improve your sales conversion rates by ensuring that your sales team focuses on the most qualified prospects and provides them with the right information at the right time.
3. Sales Automation
Sales automation streamlines the sales process by automating repetitive tasks, freeing up sales reps to focus on closing deals. Key aspects of sales automation include:
- Workflow Automation: Automate tasks such as sending follow-up emails, updating deal stages, and creating tasks for sales reps.
- Email Automation: Automate email sequences for lead nurturing, sales follow-up, and customer onboarding.
- Task Automation: Automatically create and assign tasks based on specific triggers, such as a new lead or a completed deal stage.
- Deal Management: Track the progress of deals through the sales pipeline, from initial contact to closed won.
- Sales Reporting: Generate reports on sales performance, including sales pipeline, conversion rates, and revenue.
Sales automation can significantly improve sales efficiency and productivity, allowing your team to close more deals in less time.
4. Marketing Automation
Marketing automation helps you automate marketing tasks, such as email marketing, social media posting, and lead nurturing. Key aspects of marketing automation include:
- Email Marketing: Create and send targeted email campaigns to your contacts.
- Marketing Segmentation: Segment your contacts based on demographics, behavior, or other criteria to personalize your marketing messages.
- Campaign Management: Track the performance of your marketing campaigns, including open rates, click-through rates, and conversions.
- Social Media Integration: Connect your CRM to your social media accounts to manage your social media presence and track social media engagement.
- Landing Page Creation: Create landing pages to capture leads and promote your products or services.
Marketing automation can help you reach more potential customers, nurture leads, and drive sales. It can also save you time and effort by automating repetitive marketing tasks.
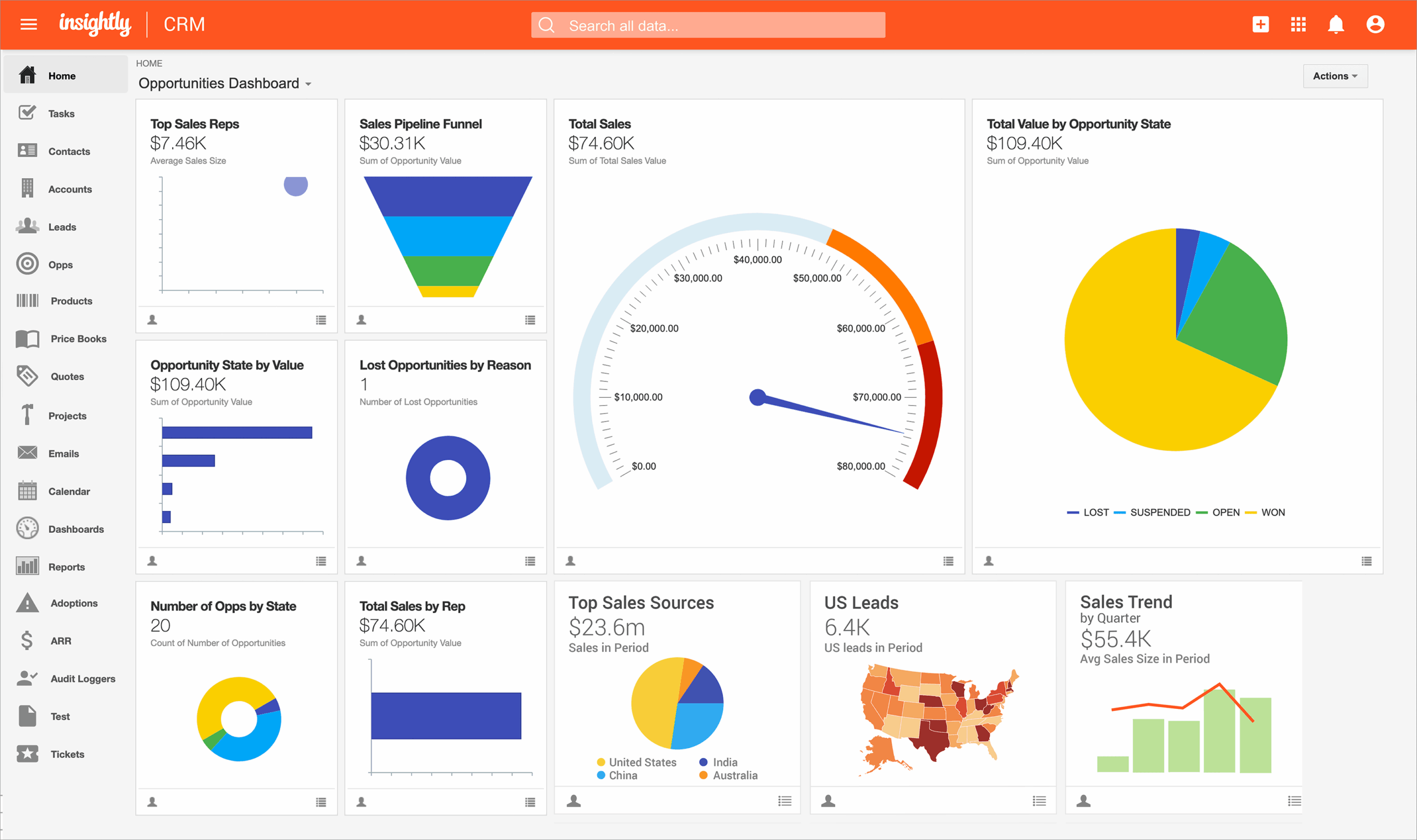
5. Reporting and Analytics
Reporting and analytics provide valuable insights into your sales and marketing performance. Key aspects of reporting and analytics include:
- Sales Reports: Track sales performance, including sales pipeline, conversion rates, and revenue.
- Marketing Reports: Track the performance of your marketing campaigns, including open rates, click-through rates, and conversions.
- Customer Analytics: Analyze customer behavior, such as purchase history and engagement with your website and marketing materials.
- Customizable Dashboards: Create custom dashboards to track the metrics that are most important to your business.
- Data Visualization: Visualize your data using charts and graphs to identify trends and insights.
Reporting and analytics provide the data you need to make informed decisions about your sales and marketing strategies. They help you identify what’s working and what’s not, so you can optimize your efforts and improve your results.
6. Integrations
Integration capabilities are crucial for a CRM to seamlessly fit within your existing tech stack. Key integration features include:
- Email Integration: Integrate with popular email providers like Gmail, Outlook, and others.
- Accounting Software Integration: Connect with accounting software such as QuickBooks or Xero.
- E-commerce Platform Integration: Integrate with platforms like Shopify or WooCommerce.
- Social Media Integration: Connect with social media platforms for social listening and engagement.
- API Access: APIs allow for custom integrations with other business applications.
Seamless integrations ensure that your CRM works in harmony with your other business tools, creating a unified view of your customers and streamlining your workflows.
Advanced CRM Features for Small Businesses
Beyond the core features, some advanced functionalities can provide a significant competitive advantage. These often provide more specialized capabilities to help businesses scale and enhance customer relationships.
1. Mobile CRM
In today’s fast-paced world, having access to your CRM on the go is essential. A mobile CRM allows your sales team to access customer information, update records, and manage deals from anywhere, anytime. Key features include:
- Mobile App: A dedicated mobile app for iOS and Android devices.
- Offline Access: Access to customer data even without an internet connection.
- Push Notifications: Receive real-time notifications about important updates and tasks.
- Geolocation Tracking: Track the location of your sales team and log customer visits.
- Voice-to-Text Input: Quickly add notes and update records using voice commands.
A mobile CRM empowers your sales team to be more productive and responsive, allowing them to close deals faster and provide better customer service.
2. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML are transforming the CRM landscape, providing advanced capabilities for data analysis, lead scoring, and personalization. Key features include:
- Predictive Analytics: Predict customer behavior and identify potential sales opportunities.
- Lead Scoring: Automatically score leads based on their likelihood to convert.
- Chatbots: Provide instant customer support and answer frequently asked questions.
- Personalized Recommendations: Recommend products or services based on customer preferences and behavior.
- Data Insights: Identify trends and insights in your customer data.
AI and ML can help you automate tasks, personalize customer interactions, and improve your sales and marketing performance.
3. Workflow Automation (Advanced)
While basic workflow automation is a core feature, advanced workflow automation offers more sophisticated capabilities. Key features include:
- Conditional Logic: Create workflows that respond to specific conditions and triggers.
- Multi-Step Workflows: Create complex workflows that involve multiple steps and actions.
- Integration with Other Systems: Integrate workflows with other business applications.
- Customizable Workflows: Customize workflows to meet your specific business needs.
- Workflow Reporting: Track the performance of your workflows and identify areas for improvement.
Advanced workflow automation can help you streamline complex business processes and improve efficiency.
4. Customer Service and Support Features
CRM systems often include features to improve customer service and support. Key features include:
- Help Desk Integration: Integrate with help desk software to manage customer support tickets.
- Live Chat: Provide real-time customer support through live chat.
- Knowledge Base: Create a knowledge base of articles and FAQs to help customers find answers to their questions.
- Customer Portal: Provide customers with a self-service portal where they can access information and manage their accounts.
- Case Management: Track and manage customer support cases.
These features can help you provide excellent customer service and build stronger customer relationships.
Choosing the Right CRM for Your Small Business
Selecting the right CRM is a crucial decision. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you choose the best CRM for your small business:
1. Define Your Needs and Goals
Before you start shopping, take the time to define your specific needs and goals. What are you hoping to achieve with a CRM? What are your biggest pain points? What features are essential for your business? Consider the following:
- Sales Goals: What are your sales targets?
- Marketing Goals: What are your marketing objectives?
- Customer Service Goals: What are your customer service standards?
- Budget: How much are you willing to spend on a CRM?
- Team Size: How many users will need access to the CRM?
- Industry: Does your industry have specific requirements or regulations?
Answering these questions will help you narrow down your options and choose a CRM that aligns with your business objectives.
2. Research CRM Providers
Once you know your needs, research the available CRM providers. Consider the following:
- Features: Does the CRM offer the features you need?
- Pricing: Is the pricing affordable and scalable?
- Ease of Use: Is the CRM easy to use and navigate?
- Integrations: Does the CRM integrate with your existing business tools?
- Customer Support: Does the CRM provider offer good customer support?
- Reviews: Read reviews from other small businesses to get an idea of the CRM’s strengths and weaknesses.
- Scalability: Can the CRM grow with your business?
Take advantage of free trials or demos to test out different CRMs and see which one best suits your needs.
3. Consider Your Budget
CRM pricing can vary widely, from free options for very small businesses to enterprise-level solutions with significant monthly fees. When considering your budget, take the following factors into account:
- Subscription Fees: Monthly or annual fees for the CRM software.
- Implementation Costs: Costs associated with setting up and configuring the CRM.
- Training Costs: Costs associated with training your team on how to use the CRM.
- Customization Costs: Costs associated with customizing the CRM to meet your specific needs.
- Ongoing Maintenance Costs: Costs associated with maintaining and updating the CRM.
Choose a CRM that fits within your budget and offers a good return on investment. Remember that free CRM options often have limitations in features or user capacity.
4. Prioritize Ease of Use
A CRM is only effective if your team actually uses it. Choose a CRM that is easy to use and navigate. Consider the following:
- User Interface: Is the user interface intuitive and user-friendly?
- Onboarding: Does the CRM provider offer good onboarding support?
- Training Materials: Are there training materials available, such as tutorials and documentation?
- Accessibility: Is the CRM accessible on mobile devices?
- Customization Options: Can you customize the CRM to meet your specific needs?
The easier the CRM is to use, the more likely your team is to adopt it and realize its benefits.
5. Plan for Implementation and Training
Implementing a CRM requires careful planning and execution. Consider the following:
- Data Migration: How will you migrate your existing customer data into the CRM?
- Customization: Will you need to customize the CRM to meet your specific needs?
- Training: How will you train your team on how to use the CRM?
- Support: What support will you need from the CRM provider?
- Timeline: How long will it take to implement the CRM?
Develop a detailed implementation plan and allocate sufficient time and resources for training your team.
6. Start Small and Scale Up
Don’t try to implement all the features of your CRM at once. Start with the core features and gradually add more features as your team becomes more comfortable with the system. This approach allows you to:
- Reduce Risk: Minimize the risk of implementation issues.
- Learn and Adapt: Learn from your experience and adapt your approach as needed.
- Increase Adoption: Encourage user adoption by making the transition gradual.
- Optimize the Process: Refine your CRM usage over time to maximize its effectiveness.
This phased approach will allow you to maximize the value of your CRM investment and minimize disruption to your business.
Real-World Examples of CRM Benefits for Small Businesses
Let’s look at a few examples of how small businesses are using CRM features to achieve tangible results:
- Example 1: A retail business. A small clothing boutique uses its CRM to track customer purchase history and preferences. The CRM automatically sends personalized email promotions to customers based on their past purchases, leading to a 15% increase in sales.
- Example 2: A consulting firm. A consulting firm uses its CRM to manage its sales pipeline and track the progress of each deal. By automating follow-up tasks and providing sales reps with real-time insights, the firm increases its close rate by 20%.
- Example 3: A landscaping company. A landscaping company uses its CRM to manage customer service requests and track the resolution of issues. By providing prompt and efficient customer service, the company improves customer satisfaction and reduces churn by 10%.
These are just a few examples of how small businesses are leveraging CRM features to achieve their goals. The specific benefits will vary depending on the nature of your business and how you use the CRM.
Conclusion: Harness the Power of CRM for Small Business Success
In today’s competitive business landscape, a CRM is no longer a luxury but a necessity for small businesses. By implementing the right CRM and utilizing its essential features, you can build stronger customer relationships, increase sales, enhance efficiency, and gain valuable insights into your business. Take the time to research your options, define your needs, and choose the CRM that’s the perfect fit for your small business. With the right CRM in place, you’ll be well-equipped to unlock growth and achieve lasting success in 2024 and beyond. Remember to start with the core features, focus on user adoption, and gradually add more advanced functionalities as your business evolves.