Small Business CRM Support: Your Ultimate Guide to Customer Relationship Management

Running a small business is a whirlwind. You’re juggling a million things, from product development and marketing to sales and customer service. Amidst the chaos, it’s easy for customer relationships to get lost in the shuffle. That’s where a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system comes in. But it’s not enough to *have* a CRM; you need to understand how to use it, and that’s where small business CRM support becomes crucial. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about CRM support, from choosing the right system to maximizing its benefits for your growing business.
What is CRM, and Why Does Your Small Business Need It?
Before diving into the specifics of support, let’s clarify what a CRM is and why it’s essential for small businesses. CRM is, at its core, a system for managing your interactions with current and potential customers. It’s a centralized database where you can store all customer-related information: contact details, purchase history, communication logs, and more. Think of it as your business’s memory, holding all the crucial details about your customers.
Why do you need a CRM? Here are some compelling reasons:
- Improved Customer Relationships: A CRM helps you understand your customers better. By tracking their preferences, needs, and interactions, you can personalize your communication and provide more tailored service, leading to stronger relationships.
- Increased Sales: With a CRM, you can identify and nurture leads more effectively. You can track the sales pipeline, automate follow-ups, and close deals faster, ultimately boosting your revenue.
- Enhanced Efficiency: A CRM automates many tedious tasks, such as data entry and email marketing. This frees up your time and your team’s time to focus on more strategic activities.
- Better Decision-Making: CRM systems provide valuable insights into your customer base and sales performance. You can use this data to make informed decisions about your marketing, sales, and product development strategies.
- Streamlined Communication: A CRM ensures that all team members have access to the same customer information, leading to consistent and effective communication.
In essence, a CRM is a powerful tool that can help your small business thrive by putting the customer at the center of everything you do.
Choosing the Right CRM for Your Small Business
The market is flooded with CRM systems, each with its own features, pricing, and target audience. Choosing the right one can feel overwhelming, but it’s a critical decision. Here’s a breakdown of factors to consider:
1. Assess Your Needs
Before looking at different CRM options, take the time to understand your business’s specific needs. What are your primary goals for implementing a CRM? Are you looking to improve sales, streamline customer service, or enhance marketing efforts? Consider the following questions:
- What are your current pain points? What challenges are you facing in managing customer relationships?
- What features are essential? Do you need features like sales automation, email marketing integration, or customer support ticketing?
- How many users will need access? This will impact the pricing and scalability of the system.
- What is your budget? CRM systems range in price from free to thousands of dollars per month.
Answering these questions will give you a clear idea of what you’re looking for in a CRM.
2. Consider Your Budget
CRM systems come in a variety of pricing models, including free, freemium, and paid subscriptions. Free CRM options are often limited in features and storage capacity, but they can be a good starting point for very small businesses with basic needs. Freemium models offer a basic set of features for free, with paid upgrades for more advanced functionality. Paid subscriptions typically offer the most comprehensive features and support.
When considering your budget, factor in not only the monthly or annual subscription cost but also the cost of implementation, training, and any potential add-ons or integrations. Be realistic about what you can afford and choose a CRM that fits within your financial constraints.
3. Evaluate Features
Different CRM systems offer different features. Some of the most common features to look for include:
- Contact Management: The ability to store and manage customer contact information.
- Sales Automation: Features that automate sales tasks, such as lead tracking, opportunity management, and quote generation.
- Marketing Automation: Features for creating and managing email campaigns, social media integration, and lead nurturing.
- Customer Service: Tools for managing customer support tickets, providing live chat, and creating a knowledge base.
- Reporting and Analytics: Features for tracking key metrics, generating reports, and gaining insights into your sales and customer service performance.
- Integrations: The ability to integrate with other business tools, such as email marketing platforms, accounting software, and e-commerce platforms.
Prioritize the features that are most important to your business and choose a CRM that offers those capabilities.
4. Research CRM Providers
Once you have a clear understanding of your needs, budget, and desired features, start researching different CRM providers. Read reviews, compare pricing plans, and check out the provider’s website to learn more about their product. Consider the following factors:
- Ease of Use: Is the system user-friendly and easy to navigate?
- Scalability: Can the system grow with your business?
- Customer Support: What kind of support does the provider offer? Is it readily available?
- Security: Does the provider have robust security measures in place to protect your data?
- Integrations: Does the system integrate with the other tools you use?
Take advantage of free trials or demos to test out the different CRM systems and see which one best fits your needs.
5. Popular CRM Options for Small Businesses
Here are some popular CRM options that are well-suited for small businesses:
- HubSpot CRM: A free CRM with powerful features for sales, marketing, and customer service. It’s known for its user-friendliness and extensive integrations.
- Zoho CRM: A feature-rich CRM with a variety of pricing plans to suit different business sizes. It offers a wide range of customization options.
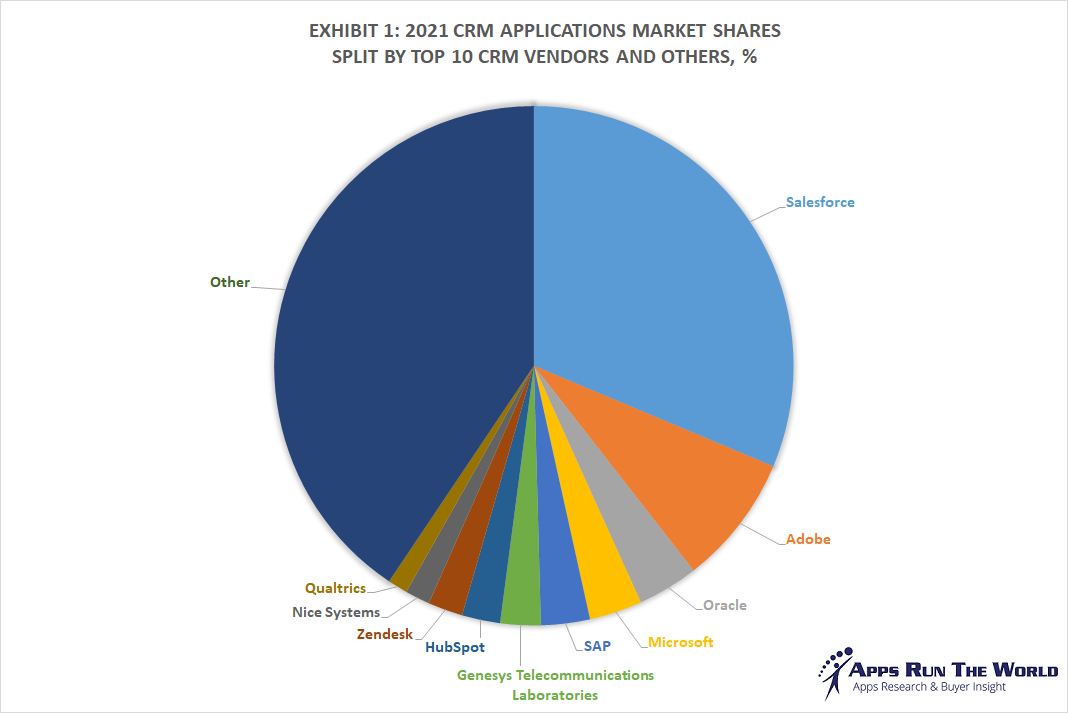
- Salesforce Sales Cloud: A leading CRM platform with a wide range of features and integrations. It can be more complex and expensive than other options.
- Pipedrive: A sales-focused CRM designed to help sales teams manage their pipelines and close deals.
- Freshsales: An easy-to-use CRM with features for sales and customer service. It offers a free plan and affordable paid options.
This is just a starting point; research and compare different options to find the best fit for your specific needs.
Understanding CRM Support Options
Once you’ve chosen a CRM, the next crucial step is understanding the support options available. This is where you’ll turn when you have questions, encounter problems, or need help maximizing the system’s capabilities. CRM support comes in various forms, each with its own advantages.
1. Vendor-Provided Support
Most CRM vendors offer some form of support to their customers. The level of support can vary depending on the vendor and the pricing plan. Common types of vendor-provided support include:
- Documentation: Online documentation, such as user manuals, FAQs, and knowledge bases, is a standard offering. This is often the first place to look for answers to your questions.
- Email Support: Many vendors provide email support, allowing you to submit questions and receive responses from their support team.
- Phone Support: Some vendors offer phone support, which allows you to speak directly with a support representative. This is often available for higher-tier pricing plans.
- Live Chat: Live chat support allows you to get immediate assistance from a support representative via a chat window.
- Training Resources: Many vendors offer training resources, such as webinars, video tutorials, and online courses, to help you learn how to use the CRM effectively.
- Community Forums: Some vendors have online community forums where users can ask questions, share tips, and get help from other users.
When evaluating CRM vendors, pay close attention to their support offerings. Consider the availability, responsiveness, and quality of their support services. Read reviews from other customers to get an idea of their experiences with the vendor’s support team.
2. Third-Party Support
In addition to vendor-provided support, you can also seek assistance from third-party providers. These providers specialize in CRM implementation, customization, training, and support. Third-party support can be a valuable resource, especially if you need specialized expertise or want to customize your CRM to meet your specific needs.
Here are some types of third-party support:
- Implementation Specialists: These specialists can help you implement your CRM system, migrate your data, and configure it to meet your business needs.
- Customization Experts: If you need to customize your CRM to add features or integrations that aren’t available out-of-the-box, customization experts can help.
- Training Providers: Training providers offer training courses and workshops to help your team learn how to use the CRM effectively.
- Consultants: CRM consultants can provide strategic advice on how to use your CRM to improve your sales, marketing, and customer service efforts.
When choosing a third-party support provider, look for providers with experience working with your specific CRM system and industry. Read reviews and testimonials to get an idea of their reputation and expertise.
3. Internal Support
While vendor and third-party support are essential, you should also consider building internal support within your own team. This involves assigning a dedicated CRM administrator or champion who is responsible for managing the CRM system, providing training to other users, and troubleshooting issues. This approach has several advantages:
- Faster Response Times: Internal support can provide faster response times to user questions and issues.
- Deeper Understanding of Your Business: Internal support staff have a deeper understanding of your business and can tailor their support accordingly.
- Reduced Reliance on External Support: Internal support can reduce your reliance on external support, saving you time and money.
- Improved User Adoption: Having an internal champion can help to improve user adoption and encourage your team to use the CRM effectively.
To build effective internal support, you’ll need to provide your CRM administrator with adequate training and resources. You should also encourage a culture of knowledge sharing and collaboration within your team.
Maximizing Your CRM Investment: Best Practices for Support
Having access to support is one thing; effectively utilizing it is another. Here are some best practices to help you maximize your CRM investment through effective support:
1. Onboarding and Training
Proper onboarding and training are crucial for ensuring that your team knows how to use the CRM effectively. This includes:
- Initial Training: Provide initial training to all users on the basic features and functionality of the CRM.
- Ongoing Training: Offer ongoing training to keep users up-to-date on new features and best practices.
- Documentation and Resources: Create and maintain comprehensive documentation and resources, such as user manuals, FAQs, and video tutorials.
- Train-the-Trainer: Identify and train internal champions who can provide ongoing support and training to other users.
Investing in training will help your team to use the CRM more effectively, leading to improved productivity and better customer relationships.
2. Data Migration and Management
Migrating your existing data to the CRM and keeping it clean and up-to-date is essential for ensuring that your CRM provides accurate and reliable information. This includes:
- Data Import: Carefully import your data into the CRM, ensuring that all fields are mapped correctly.
- Data Cleansing: Regularly cleanse your data to remove duplicates, correct errors, and update outdated information.
- Data Security: Implement security measures to protect your data from unauthorized access.
- Data Backup: Regularly back up your CRM data to prevent data loss.
Proper data management will ensure that your CRM provides accurate insights and helps you make informed decisions.
3. Customization and Integration
Customizing your CRM to meet your specific needs and integrating it with other business tools can significantly enhance its value. This includes:
- Customization: Customize the CRM to add features or integrations that aren’t available out-of-the-box.
- Integration: Integrate the CRM with other business tools, such as email marketing platforms, accounting software, and e-commerce platforms.
- Workflow Automation: Automate repetitive tasks to streamline your processes and improve efficiency.
- Regular Review: Regularly review your customizations and integrations to ensure that they are still meeting your needs.
Customization and integration will help you to tailor the CRM to your specific business processes and improve its overall functionality.
4. Troubleshooting and Issue Resolution
When you encounter issues with your CRM, it’s important to have a process for troubleshooting and resolving them quickly. This includes:
- Issue Tracking: Track all issues and their resolutions to identify recurring problems.
- Documentation: Document all troubleshooting steps and solutions to help resolve future issues.
- Vendor Support: Contact your CRM vendor for support when you encounter complex issues.
- Internal Support: Leverage your internal support team to troubleshoot issues and provide assistance to users.
A well-defined troubleshooting process will help you to resolve issues quickly and minimize disruptions to your business.
5. Monitoring and Optimization
Regularly monitoring your CRM usage and performance is crucial for identifying areas for improvement. This includes:
- Usage Metrics: Track key metrics, such as user adoption, data entry accuracy, and sales performance.
- User Feedback: Gather feedback from users to identify areas for improvement.
- Performance Analysis: Analyze your CRM performance to identify bottlenecks and opportunities for optimization.
- Continuous Improvement: Implement changes based on your monitoring and analysis to continuously improve your CRM usage and performance.
Monitoring and optimization will help you to ensure that your CRM is meeting your business needs and delivering the desired results.
Common CRM Support Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Even with the best CRM and support in place, you may encounter some common challenges. Here’s how to overcome them:
1. User Adoption Issues
One of the biggest challenges is getting your team to actually *use* the CRM. Resistance to change, lack of training, or a perception that the CRM is too complex can all contribute to low user adoption. Here’s how to address it:
- Provide Comprehensive Training: Ensure all users receive thorough training on the CRM’s features and benefits.
- Highlight the Benefits: Clearly communicate how the CRM will make their jobs easier and more efficient.
- Lead by Example: Encourage managers and team leaders to actively use the CRM and demonstrate its value.
- Gather Feedback: Regularly solicit feedback from users to identify and address any pain points.
- Make it Easy to Use: Simplify the CRM interface and make it easy for users to access the information they need.
2. Data Quality Problems
Garbage in, garbage out. If your data is inaccurate, incomplete, or outdated, your CRM will be useless. To solve this:
- Implement Data Entry Standards: Establish clear guidelines for data entry to ensure consistency and accuracy.
- Automate Data Entry: Use automation features to minimize manual data entry and reduce errors.
- Regularly Cleanse Data: Schedule regular data cleansing to remove duplicates, correct errors, and update outdated information.
- Validate Data: Implement data validation rules to prevent incorrect data from being entered in the first place.
3. Integration Difficulties
Integrating your CRM with other systems can be complex. Here’s how to smooth the process:
- Plan Carefully: Before integrating, carefully plan the integration process and identify any potential challenges.
- Choose Compatible Systems: Ensure that the CRM and other systems you’re integrating are compatible.
- Seek Expert Help: Consider hiring a CRM expert to help with the integration process.
- Test Thoroughly: Thoroughly test the integration to ensure that it’s working correctly.
- Monitor and Maintain: Monitor the integration regularly and make adjustments as needed.
4. Lack of Customization
Your CRM may not perfectly fit your business needs out-of-the-box. Here’s how to address this:
- Assess Your Needs: Clearly define your customization requirements.
- Choose a Flexible CRM: Select a CRM that offers robust customization options.
- Work with a CRM Expert: Consider hiring a CRM expert to help you customize the system.
- Prioritize Customization: Focus on the customizations that will have the biggest impact on your business.
- Test Thoroughly: Test all customizations to ensure they work as expected.
5. Vendor Support Issues
Sometimes, you may encounter issues with your CRM vendor’s support. If this happens:
- Document Everything: Keep detailed records of all your interactions with the vendor’s support team.
- Escalate Issues: If you’re not getting the support you need, escalate the issue to a higher level of the vendor’s support team.
- Consider Alternatives: If the vendor’s support is consistently poor, consider switching to a different CRM provider.
- Read Reviews: Before choosing a CRM, read reviews from other customers to gauge the quality of the vendor’s support.
The Future of CRM Support
The world of CRM is constantly evolving, and so is CRM support. Here are some trends to watch:
- AI-Powered Support: Artificial intelligence is being used to automate support tasks, such as answering frequently asked questions and providing personalized recommendations.
- Proactive Support: CRM vendors are increasingly providing proactive support, such as monitoring your system for potential issues and alerting you to problems before they impact your business.
- Mobile Support: CRM systems are becoming more mobile-friendly, allowing you to access support and manage your CRM from anywhere.
- Self-Service Support: CRM vendors are investing in self-service support resources, such as knowledge bases, FAQs, and video tutorials, to empower users to find answers on their own.
- Integration with Emerging Technologies: CRM systems are integrating with new technologies, such as chatbots, virtual assistants, and augmented reality, to provide even more innovative support options.
Staying up-to-date with these trends will help you to ensure that you’re getting the best possible CRM support for your small business.
Conclusion: CRM Support – The Key to Small Business Success
In the fast-paced world of small business, having a robust CRM system is no longer a luxury; it’s a necessity. But a CRM is only as good as the support you have to back it up. From choosing the right system and understanding your support options to implementing best practices and overcoming common challenges, this guide has provided you with the knowledge you need to succeed. By investing in CRM support, you’re not just investing in a system; you’re investing in your customers, your team, and the future of your business. Embrace the power of CRM and watch your small business thrive.