The Ultimate Small Business CRM Checklist: Your Step-by-Step Guide to Success

Running a small business is a whirlwind of activity. You’re juggling a million things at once: managing inventory, marketing your services, keeping track of finances, and, of course, building relationships with your customers. In this chaotic landscape, customer relationship management (CRM) software isn’t just a nice-to-have; it’s a necessity. But where do you even begin? That’s where this comprehensive small business CRM checklist comes in. We’ll walk you through everything, from understanding your needs to choosing the right CRM and implementing it successfully.
Why Your Small Business Needs a CRM
Before we dive into the checklist, let’s talk about why a CRM is so crucial for your small business. Think of it as your central nervous system for all things customer-related. It helps you:
- Organize Customer Data: Say goodbye to scattered spreadsheets and sticky notes. A CRM centralizes all your customer information – contact details, purchase history, communication logs, and more – in one accessible place.
- Improve Customer Relationships: By understanding your customers better, you can personalize your interactions, provide better service, and build stronger relationships.
- Boost Sales: CRM tools help you track leads, manage your sales pipeline, and close deals more effectively.
- Increase Efficiency: Automate repetitive tasks, streamline workflows, and free up your time to focus on what matters most – growing your business.
- Gain Valuable Insights: CRM systems provide data-driven insights into customer behavior, sales performance, and marketing effectiveness, helping you make informed decisions.
In short, a CRM is a powerful tool that can help you work smarter, not harder, and ultimately drive business growth. Now, let’s get to the checklist!
Phase 1: Assessing Your Needs and Goals
Before you even start shopping for CRM software, it’s essential to understand your specific needs and goals. This will guide your selection process and ensure you choose a system that truly fits your business. Here’s what you need to do:
1. Define Your Business Goals
What are you hoping to achieve with a CRM? Are you looking to increase sales, improve customer satisfaction, streamline marketing efforts, or all of the above? Be specific. For example, instead of saying “increase sales,” aim for “increase sales by 15% in the next quarter.”
- Example Goals:
- Increase lead conversion rates by 10%.
- Improve customer retention rates by 5%.
- Reduce customer service response times by 20%.
- Increase average order value by 8%.
Write down your goals and make sure they are SMART: Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound.
2. Identify Your Key Customer Touchpoints
Where do your customers interact with your business? This could include your website, social media channels, email, phone calls, in-person interactions, and more. Mapping out these touchpoints will help you understand where you need to gather and manage customer data.
- Touchpoint Examples:
- Website contact forms
- Social media inquiries
- Email marketing campaigns
- Phone calls with sales reps
- In-store purchases
3. Analyze Your Current Processes
How do you currently manage customer interactions and data? Are you using spreadsheets, email, or a combination of different tools? Identify any inefficiencies, bottlenecks, or areas where you’re losing track of information. This will highlight the features you’ll need in a CRM.
- Process Examples:
- Lead generation and qualification
- Sales pipeline management
- Customer service and support
- Marketing campaign management
- Order processing and fulfillment
4. Determine Your Budget
CRM software pricing varies widely, from free basic plans to enterprise-level solutions. Set a realistic budget based on your business size, needs, and financial resources. Remember to factor in not just the software cost but also the costs of implementation, training, and ongoing maintenance.
5. Involve Key Stakeholders
Gather input from all the departments that will be using the CRM, such as sales, marketing, customer service, and operations. Their feedback will be crucial in determining the features and functionality you need.
Phase 2: Researching and Selecting a CRM
Once you know what you need, it’s time to start exploring your CRM options. This phase involves researching different vendors, comparing features, and evaluating pricing models.
1. Identify Potential CRM Vendors
Start by researching the leading CRM providers in the market. Look for vendors that specialize in small businesses. Some popular options include:
- HubSpot CRM: A popular, free CRM with robust features and integrations.
- Zoho CRM: A comprehensive CRM with a wide range of features and affordable pricing.
- Salesforce Sales Cloud: A powerful CRM with a wide range of customization options, suitable for businesses of all sizes.
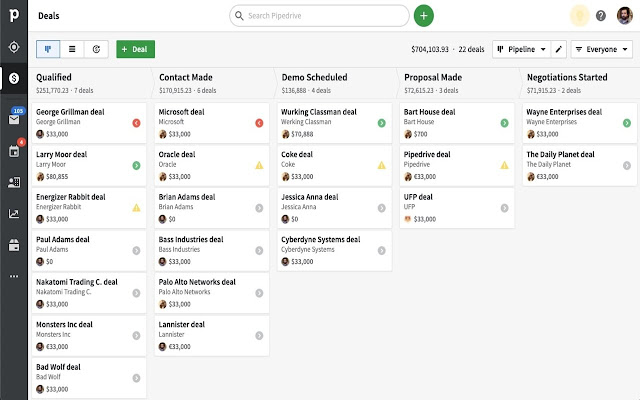
- Pipedrive: A sales-focused CRM with a visual pipeline and intuitive interface.
- Freshsales: An easy-to-use CRM with built-in phone and email features.
- Microsoft Dynamics 365: A complete CRM and ERP solution.
Read reviews, compare features, and create a shortlist of potential vendors.
2. Evaluate Key Features
Consider the following features when evaluating different CRM systems:
- Contact Management: The ability to store and manage customer contact information, including names, addresses, phone numbers, email addresses, and social media profiles.
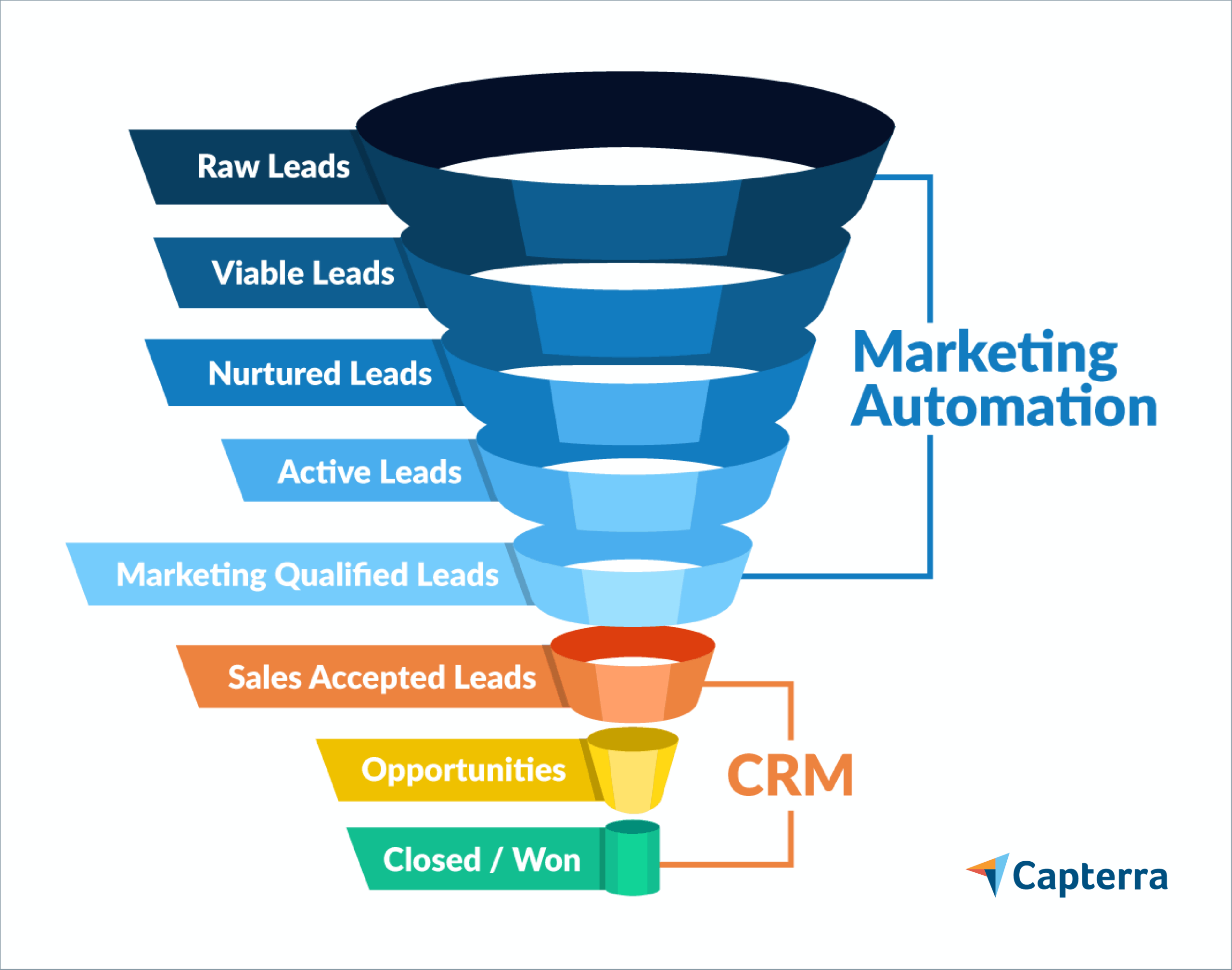
- Lead Management: Tools for capturing, tracking, and nurturing leads, including lead scoring, lead segmentation, and automated follow-up.
- Sales Automation: Features that automate repetitive sales tasks, such as email follow-ups, appointment scheduling, and task management.
- Sales Pipeline Management: A visual representation of your sales pipeline, allowing you to track deals through each stage and identify potential bottlenecks.
- Marketing Automation: Features for automating marketing tasks, such as email marketing, social media posting, and lead nurturing campaigns.
- Customer Service and Support: Tools for managing customer inquiries, resolving issues, and providing excellent customer service.
- Reporting and Analytics: The ability to generate reports and track key performance indicators (KPIs), such as sales revenue, conversion rates, and customer satisfaction.
- Integrations: Compatibility with other tools you use, such as email marketing platforms, accounting software, and e-commerce platforms.
- Mobile Access: The ability to access your CRM data and functionality on the go, via mobile apps or a mobile-friendly interface.
- Customization: The ability to customize the CRM to fit your specific business needs, including custom fields, workflows, and reports.
3. Consider Ease of Use
A CRM is only useful if your team actually uses it. Choose a system that is intuitive, user-friendly, and easy to navigate. Look for a clean interface, clear instructions, and helpful tutorials.
4. Evaluate Pricing and Plans
CRM pricing models vary. Some vendors offer free plans with limited features, while others offer subscription-based plans with different tiers of functionality. Compare the pricing plans of different vendors and choose the one that best fits your budget and needs. Consider the number of users, the storage capacity, and the features included in each plan.
5. Request Demos and Trials
Most CRM vendors offer free demos or trial periods. Take advantage of these opportunities to test out the software, explore its features, and see if it’s a good fit for your business. Involve your team in the demo process and gather their feedback.
6. Check for Integrations
Consider how the CRM integrates with the other tools you’re already using. Does it integrate with your email marketing platform (e.g., Mailchimp, Constant Contact), your accounting software (e.g., QuickBooks, Xero), your e-commerce platform (e.g., Shopify, WooCommerce), and other essential business applications? Seamless integrations will save you time and improve efficiency.
Phase 3: Implementing Your CRM
Once you’ve chosen a CRM, it’s time to implement it. This phase involves setting up the system, importing your data, training your team, and customizing the software to meet your specific needs.
1. Plan Your Implementation
Before you start, create a detailed implementation plan. This plan should outline the steps you need to take, the timeline, and the resources required. Assign roles and responsibilities to different team members.
2. Set Up Your CRM
Follow the vendor’s instructions to set up your CRM. This typically involves creating user accounts, configuring settings, and customizing the interface. Pay attention to the initial setup, because this will be the foundation for all your future work.
3. Import Your Data
Import your existing customer data into the CRM. Most CRM systems allow you to import data from spreadsheets or other databases. Ensure your data is clean and organized before importing it. You might need to clean up your data before you import it – removing duplicates, standardizing formats, and filling in missing information.
4. Customize Your CRM
Tailor the CRM to your business’s specific needs. This might involve creating custom fields, configuring workflows, and setting up reports. Take advantage of the customization options to optimize the system for your unique processes.
5. Train Your Team
Provide comprehensive training to your team on how to use the CRM. Offer training sessions, create user guides, and provide ongoing support. Ensure everyone understands how to use the system and how it can help them do their jobs more effectively. Encourage your team to ask questions and provide feedback.
6. Test and Refine
Before you fully launch the CRM, test it thoroughly. Make sure all features are working correctly and that the system is meeting your needs. Gather feedback from your team and make any necessary adjustments. Be prepared to refine your processes based on how your team is actually using the CRM.
7. Integrate with Other Tools
Connect your CRM with your other business tools. Set up integrations with your email marketing platform, accounting software, and any other applications you use. This will streamline your workflow and eliminate the need for manual data entry.
8. Go Live!
Once you’ve tested the system, trained your team, and integrated with your other tools, it’s time to go live. Encourage your team to start using the CRM and provide ongoing support as they get familiar with the system.
Phase 4: Ongoing Management and Optimization
Implementing a CRM is not a one-time task. It’s an ongoing process that requires continuous management and optimization. Here’s what you need to do:
1. Monitor Your CRM Usage
Track how your team is using the CRM. Are they logging customer interactions, updating contact information, and using the sales pipeline? Identify any areas where they’re struggling or not utilizing the system to its full potential.
2. Analyze Your Data
Regularly review your CRM data to identify trends, patterns, and insights. Use the data to track your progress toward your goals, identify areas for improvement, and make data-driven decisions.
3. Provide Ongoing Training and Support
Offer ongoing training and support to your team. This can include refresher courses, tutorials, and one-on-one coaching. Address any questions or concerns they have and provide support as needed.
4. Review and Update Your Processes
Periodically review your business processes and workflows. Identify any inefficiencies or bottlenecks and update your CRM configuration to optimize your processes. As your business evolves, your CRM needs will change as well.
5. Regularly Update and Maintain Your CRM
Keep your CRM software up to date with the latest features and security updates. Regularly back up your data to ensure its safety. Consider reviewing your data storage and making sure you’re compliant with any relevant data privacy regulations, such as GDPR or CCPA.
6. Seek User Feedback
Ask your team for feedback on the CRM. What do they like? What could be improved? Use their feedback to make adjustments and improve the system’s usability. Remember, the CRM is a tool for your team, so their input is invaluable.
Common CRM Mistakes to Avoid
Even with the best intentions, small businesses can make mistakes when implementing and using a CRM. Here are some common pitfalls to avoid:
- Not Defining Clear Goals: Without clear goals, you won’t be able to measure your success or determine if the CRM is delivering the desired results.
- Choosing the Wrong CRM: Selecting a CRM that doesn’t fit your business needs can lead to frustration and wasted resources.
- Not Involving Your Team: Failing to involve your team in the selection and implementation process can lead to resistance and low adoption rates.
- Poor Data Quality: Inaccurate or incomplete data will undermine the value of your CRM.
- Insufficient Training: Without proper training, your team won’t be able to use the CRM effectively.
- Not Customizing the CRM: Failing to customize the CRM to your specific needs will limit its effectiveness.
- Neglecting Ongoing Management: A CRM requires ongoing maintenance and optimization to remain effective.
- Trying to Do Too Much Too Soon: Don’t try to implement every feature all at once. Start with the essentials and gradually add more functionality.
- Ignoring User Feedback: Failing to listen to your team’s feedback can lead to dissatisfaction and low adoption rates.
- Not Integrating with Other Tools: If you don’t integrate your CRM with your other tools, you’ll miss out on the benefits of a connected system.
The Benefits of a CRM for Your Small Business
Investing in a CRM can pay significant dividends for your small business. Here are some of the key benefits:
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: By understanding your customers better and providing personalized service, you can increase customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Increased Sales: A CRM helps you manage your leads, track your sales pipeline, and close deals more effectively, leading to increased sales.
- Enhanced Marketing ROI: A CRM provides valuable insights into customer behavior, allowing you to target your marketing efforts more effectively and improve your return on investment.
- Increased Efficiency: CRM automation features can streamline your workflows and free up your time to focus on other important tasks.
- Better Data Management: A CRM centralizes all your customer data in one accessible location, making it easier to manage and analyze.
- Improved Collaboration: CRM systems facilitate collaboration among your team members, ensuring everyone is on the same page.
- Better Decision Making: CRM reporting and analytics provide valuable insights that can help you make data-driven decisions.
- Scalability: A CRM can scale with your business as it grows, allowing you to adapt to changing needs.
Conclusion: The CRM Checklist – Your Path to Customer Relationship Success
Implementing a CRM can seem like a daunting task, but by following this checklist, you can navigate the process with confidence. Remember to start by understanding your needs, researching your options, and planning your implementation carefully. Once you’ve implemented your CRM, be sure to provide ongoing training, monitor your usage, and continuously refine your processes. With the right CRM and a commitment to best practices, you can transform your customer relationships, boost your sales, and drive sustainable growth for your small business. Embrace the power of a CRM and watch your business thrive!
By taking the time to plan, implement, and manage your CRM effectively, you can unlock its full potential and reap the rewards of improved customer relationships, increased sales, and enhanced business efficiency. This checklist is your roadmap to success. Good luck!