Small Business CRM Implementation: A Comprehensive Guide to Success
Introduction: Why Your Small Business Needs a CRM
In today’s hyper-competitive market, small businesses are constantly searching for ways to gain an edge. One of the most effective tools for achieving this is a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system. But what exactly is a CRM, and why is it so crucial for your small business? At its core, a CRM is a system that helps you manage and analyze customer interactions and data throughout the customer lifecycle, with the goal of improving business relationships, assisting in customer retention, and driving sales growth. It’s more than just a contact list; it’s the central nervous system of your customer-facing operations.
For small businesses, a CRM can be a game-changer. It allows you to:
- Centralize Customer Data: Say goodbye to scattered spreadsheets and siloed information. A CRM consolidates all customer data in one accessible location.
- Improve Customer Relationships: By understanding your customers better, you can personalize interactions and build stronger relationships.
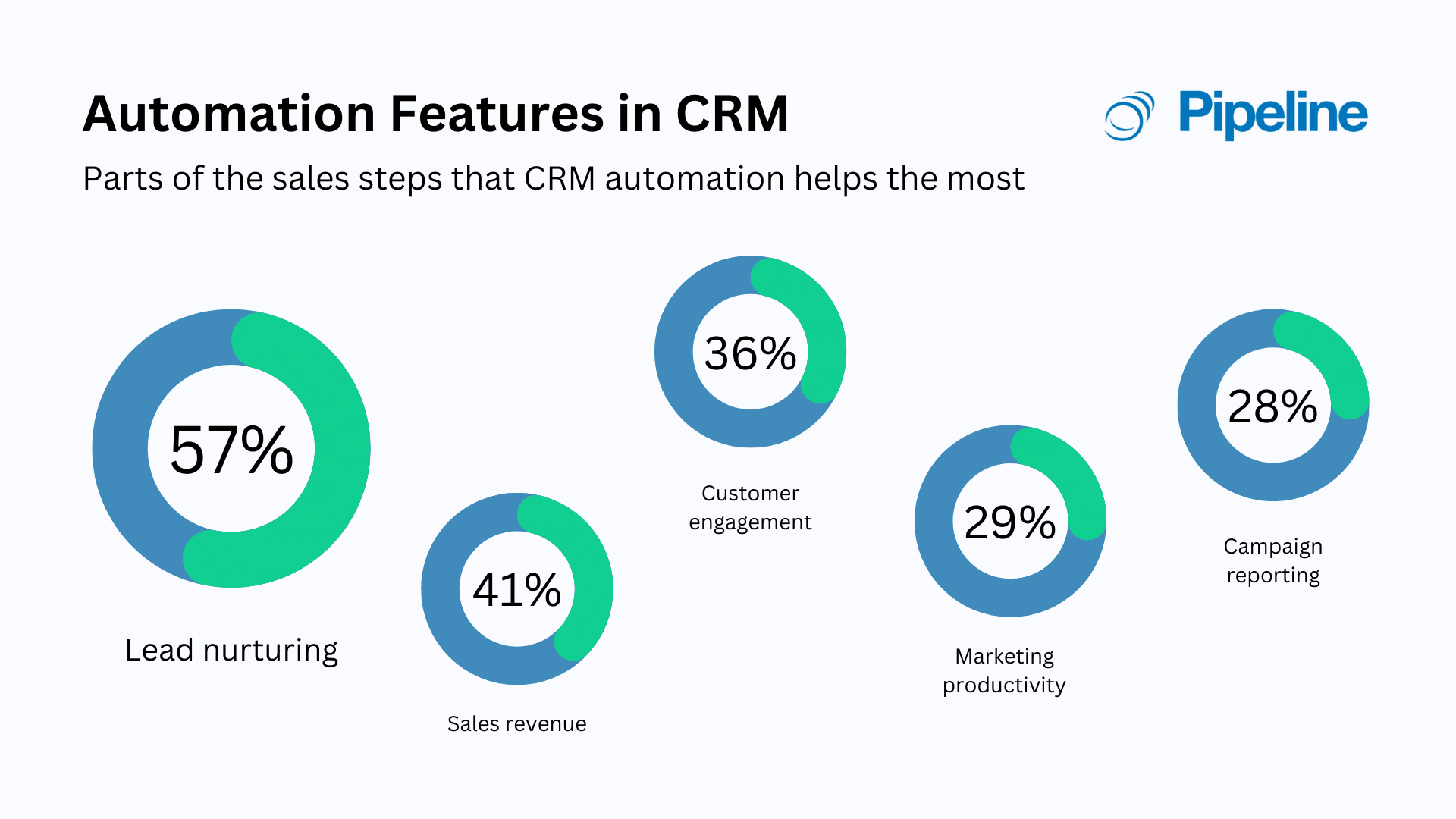
- Boost Sales: CRM systems help you identify and nurture leads, track sales progress, and close deals more efficiently.
- Increase Efficiency: Automate repetitive tasks, freeing up your team to focus on more strategic activities.
- Enhance Collaboration: Ensure everyone on your team has access to the same customer information, promoting seamless communication and teamwork.
Implementing a CRM might seem daunting, but with the right approach, it can be a smooth and rewarding process. This comprehensive guide will walk you through every step, from choosing the right CRM to training your team and measuring your success.
Chapter 1: Assessing Your Needs and Defining Your Goals
Before you even start looking at CRM software, it’s essential to take a step back and assess your business needs. This is the foundation upon which your entire CRM strategy will be built. Without a clear understanding of your goals, you risk choosing a system that doesn’t fit your requirements or, worse, failing to implement it effectively.
1.1 Identify Your Pain Points
What challenges are you currently facing in managing your customer relationships? Are you struggling with:
- Lost Leads: Are leads slipping through the cracks? Do you have a system for following up with potential customers?
- Inefficient Sales Processes: Are your sales reps spending too much time on administrative tasks and not enough time selling?
- Poor Customer Service: Are customers complaining about slow response times or a lack of personalized attention?
- Data Silos: Is customer information scattered across different departments or systems?
- Lack of Visibility: Do you have a clear view of your sales pipeline and customer interactions?
Make a list of these pain points. These will become the primary drivers for your CRM implementation.
1.2 Define Your CRM Goals
Based on your pain points, define specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals for your CRM implementation. For example:
- Increase Lead Conversion Rate: Increase your lead conversion rate by 15% within six months.
- Improve Customer Retention: Reduce customer churn by 10% within a year.
- Shorten Sales Cycle: Reduce the average sales cycle by 20% within three months.
- Enhance Customer Satisfaction: Increase customer satisfaction scores by 10 points within a year.
These goals will serve as your benchmarks for measuring the success of your CRM implementation.
1.3 Map Your Customer Journey
Understand the different stages of the customer journey, from initial awareness to becoming a loyal customer. Map out the touchpoints at each stage and identify the information you need to collect at each point. This will help you determine the CRM features you need.
1.4 Determine Your Budget
CRM systems come in various price ranges, from free to enterprise-level. Determine a realistic budget that includes not only the software costs but also implementation, training, and ongoing maintenance. Consider both the initial investment and the recurring costs.
Chapter 2: Choosing the Right CRM System for Your Small Business
Selecting the right CRM is a critical decision. The market is flooded with options, each offering a unique set of features and benefits. The key is to find the system that best aligns with your specific needs, budget, and technical capabilities.
2.1 Research and Evaluate CRM Options
Start by researching the leading CRM providers. Some popular options for small businesses include:
- Zoho CRM: A versatile and affordable option with a wide range of features.
- HubSpot CRM: A free CRM with powerful marketing and sales tools.
- Salesforce Sales Cloud: A robust and scalable solution, suitable for growing businesses.
- Pipedrive: A sales-focused CRM with an intuitive interface.
- Freshsales: A user-friendly CRM with built-in telephony and email integration.
Read reviews, compare features, and consider the following factors:
- Features: Does the CRM offer the features you need, such as contact management, lead management, sales automation, reporting, and analytics?
- Ease of Use: Is the interface intuitive and easy to navigate? Will your team be able to quickly learn and adopt the system?
- Integration: Does the CRM integrate with your existing tools, such as email marketing platforms, accounting software, and social media channels?
- Scalability: Can the CRM grow with your business? Will it be able to handle increasing data volumes and user numbers?
- Pricing: Does the pricing model fit your budget? Consider both the upfront costs and the ongoing subscription fees.
- Customer Support: Does the provider offer adequate customer support and training resources?
2.2 Consider Your Business Size and Industry
Some CRM systems are better suited for certain business sizes and industries. For example:
- Small Businesses: Look for user-friendly, affordable solutions with essential features.
- Growing Businesses: Consider systems with advanced features, scalability, and customization options.
- Specific Industries: Some CRMs are designed for specific industries, such as real estate, healthcare, or financial services. These often have industry-specific features and workflows.
2.3 Evaluate Free Trials and Demos
Most CRM providers offer free trials or demos. Take advantage of these opportunities to test the system and see if it’s a good fit for your business. Involve your team in the evaluation process to gather feedback and ensure that the system meets their needs.
2.4 Prioritize Security and Data Privacy
Ensure that the CRM provider has robust security measures in place to protect your customer data. Look for features such as data encryption, access controls, and compliance with data privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA.
Chapter 3: Planning Your CRM Implementation
Once you’ve chosen your CRM, it’s time to plan your implementation. A well-defined plan will help you avoid common pitfalls and ensure a smooth transition.
3.1 Define Your Implementation Scope
Determine the scope of your implementation. Will you implement all features at once, or will you roll out the CRM in phases? Consider starting with the core features, such as contact management and lead tracking, and then gradually adding more functionality as your team becomes comfortable with the system.
3.2 Data Migration Strategy
Plan how you’ll migrate your existing customer data to the new CRM. This may involve:
- Data Cleanup: Cleanse your data by removing duplicates, correcting errors, and standardizing formatting.
- Data Mapping: Map your existing data fields to the corresponding fields in the new CRM.
- Data Import: Import your data into the CRM using the provided import tools or APIs.
- Data Validation: Verify that your data has been imported correctly.
Consider using a third-party data migration service to simplify this process.
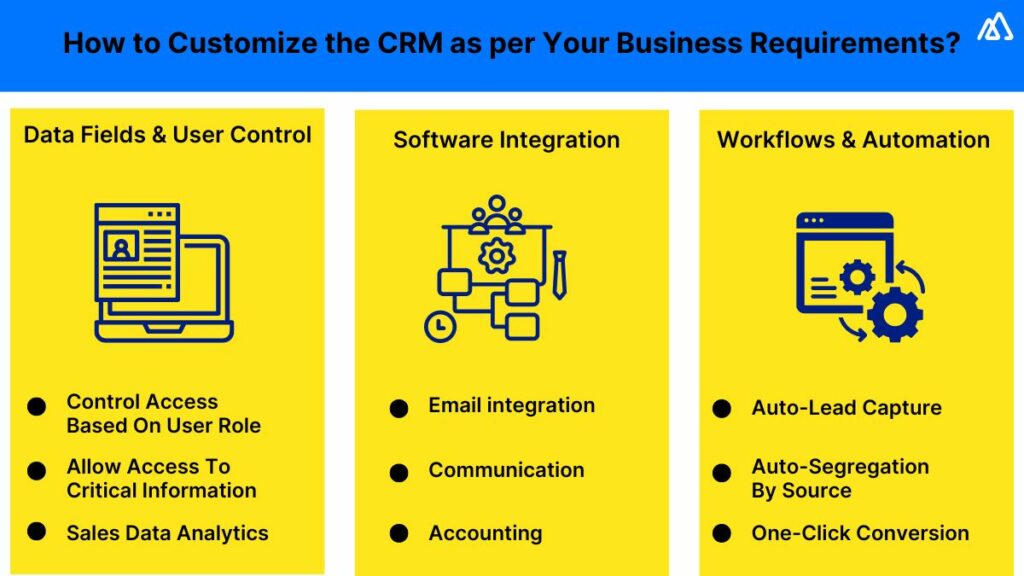
3.3 Customize Your CRM
Customize the CRM to fit your specific business needs. This may involve:
- Adding Custom Fields: Create custom fields to store information that is unique to your business.
- Customizing Workflows: Automate your business processes by creating custom workflows.
- Configuring User Roles and Permissions: Define user roles and permissions to control access to data and features.
- Branding: Customize the CRM’s appearance to match your brand.
3.4 Establish a Timeline and Budget
Create a realistic timeline for your implementation. Consider the time required for data migration, customization, training, and testing. Allocate a budget for the software, implementation services, training, and ongoing maintenance.
3.5 Assemble Your Implementation Team
Designate a project manager to oversee the implementation. Assemble a team that includes representatives from sales, marketing, customer service, and IT. This team will be responsible for the implementation, training, and ongoing support of the CRM.
Chapter 4: Implementing Your CRM
With a solid plan in place, it’s time to implement your CRM. This is where the rubber meets the road. Careful execution is key to a successful implementation.
4.1 Data Migration
Follow your data migration plan. Ensure that your data is imported accurately and completely. Validate the data to ensure that all information is correctly transferred.
4.2 System Configuration
Configure the CRM according to your plan. This includes setting up user roles and permissions, creating custom fields, and customizing workflows. Test the system thoroughly to ensure that it functions as expected.
4.3 Integration with Other Systems
Integrate the CRM with your other business systems, such as your email marketing platform, accounting software, and website. This will streamline your business processes and provide a more comprehensive view of your customer data.
4.4 User Training
Provide comprehensive training to your team. This should include:
- Overview of the CRM: Introduce your team to the CRM’s features and functionality.
- Hands-on Training: Provide hands-on training on how to use the CRM for their specific tasks.
- Best Practices: Teach your team best practices for using the CRM, such as data entry guidelines and communication protocols.
- Ongoing Support: Provide ongoing support and resources, such as user manuals and video tutorials.
Consider using a train-the-trainer approach, where you train a few key individuals who can then train the rest of the team.
4.5 Testing and Refinement
Thoroughly test the CRM before launching it to your entire team. Identify and resolve any issues or bugs. Refine your configuration and workflows based on user feedback.
Chapter 5: Training Your Team for CRM Success
The success of your CRM implementation hinges on how well your team adopts and uses the system. Effective training is crucial for ensuring user adoption and maximizing the value of your CRM investment.
5.1 Develop a Training Plan
Create a comprehensive training plan that includes:
- Training Objectives: Clearly define the learning objectives for each training session.
- Training Content: Develop training materials that are relevant to your team’s roles and responsibilities.
- Training Methods: Use a variety of training methods, such as classroom training, online tutorials, and hands-on exercises.
- Training Schedule: Schedule training sessions that fit your team’s availability.
- Training Evaluation: Evaluate the effectiveness of your training sessions by gathering feedback from your team.
5.2 Tailor Training to Different Roles
Recognize that different team members will use the CRM in different ways. Tailor your training to the specific needs of each role. For example:
- Sales Representatives: Train them on lead management, opportunity tracking, and sales reporting.
- Marketing Team: Train them on contact management, campaign management, and marketing automation.
- Customer Service Representatives: Train them on case management, customer support, and issue resolution.
5.3 Provide Hands-on Training and Practice
Provide plenty of hands-on training and practice. Encourage your team to use the CRM during the training sessions. Provide real-world examples and scenarios to help them understand how to use the system effectively.
5.4 Foster a Culture of Adoption
Create a culture where CRM adoption is encouraged and supported. Make it clear that using the CRM is a priority. Provide ongoing support and encouragement. Celebrate successes and recognize team members who are actively using the CRM.
5.5 Ongoing Support and Resources
Provide ongoing support and resources to help your team stay proficient with the CRM. This includes:
- User Manuals: Create user manuals that provide step-by-step instructions on how to use the CRM.
- Video Tutorials: Create video tutorials that demonstrate how to perform specific tasks.
- FAQ: Create a frequently asked questions (FAQ) section to address common questions and issues.
- Ongoing Training: Provide ongoing training sessions to address new features and functionalities.
- Help Desk: Establish a help desk or support channel to answer questions and provide assistance.
Chapter 6: Measuring and Optimizing Your CRM Implementation
Implementing a CRM is not a one-time project. It’s an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring and optimization. By tracking key metrics and making adjustments, you can ensure that your CRM is delivering the desired results.
6.1 Define Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Identify the KPIs that are most important to your business goals. These KPIs will help you measure the success of your CRM implementation. Examples of KPIs include:
- Lead Conversion Rate: The percentage of leads that convert into customers.
- Sales Cycle Length: The average time it takes to close a deal.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): The cost of acquiring a new customer.
- Customer Retention Rate: The percentage of customers who remain customers over a period of time.
- Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT): A measure of customer satisfaction.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV): The predicted revenue a customer will generate over their relationship with your business.
- Sales Revenue: The total revenue generated by sales.
- Number of Deals Closed: The total number of successful sales transactions.
- Marketing ROI: The return on investment for your marketing campaigns.
6.2 Track and Analyze Your Data
Regularly track your KPIs. Use the CRM’s reporting and analytics features to generate reports and dashboards. Analyze your data to identify trends and patterns. Look for areas where you can improve your CRM processes.
6.3 Make Adjustments and Optimizations
Based on your data analysis, make adjustments to your CRM implementation. This may involve:
- Refining Your Sales Processes: Optimize your sales processes to improve lead conversion rates and shorten sales cycles.
- Improving Your Marketing Campaigns: Optimize your marketing campaigns to generate more qualified leads.
- Enhancing Your Customer Service: Improve your customer service processes to increase customer satisfaction and retention.
- Customizing Your CRM: Customize your CRM to better meet your needs.
- Providing Additional Training: Provide additional training to your team to improve their CRM skills.
6.4 Continuous Improvement
CRM implementation is an ongoing process. Continuously monitor your KPIs, analyze your data, and make adjustments to optimize your CRM performance. Stay up-to-date on the latest CRM features and best practices.
Chapter 7: Common CRM Implementation Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Implementing a CRM can be challenging. However, by anticipating potential problems and taking proactive steps, you can minimize the risks and increase your chances of success.
7.1 Lack of User Adoption
One of the most common challenges is a lack of user adoption. To overcome this, you can:
- Involve Your Team: Involve your team in the selection and implementation process.
- Provide Comprehensive Training: Provide thorough training and ongoing support.
- Make it Easy to Use: Customize the CRM to meet your team’s needs.
- Highlight the Benefits: Communicate the benefits of using the CRM to your team.
- Lead by Example: Encourage managers and leaders to use the CRM.
7.2 Data Migration Issues
Data migration can be a complex process. To avoid problems, you can:
- Clean Your Data: Cleanse and standardize your data before migrating it.
- Map Your Data: Carefully map your data fields to the corresponding fields in the new CRM.
- Test Your Data: Test your data migration process thoroughly.
- Use a Data Migration Service: Consider using a data migration service.
7.3 Poor Data Quality
Poor data quality can undermine the effectiveness of your CRM. To maintain data quality, you can:
- Establish Data Entry Guidelines: Establish clear data entry guidelines and provide training.
- Validate Data: Validate data entry to ensure accuracy.
- Regularly Clean Your Data: Regularly clean and update your data.
- Use Data Enrichment Tools: Use data enrichment tools to automatically update your data.
7.4 Integration Challenges
Integrating your CRM with other systems can be challenging. To avoid problems, you can:
- Plan Your Integrations: Plan your integrations carefully.
- Test Your Integrations: Test your integrations thoroughly.
- Use APIs: Use APIs to connect your CRM with other systems.
- Seek Expert Help: Seek expert help if needed.
7.5 Budget Overruns
Budget overruns can be a problem. To stay within budget, you can:
- Create a Realistic Budget: Create a realistic budget that includes all costs.
- Track Your Expenses: Track your expenses carefully.
- Prioritize Features: Prioritize the features that are most important to your business.
- Negotiate with Vendors: Negotiate with vendors to get the best prices.
Chapter 8: Maximizing the ROI of Your CRM
Investing in a CRM is a significant commitment. To maximize your return on investment (ROI), you need to focus on the following key areas:
8.1 Align CRM with Business Goals
Ensure that your CRM implementation is aligned with your overall business goals. This means that your CRM should support your sales, marketing, and customer service strategies.
8.2 Focus on User Adoption
User adoption is critical for CRM success. Encourage your team to use the CRM consistently. Provide ongoing training and support.
8.3 Leverage CRM Features
Take advantage of the CRM’s features to automate your business processes. This will free up your team to focus on more strategic activities. Explore all available features, including automation, reporting, and integrations.
8.4 Monitor and Analyze Your Data
Regularly monitor and analyze your data to identify areas for improvement. Use your CRM’s reporting and analytics features to track your KPIs. Make data-driven decisions.
8.5 Continuous Improvement
CRM implementation is an ongoing process. Continuously monitor your KPIs, analyze your data, and make adjustments to optimize your CRM performance. Stay up-to-date on the latest CRM features and best practices.
Conclusion: Embracing CRM for Small Business Growth
Implementing a CRM is a significant step toward improving your small business’s customer relationships and driving growth. While the process may seem complex, the benefits are well worth the effort. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can successfully implement a CRM and empower your team to build stronger customer relationships, close more deals, and achieve your business goals. Remember that consistency, ongoing optimization, and a commitment to customer-centricity are key to long-term success.
By centralizing your customer data, streamlining your sales processes, and providing exceptional customer service, you can create a loyal customer base that fuels sustainable growth. Embrace the power of CRM, and watch your small business thrive.