Small Business CRM Implementation: Your Ultimate Guide to Success
Understanding the Power of a Small Business CRM
Running a small business is a whirlwind. You’re juggling a million things at once – from product development and marketing to customer service and accounting. It’s a constant race against time, and the need to stay organized is paramount. This is where a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system steps in, acting as your digital command center. But what exactly is a CRM, and why is it so crucial for small business success?
A CRM is essentially a database that centralizes all your customer interactions and data. Think of it as a single source of truth for everything related to your customers. It stores contact information, tracks interactions, manages sales pipelines, and automates various tasks. This centralized approach eliminates the chaos of scattered spreadsheets, sticky notes, and siloed information, leading to a more efficient and customer-focused operation.
Why is this so important? Well, consider these points:
- Improved Customer Relationships: A CRM allows you to understand your customers better. You can track their purchase history, preferences, and communication history, enabling you to personalize interactions and provide better service.
- Increased Sales: By managing your sales pipeline, a CRM helps you identify and nurture leads, track opportunities, and close deals more effectively.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Automation features streamline tasks like email marketing, appointment scheduling, and follow-ups, freeing up your time to focus on core business activities.
- Better Decision-Making: CRM systems provide valuable insights into customer behavior and sales performance, empowering you to make data-driven decisions.
- Cost Savings: By automating tasks and improving efficiency, a CRM can help you reduce operational costs.
For a small business, these benefits are amplified. You’re often resource-constrained, so every efficiency gain and improved customer interaction can make a significant difference in your growth and profitability. Implementing a CRM is not just a tech upgrade; it’s a strategic investment in your future.
Choosing the Right CRM for Your Small Business
The market is flooded with CRM solutions, each boasting a unique set of features and capabilities. Choosing the right one for your small business can feel overwhelming, but it doesn’t have to be. The key is to understand your specific needs and priorities. Here’s a step-by-step approach to guide you:
1. Define Your Needs and Goals
Before you start researching CRM systems, take some time to identify your business objectives. What do you want to achieve with a CRM? Are you primarily focused on:
- Improving Sales? Look for features like lead management, sales pipeline tracking, and sales automation.
- Enhancing Customer Service? Prioritize features like ticket management, knowledge base integration, and customer support portals.
- Boosting Marketing Efforts? Seek out features like email marketing, marketing automation, and social media integration.
- Streamlining Operations? Focus on features like task management, workflow automation, and reporting.
Also, consider your current pain points. Where are you struggling with customer management, sales processes, or marketing efforts? A CRM can address these challenges, so make a list of your most pressing needs.
2. Determine Your Budget
CRM systems range in price from free or very low cost to several hundred dollars per user per month. Set a realistic budget before you begin your search. Consider not just the monthly subscription fees but also implementation costs, training expenses, and potential add-ons. Remember that the most expensive option isn’t always the best; the most appropriate option is the one that best fits your needs and budget.
3. Assess Your Technical Skills and Resources
How comfortable are you with technology? Some CRM systems are user-friendly and require minimal technical expertise, while others are more complex and may require dedicated IT support. Consider your team’s technical capabilities and whether you have the resources to handle the implementation and ongoing maintenance of a more sophisticated system. Cloud-based (SaaS) CRM solutions are generally easier to implement and maintain than on-premise solutions.
4. Research and Compare CRM Systems
Once you have a clear understanding of your needs, budget, and technical capabilities, it’s time to start researching different CRM systems. Here are some popular options for small businesses, along with their strengths:
- Zoho CRM: Offers a comprehensive suite of features at an affordable price, making it a great option for small businesses with diverse needs. Known for its customization options and integrations.
- HubSpot CRM: A free CRM with powerful features, particularly for marketing and sales. Easy to use and integrates seamlessly with HubSpot’s marketing automation tools.
- Pipedrive: Designed specifically for sales teams, with a focus on pipeline management and deal tracking. Simple and intuitive interface.
- Salesforce Sales Cloud: A robust and highly customizable CRM, suitable for businesses with complex sales processes. Can be more expensive and complex to implement than other options.
- Freshsales: User-friendly and affordable, with features for sales automation, lead management, and phone integration.
When comparing systems, consider the following factors:
- Features: Does the CRM offer the features you need to achieve your goals?
- Ease of Use: Is the interface intuitive and easy to navigate?
- Integrations: Does the CRM integrate with your existing tools, such as email marketing platforms, accounting software, and social media channels?
- Pricing: Does the pricing model fit your budget?
- Customer Support: Does the vendor offer adequate customer support and training resources?
- Reviews and Ratings: Read reviews from other small businesses to get insights into their experiences with the CRM.
5. Consider a Free Trial or Demo
Most CRM vendors offer free trials or demos. Take advantage of these opportunities to test the system and see if it meets your needs. Get your team involved in the testing process to gather feedback and ensure that the CRM is a good fit for everyone.
The CRM Implementation Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
Once you’ve chosen the right CRM, the next step is implementation. This process can seem daunting, but with careful planning and execution, you can ensure a smooth transition and maximize the benefits of your new system. Here’s a detailed step-by-step guide:
1. Plan Your Implementation
Before you dive in, create a detailed implementation plan. This plan should include:
- Project Goals: Clearly define what you want to achieve with the CRM implementation.
- Timeline: Set realistic deadlines for each stage of the implementation process.
- Team Roles and Responsibilities: Assign roles to team members and define their responsibilities. Who will be the project manager? Who will handle data migration? Who will be responsible for training?
- Data Migration Strategy: Outline how you will migrate your existing data into the CRM.
- Training Plan: Develop a plan for training your team on how to use the CRM.
- Budget: Allocate resources for implementation costs, including software subscriptions, training, and potential consulting fees.
2. Data Migration
Migrating your existing data into the CRM is a critical step. This involves transferring data from your current systems, such as spreadsheets, contact lists, and other databases, into the new CRM. Here’s how to approach data migration:
- Data Cleaning: Before migrating your data, clean it up to ensure accuracy and consistency. Remove duplicates, correct errors, and standardize formatting.
- Data Mapping: Map your existing data fields to the corresponding fields in the CRM. This ensures that your data is transferred correctly.
- Data Import: Import your data into the CRM. Most CRM systems provide tools for importing data from CSV files, spreadsheets, or other sources.
- Data Validation: After importing your data, validate it to ensure that it was transferred correctly. Check for any errors or inconsistencies.
Consider using a data migration tool or hiring a consultant to help with this process, especially if you have a large amount of data.
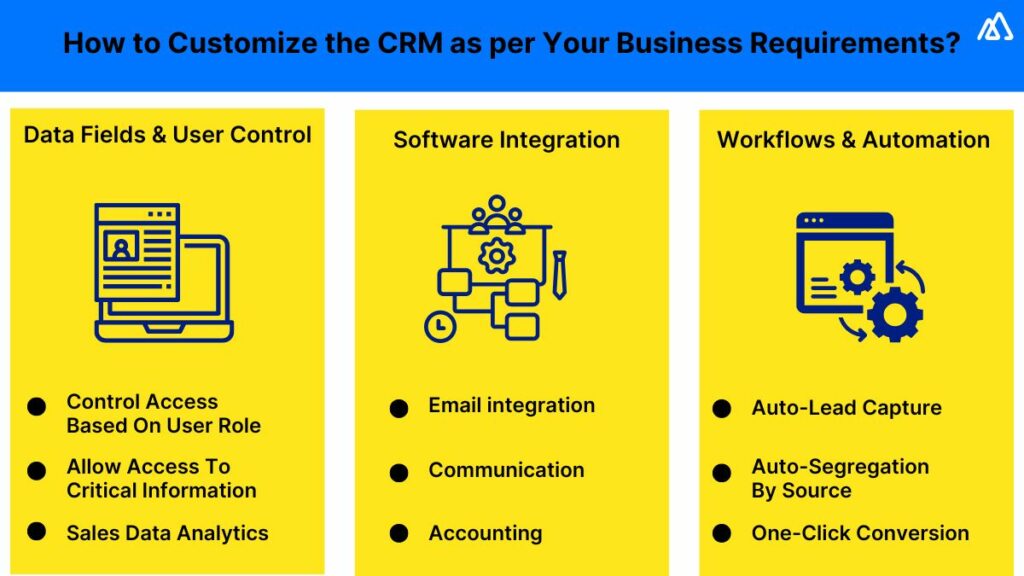
3. Customization and Configuration
Most CRM systems are highly customizable. Tailor the CRM to your specific business needs and workflows by:
- Customizing Fields: Add custom fields to capture the specific information that is relevant to your business.
- Configuring Workflows: Automate repetitive tasks, such as sending follow-up emails or updating deal stages, by configuring workflows.
- Setting Up User Roles and Permissions: Define user roles and permissions to control access to data and features.
- Integrating with Other Tools: Integrate the CRM with your other business tools, such as email marketing platforms, accounting software, and social media channels.
Take your time to experiment with the customization options to ensure that the CRM aligns with your business processes.
4. User Training
Successful CRM implementation requires proper user training. Train your team on how to use the CRM effectively and explain the benefits of using the system. Provide training materials, such as user manuals, video tutorials, and online documentation. Consider the following training methods:
- Instructor-Led Training: Conduct in-person training sessions to provide hands-on instruction.
- Online Training: Provide access to online training resources, such as webinars and video tutorials.
- On-the-Job Training: Encourage users to learn by doing, with guidance from experienced users.
- Ongoing Support: Provide ongoing support to address user questions and provide assistance.
Make training a continuous process. As your business evolves and the CRM is updated, provide refresher training to keep your team up-to-date.
5. Testing and Go-Live
Before you launch the CRM, thoroughly test it to ensure that it’s working correctly. Involve your team in the testing process to gather feedback and identify any issues. Perform the following tests:
- Functionality Testing: Test all the features of the CRM to ensure they are working as expected.
- User Acceptance Testing (UAT): Have users test the system to ensure that it meets their needs.
- Data Integrity Testing: Verify that the data is being stored and processed correctly.
- Performance Testing: Ensure that the system can handle the expected workload.
Once you’re satisfied with the testing results, you can go live with the CRM. Announce the launch to your team and provide ongoing support to ensure a smooth transition.
6. Post-Implementation Review and Optimization
After the CRM is implemented, monitor its performance and make adjustments as needed. Regularly review the following:
- User Adoption: Track how frequently users are logging into the CRM and using its features.
- Data Accuracy: Monitor the accuracy of the data in the CRM.
- Performance: Assess the performance of the CRM and identify any areas for improvement.
- User Feedback: Gather feedback from users to identify areas for improvement and address any issues.
Continuously optimize your CRM implementation by making adjustments to the system, workflows, and training materials based on your findings. Regular review ensures that your CRM remains aligned with your business goals and continues to deliver value.
Maximizing CRM Adoption and Usage
Implementing a CRM is just the first step; the real value comes from how effectively your team uses it. Here’s how to foster widespread adoption and ensure your CRM becomes an integral part of your business operations:
1. Leadership Buy-In
Leadership support is crucial for CRM adoption. When leaders champion the CRM and actively use it themselves, it sets a positive example for the rest of the team. Communicate the benefits of the CRM to your team and explain how it will help them achieve their goals. Make sure leaders demonstrate their commitment by regularly using the CRM and encouraging its use.
2. Training and Support
Adequate training is essential for successful CRM adoption. Provide comprehensive training to all team members, covering all aspects of the CRM. Offer ongoing support and resources to address user questions and provide assistance. Make sure training is engaging and relevant to the users’ roles and responsibilities. Continually provide updates and refresh training as new features are added or processes change.
3. Simplify the Process
Make the CRM easy to use. Simplify workflows and customize the system to meet the needs of your users. Avoid overwhelming users with unnecessary features or complex processes. Provide clear and concise instructions and documentation. The more user-friendly the CRM is, the more likely your team will embrace it.
4. Integrate with Existing Workflows
Integrate the CRM with your existing tools and workflows. This will make it easier for users to incorporate the CRM into their daily routines. Connect the CRM to your email marketing platform, accounting software, and other essential tools. Automate tasks and processes to reduce manual effort and improve efficiency.
5. Promote Data Entry
Encourage users to regularly enter data into the CRM. Make data entry a priority and emphasize its importance. Ensure that users understand how the data they enter contributes to the overall success of the business. Implement data validation rules to ensure data accuracy and consistency. Consider gamifying data entry to make it more engaging.
6. Measure and Communicate Results
Track the results of your CRM implementation and communicate them to your team. Show how the CRM is improving sales, customer service, and other key metrics. Regularly provide updates on CRM usage and performance. Celebrate successes and recognize users who are actively using the CRM. This will motivate your team and demonstrate the value of the system.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Implementing a CRM can be challenging, but many common hurdles can be overcome with careful planning and execution. Here are some common challenges and how to address them:
1. Lack of User Adoption
One of the biggest challenges is getting your team to actually use the CRM. Address this by providing thorough training, simplifying the system, and emphasizing the benefits of using the CRM. Leadership buy-in is also critical. Make sure leaders are actively using the CRM and encouraging its use.
2. Data Migration Issues
Data migration can be a complex process. To avoid issues, clean your data before migrating it, map your data fields correctly, and validate your data after importing it. Consider using a data migration tool or hiring a consultant to help with this process.
3. Poor Data Quality
Inaccurate or incomplete data can undermine the value of your CRM. Implement data validation rules to ensure data accuracy and consistency. Encourage users to regularly enter accurate data. Regularly review and clean your data to remove duplicates and correct errors.
4. Integration Problems
Integrating your CRM with other tools can be challenging. Choose a CRM that integrates well with your existing tools. Work with the CRM vendor or a consultant to ensure that the integrations are set up correctly. Test the integrations thoroughly to ensure that they are working as expected.
5. Lack of Customization
If your CRM isn’t customized to your business needs, it won’t be as effective. Take the time to customize the CRM to your specific workflows and processes. Add custom fields, configure workflows, and set up user roles and permissions. Make sure the CRM aligns with your business goals.
6. Budget Overruns
CRM implementation costs can sometimes exceed your budget. Set a realistic budget and stick to it. Factor in the cost of software subscriptions, training, and potential consulting fees. Consider starting with a simpler CRM and upgrading later as your needs evolve.
The Long-Term Benefits of a CRM for Small Businesses
The initial investment in a CRM system can pay off handsomely over time, contributing to your small business’s sustainable growth. Beyond the immediate benefits of improved sales and customer service, a well-implemented CRM lays the groundwork for long-term success.
1. Scalability and Growth
A CRM system is designed to scale with your business. As your customer base grows and your sales team expands, the CRM can handle the increased volume of data and interactions. You won’t have to worry about outgrowing your CRM, as it can adapt to your evolving needs. The CRM provides a solid foundation for future expansion, allowing you to manage more customers, sales, and marketing efforts efficiently.
2. Enhanced Customer Loyalty
By providing personalized customer experiences, a CRM helps you build stronger relationships with your customers. You can track their purchase history, preferences, and communication history, enabling you to provide tailored recommendations and offers. Customers who feel valued and understood are more likely to remain loyal to your brand and become repeat customers. This, in turn, leads to increased revenue and positive word-of-mouth referrals.
3. Improved Marketing ROI
A CRM system provides valuable insights into your customer base, allowing you to segment your audience and target your marketing efforts more effectively. You can track the performance of your marketing campaigns and make data-driven decisions to optimize your ROI. By personalizing your marketing messages and targeting the right customers with the right offers, you can increase your conversion rates and generate more leads.
4. Streamlined Communication and Collaboration
A CRM system centralizes all customer interactions, making it easier for your team to communicate and collaborate. Sales, marketing, and customer service teams can access the same customer data, ensuring a consistent customer experience. This streamlined communication reduces the risk of miscommunication and improves the overall efficiency of your business. A CRM fosters a collaborative environment, where everyone can access and share important information.
5. Competitive Advantage
In today’s competitive market, a CRM system can give your small business a significant edge. By improving customer relationships, streamlining operations, and making data-driven decisions, you can outperform your competitors. A CRM enables you to provide exceptional customer service, personalize your marketing efforts, and identify new opportunities for growth. By embracing a CRM, you can create a more customer-centric business that is well-positioned for long-term success.
Conclusion: Embracing CRM for Small Business Success
Implementing a CRM is a strategic move for any small business looking to improve customer relationships, boost sales, and streamline operations. By carefully selecting the right CRM, following a systematic implementation process, and fostering widespread adoption, you can unlock the full potential of this powerful tool.
Remember that the journey doesn’t end with implementation. Continuous monitoring, optimization, and adaptation are key to maximizing the benefits of your CRM. By embracing the power of CRM, you’ll be well-equipped to navigate the challenges of the business world, build stronger customer relationships, and achieve long-term success.