Small Business CRM Security in 2025: Fortifying Your Data Against Tomorrow’s Threats

Small Business CRM Security in 2025: A Proactive Approach
The digital landscape is evolving at warp speed. For small businesses, this rapid transformation presents both incredible opportunities and significant challenges, especially when it comes to data security. Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems are the lifeblood of many small enterprises, housing sensitive customer information, sales data, and critical business insights. In 2025, the security of your CRM is not just a technical necessity; it’s a fundamental requirement for survival. This article delves deep into the evolving world of small business CRM security, providing a comprehensive guide to navigating the threats and securing your valuable data.
The Rising Tide of Cyber Threats in 2025
The threat landscape in 2025 is far more sophisticated than it is today. Cybercriminals are becoming increasingly adept, leveraging advanced technologies and tactics to exploit vulnerabilities. Small businesses, often perceived as easier targets due to their typically smaller security budgets and less robust defenses, are increasingly in the crosshairs. Here are some of the key threats you should be aware of:
- Sophisticated Phishing Attacks: Phishing remains a persistent threat, but it’s evolving. In 2025, expect to see more targeted phishing campaigns using AI-powered tools to create highly convincing emails and impersonate trusted sources. These attacks can lead to credential theft, malware installation, and data breaches.
- Ransomware 2.0: Ransomware attacks are becoming more destructive and targeted. Cybercriminals are not only encrypting your data but also exfiltrating it, threatening to release sensitive information if the ransom is not paid. They are also targeting cloud-based CRM systems, making data recovery even more complex.
- Supply Chain Attacks: Small businesses are often vulnerable through their vendors and partners. Cybercriminals can exploit vulnerabilities in third-party software or services that your CRM system relies on, gaining access to your data indirectly.
- Insider Threats: While often overlooked, insider threats – malicious or accidental – pose a significant risk. This includes disgruntled employees, careless users, and those who fall victim to social engineering tactics.
- AI-Powered Attacks: Cybercriminals are leveraging AI for everything from automating attacks to creating highly realistic deepfakes that can be used to deceive employees and access sensitive information.
The Importance of CRM Security for Small Businesses
Why is CRM security so crucial for small businesses? The answer is multifaceted:
- Protecting Customer Data: CRM systems contain Personally Identifiable Information (PII) such as names, addresses, contact details, and purchase history. Breaches can lead to identity theft, financial loss, and reputational damage for your customers, which in turn reflects poorly on your business.
- Maintaining Customer Trust: Customers are increasingly concerned about data privacy. A security breach can erode trust, leading to lost customers and a damaged brand reputation.
- Complying with Regulations: Businesses must comply with data privacy regulations, such as GDPR, CCPA, and others. Failure to comply can result in hefty fines and legal action.
- Avoiding Financial Losses: Data breaches can be incredibly costly, involving expenses for incident response, data recovery, legal fees, regulatory fines, and customer notification.
- Ensuring Business Continuity: A ransomware attack or data breach can disrupt business operations, potentially leading to downtime and lost revenue. A secure CRM system helps ensure that your business can continue to function even in the face of adversity.
Key Security Measures for Your CRM in 2025
Securing your CRM system in 2025 requires a multi-layered approach. Here are some of the most important security measures to implement:
1. Robust Access Controls and Authentication
Controlling who has access to your CRM data is paramount. Implement the following measures:
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Require MFA for all users, including employees and administrators. This adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to verify their identity through a second factor, such as a code from a mobile app or a biometric scan.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Grant users access only to the data and functionalities they need to perform their jobs. This minimizes the impact of a potential breach by limiting the exposure of sensitive information.
- Regular Password Audits and Updates: Enforce strong password policies, including minimum length, complexity requirements, and regular password changes. Conduct regular audits to identify and address weak passwords.
- Privileged Access Management (PAM): Implement PAM to manage and monitor access to privileged accounts, such as administrator accounts. This helps prevent unauthorized access and control.
2. Data Encryption
Encryption protects your data both at rest (stored on servers) and in transit (when it’s being transmitted over the network). Key measures include:
- Encryption at Rest: Encrypt the data stored in your CRM database using robust encryption algorithms.
- Encryption in Transit: Use HTTPS to encrypt all communication between users and the CRM system. Ensure that the CRM provider uses strong encryption protocols.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Implement DLP solutions to monitor and prevent sensitive data from leaving your organization. These solutions can identify and block unauthorized data transfers.
3. Regular Security Assessments and Vulnerability Management
Proactive security assessments are essential to identify and address vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. This includes:
- Vulnerability Scanning: Regularly scan your CRM system and related infrastructure for known vulnerabilities. Use automated scanning tools to identify potential weaknesses.
- Penetration Testing: Conduct periodic penetration tests (pen tests) to simulate real-world attacks and identify vulnerabilities that may not be detected by automated scanning.
- Security Audits: Hire a third-party security expert to conduct security audits of your CRM system, policies, and procedures.
- Patch Management: Implement a robust patch management process to ensure that all software and systems are up-to-date with the latest security patches.
4. Incident Response Planning and Disaster Recovery
Even with the best security measures in place, breaches can still happen. Having a well-defined incident response plan and disaster recovery plan is critical:
- Incident Response Plan: Develop a detailed incident response plan that outlines the steps to take in the event of a security breach. This plan should include procedures for identifying, containing, eradicating, and recovering from the breach.
- Disaster Recovery Plan: Create a disaster recovery plan to ensure that your CRM system can be restored quickly in the event of a disaster, such as a data breach, natural disaster, or system failure. This should include regular data backups and offsite storage.
- Regular Testing and Drills: Regularly test your incident response and disaster recovery plans through simulated exercises to ensure that they are effective.
5. Employee Training and Awareness
Your employees are your first line of defense against cyber threats. Comprehensive security training is essential:
- Security Awareness Training: Provide regular security awareness training to all employees, covering topics such as phishing, social engineering, password security, and data privacy.
- Phishing Simulations: Conduct regular phishing simulations to test employees’ ability to recognize and avoid phishing attacks.
- Data Privacy Training: Train employees on data privacy regulations and best practices, such as GDPR and CCPA, and the importance of safeguarding customer data.
- Background Checks: Conduct background checks on new employees, particularly those with access to sensitive data.
6. CRM Provider Security
If you use a cloud-based CRM system, the security of your provider is critical. Choose a provider that:
- Has a Strong Security Posture: Ensure that the provider has a robust security program, including certifications such as ISO 27001 and SOC 2.
- Offers Security Features: Look for features such as MFA, data encryption, and activity logging.
- Provides Regular Security Updates: Ensure that the provider regularly updates its systems with the latest security patches.
- Has a Clear Data Privacy Policy: Review the provider’s data privacy policy to understand how they handle customer data.
- Offers Data Backup and Recovery: Verify that the provider offers data backup and recovery services to ensure that your data can be restored in the event of a disaster.
7. Monitoring and Logging
Continuous monitoring of your CRM system and related infrastructure is essential to detect and respond to security incidents in a timely manner:
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): Implement a SIEM solution to collect and analyze security logs from various sources, such as your CRM system, network devices, and servers. This can help you identify suspicious activity and security threats.
- Activity Logging: Enable detailed activity logging in your CRM system to track user actions, such as logins, data changes, and file downloads. Review these logs regularly to detect any unusual or suspicious activity.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS): Deploy IDPS to monitor network traffic and identify and prevent malicious activity.
- Alerting and Notifications: Configure alerts and notifications to be notified of security incidents in real-time.
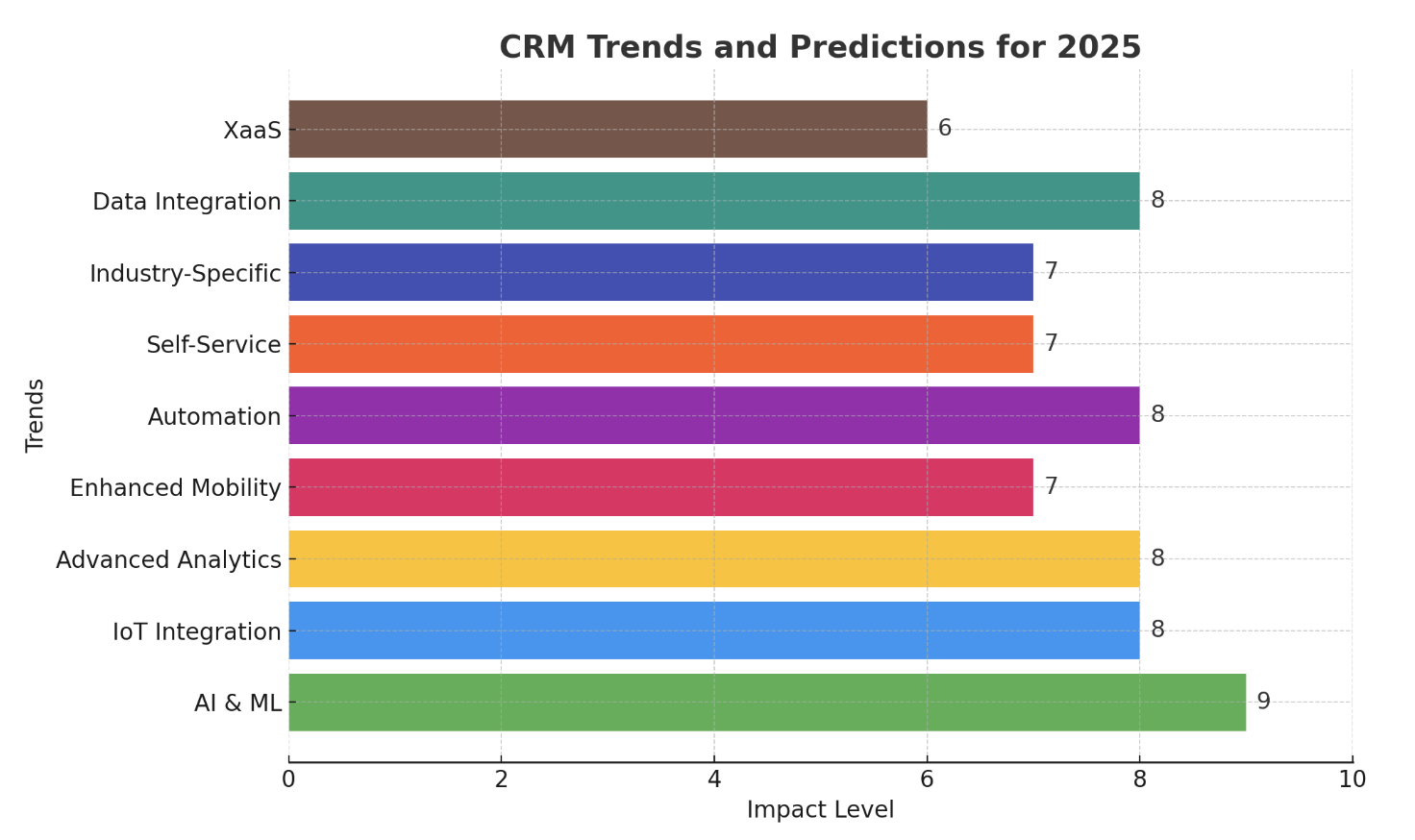
Emerging Technologies Shaping CRM Security in 2025
The rapid advancement of technology is transforming the way businesses operate, and CRM security is no exception. Several emerging technologies will play a crucial role in securing CRM systems in 2025 and beyond:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML are being used to automate threat detection, identify anomalies, and improve incident response. AI-powered security solutions can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and predict potential threats before they materialize.
- Zero Trust Security: The zero-trust model assumes that no user or device, inside or outside the network, can be trusted by default. This approach requires verifying every user and device before granting access to resources, which significantly reduces the attack surface.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain can be used to secure data integrity and improve data privacy. It can be used to create tamper-proof audit trails and secure data sharing.
- Behavioral Analytics: Analyzing user behavior can help detect and prevent insider threats. By monitoring user activity, businesses can identify unusual behavior that could indicate a security breach.
- Automated Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR): SOAR platforms automate security tasks, such as incident response and threat hunting, improving efficiency and reducing the time it takes to respond to security incidents.
Building a Security-First Culture
Security is not just a technical issue; it’s a cultural one. Building a security-first culture within your small business is essential for long-term success. This involves:
- Leadership Commitment: Security must be a priority for leadership, with clear communication and support for security initiatives.
- Employee Engagement: Involve employees in security discussions and encourage them to report potential security risks.
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly review and update your security policies and procedures to adapt to the evolving threat landscape.
- Collaboration and Information Sharing: Share information about security threats and best practices with other businesses and industry groups.
- Staying Informed: Keep abreast of the latest security threats, trends, and best practices by reading industry publications, attending conferences, and participating in online forums.
Choosing the Right CRM for Security in 2025
When selecting a CRM system in 2025, security should be a primary consideration. Here’s what to look for:
- Security Certifications: Look for CRM providers with relevant security certifications, such as ISO 27001, SOC 2, and GDPR compliance.
- Security Features: Prioritize CRM systems that offer robust security features, such as MFA, encryption, access controls, and audit trails.
- Data Privacy: Carefully review the CRM provider’s data privacy policy to understand how they handle customer data.
- Vendor Reputation: Research the CRM provider’s reputation for security and data privacy. Read reviews and check for any past security incidents.
- Integration Capabilities: Ensure that the CRM system integrates with your existing security tools and infrastructure.
- Scalability: Choose a CRM system that can scale to meet your business’s growing needs without compromising security.
The Path Forward: Securing Your CRM for the Future
Securing your small business CRM in 2025 is an ongoing process, not a one-time fix. By implementing the security measures discussed in this article, embracing emerging technologies, and fostering a security-first culture, you can significantly reduce your risk of a data breach and protect your valuable customer data. Remember that the key is to be proactive, stay informed, and continuously adapt to the evolving threat landscape. By taking a proactive approach to CRM security, you can safeguard your business, protect your customers, and thrive in the competitive landscape of 2025 and beyond.
Securing your CRM system is not just a matter of compliance; it’s about building trust with your customers and ensuring the long-term success of your business. Invest in your security, and you’ll be investing in your future.