Supercharge Your Workflow: A Deep Dive into CRM Integration with Flow
The Power of Synergy: Why CRM Integration with Flow Matters
In today’s fast-paced business landscape, efficiency is king. Companies are constantly seeking ways to streamline operations, reduce manual tasks, and boost productivity. One of the most effective strategies for achieving these goals is through the seamless integration of Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems with workflow automation tools, often referred to as ‘Flow’ tools. This article delves deep into the world of CRM integration with Flow, exploring its benefits, implementation strategies, and real-world examples to help you harness its transformative power.
Understanding the Core Components: CRM and Flow
Before we dive into the intricacies of integration, let’s clarify the roles of each component:
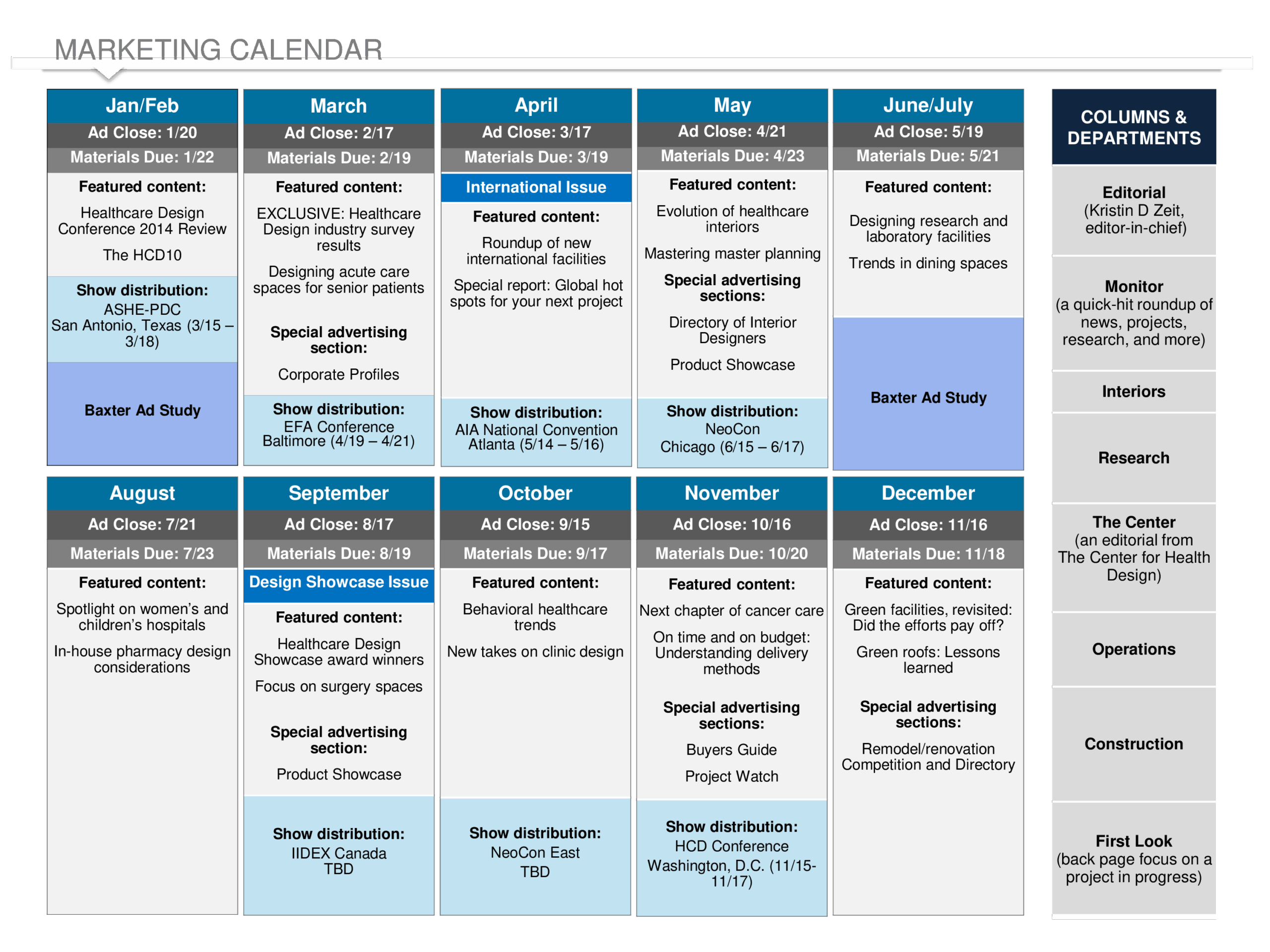
CRM: The Heart of Customer Relationships
A CRM system is a centralized platform designed to manage all interactions with current and potential customers. It serves as a repository for customer data, including contact information, purchase history, communication logs, and more. Key functions of a CRM include:
- Contact Management: Storing and organizing customer contact details.
- Sales Automation: Automating sales processes, such as lead nurturing and opportunity management.
- Marketing Automation: Managing marketing campaigns and tracking their effectiveness.
- Customer Service: Providing a centralized platform for handling customer inquiries and support requests.
- Analytics and Reporting: Providing insights into customer behavior and business performance.
Popular CRM systems include Salesforce, HubSpot, Zoho CRM, Microsoft Dynamics 365, and many others.
Flow: The Engine of Automation
Workflow automation tools, often referred to as ‘Flow’ tools, are designed to automate repetitive tasks and processes. They enable businesses to create automated workflows that trigger actions based on specific events or conditions. Key features of a Flow tool include:
- Workflow Design: A visual interface for creating and managing automated workflows.
- Integration with Various Apps: Connecting to a wide range of applications, including CRM systems, email platforms, and social media channels.
- Conditional Logic: Implementing decision-making processes within workflows based on pre-defined rules.
- Task Automation: Automating tasks such as data entry, email sending, and document generation.
- Real-time Monitoring: Tracking the progress and performance of automated workflows.
Examples of popular Flow tools include Zapier, Microsoft Power Automate, Integromat (now Make), and Tray.io.
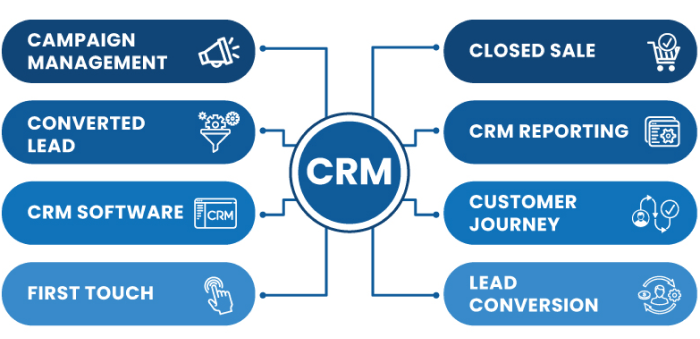
The Compelling Benefits of CRM Integration with Flow
The integration of CRM and Flow tools creates a powerful synergy, leading to a multitude of benefits for businesses of all sizes:
Enhanced Efficiency and Productivity
One of the most significant advantages is the boost in efficiency. By automating repetitive tasks, employees can focus on more strategic activities, leading to improved productivity. For example, when a new lead is created in the CRM, a flow can automatically trigger an email to be sent, a task to be assigned to a sales representative, and data to be updated in other connected systems. This eliminates manual data entry and reduces the risk of errors.
Improved Data Accuracy and Consistency
Manual data entry is prone to errors. CRM integration with Flow helps ensure that data is accurate and consistent across all systems. When data is updated in the CRM, it can be automatically synchronized with other connected applications, eliminating the need for manual updates and minimizing the chances of discrepancies.
Faster Lead Response Times
Automated workflows can significantly reduce lead response times. When a lead submits a form or expresses interest in a product or service, a flow can immediately notify the sales team, assign the lead to a representative, and provide relevant information. This helps sales teams connect with leads quickly, increasing the likelihood of conversion.
Personalized Customer Experiences
CRM integration with Flow allows businesses to personalize customer interactions. By leveraging customer data stored in the CRM, flows can trigger personalized email campaigns, send targeted offers, and provide customized support experiences. This level of personalization can lead to increased customer engagement and loyalty.
Reduced Operational Costs
By automating tasks and processes, CRM integration with Flow can help businesses reduce operational costs. Automating manual tasks frees up employees to focus on more strategic initiatives, reducing the need for additional headcount. Additionally, automation can minimize errors, leading to fewer rework and reduced costs.
Better Sales and Marketing Alignment
Integration facilitates better alignment between sales and marketing teams. Flows can automate the sharing of lead information, track the effectiveness of marketing campaigns, and provide insights into the customer journey. This helps sales and marketing teams work together more effectively, leading to improved sales performance.
Improved Reporting and Analytics
By integrating CRM and Flow, businesses gain a more comprehensive view of their data. Flows can automatically collect and consolidate data from various sources, enabling businesses to generate more accurate reports and gain valuable insights into their operations. This data-driven approach can help businesses make informed decisions and improve their performance.
Real-World Applications: Examples of CRM Integration with Flow
The possibilities of CRM integration with Flow are vast. Here are some real-world examples of how businesses are leveraging this technology:
Lead Qualification and Nurturing
When a new lead is created in the CRM, a flow can automatically:
- Score the lead based on predefined criteria (e.g., job title, company size, website activity).
- Send a series of automated emails to nurture the lead.
- Assign the lead to the appropriate sales representative.
- Update the lead’s status in the CRM based on their interactions.
Automated Sales Follow-up
A flow can automatically:
- Send follow-up emails to leads after a sales call or meeting.
- Create tasks for sales representatives to follow up with leads.
- Update the lead’s status in the CRM based on the sales representative’s actions.
Customer Onboarding
When a new customer is created in the CRM, a flow can automatically:
- Send a welcome email with onboarding instructions.
- Create a support ticket for the customer.
- Assign a customer success manager to the customer.
- Update the customer’s status in the CRM.
Order Processing and Management
When an order is placed in the CRM, a flow can automatically:
- Create an invoice.
- Send an order confirmation email.
- Update the inventory levels.
- Notify the fulfillment team.
Customer Support Automation
When a customer submits a support ticket, a flow can automatically:
- Assign the ticket to the appropriate support agent.
- Send an automated response to the customer acknowledging their issue.
- Update the ticket status in the CRM.
- Escalate the ticket to a supervisor if it’s not resolved within a specific timeframe.
Marketing Campaign Automation
When a customer completes a specific action, a flow can automatically:
- Add the customer to a marketing segment.
- Send a targeted email campaign.
- Update the customer’s profile in the CRM.
- Track the campaign’s performance.
Implementing CRM Integration with Flow: A Step-by-Step Guide
Successfully integrating your CRM with a Flow tool requires careful planning and execution. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you get started:
1. Define Your Goals and Objectives
Before you begin, clearly define your goals and objectives. What do you want to achieve through this integration? Identify the specific tasks and processes you want to automate. This will help you determine the scope of the project and choose the right tools and integrations.
2. Choose the Right Tools
Select the appropriate CRM and Flow tools for your business needs. Consider factors such as ease of use, features, pricing, and integration capabilities. Research different platforms and compare their features to find the best fit for your requirements. Ensure that the CRM and Flow tools you select are compatible and offer the integrations you need.
3. Plan Your Workflows
Design your workflows carefully. Map out the steps involved in each automated process, including the triggers, actions, and conditions. Use flowcharts or diagrams to visualize the workflows and ensure they are logical and efficient. Consider all possible scenarios and edge cases to ensure your workflows are robust.
4. Set Up the Integration
Connect your CRM and Flow tools. This typically involves authenticating your accounts and granting the necessary permissions. Follow the instructions provided by your chosen platforms to establish the connection. Test the connection to ensure that data can flow seamlessly between the two systems.
5. Build Your Workflows
Create your automated workflows using the Flow tool’s interface. Configure the triggers, actions, and conditions based on your workflow design. Test each workflow thoroughly to ensure it functions as expected. Start with simple workflows and gradually build more complex ones as you gain experience.
6. Test and Refine
Thoroughly test your workflows before deploying them. Simulate different scenarios and verify that the automated processes function correctly. Monitor the performance of your workflows and make adjustments as needed. Refine your workflows based on feedback and performance data to optimize their efficiency.
7. Train Your Team
Provide training to your team on how to use the integrated system. Explain the automated processes and how they impact their daily tasks. Ensure that your team members understand how to access and utilize the data in the CRM and Flow tools. Encourage them to provide feedback and suggestions for improvement.
8. Monitor and Maintain
Continuously monitor the performance of your integrated system. Track key metrics, such as lead response times, conversion rates, and customer satisfaction. Regularly review your workflows and make adjustments as needed to optimize their performance. Stay up-to-date with the latest features and updates of your CRM and Flow tools.
Choosing the Right Integration Platform
Selecting the right integration platform is crucial for success. Here are some factors to consider:
Integration Capabilities
Does the platform support the specific CRM and Flow tools you use? Check the available pre-built integrations and the level of customization available. The platform should offer robust connectivity options for the apps you rely on.
Ease of Use
How user-friendly is the platform? Look for a platform with an intuitive interface and easy-to-understand documentation. Choose a platform that allows you to build and manage integrations without extensive coding knowledge.
Scalability
Can the platform handle your current and future needs? Consider the number of integrations you’ll need and the volume of data that will be processed. The platform should be able to scale to accommodate your growing business.
Pricing
What is the pricing model? Compare the costs of different platforms and choose one that fits your budget. Consider the features offered and the value you’ll receive for your investment.
Support and Documentation
Does the platform offer adequate support and documentation? Look for a platform with comprehensive documentation, helpful tutorials, and responsive customer support. Ensure that you have access to the resources you need to troubleshoot issues and get help when you need it.
Overcoming Common Challenges in CRM and Flow Integration
While CRM integration with Flow offers numerous benefits, businesses may encounter certain challenges. Here are some common obstacles and how to overcome them:
Data Mapping Issues
Ensuring data is mapped correctly between the CRM and Flow tools can be complex. Incorrect data mapping can lead to errors and inconsistencies. Carefully review the data fields in both systems and ensure that they are mapped accurately. Test the data flow thoroughly to identify and correct any mapping errors.
Workflow Complexity
Creating complex workflows can be challenging. Overly complicated workflows can be difficult to manage and troubleshoot. Start with simple workflows and gradually build more complex ones. Break down complex processes into smaller, more manageable steps. Use clear and concise naming conventions for your workflows and steps.
Integration Limitations
Some CRM and Flow tools may have limitations in their integration capabilities. Certain features or data fields may not be supported. Research the integration capabilities of your chosen platforms before you begin. Consider alternative solutions or workarounds if you encounter any limitations.
Security Concerns
Protecting sensitive customer data is paramount. Ensure that your integration platform has robust security features to protect your data. Use secure connections and follow best practices for data security. Regularly review your security protocols and update them as needed.
Lack of User Adoption
If employees are not properly trained or don’t understand the benefits of the integrated system, they may resist adopting it. Provide comprehensive training to your team and explain the advantages of the new system. Encourage feedback and address any concerns they may have. Make the system easy to use and provide ongoing support.
The Future of CRM Integration with Flow
The integration of CRM and Flow tools is constantly evolving. As technology advances, we can expect to see even more sophisticated integrations and automation capabilities. Here are some trends to watch for:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML are increasingly being integrated into CRM and Flow tools. These technologies can automate more complex tasks, provide predictive insights, and personalize customer experiences. For example, AI-powered chatbots can handle customer inquiries, and ML algorithms can predict customer behavior.
Hyper-Personalization
Businesses will continue to focus on hyper-personalization, tailoring their interactions with customers based on their individual preferences and behaviors. CRM integration with Flow will play a crucial role in enabling hyper-personalization by allowing businesses to deliver personalized content and offers at scale.
No-Code/Low-Code Automation
The trend towards no-code and low-code automation will continue. This will enable businesses to automate more processes without requiring extensive coding knowledge. This will make CRM integration with Flow accessible to a wider range of users.
Integration with Emerging Technologies
CRM and Flow tools will integrate with emerging technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and blockchain. This will enable businesses to collect and analyze data from new sources and create more innovative solutions.
Focus on User Experience
The user experience will become increasingly important. CRM and Flow tools will be designed with intuitive interfaces and user-friendly features. This will make it easier for users to create and manage automated workflows.
Conclusion: Embracing the Automation Revolution
CRM integration with Flow is a powerful strategy for businesses seeking to improve efficiency, enhance customer experiences, and drive growth. By automating repetitive tasks, streamlining processes, and gaining deeper insights into customer behavior, businesses can unlock significant value. As technology continues to evolve, the possibilities for CRM integration with Flow are endless. By embracing the automation revolution, businesses can position themselves for success in the ever-changing business landscape. Take the time to explore the opportunities that CRM and Flow integration provides. Analyze your current workflows and identify areas for automation. By carefully planning your implementation and choosing the right tools, you can unlock the full potential of CRM integration with Flow and transform your business for the better.