Small Business CRM Setup: Your Ultimate Guide to Customer Relationship Management

Small Business CRM Setup: Your Ultimate Guide to Customer Relationship Management
Starting a small business is a thrilling journey. You’re the captain of your own ship, charting a course through uncharted waters. But as your business grows, keeping track of everything – from leads and prospects to existing customers and their needs – can feel like herding cats. That’s where a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system comes in. Setting up a CRM for your small business isn’t just a good idea; it’s a strategic imperative. It’s about building lasting relationships, streamlining your operations, and ultimately, boosting your bottom line. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about small business CRM setup, from the basics to advanced strategies.
What is a CRM and Why Does Your Small Business Need One?
Let’s start with the basics. CRM stands for Customer Relationship Management. At its core, a CRM system is a software solution designed to manage and analyze customer interactions and data throughout the customer lifecycle. It helps you understand your customers better, personalize your interactions, and provide exceptional service. But why is this so crucial for a small business?
For starters, it’s all about efficiency. Imagine juggling multiple spreadsheets, email threads, and sticky notes to keep track of your customer interactions. It’s a recipe for chaos and missed opportunities. A CRM centralizes all this information, making it easily accessible to your team. This means no more lost leads, forgotten follow-ups, or duplicated efforts. Everyone on your team has a unified view of each customer, leading to better collaboration and faster problem-solving.
Beyond efficiency, a CRM empowers you to build stronger customer relationships. By tracking customer interactions, preferences, and purchase history, you can tailor your communication and offer personalized experiences. This fosters loyalty and encourages repeat business. Happy customers are the lifeblood of any small business, and a CRM helps you keep them that way.
Finally, a CRM provides valuable insights into your sales and marketing efforts. By analyzing data on leads, conversions, and customer behavior, you can identify what’s working and what’s not. This allows you to optimize your strategies, allocate your resources effectively, and make data-driven decisions that drive growth. In a nutshell, a CRM is an investment in your future success.
Choosing the Right CRM for Your Small Business
The market is flooded with CRM solutions, each with its own set of features and pricing plans. Choosing the right one can feel overwhelming, but it doesn’t have to be. Here’s a breakdown of the key factors to consider:
1. Features and Functionality
First, assess your needs. What do you want your CRM to do? Common features include:
- Contact Management: Store and organize customer information, including contact details, demographics, and communication history.
- Lead Management: Track leads through the sales pipeline, from initial contact to conversion.
- Sales Automation: Automate repetitive sales tasks, such as sending emails, scheduling appointments, and creating follow-up tasks.
- Marketing Automation: Automate marketing campaigns, such as email marketing, social media posting, and lead nurturing.
- Reporting and Analytics: Generate reports on sales performance, customer behavior, and marketing effectiveness.
- Integration: Integrate with other tools you use, such as email marketing platforms, accounting software, and social media channels.
Make a list of the features that are essential for your business and look for CRM solutions that offer them. Don’t pay for features you won’t use. Consider your current and future needs to ensure the CRM can scale with your business.
2. Ease of Use
A CRM is only useful if your team actually uses it. Choose a system that is intuitive and easy to learn. Look for a user-friendly interface, clear navigation, and helpful tutorials or training resources. A complex or clunky CRM will likely be abandoned by your team, defeating the purpose of the investment.
3. Price and Pricing Plans
CRM solutions range in price, from free options to enterprise-level packages. Consider your budget and choose a plan that fits your needs. Many CRM providers offer tiered pricing plans, with different features and user limits at each tier. Start with a plan that meets your current needs and upgrade as your business grows. Be sure to factor in the cost of implementation, training, and ongoing support.
4. Scalability
Your CRM should be able to grow with your business. As you add more customers, employees, and features, your CRM should be able to handle the increased workload. Choose a CRM that offers scalability options, such as the ability to add more users, storage, or integrations.
5. Customer Support
When you encounter issues, you’ll want access to reliable customer support. Check the CRM provider’s support options, such as online documentation, email support, phone support, and live chat. Read reviews and testimonials to get an idea of the quality of their support. A responsive and helpful support team can make a big difference in your experience.
6. Reviews and Reputation
Research the CRM provider’s reputation. Read reviews from other small businesses to see what they say about the software and the company. Look for independent reviews and ratings from reputable sources. Consider the provider’s experience in the industry and their commitment to innovation.
Step-by-Step Guide to Setting Up Your CRM
Once you’ve chosen a CRM, it’s time to set it up. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you get started:
1. Planning and Preparation
Before you dive in, take some time to plan your CRM setup. This will save you time and frustration in the long run. Define your goals for the CRM. What do you want to achieve? Identify your key metrics. What will you measure to track your success? Determine your data requirements. What information do you need to collect about your customers? Create a data migration plan. How will you transfer your existing customer data into the CRM? Document your processes. How will you use the CRM in your daily workflows?
2. Choosing Your CRM and Signing Up
Select the CRM solution that best meets your needs, based on the research you’ve done in the previous step. Sign up for an account. Most CRM providers offer free trials, so take advantage of this opportunity to test the software before committing to a paid plan.
3. Customization and Configuration
This is where you tailor the CRM to your specific needs. Customize the fields and data entry forms to capture the information that’s most relevant to your business. Configure the sales pipeline to reflect your sales process. Set up automated workflows to streamline your processes. Integrate the CRM with other tools you use, such as email marketing platforms and accounting software. Define user roles and permissions to control access to data and features.
4. Data Import and Migration
Import your existing customer data into the CRM. Clean up your data before importing it to ensure accuracy and consistency. Map your data fields to the corresponding fields in the CRM. Test your data import to make sure everything is working correctly. This is a crucial step, as the quality of your data will directly impact the effectiveness of your CRM.
5. Training and Onboarding
Train your team on how to use the CRM. Provide clear instructions, tutorials, and support resources. Encourage your team to embrace the CRM and use it consistently. Provide ongoing training and support to address any questions or issues that arise. This can be done through internal workshops, online tutorials, or by utilizing the CRM provider’s training materials.
6. Testing and Refinement
Test the CRM thoroughly to ensure it’s working as expected. Identify and resolve any issues or bugs. Gather feedback from your team and make adjustments as needed. Continuously refine your CRM setup to optimize its performance and meet your evolving needs. This is an ongoing process of improvement and adaptation.
7. Ongoing Maintenance and Optimization
Keep your CRM up-to-date with the latest features and updates. Regularly review your data and clean up any inaccuracies. Monitor your CRM’s performance and identify areas for improvement. Adjust your CRM setup as your business evolves and your needs change. This is a long-term commitment, not a one-time setup.
Key Features to Implement in Your Small Business CRM
While the specific features you implement will depend on your business, here are some key features that are essential for most small businesses:
1. Contact Management
This is the foundation of any CRM. Store and organize customer contact information, including names, email addresses, phone numbers, and physical addresses. Track customer demographics, such as age, gender, and location. Capture customer communication history, including emails, phone calls, and meetings. This gives you a 360-degree view of each customer.
2. Lead Management
Track leads through the sales pipeline, from initial contact to conversion. Capture lead information, such as source, interest, and qualification status. Assign leads to sales representatives. Track lead activity, such as emails, calls, and meetings. Monitor lead conversion rates to identify areas for improvement. This helps you manage your sales process efficiently.
3. Sales Automation
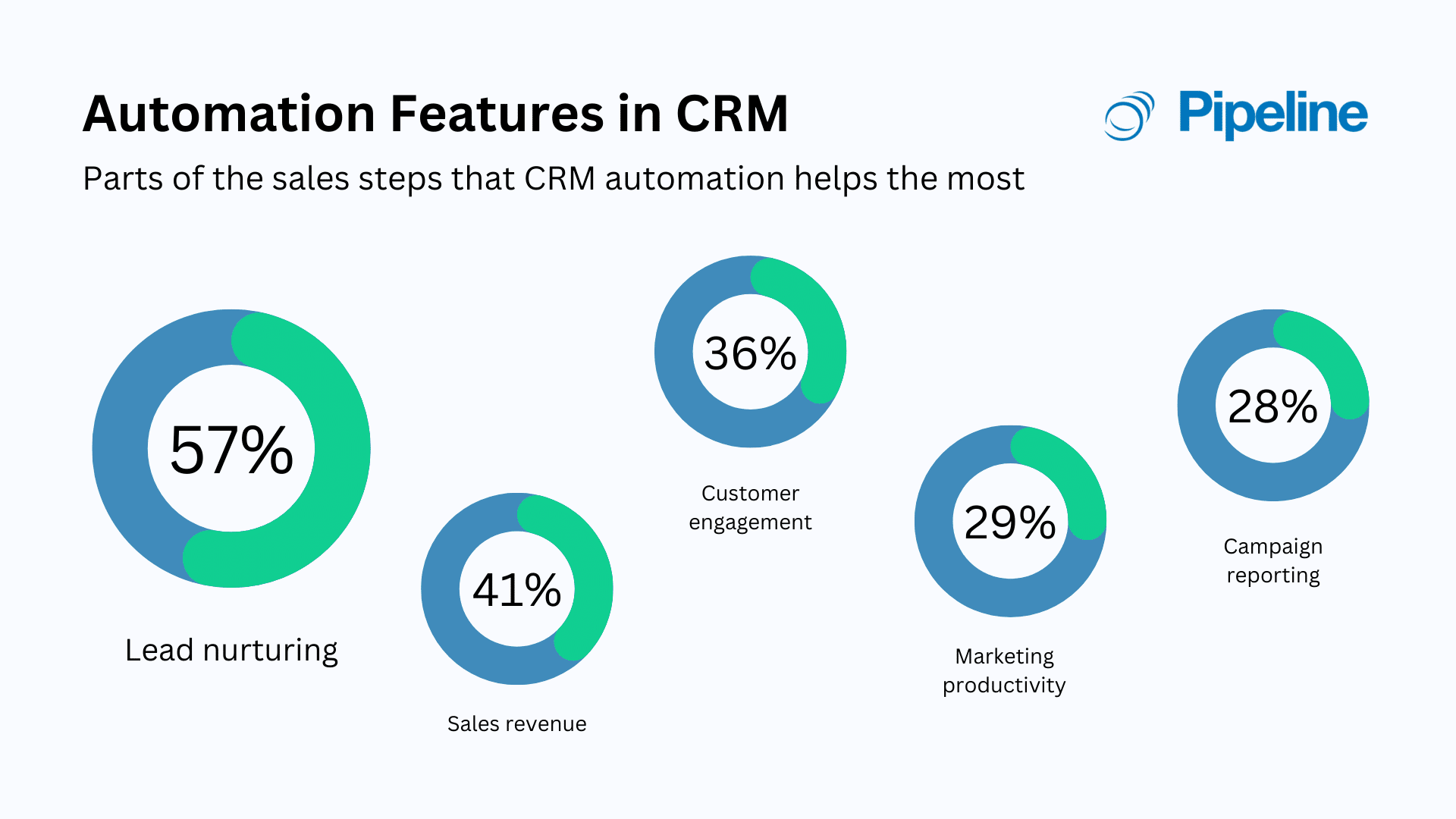
Automate repetitive sales tasks, such as sending emails, scheduling appointments, and creating follow-up tasks. Automate lead nurturing campaigns to engage leads and move them through the sales pipeline. Automate sales reporting to track your sales performance. This frees up your sales team to focus on closing deals.
4. Marketing Automation
Automate marketing campaigns, such as email marketing, social media posting, and lead nurturing. Segment your customer base and personalize your marketing messages. Track marketing campaign performance to measure your ROI. This streamlines your marketing efforts and improves your results.
5. Reporting and Analytics
Generate reports on sales performance, customer behavior, and marketing effectiveness. Track key metrics, such as sales revenue, customer acquisition cost, and customer lifetime value. Use data to identify trends, patterns, and insights that can inform your business decisions. This helps you make data-driven decisions and improve your performance.
6. Integrations
Integrate your CRM with other tools you use, such as email marketing platforms, accounting software, and social media channels. This allows you to streamline your workflows and improve your efficiency. Ensure the CRM can integrate with the tools you already use to avoid data silos and manual processes.
Best Practices for Successful CRM Implementation
Implementing a CRM is a significant undertaking, but following these best practices can increase your chances of success:
1. Define Clear Goals and Objectives
Before you start, clearly define your goals for the CRM. What do you want to achieve? This will help you choose the right CRM and customize it to meet your specific needs. Have a clear understanding of what you want to accomplish with the CRM before you begin.
2. Involve Your Team
Get your team involved in the selection and implementation process. Their input is crucial to ensure the CRM meets their needs and is easy to use. This will also increase their buy-in and encourage them to use the CRM consistently. Involve your sales, marketing, and customer service teams early on.
3. Start Small and Scale Gradually
Don’t try to do everything at once. Start with the core features and gradually add more features as your team becomes comfortable with the system. This will make the implementation process less overwhelming and increase your chances of success. Begin with the essentials and expand as needed.
4. Clean Your Data
Before importing your data, clean it up to ensure accuracy and consistency. This will improve the quality of your data and make it more useful. Remove duplicates, correct errors, and standardize your data format. A good CRM is only as good as the data it contains.
5. Provide Adequate Training
Train your team on how to use the CRM. Provide clear instructions, tutorials, and support resources. Ongoing training will help your team stay up-to-date with the latest features and best practices. Invest in training to ensure your team is proficient with the system.
6. Monitor and Measure Your Results
Track your CRM’s performance and measure your results. Use data to identify areas for improvement and make adjustments as needed. Regularly review your CRM’s setup and make sure it’s still meeting your needs. Evaluate your progress and make adjustments as needed.
7. Get Executive Buy-In
Secure buy-in from your company’s leadership. Their support is crucial for the success of your CRM implementation. Having a champion at the executive level can help ensure that the CRM is prioritized and that resources are allocated to support its implementation. Ensure that the leadership team understands the value of a CRM and is committed to its success.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Implementing a CRM isn’t always smooth sailing. Here are some common challenges and how to overcome them:
1. Lack of User Adoption
One of the biggest challenges is getting your team to actually use the CRM. This can happen if the system is too complex, the training is inadequate, or the team doesn’t see the value. To overcome this, choose a user-friendly CRM, provide thorough training, and clearly communicate the benefits of using the system. Get user feedback and make adjustments as needed. Make sure your team understands the ‘why’ behind the CRM.
2. Data Migration Issues
Migrating data from your existing systems to the CRM can be time-consuming and challenging. To avoid problems, plan your data migration carefully, clean your data before importing it, and test your import process thoroughly. If necessary, consider seeking professional help with data migration. Ensure the data is accurately transferred to avoid data loss or corruption.
3. Integration Problems
Integrating your CRM with other tools can sometimes be tricky. Make sure the CRM you choose integrates with the tools you use. Test your integrations thoroughly and seek help from the vendor’s support team if needed. Ensure that the integrations are functioning correctly and that data is flowing smoothly between systems.
4. Budget Overruns
CRM implementations can sometimes go over budget. To avoid this, create a detailed budget and stick to it. Carefully evaluate the costs of the CRM, including software, implementation, training, and ongoing support. Be realistic about the time and resources required. Plan for unexpected costs and include a buffer in your budget. Regularly review your spending and make adjustments as needed.
5. Lack of Ongoing Support
It’s important to have ongoing support from the CRM vendor. Make sure the vendor offers adequate support options, such as online documentation, email support, and phone support. Ensure that you have access to the support you need to resolve any issues that arise. Read reviews of the vendor’s support to assess its quality.
The Future of CRM for Small Businesses
The CRM landscape is constantly evolving, and small businesses need to stay ahead of the curve. Here are some trends to watch:
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is being used to automate tasks, personalize customer interactions, and provide data-driven insights. Expect to see more AI-powered features in CRM systems, such as chatbots, predictive analytics, and automated lead scoring. AI will help small businesses be more efficient and effective.
2. Mobile CRM
Mobile CRM allows your team to access customer data and manage interactions on the go. Look for CRM solutions that offer robust mobile apps that provide access to key features and functionality. Mobile CRM empowers your team to stay connected and productive from anywhere. Mobile access is essential in today’s fast-paced world.
3. Enhanced Integrations
CRM systems are integrating with an ever-increasing number of tools and platforms. This allows you to streamline your workflows and improve your efficiency. Look for CRM solutions that offer seamless integrations with the tools you use. Integration is key to creating a unified view of your customer.
4. Data Privacy and Security
Data privacy and security are becoming increasingly important. Choose a CRM that prioritizes data security and complies with relevant regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA. Ensure that your CRM provider has robust security measures in place to protect your customer data. Prioritize data protection and compliance.
5. Focus on Customer Experience
The focus is shifting towards providing exceptional customer experiences. CRM systems are being designed to help businesses personalize their interactions and build stronger customer relationships. Look for CRM solutions that offer features that enhance customer experience, such as personalized marketing, self-service portals, and proactive customer support. Customer experience is the new battleground for businesses.
Conclusion: Embracing CRM for Small Business Success
Implementing a CRM for your small business is a strategic investment that can yield significant rewards. By choosing the right CRM, setting it up correctly, and following best practices, you can build stronger customer relationships, streamline your operations, and drive sustainable growth. Don’t be intimidated by the process. Start small, focus on your goals, and embrace the power of CRM to transform your business. The future of your small business may very well depend on it. Take the leap, and watch your business flourish!