Small Business CRM Training: Your Complete Guide to Customer Relationship Management Success

Small Business CRM Training: Your Complete Guide to Customer Relationship Management Success
Running a small business is a whirlwind of activity. You’re juggling everything from sales and marketing to customer service and operations. In the midst of all this, it’s easy for customer relationships to get lost in the shuffle. That’s where a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system comes in. But a CRM is only as good as your understanding of it. This comprehensive guide provides in-depth small business CRM training, equipping you with the knowledge and skills to harness the power of CRM and drive your business forward.
What is a CRM System and Why Does Your Small Business Need One?
Before diving into the training, let’s establish the fundamentals. A CRM system is essentially a centralized database that stores all your customer interactions and data. Think of it as a digital Rolodex, but far more sophisticated. It tracks everything from initial contact to purchase history, support tickets, and beyond.
So, why is this important for a small business? Here’s why:
- Improved Customer Relationships: A CRM provides a 360-degree view of your customers, allowing you to personalize interactions and build stronger relationships. You can remember important details, anticipate their needs, and provide tailored solutions.
- Increased Sales: By tracking leads, managing the sales pipeline, and automating tasks, a CRM can significantly boost your sales efficiency and close more deals.
- Enhanced Customer Service: A CRM enables you to provide faster, more efficient, and more personalized customer service. You can track support tickets, resolve issues quickly, and ensure customer satisfaction.
- Better Data Insights: A CRM provides valuable data and analytics, allowing you to understand customer behavior, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions.
- Streamlined Operations: CRM systems automate many repetitive tasks, freeing up your team to focus on more strategic initiatives.
- Scalability: As your business grows, a CRM system can scale with you, ensuring you have the infrastructure to manage your customer relationships effectively.
Choosing the Right CRM for Your Small Business: A Step-by-Step Guide
Selecting the right CRM is a crucial first step. There’s no one-size-fits-all solution. The best CRM for your business depends on your specific needs, budget, and technical capabilities. Here’s how to choose the right CRM:
- Assess Your Needs: Start by identifying your business goals and the specific challenges you want to solve with a CRM. What are your key priorities? Do you need help with lead management, sales automation, customer service, or marketing?
- Define Your Budget: CRM systems come in a variety of price points, from free to enterprise-level. Determine how much you’re willing to spend on a CRM, considering both the initial setup costs and ongoing subscription fees.
- Research CRM Providers: Explore the different CRM providers available, such as HubSpot, Salesforce, Zoho CRM, Pipedrive, Freshsales, and others. Read reviews, compare features, and see which ones align with your needs.
- Consider Your Team’s Technical Skills: Some CRM systems are more user-friendly than others. Choose a CRM that your team can easily learn and use. Consider whether you’ll need training or support.
- Evaluate Features: Make a list of the features you need, such as lead management, sales automation, contact management, email integration, reporting, and analytics. Ensure the CRM you choose offers these features.
- Check for Integrations: Does the CRM integrate with the other tools you use, such as your email marketing software, accounting software, and social media platforms? Integrations can streamline your workflow and save you time.
- Consider Scalability: Choose a CRM that can grow with your business. Make sure it can handle an increasing number of contacts, users, and data.
- Request Demos and Trials: Most CRM providers offer free demos or trial periods. Take advantage of these to test the CRM and see if it’s a good fit for your business.
- Read Reviews and Case Studies: See what other businesses are saying about the CRM. Read reviews and case studies to get an idea of its strengths and weaknesses.
- Make a Decision: Once you’ve evaluated all the factors, make a decision and choose the CRM that best meets your needs.
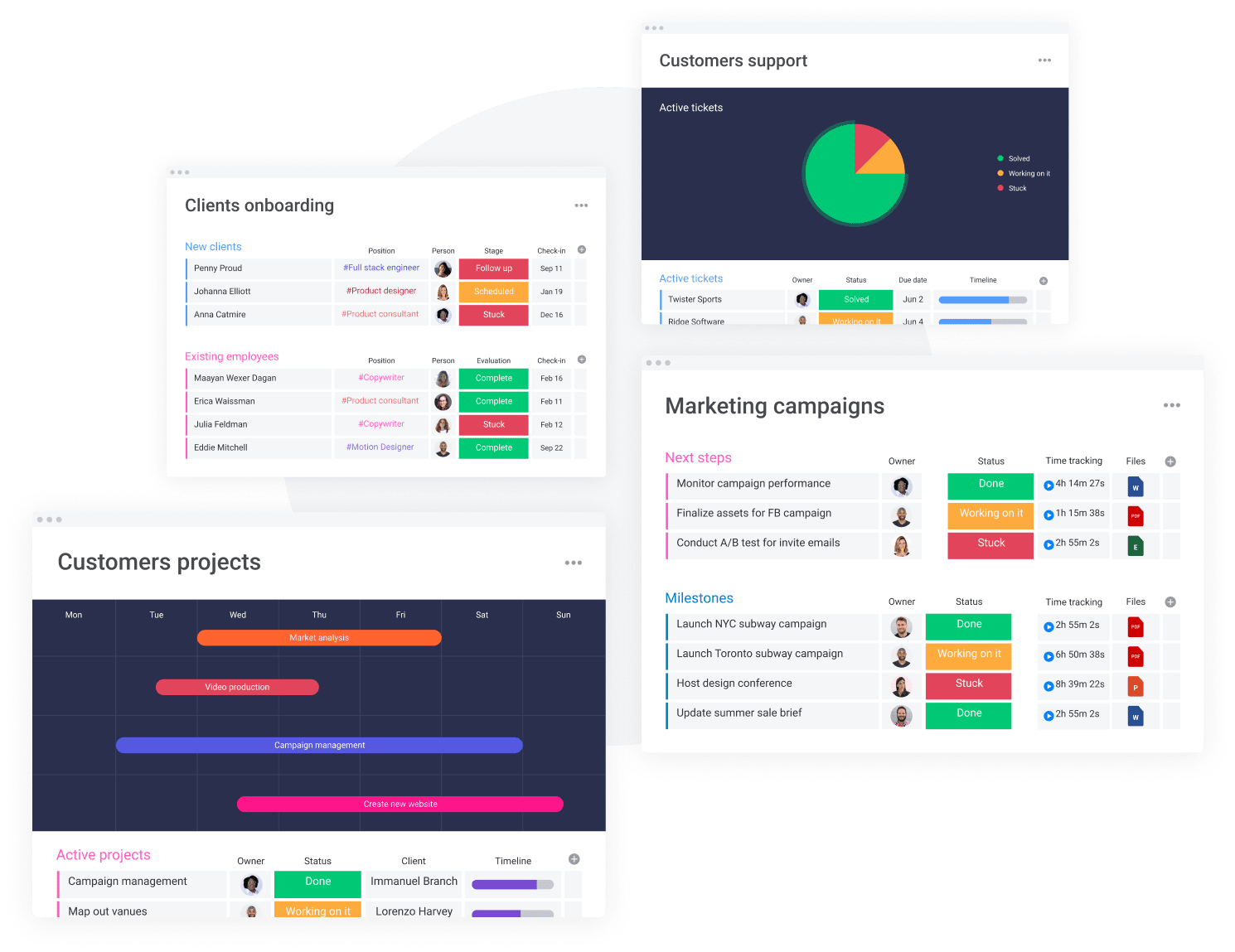
Essential CRM Features for Small Businesses
Once you’ve chosen your CRM, it’s time to understand the essential features that will drive your success. Here’s a breakdown of the key features to focus on:
- Contact Management: This is the core of any CRM. It allows you to store and manage all your customer contact information, including names, addresses, phone numbers, email addresses, and social media profiles.
- Lead Management: Track and nurture leads through the sales pipeline. Manage lead sources, qualify leads, and assign them to sales reps.
- Sales Automation: Automate repetitive sales tasks, such as sending emails, scheduling appointments, and creating tasks.
- Sales Pipeline Management: Visualize your sales pipeline and track the progress of deals through each stage.
- Email Integration: Integrate your CRM with your email provider to track email interactions and send personalized emails.
- Reporting and Analytics: Generate reports and analyze data to gain insights into your sales performance, customer behavior, and marketing effectiveness.
- Customer Service Management: Manage customer support tickets, track customer issues, and provide timely resolutions.
- Mobile Access: Access your CRM data from your mobile devices, so you can stay connected on the go.
- Integrations: Integrate your CRM with other tools you use, such as your email marketing software, accounting software, and social media platforms.
Small Business CRM Training: Getting Started and Mastering the Basics
Now that you’ve got a CRM and understand the key features, it’s time for the actual training. Here’s a structured approach to getting started and mastering the basics:
1. Setting Up Your CRM Account
The first step is to set up your CRM account. This typically involves:
- Creating an Account: Sign up for an account with your chosen CRM provider.
- Customizing Settings: Configure your account settings, such as your company information, user roles, and security settings.
- Importing Data: Import your existing customer data into the CRM. This may involve importing data from spreadsheets or other systems.
- Connecting Integrations: Connect your CRM with other tools you use, such as your email provider and social media platforms.
2. Understanding the CRM Interface
Take some time to familiarize yourself with the CRM interface. This includes:
- Navigation: Learn how to navigate the different sections of the CRM, such as contacts, leads, deals, and reports.
- Dashboard: Understand the information displayed on your dashboard, such as key metrics, recent activities, and upcoming tasks.
- User Roles and Permissions: If you have multiple users, understand the different user roles and permissions and how they affect access to data and features.
- Customization: Learn how to customize the CRM to meet your specific needs, such as adding custom fields, creating custom views, and configuring workflows.
3. Data Entry and Management
Accurate data is critical for the success of your CRM. Learn how to:
- Entering Contacts: Enter your customer contacts into the CRM, including their name, contact information, and other relevant details.
- Adding Leads: Add leads to the CRM, including their source, contact information, and lead status.
- Updating Data: Keep your data up-to-date by regularly updating contact information, lead status, and other relevant details.
- Data Organization: Learn how to organize your data using tags, custom fields, and other features.
- Data Segmentation: Learn how to segment your data to target specific customer groups.
4. Sales Pipeline Management
Mastering sales pipeline management is key to closing deals. Here’s what you need to know:
- Creating Deals: Create deals in the CRM and assign them to sales reps.
- Tracking Deal Progress: Track the progress of deals through each stage of the sales pipeline.
- Managing Tasks and Activities: Schedule tasks and activities, such as calls, emails, and meetings, to move deals forward.
- Analyzing Sales Performance: Use reports and analytics to track your sales performance and identify areas for improvement.
5. Email Integration and Communication
Email integration is a powerful feature for communicating with customers. Here’s how to use it effectively:
- Connecting Your Email: Connect your email account to the CRM.
- Sending Emails: Send personalized emails to customers directly from the CRM.
- Tracking Email Interactions: Track email opens, clicks, and replies.
- Using Email Templates: Use email templates to save time and ensure consistency.
- Email Automation: Set up automated email sequences to nurture leads and engage customers.
6. Reporting and Analytics
Reports and analytics provide valuable insights into your business performance. Learn how to:
- Generating Reports: Generate reports on sales performance, customer behavior, and marketing effectiveness.
- Analyzing Data: Analyze data to identify trends, track progress, and make data-driven decisions.
- Creating Custom Reports: Create custom reports to track the metrics that are most important to your business.
- Using Dashboards: Use dashboards to visualize key metrics and track your progress over time.
7. Customer Service and Support
Use your CRM to provide excellent customer service. Here’s how:
- Managing Support Tickets: Track and manage customer support tickets.
- Providing Timely Resolutions: Provide timely resolutions to customer issues.
- Personalizing Customer Interactions: Personalize your interactions with customers by using their data to understand their needs and preferences.
- Tracking Customer Satisfaction: Track customer satisfaction using surveys and feedback forms.
Advanced CRM Training for Small Businesses
Once you’ve mastered the basics, you can explore advanced features and techniques to further optimize your CRM usage. Here are some areas to consider:
1. Workflow Automation
Workflow automation allows you to automate repetitive tasks and streamline your processes. This can save you time and improve efficiency. Examples include:
- Automated Lead Assignment: Automatically assign leads to sales reps based on criteria such as industry, location, or lead source.
- Automated Email Sequences: Send automated email sequences to nurture leads and engage customers.
- Automated Task Creation: Automatically create tasks for sales reps, such as follow-up calls or meetings.
- Automated Notifications: Send automated notifications to sales reps when deals are nearing their closing date or when a customer issue requires attention.
2. Integration with Marketing Automation Tools
Integrate your CRM with marketing automation tools to streamline your marketing efforts. This allows you to:
- Sync Data: Sync customer data between your CRM and marketing automation tools.
- Personalize Marketing Campaigns: Personalize your marketing campaigns based on customer data stored in your CRM.
- Track Marketing ROI: Track the return on investment of your marketing campaigns.
3. Data Segmentation and Targeting
Use data segmentation to target specific customer groups with personalized messages and offers. This can improve your conversion rates and customer engagement. Examples include:
- Segmenting by Demographics: Segment your customers by demographics, such as age, gender, location, or income.
- Segmenting by Behavior: Segment your customers by their behavior, such as purchase history, website activity, or email engagement.
- Creating Targeted Campaigns: Create targeted marketing campaigns for each segment.
4. CRM Customization and Development
Customize your CRM to meet your specific needs. This may involve:
- Adding Custom Fields: Add custom fields to store additional customer data.
- Creating Custom Views: Create custom views to display data in a way that is most useful to your team.
- Developing Custom Integrations: Develop custom integrations to connect your CRM with other tools you use.
5. Advanced Reporting and Analytics
Go beyond basic reporting and analytics to gain deeper insights into your business performance. This may involve:
- Using Advanced Report Filters: Use advanced report filters to analyze data in more detail.
- Creating Custom Metrics: Create custom metrics to track the metrics that are most important to your business.
- Analyzing Trends: Analyze trends over time to identify opportunities and challenges.
- Predictive Analytics: Use predictive analytics to forecast future performance.
Best Practices for Small Business CRM Training
To ensure the effectiveness of your CRM training, follow these best practices:
- Develop a Training Plan: Create a comprehensive training plan that covers all the essential features and functionalities of your CRM.
- Provide Hands-on Training: Provide hands-on training that allows users to practice using the CRM.
- Use Real-World Examples: Use real-world examples to illustrate how the CRM can be used to solve specific business challenges.
- Provide Ongoing Support: Provide ongoing support to users, such as training materials, FAQs, and a help desk.
- Encourage User Feedback: Encourage users to provide feedback on the CRM and the training program.
- Regularly Review and Update Training Materials: Regularly review and update your training materials to ensure they are up-to-date and relevant.
- Gamify the Training Process: Introduce gamification elements, such as points, badges, and leaderboards, to make the training process more engaging.
- Train the Trainer: Consider training a dedicated CRM administrator or trainer within your team.
- Measure Training Effectiveness: Measure the effectiveness of your training program by tracking user adoption, data entry accuracy, and sales performance.
Common CRM Training Challenges and How to Overcome Them
CRM training can sometimes present challenges. Here’s how to overcome some common obstacles:
- Lack of Time: Schedule dedicated training time and make it a priority. Consider breaking the training into smaller, more manageable sessions.
- Lack of User Adoption: Make the CRM easy to use and provide ongoing support. Demonstrate the value of the CRM and how it can benefit users.
- Data Entry Errors: Implement data validation rules and provide training on data entry best practices.
- Resistance to Change: Communicate the benefits of the CRM and involve users in the implementation process. Address any concerns and provide ongoing support.
- Lack of Training Resources: Utilize online tutorials, videos, and other training resources. Consider hiring a CRM consultant to provide training.
Measuring the Success of Your CRM Training
How do you know if your CRM training has been successful? Here are some key metrics to track:
- User Adoption Rate: Track the percentage of users who are actively using the CRM.
- Data Entry Accuracy: Measure the accuracy of data entered into the CRM.
- Sales Performance: Track key sales metrics, such as lead conversion rates, deal closing rates, and revenue.
- Customer Satisfaction: Track customer satisfaction using surveys and feedback forms.
- Time Savings: Measure the time saved by automating tasks and streamlining processes.
- Return on Investment (ROI): Calculate the return on investment of your CRM by comparing the cost of the CRM and training with the benefits gained.
Continuous Improvement and Ongoing CRM Training
CRM training isn’t a one-time event. It’s an ongoing process. To ensure your CRM remains a valuable asset, focus on continuous improvement and ongoing training. This includes:
- Regular Training Updates: Provide regular training updates to keep users informed of new features and functionalities.
- Refresher Courses: Offer refresher courses to reinforce key concepts and skills.
- User Feedback and Iteration: Gather user feedback and use it to improve your training program and the CRM itself.
- Staying Up-to-Date: Stay up-to-date on the latest CRM trends and best practices.
- Adaptability: Be prepared to adapt your CRM strategy and training as your business evolves.
Conclusion: Unleashing the Power of CRM for Small Business Growth
Investing in small business CRM training is an investment in your future success. By understanding the fundamentals, choosing the right CRM, mastering the essential features, and implementing best practices, you can transform your customer relationships, boost sales, and streamline your operations. Remember, CRM is a journey, not a destination. Embrace continuous learning, adapt to change, and continuously strive to optimize your CRM usage. With the right training and a commitment to excellence, your small business can harness the full power of CRM and achieve sustainable growth. Don’t just implement a CRM; master it. Your customers, and your bottom line, will thank you for it.