Small Business CRM Pricing: A Comprehensive Guide to Cost-Effective Solutions
Small Business CRM Pricing: Your Ultimate Guide
Running a small business is a whirlwind of activity. You’re juggling everything from product development and marketing to customer service and sales. In the midst of all this, keeping track of your customers and managing those crucial relationships can feel like herding cats. That’s where a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system steps in – it’s your central hub for all things customer-related. But with a plethora of CRM options available, and pricing models that can seem as complex as quantum physics, figuring out the right solution for your small business can be daunting. This comprehensive guide breaks down everything you need to know about small business CRM pricing, helping you make an informed decision that won’t break the bank.
What is a CRM and Why Do You Need One?
Before we dive into the nitty-gritty of pricing, let’s revisit the fundamentals. A CRM is more than just a contact list; it’s a system designed to manage and analyze customer interactions and data throughout the customer lifecycle. Think of it as the brain of your customer-facing operations. It allows you to:
- Centralize Customer Data: Store all customer information in one accessible location, from contact details and purchase history to communication logs.
- Improve Customer Relationships: Gain a 360-degree view of each customer, enabling personalized interactions and better service.
- Boost Sales: Identify and nurture leads, track sales opportunities, and close deals more efficiently.
- Enhance Marketing Efforts: Segment your audience, personalize marketing campaigns, and track campaign performance.
- Streamline Customer Service: Provide faster and more effective support, resolving issues and building customer loyalty.
For a small business, a CRM can be a game-changer. It helps you compete with larger companies by providing the tools to deliver exceptional customer experiences. It helps you to work smarter, not harder, freeing up your time to focus on growing your business.
Understanding CRM Pricing Models
CRM pricing is not a one-size-fits-all affair. Vendors offer various pricing models, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these models is crucial for choosing the right CRM for your budget and business needs. Here are the most common pricing structures:
1. Per-User, Per-Month Pricing
This is the most prevalent pricing model, particularly for cloud-based CRM systems. You pay a monthly fee for each user who accesses the CRM. The price per user can vary widely, depending on the features included and the vendor. This model is often scalable, allowing you to add or remove users as your business grows. It’s generally predictable, making budgeting easier.
Pros:
- Predictable costs.
- Scalable – easily add or remove users.
- Often includes regular updates and support.
Cons:
- Can become expensive as your team grows.
- You pay for users even if they don’t actively use the system.
2. Tiered Pricing
Tiered pricing is a variation of the per-user model. Vendors offer different pricing tiers, each with a different set of features and a different price point. This allows you to choose the tier that best aligns with your business needs and budget. You might start with a basic tier and upgrade as your requirements evolve.
Pros:
- Flexibility to choose features.
- Scalable – upgrade as needed.
- Potentially lower starting costs.
Cons:
- Feature limitations in lower tiers.
- May need to upgrade to access essential features.
3. Usage-Based Pricing
Some CRM vendors charge based on usage, such as the number of contacts stored, emails sent, or transactions processed. This model can be cost-effective for businesses with fluctuating CRM needs or those with a large number of contacts but infrequent interactions. However, it can be challenging to predict costs accurately.
Pros:
- Potentially lower costs for low-volume users.
- Pay only for what you use.
Cons:
- Unpredictable costs.
- May require careful monitoring of usage.
4. Perpetual License (On-Premise) Pricing
This model is less common now, especially for small businesses, but it still exists. You purchase a license to use the CRM software, typically with an upfront fee. You then pay ongoing maintenance and support fees. This model gives you more control over your data and infrastructure but requires a significant upfront investment and technical expertise to manage the system.
Pros:
- Complete control over data.
- Potentially lower long-term costs.
Cons:
- High upfront costs.
- Requires IT infrastructure and expertise.
- Maintenance and support fees.
5. Free CRM Options
Several CRM vendors offer free versions of their software. These versions typically have limited features and are designed for very small businesses or individuals. They can be a good starting point for testing a CRM or for managing a small number of contacts.
Pros:
- No upfront cost.
- Good for testing the waters.
- Can be sufficient for very small businesses.
Cons:
- Limited features.
- May have restrictions on the number of users or contacts.
- May lack advanced functionality.
Key Factors Influencing CRM Pricing
Several factors influence the cost of a CRM system. Understanding these factors will help you evaluate different options and choose the best fit for your budget.
1. Features and Functionality
The more features a CRM offers, the higher the price. Basic CRM systems may include contact management, sales tracking, and basic reporting. More advanced systems offer features such as marketing automation, lead scoring, advanced analytics, and integrations with other business applications. Determine which features are essential for your business and choose a CRM that provides them without unnecessary bells and whistles.
2. Number of Users
Most CRM vendors charge per user, so the number of users you need will significantly impact the cost. Consider how many team members will need access to the CRM and whether you need to provide access to external stakeholders, such as partners or clients. Factor in potential growth when determining the number of users.
3. Data Storage and Usage Limits
Some CRM vendors limit the amount of data you can store or the number of emails you can send. If you have a large number of contacts or send frequent emails, you’ll need to choose a CRM with sufficient storage and usage limits. Be sure to review the vendor’s terms of service carefully.
4. Integrations
If you need to integrate your CRM with other business applications, such as email marketing platforms, accounting software, or e-commerce platforms, consider the cost of these integrations. Some CRM systems offer native integrations, while others require third-party connectors, which may incur additional fees.
5. Support and Training
The level of support and training provided by the CRM vendor can also affect the price. Some vendors offer basic support, while others provide premium support options, such as dedicated account managers and personalized training. Factor in the cost of training your team to ensure they can effectively use the CRM.
6. Customization
If you need to customize the CRM to meet your specific business needs, consider the cost of customization. Some vendors offer customization options, while others require you to hire a developer or consultant. Customization can add significant costs, so choose a CRM that offers the features you need out of the box.
Comparing CRM Pricing for Small Businesses
Let’s look at some popular CRM systems and their pricing structures to give you a clearer picture of what’s available.
1. HubSpot CRM
HubSpot offers a free CRM that’s ideal for small businesses just starting out. It includes contact management, deal tracking, and basic sales and marketing tools. HubSpot also offers paid plans with more advanced features, such as marketing automation, sales analytics, and customer service tools. They have a tiered pricing structure, with different features available at each level. Prices increase as you need more functionality.
Pricing Overview:
- Free: Contact management, deal tracking, basic marketing tools.
- Starter: Starts around $45/month (billed annually) – includes additional marketing and sales features.
- Professional: Starts around $450/month (billed annually) – includes advanced marketing, sales, and service features.
- Enterprise: Custom pricing – offers the most advanced features and customization options.
Pros:
- Free plan is excellent for getting started.
- User-friendly interface.
- Comprehensive suite of tools.
- Strong marketing automation capabilities.
Cons:
- Limited features in the free plan.
- Can become expensive as your needs grow.
2. Zoho CRM
Zoho CRM is a popular and affordable CRM option for small businesses. It offers a free plan for up to three users with limited features. Paid plans offer a wide range of features, including sales force automation, marketing automation, and customer service tools. Zoho CRM’s pricing is competitive, making it a good value for the money. They offer several plans with different feature sets.
Pricing Overview:
- Free: Up to 3 users, basic CRM features.
- Standard: Starts around $14/user/month (billed annually) – includes sales force automation and basic customization.
- Professional: Starts around $23/user/month (billed annually) – includes marketing automation and advanced customization.
- Enterprise: Starts around $40/user/month (billed annually) – includes advanced analytics and customization options.
Pros:
- Affordable pricing.
- Wide range of features.
- Good for businesses of all sizes.
- Strong integration capabilities.
Cons:
- Free plan is limited.
- Interface can be overwhelming for some users.
3. Pipedrive
Pipedrive is a sales-focused CRM that’s designed to help small businesses manage their sales pipeline. It’s known for its intuitive interface and ease of use. Pipedrive’s pricing is straightforward, with per-user, per-month pricing based on the features included. They offer several plans tailored to different sales team needs.
Pricing Overview:
- Essential: Starts around $15/user/month (billed annually) – includes basic sales features.
- Advanced: Starts around $29/user/month (billed annually) – includes automation and integrations.
- Professional: Starts around $59/user/month (billed annually) – includes advanced reporting and customization.
- Enterprise: Starts around $99/user/month (billed annually) – offers the most advanced features and support.
Pros:
- User-friendly interface.
- Focus on sales pipeline management.
- Easy to set up and use.
Cons:
- Limited marketing automation features.
- Can be expensive for larger teams.
4. Freshsales
Freshsales is a CRM from Freshworks that’s designed to help sales teams manage leads, track deals, and close more sales. It offers a free plan for a limited number of users, as well as paid plans with more features, such as email marketing, phone integration, and advanced analytics. Freshsales is a good option for businesses looking for a CRM with a focus on sales. Their pricing is competitive, offering value for features.
Pricing Overview:
- Free: Up to 3 users, basic CRM features.
- Growth: Starts around $15/user/month (billed annually) – includes sales force automation and basic customization.
- Pro: Starts around $39/user/month (billed annually) – includes advanced marketing automation and customization.
- Enterprise: Starts around $69/user/month (billed annually) – includes advanced analytics and customization options.
Pros:
- User-friendly interface.
- Good sales features.
- Affordable pricing.
- Free plan is a good starting point.
Cons:
- Limited customization options.
- May not be suitable for businesses with complex needs.
5. Salesforce Sales Cloud
Salesforce is a market leader in CRM, offering a comprehensive suite of features for businesses of all sizes. Salesforce Sales Cloud offers a range of pricing plans, from basic to enterprise-level. While Salesforce can be a powerful tool, it can also be expensive, especially for small businesses. It is important to carefully evaluate your needs before committing to Salesforce. They offer a wide range of features and plans.
Pricing Overview:
- Salesforce Essentials: Starts around $25/user/month (billed annually) – includes basic sales features.
- Professional: Starts around $75/user/month (billed annually) – includes sales force automation and customization.
- Enterprise: Starts around $150/user/month (billed annually) – includes advanced customization and sales features.
- Unlimited: Starts around $300/user/month (billed annually) – offers the most advanced features and support.
Pros:
- Comprehensive features.
- Highly customizable.
- Large ecosystem of apps and integrations.
Cons:
- Can be expensive.
- Complex interface.
- Requires significant training.
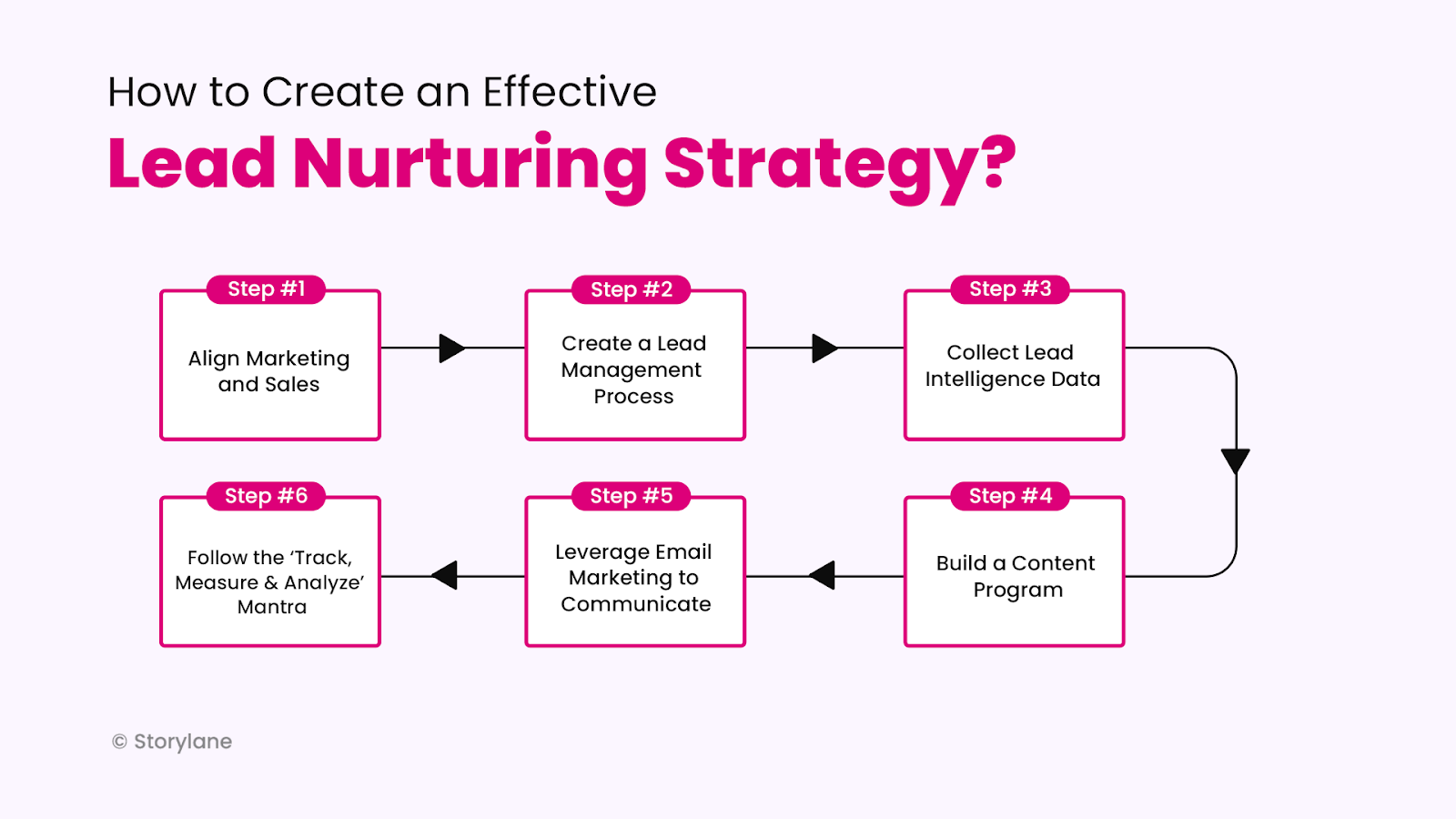
Tips for Choosing the Right CRM for Your Small Business
Choosing the right CRM is a significant decision. Here are some tips to help you make the right choice:
1. Define Your Needs
Before you start comparing CRM systems, take the time to identify your business needs. What are your goals for using a CRM? What features are essential for your business? What are your budget constraints? Knowing your needs will help you narrow down your options and choose a CRM that meets your requirements.
2. Determine Your Budget
Set a realistic budget for your CRM. Consider the initial cost, the ongoing monthly fees, and any additional costs, such as implementation, training, and customization. Don’t overspend on features you don’t need. Remember that a free plan might be a good starting point to test the waters, but it might limit your growth.
3. Research and Compare Options
Once you know your needs and budget, research different CRM systems. Compare their features, pricing, and reviews. Read online reviews and talk to other small business owners to get their feedback. Take advantage of free trials to test out different CRM systems before making a decision. Don’t be afraid to ask for demos and clarification on pricing.
4. Consider Scalability
Choose a CRM that can grow with your business. As your business expands, you’ll need a CRM that can accommodate more users, more data, and more features. Make sure the CRM you choose offers the flexibility and scalability you need.
5. Prioritize Ease of Use
A CRM is only useful if your team actually uses it. Choose a CRM with a user-friendly interface and intuitive features. If the CRM is too complex or difficult to use, your team won’t adopt it, and you won’t get the benefits you expect. Look for a system that is easy to learn and use.
6. Evaluate Integration Capabilities
Consider how well the CRM integrates with other business applications you use, such as email marketing platforms, accounting software, and e-commerce platforms. Seamless integration can save you time and improve efficiency. Check which integrations are available and their associated costs.
7. Assess Customer Support
Make sure the CRM vendor offers adequate customer support. Check the availability of support channels, such as phone, email, and chat. Read reviews to assess the quality of support provided. Good customer support can be invaluable, especially when you’re first implementing a CRM.
Making the Right Choice
Choosing the right CRM for your small business is an investment in your future. By understanding the different pricing models, considering the key factors that influence pricing, and comparing your options carefully, you can find a CRM that fits your budget and meets your business needs. Remember to define your needs, set a budget, research your options, and prioritize ease of use and scalability. With the right CRM, you can streamline your customer relationship management, boost your sales, and grow your business.
Don’t be afraid to take your time, ask questions, and test out different solutions. The perfect CRM is out there, waiting to help you take your small business to the next level.