Small Business CRM Pricing: A Comprehensive Guide to Finding the Perfect Fit
Small Business CRM Pricing: Navigating the Landscape
Choosing the right Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system is a pivotal decision for any small business. It’s about more than just managing contacts; it’s about streamlining processes, boosting sales, improving customer satisfaction, and ultimately, driving growth. But with a plethora of CRM options available, understanding the pricing structures can feel overwhelming. This comprehensive guide will break down the complexities of small business CRM pricing, helping you find the perfect fit for your budget and needs.
Why CRM is Crucial for Small Businesses
Before diving into the pricing specifics, let’s reiterate the importance of a CRM for small businesses. In today’s competitive market, you need every advantage you can get. A CRM provides that advantage by:
- Centralizing Customer Data: No more scattered spreadsheets or lost contact information. A CRM consolidates all customer interactions, preferences, and purchase history in one easily accessible location.
- Improving Sales Efficiency: CRM automates repetitive tasks, such as data entry and email follow-ups, freeing up your sales team to focus on closing deals.
- Enhancing Customer Service: Accessing a complete customer profile allows your support team to provide personalized and effective assistance, leading to higher satisfaction and loyalty.
- Boosting Marketing Effectiveness: Segment your audience based on demographics, behavior, and purchase history to deliver targeted marketing campaigns that generate better results.
- Providing Actionable Insights: CRM offers reports and analytics that help you understand your customers, track performance, and make data-driven decisions.
Understanding CRM Pricing Models
CRM pricing models vary widely, and each has its pros and cons. Here’s a breakdown of the most common structures:
1. Per-User, Per-Month Pricing
This is perhaps the most prevalent pricing model. You pay a fixed monthly fee for each user who accesses the CRM system. This model is straightforward, making it easy to budget. However, it can become expensive as your team grows. It’s crucial to assess how many users truly need access to the CRM. Consider whether all employees need full access or if some can operate with limited roles.
Pros:
- Predictable costs.
- Scalable – you can easily add or remove users.
- Often includes support and updates.
Cons:
- Can be expensive for large teams.
- You pay for users, even if they don’t actively use the system.
2. Tiered Pricing
Tiered pricing offers different pricing levels based on the features and functionality you need. Each tier typically includes a set of features, and the price increases as you move up the tiers. This model allows you to choose a plan that aligns with your specific requirements and budget. It’s suitable if you don’t need all the bells and whistles of a top-tier plan.
Pros:
- Flexible – you can choose a plan that fits your needs.
- Potentially lower costs if you only need basic features.
- Scalable – you can upgrade to a higher tier as your business grows.
Cons:
- Can be complex to compare different plans.
- You may need to upgrade to a higher tier as your needs evolve.
3. Usage-Based Pricing
With usage-based pricing, you’re charged based on your actual usage of the CRM system. This might involve the number of contacts stored, emails sent, or features used. This model can be cost-effective for businesses with fluctuating needs or those that are just starting. However, it’s essential to carefully monitor your usage to avoid unexpected costs.
Pros:
- Potentially lower costs for infrequent users.
- Pay only for what you use.
Cons:
- Costs can be unpredictable.
- Requires careful monitoring of usage.
4. Free CRM Options
Many CRM providers offer free versions of their software. These free plans typically have limited features and user capacity. They can be a great starting point for very small businesses or those with basic CRM needs. However, be prepared to upgrade to a paid plan as your business grows and your requirements become more sophisticated.
Pros:
- No upfront cost.
- Good for testing the waters or for basic needs.
Cons:
- Limited features and functionality.
- May have limitations on user count and data storage.
5. On-Premise CRM
This model involves purchasing a software license and installing the CRM on your own servers. You’re responsible for the infrastructure, maintenance, and security. This option offers greater control and customization but requires significant upfront investment and technical expertise. It’s generally not recommended for small businesses unless they have specific security or compliance requirements.
Pros:
- Greater control and customization.
- Data security and privacy.
Cons:
- High upfront costs.
- Requires technical expertise to manage.
- Responsibility for maintenance and security.
Key Factors Influencing CRM Pricing
Several factors influence the cost of a CRM system. Understanding these factors will help you make an informed decision and find a solution that aligns with your budget. Here are some key considerations:
1. Number of Users
As mentioned earlier, the number of users is a primary driver of cost in many pricing models. Determine how many employees will need access to the CRM and factor this into your budget. Consider whether everyone needs full access or if you can assign different roles and permissions to control costs.
2. Features and Functionality
The features you need will significantly impact the price. Basic CRM systems offer contact management, sales pipeline tracking, and basic reporting. More advanced systems may include marketing automation, email integration, social media integration, lead scoring, and advanced analytics. Assess your needs carefully and only pay for the features you require.
3. Data Storage and Usage Limits
Some CRM providers impose limits on data storage, the number of contacts you can store, or the number of emails you can send. Make sure the plan you choose offers sufficient capacity for your needs. If you anticipate rapid growth, consider a plan with generous limits or the ability to scale up easily.
4. Integrations
Integration with other business applications, such as email marketing platforms, accounting software, and e-commerce platforms, can enhance the value of your CRM. However, integrations may come at an additional cost. Check which integrations are included in the pricing plan and factor in any extra costs for those you need.
5. Customer Support and Training
The level of customer support and training provided by the CRM vendor can vary. Some vendors offer comprehensive support, including phone, email, and live chat, while others provide limited support. Consider the level of support you need and factor in the cost of any additional training or support services.
6. Customization Options
If you require extensive customization to tailor the CRM to your specific business processes, this can impact the price. Some vendors offer customization services at an additional cost, while others provide tools that allow you to customize the system yourself. Assess your customization needs and factor in any associated costs.
7. Contract Length
Some CRM providers offer discounts for longer-term contracts. If you’re confident in your choice, consider signing up for an annual or multi-year plan to save money. However, make sure the provider offers a cancellation policy in case your needs change.
Comparing CRM Pricing Plans: A Practical Approach
Now that you understand the pricing models and factors that influence cost, here’s a practical approach to comparing CRM pricing plans:
1. Define Your Requirements
Before you start comparing plans, create a list of your essential CRM requirements. This should include the features you need, the number of users, data storage capacity, and any integrations you require. This will help you narrow down your options and focus on plans that meet your specific needs.
2. Research Different CRM Providers
Explore the market and identify CRM providers that cater to small businesses. Read reviews, compare features, and explore their pricing pages. Make a shortlist of providers that seem like a good fit.
3. Evaluate Pricing Plans
Carefully review the pricing plans offered by your shortlisted providers. Compare the features, user limits, data storage capacity, and integrations included in each plan. Consider the long-term costs and any potential hidden fees.
4. Calculate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Don’t just look at the monthly or annual fee. Calculate the total cost of ownership (TCO), which includes the initial setup costs, any additional fees for integrations or customization, and the cost of training and support. This will give you a more accurate picture of the overall cost.
5. Consider Scalability
Choose a CRM system that can scale with your business. As your business grows, you’ll likely need to add users, increase data storage, and expand your feature set. Make sure the CRM provider offers flexible plans that allow you to scale up easily without incurring excessive costs.
6. Take Advantage of Free Trials and Demos
Most CRM providers offer free trials or demos. Take advantage of these opportunities to test the system and see if it meets your needs. This will allow you to evaluate the user interface, features, and performance before committing to a paid plan.
7. Read Reviews and Testimonials
Read reviews and testimonials from other small businesses to get insights into the pros and cons of different CRM systems. Pay attention to feedback on customer support, ease of use, and overall satisfaction.
Top CRM Systems for Small Businesses (and their pricing)
Here’s a look at some of the top CRM systems for small businesses and a general overview of their pricing (Note: Pricing is subject to change, always refer to the provider’s website for the most up-to-date information):
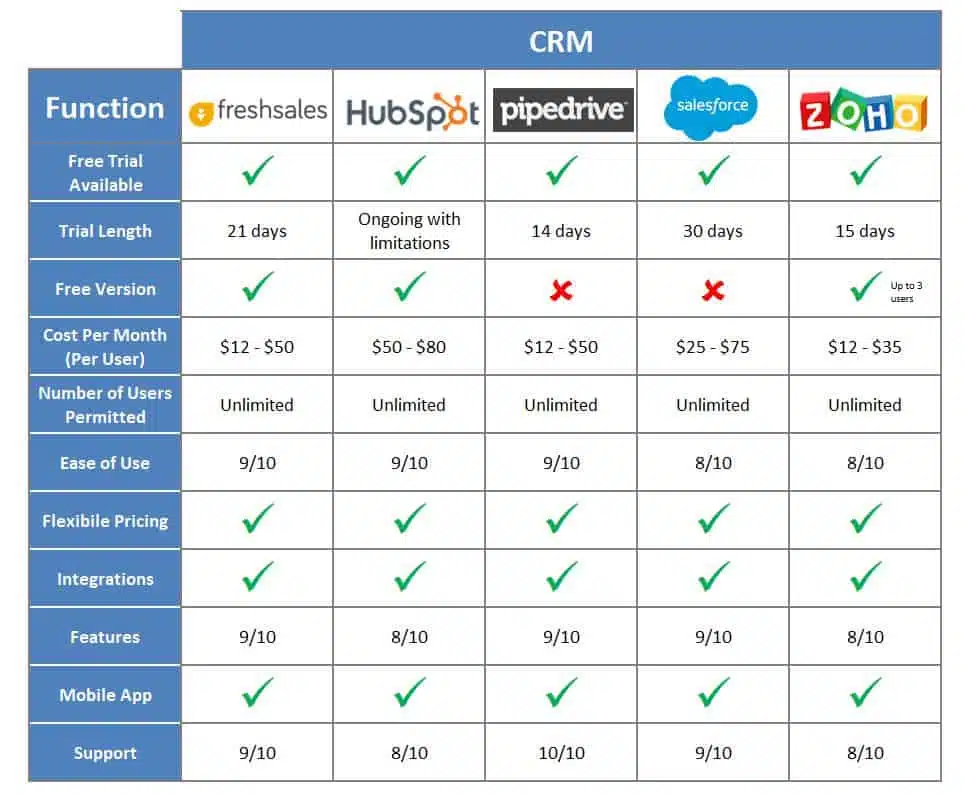
1. HubSpot CRM
Pricing: HubSpot offers a free CRM with unlimited users and a range of features, including contact management, deal tracking, and email marketing. Paid plans start at a relatively affordable price and offer more advanced features, such as marketing automation and sales analytics. They have a tiered pricing model, with different tiers for Sales Hub, Marketing Hub, Service Hub, and CMS Hub.
Key Features: Contact management, sales pipeline tracking, email marketing, marketing automation, reporting and analytics, integrations with other tools.
Pros: Free option available, user-friendly interface, comprehensive features, strong integrations.
Cons: Some advanced features are only available in higher-priced plans.
2. Zoho CRM
Pricing: Zoho CRM offers a free plan for up to 3 users with limited features. Paid plans are available with different tiers, each offering more features and user capacity. They use a per-user, per-month pricing model.
Key Features: Contact management, sales force automation, workflow automation, marketing automation, analytics and reporting, integrations with other Zoho apps and third-party tools.
Pros: Affordable pricing, extensive features, customizable, strong integrations.
Cons: Free plan is limited, some features may require additional add-ons.
3. Freshsales (by Freshworks)
Pricing: Freshsales offers a free plan with limited features. They have tiered pricing with a per-user, per-month model. Their plans offer various levels of features, with higher tiers unlocking more advanced options like automation and analytics.
Key Features: Contact management, sales pipeline management, built-in phone and email, sales automation, reporting and analytics.
Pros: User-friendly interface, built-in phone and email, affordable pricing.
Cons: Limited features in the free plan, some advanced features only available in higher-priced plans.
4. Pipedrive
Pricing: Pipedrive offers a per-user, per-month pricing model, with different tiers based on the features you need. It is specifically designed for sales teams and focuses on pipeline management.
Key Features: Sales pipeline management, contact management, deal tracking, email integration, reporting and analytics.
Pros: User-friendly interface, strong focus on sales, visual pipeline management.
Cons: Limited features outside of sales, may not be suitable for businesses with complex needs.
5. Agile CRM
Pricing: Agile CRM offers a free plan for up to 10 users with limited features. Paid plans offer various levels of features with a per-user, per-month pricing model. They offer a good balance of features and affordability.
Key Features: Contact management, sales automation, marketing automation, helpdesk, reporting and analytics.
Pros: Affordable pricing, comprehensive features, user-friendly interface.
Cons: Free plan is limited, may require some learning to master all the features.
Hidden Costs to Watch Out For
Beyond the base pricing, be mindful of potential hidden costs that can inflate your overall expenses:
- Implementation Fees: Some vendors charge fees for setting up the CRM and migrating your data.
- Training Costs: Training your team on how to use the CRM can be an additional expense.
- Integration Fees: Integrating the CRM with other software may involve additional costs.
- Customization Fees: Customizing the CRM to meet your specific needs can add to the cost.
- Data Storage Overages: Exceeding your data storage limits can result in extra charges.
- Support Fees: Premium support options may come with an extra cost.
Making the Right Choice: A Summary
Choosing the right small business CRM is a journey, not a destination. It demands careful consideration of your requirements, budget, and long-term goals. Here’s a recap of the key takeaways:
- Define Your Needs: Clearly outline your requirements, including features, user count, and integrations.
- Understand Pricing Models: Familiarize yourself with the different pricing models and their implications.
- Compare Plans: Evaluate pricing plans based on features, user limits, and total cost of ownership.
- Consider Scalability: Choose a CRM that can grow with your business.
- Take Advantage of Trials: Test the system before committing to a paid plan.
- Factor in Hidden Costs: Be aware of potential hidden expenses, such as implementation fees and training costs.
- Read Reviews: Learn from the experiences of other small businesses.
By following these steps, you can navigate the complexities of small business CRM pricing and find a solution that empowers your team, streamlines your processes, and drives your business towards success. Don’t be afraid to ask questions, negotiate, and take your time. The right CRM system is an investment in your future.
The Future of CRM Pricing
The CRM landscape is constantly evolving. We can expect to see a few trends in the future:
- More AI-Powered Features: CRM systems will increasingly integrate artificial intelligence (AI) to automate tasks, provide insights, and personalize customer interactions.
- Greater Focus on Mobile: With the increasing use of mobile devices, CRM providers will continue to prioritize mobile accessibility and functionality.
- More Flexible Pricing: Providers may offer even more flexible pricing models, such as pay-as-you-go options, to cater to the diverse needs of small businesses.
- Emphasis on Customer Experience: CRM systems will place greater emphasis on improving the overall customer experience, with features designed to enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Staying informed about these trends will help you make the best decisions for your business and ensure that your CRM system remains a valuable asset for years to come. The right CRM system is an investment in your future.