Supercharge Your Small Business: Actionable CRM Tips to Skyrocket Growth
Running a small business is an adventure, a rollercoaster of triumphs and challenges. You’re the CEO, the marketer, the customer service rep, and sometimes, the janitor. In the midst of this whirlwind, it’s easy to feel overwhelmed, like you’re juggling flaming torches on a unicycle. But amidst the chaos, one tool can be your secret weapon, your trusty sidekick: a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system.
This isn’t just about fancy software; it’s about building lasting relationships with your customers, understanding their needs, and ultimately, driving sustainable growth. This in-depth guide will equip you with actionable CRM tips specifically tailored for small businesses. We’ll delve into the core functionalities, explore best practices, and provide practical advice to help you choose, implement, and leverage a CRM to its full potential. Get ready to transform your customer interactions and watch your business thrive!
Chapter 1: Understanding the Power of CRM for Small Businesses
Before we dive into the nitty-gritty, let’s establish a solid foundation. What exactly is CRM, and why is it so crucial for small businesses? Think of it as a central hub for all your customer-related information. It’s where you store contact details, track interactions, manage sales pipelines, and gain valuable insights into customer behavior.
For small businesses, the benefits are immense:
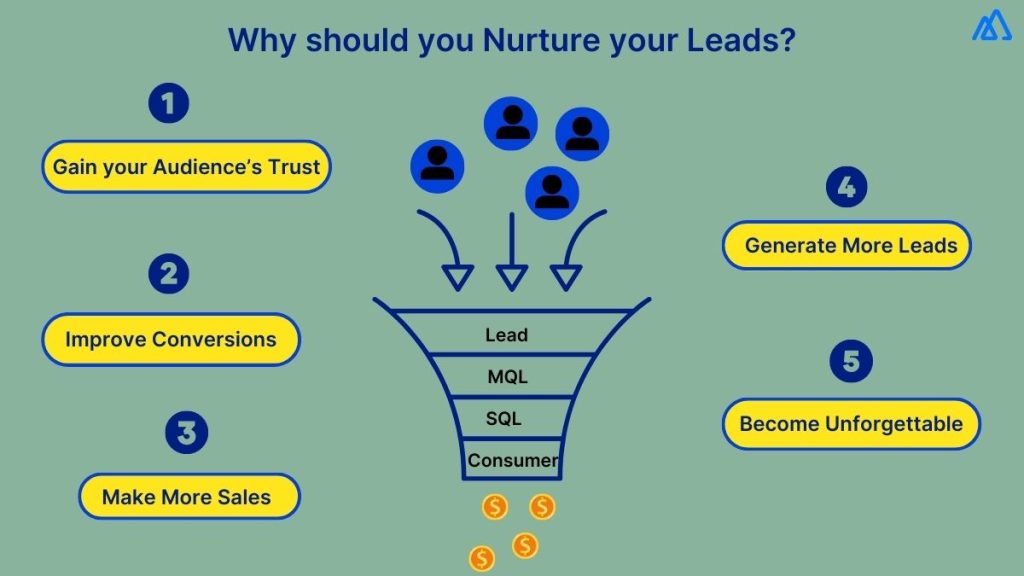
- Improved Customer Relationships: CRM allows you to personalize interactions, remember past conversations, and anticipate customer needs. This leads to increased satisfaction and loyalty.
- Enhanced Sales Efficiency: Streamline your sales process, automate repetitive tasks, and track leads more effectively. This frees up your time to focus on closing deals.
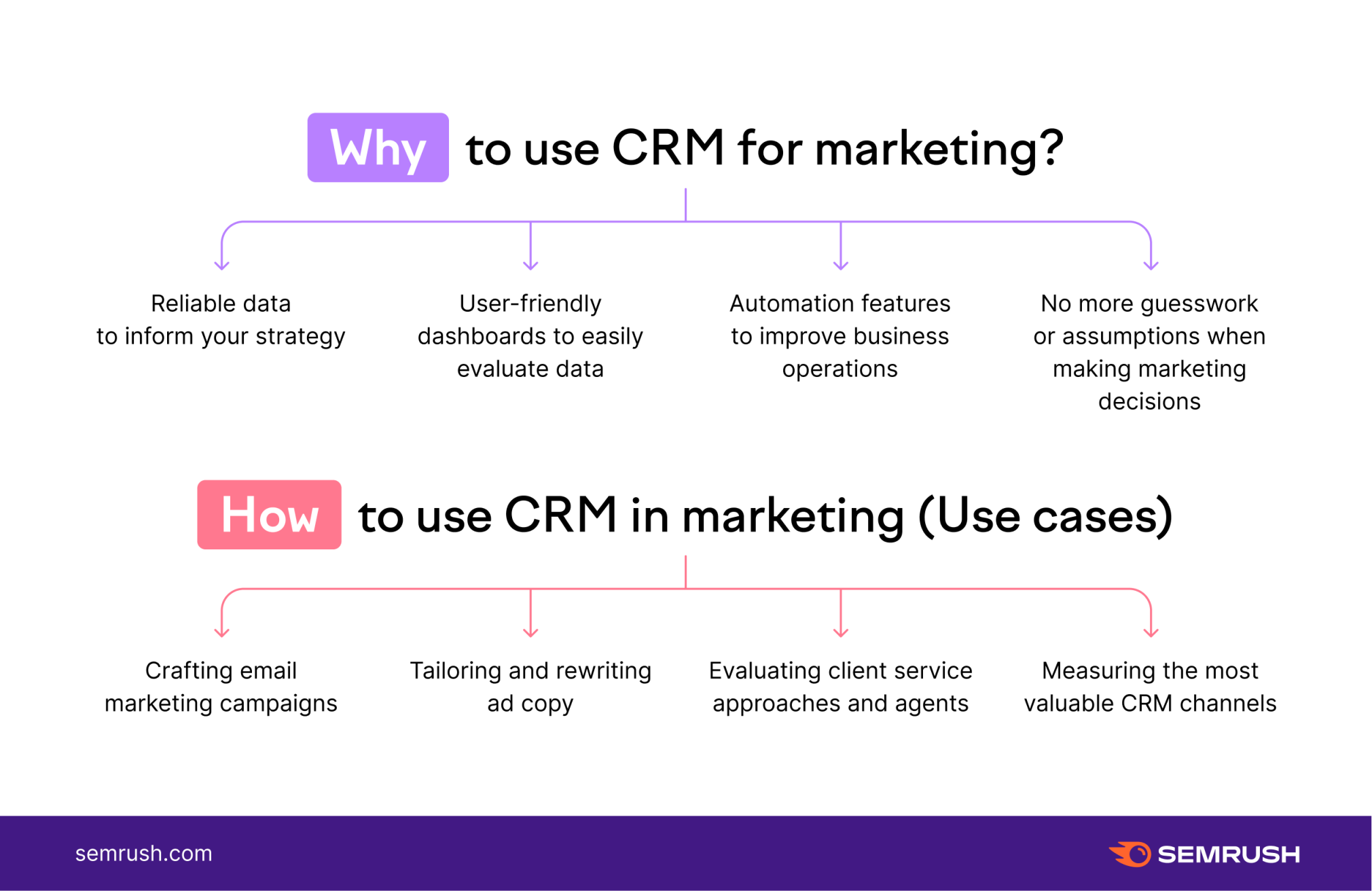
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Gain valuable insights into customer behavior, sales performance, and marketing effectiveness. This empowers you to make informed decisions and optimize your strategies.
- Increased Productivity: Automate tasks, centralize information, and eliminate manual data entry. This boosts your team’s productivity and frees up valuable time.
- Scalability: Choose a CRM that can grow with your business. As your customer base expands, your CRM can adapt to handle the increased volume of data and interactions.
In essence, a CRM system is your business’s memory, your sales assistant, and your customer service guru all rolled into one. It’s the key to unlocking sustainable growth and building a thriving business.
Chapter 2: Choosing the Right CRM for Your Small Business
The CRM market is vast, with a plethora of options vying for your attention. Choosing the right one can feel like navigating a maze. But don’t worry; we’ll break down the key considerations to help you make an informed decision.
2.1: Assessing Your Needs
Before you start comparing CRM systems, take a step back and assess your specific needs and requirements. Consider the following questions:
- What are your primary business goals? Are you focused on increasing sales, improving customer service, or streamlining marketing efforts?
- What are your current pain points? What challenges are you facing in managing customer relationships, tracking leads, or closing deals?
- What are your team’s technical skills? Choose a CRM that aligns with your team’s capabilities. Some systems are more complex than others.
- How many users will need access to the CRM? This will influence the pricing and features you require.
- What integrations do you need? Do you need to integrate with your existing email marketing software, accounting software, or other business tools?
Answering these questions will help you create a clear picture of your needs and narrow down your options.
2.2: Key Features to Look For
Once you have a clear understanding of your needs, it’s time to evaluate the features offered by different CRM systems. Here are some essential features to consider:
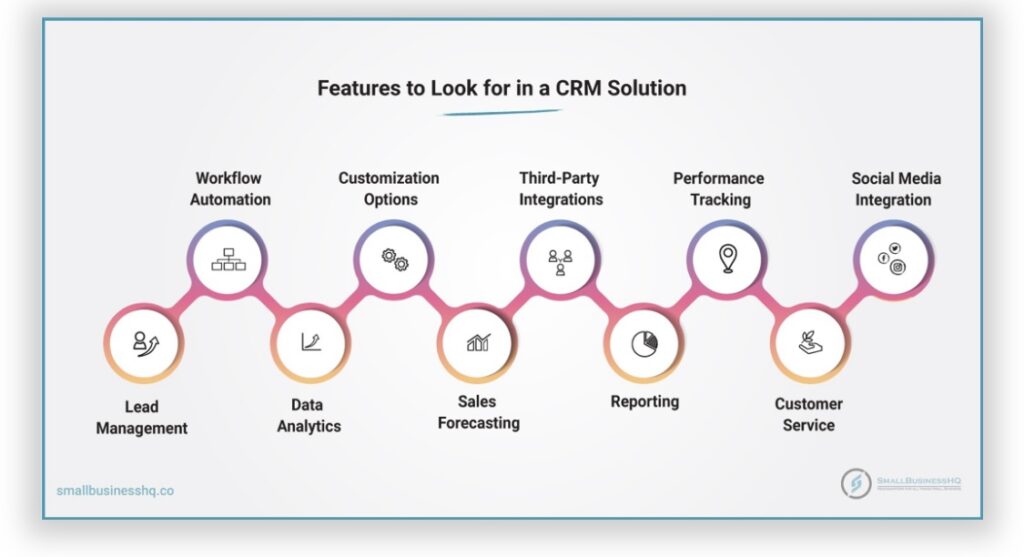
- Contact Management: The ability to store and organize contact information, including names, addresses, phone numbers, email addresses, and social media profiles.
- Lead Management: Track leads, qualify them, and nurture them through the sales pipeline. This includes features like lead scoring and lead assignment.
- Sales Automation: Automate repetitive sales tasks, such as sending follow-up emails, scheduling appointments, and creating sales reports.
- Email Marketing Integration: Integrate with your email marketing software to send targeted campaigns and track their performance.
- Reporting and Analytics: Generate reports on sales performance, customer behavior, and marketing effectiveness. This provides valuable insights for decision-making.
- Mobile Access: Access your CRM data on the go with a mobile app. This is crucial for sales teams and anyone who needs to stay connected.
- Integration with Other Tools: Ensure the CRM integrates with the other tools you use, such as your email provider, accounting software, and social media platforms.
- Customization Options: The ability to customize the CRM to fit your specific business needs. This includes customizing fields, creating workflows, and designing reports.
2.3: Popular CRM Systems for Small Businesses
Here are a few popular CRM systems that are well-suited for small businesses:
- HubSpot CRM: A free, user-friendly CRM with a wide range of features. It’s a great option for businesses that are just starting out.
- Zoho CRM: A comprehensive CRM with a variety of pricing plans to suit different budgets. It offers a robust set of features and integrations.
- Salesforce Sales Cloud: A powerful CRM that’s suitable for businesses of all sizes. It offers a wide range of features and customization options, but it can be more expensive.
- Pipedrive: A sales-focused CRM that’s designed to help you manage your sales pipeline and close deals. It’s known for its ease of use and visual interface.
- Freshsales: A sales-focused CRM that is simple to set up and offers features such as built-in phone and email.
Remember to research each option thoroughly, read reviews, and compare pricing plans before making a decision. Many CRM providers offer free trials, so take advantage of them to test out the system and see if it’s a good fit for your business.
Chapter 3: Implementing Your CRM: A Step-by-Step Guide
Choosing a CRM is only the first step. The real work begins with implementation. A successful implementation is crucial for maximizing the benefits of your CRM. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you get started:
3.1: Planning and Preparation
Before you dive into the technical aspects, take some time to plan and prepare. This will set you up for a smoother implementation process.
- Define Your Goals: What do you hope to achieve with your CRM? Set clear, measurable goals to track your progress.
- Clean Up Your Data: Ensure your existing customer data is accurate, complete, and up-to-date. This includes removing duplicates, correcting errors, and standardizing formatting.
- Assign Roles and Responsibilities: Determine who will be responsible for different aspects of the CRM implementation, such as data entry, training, and reporting.
- Create a Timeline: Develop a realistic timeline for the implementation process, including key milestones and deadlines.
3.2: Setting Up Your CRM
Once you’ve done your planning, it’s time to set up your CRM. This will involve the following steps:
- Customize Your CRM: Configure the CRM to fit your specific business needs. This includes customizing fields, creating workflows, and designing reports.
- Import Your Data: Import your existing customer data into the CRM.
- Integrate with Other Tools: Connect your CRM with your other business tools, such as your email provider, accounting software, and social media platforms.
- Set Up User Accounts: Create user accounts for each member of your team and assign appropriate permissions.
3.3: Training Your Team
Training is essential for ensuring that your team can effectively use the CRM. Provide comprehensive training on all aspects of the system, including:
- Basic Navigation: How to navigate the CRM interface, find information, and perform basic tasks.
- Data Entry: How to enter and update customer data accurately.
- Sales Process: How to use the CRM to manage leads, track deals, and close sales.
- Reporting and Analytics: How to generate reports and analyze data to gain insights into customer behavior and sales performance.
- Best Practices: Provide guidance on best practices for using the CRM, such as how to personalize interactions, follow up with leads, and manage customer communications.
Offer ongoing support and training as needed. Consider creating a knowledge base or FAQ section to help your team troubleshoot common issues.
Chapter 4: Actionable CRM Tips for Small Business Success
Now that you’ve chosen and implemented your CRM, it’s time to put it to work. Here are some actionable tips to help you maximize its impact and achieve success:
4.1: Data Entry and Management Best Practices
The quality of your CRM data directly impacts its effectiveness. Follow these best practices for data entry and management:
- Be Consistent: Establish consistent data entry standards and guidelines. This ensures that your data is accurate and easy to understand.
- Use Standardized Fields: Utilize standardized fields to ensure that your data is consistent and can be easily analyzed.
- Keep Data Up-to-Date: Regularly update your customer data to ensure it’s accurate and reflects the latest changes.
- Regularly Clean Your Data: Regularly clean your data to remove duplicates, correct errors, and ensure that your data is accurate and complete.
- Automate Data Entry: Automate data entry whenever possible to reduce manual effort and minimize errors.
- Set Clear Data Ownership: Assign data ownership to specific team members to ensure accountability.
4.2: Leveraging CRM for Sales Success
Your CRM can be a powerful tool for driving sales. Here are some tips for leveraging it to its full potential:
- Track Leads Effectively: Use your CRM to track leads, qualify them, and nurture them through the sales pipeline.
- Automate Sales Processes: Automate repetitive sales tasks, such as sending follow-up emails, scheduling appointments, and creating sales reports.
- Personalize Your Outreach: Use your CRM data to personalize your communications and tailor your message to each customer’s individual needs.
- Prioritize Leads: Use lead scoring to prioritize your leads and focus your efforts on the most promising prospects.
- Analyze Sales Performance: Generate reports on sales performance to identify areas for improvement and track your progress.
- Use Sales Forecasting: Use your CRM to forecast sales and plan your resources effectively.
4.3: Enhancing Customer Service with CRM
A CRM can transform your customer service efforts. Here’s how:
- Provide Personalized Service: Use your CRM data to personalize your customer service interactions and provide a more tailored experience.
- Track Customer Interactions: Track all customer interactions, including phone calls, emails, and live chat conversations, to gain a complete view of the customer journey.
- Resolve Issues Quickly: Use your CRM to track customer issues and resolve them quickly and efficiently.
- Provide Self-Service Options: Offer self-service options, such as a knowledge base or FAQ section, to empower customers and reduce the burden on your customer service team.
- Solicit Feedback: Use your CRM to solicit customer feedback and gather insights into their experiences.
- Measure Customer Satisfaction: Measure customer satisfaction to track your progress and identify areas for improvement.
4.4: Using CRM for Marketing Automation
CRM can automate your marketing efforts and help you reach the right customers with the right message at the right time. Here’s how:
- Segment Your Audience: Segment your audience based on demographics, behavior, and other criteria to create targeted marketing campaigns.
- Automate Email Marketing: Automate your email marketing efforts, such as sending welcome emails, nurture sequences, and promotional offers.
- Track Campaign Performance: Track the performance of your marketing campaigns to measure their effectiveness and identify areas for improvement.
- Personalize Marketing Messages: Personalize your marketing messages to increase engagement and drive conversions.
- Use Lead Scoring: Use lead scoring to identify and target your most qualified leads.
- Integrate with Social Media: Integrate your CRM with your social media platforms to track social media interactions and engage with your customers.
4.5: Optimizing Workflows and Automation
Automation is key to efficiency. Here’s how to optimize workflows:
- Identify Repetitive Tasks: Analyze your business processes and identify repetitive tasks that can be automated.
- Create Automated Workflows: Create automated workflows to streamline your processes and reduce manual effort.
- Use Triggers and Actions: Use triggers and actions to automate tasks based on specific events, such as a new lead being created or a deal being closed.
- Monitor and Refine Workflows: Regularly monitor your automated workflows and refine them as needed to optimize their performance.
Chapter 5: Measuring Success and Continuous Improvement
Implementing a CRM is an ongoing process, not a one-time event. To ensure you’re getting the most out of your CRM, it’s crucial to measure your success and continuously improve your strategies.
5.1: Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to Track
Tracking the right KPIs will give you a clear picture of your CRM’s impact. Here are some key metrics to monitor:
- Sales Conversion Rate: The percentage of leads that convert into paying customers.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): The cost of acquiring a new customer.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV): The predicted revenue a customer will generate over their relationship with your business.
- Customer Retention Rate: The percentage of customers who remain customers over a specific period.
- Lead Response Time: The time it takes to respond to a new lead.
- Sales Cycle Length: The average time it takes to close a deal.
- Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT): A measure of customer satisfaction.
- Net Promoter Score (NPS): A measure of customer loyalty.
5.2: Analyzing Your Data
Regularly analyze your CRM data to identify trends, patterns, and insights. This will help you understand what’s working and what’s not.
- Identify Top-Performing Activities: Identify the activities that are contributing most to your success.
- Pinpoint Bottlenecks: Identify any bottlenecks in your sales process or customer service operations.
- Understand Customer Behavior: Gain insights into customer behavior to personalize your interactions and improve your marketing efforts.
- Track ROI: Track the return on investment (ROI) of your CRM to determine its effectiveness.
5.3: Making Adjustments and Optimizing
Based on your data analysis, make adjustments to your strategies and optimize your CRM settings. This is an ongoing process of continuous improvement.
- Refine Your Sales Process: Optimize your sales process to improve efficiency and increase conversion rates.
- Improve Your Customer Service: Enhance your customer service efforts to improve customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Optimize Your Marketing Campaigns: Optimize your marketing campaigns to improve engagement and drive conversions.
- Refine Your Workflows: Refine your automated workflows to improve efficiency and reduce manual effort.
- Regularly Review Your Goals: Regularly review your goals and make adjustments as needed to ensure you’re on track to achieve them.
Chapter 6: Overcoming Common CRM Challenges
Implementing and using a CRM isn’t always smooth sailing. Here are some common challenges and how to overcome them:
- Lack of User Adoption: Ensure your team is fully trained and understands the benefits of using the CRM. Provide ongoing support and encouragement.
- Poor Data Quality: Implement data entry best practices and regularly clean your data to maintain accuracy.
- Integration Issues: Ensure your CRM integrates seamlessly with your other business tools.
- Complexity: Choose a CRM that’s easy to use and customize.
- Cost: Choose a CRM that fits your budget and offers the features you need.
- Resistance to Change: Address any resistance to change by communicating the benefits of the CRM and providing ongoing support.
Chapter 7: The Future of CRM and What It Means for Your Small Business
The CRM landscape is constantly evolving. Staying informed about the latest trends is essential for maximizing the value of your CRM.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is transforming CRM by automating tasks, providing predictive analytics, and personalizing customer interactions.
- Mobile CRM: Mobile CRM is becoming increasingly important as businesses become more mobile.
- Social CRM: Social CRM integrates social media data with CRM data to provide a more complete view of the customer.
- Personalized Experiences: Customers expect personalized experiences. CRM allows businesses to deliver them.
- Focus on Customer Experience: The focus is shifting from simply managing customer data to creating exceptional customer experiences.
By embracing these trends, you can ensure that your CRM remains a valuable tool for driving growth and building lasting customer relationships.
Conclusion: Embracing CRM for a Brighter Future
Implementing and utilizing a CRM is an investment in your small business’s future. By following the tips and strategies outlined in this guide, you can transform your customer interactions, streamline your operations, and drive sustainable growth. Remember, a CRM is not just software; it’s a philosophy – a commitment to building strong customer relationships and creating a thriving business.
Embrace the power of CRM. Your customers – and your business – will thank you for it.