Small Business CRM for Beginners: Your Ultimate Guide to Customer Relationship Management

Small Business CRM for Beginners: Your Ultimate Guide to Customer Relationship Management
Starting a small business is an exciting journey, filled with passion, innovation, and the thrill of building something from the ground up. But amidst the hustle and bustle of daily operations, one crucial aspect often gets overlooked: managing your customer relationships. That’s where a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system comes in. For beginners, the world of CRM can seem complex, but trust me, it doesn’t have to be. This guide will break down everything you need to know about CRM, specifically tailored for small businesses, making it easy to understand and implement.
What is a CRM and Why Does Your Small Business Need One?
At its core, a CRM is a system that helps you manage your interactions with current and potential customers. Think of it as a centralized hub for all your customer data. It’s where you store contact information, track interactions, manage sales pipelines, and analyze customer behavior. But why is this so important for a small business? Here’s why:
- Improved Customer Relationships: A CRM helps you understand your customers better. By tracking their preferences, purchase history, and communication, you can personalize your interactions and provide a better customer experience.
- Increased Sales: CRM systems streamline the sales process. They help you track leads, manage follow-ups, and close deals more efficiently. This leads to more sales and revenue.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Automating tasks and centralizing data saves time and reduces errors. Your team can focus on more important activities, like building relationships and providing excellent service.
- Better Data Analysis: CRMs provide valuable insights into your sales and marketing efforts. You can track key metrics, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions to improve your business performance.
- Improved Collaboration: A CRM ensures everyone on your team has access to the same customer information. This leads to better communication and collaboration, ensuring a seamless customer experience.
Key Features to Look for in a Small Business CRM
Choosing the right CRM can feel overwhelming with so many options available. However, focusing on essential features will help you find the perfect fit for your small business. Here are some key features to consider:
Contact Management
This is the foundation of any CRM. It allows you to store and organize customer contact information, including names, addresses, phone numbers, email addresses, and other relevant details. Look for features like:
- Contact Segmentation: Grouping customers based on demographics, behavior, or other criteria for targeted marketing.
- Custom Fields: Ability to add custom fields to capture specific information relevant to your business.
- Import/Export Capabilities: Easy import and export of contact data from spreadsheets or other systems.
Sales Pipeline Management
This feature helps you track leads through the sales process, from initial contact to closing the deal. Key functionalities include:
- Lead Tracking: Monitoring leads as they move through the sales stages.
- Deal Stages: Defining and customizing sales stages to match your sales process.
- Task Management: Setting reminders and assigning tasks related to specific deals.
- Reporting: Generating reports to track sales performance and identify bottlenecks.
Marketing Automation
Marketing automation features help you streamline your marketing efforts and nurture leads. Look for:
- Email Marketing: Sending targeted email campaigns to segmented customer groups.
- Lead Scoring: Automatically assigning scores to leads based on their behavior and engagement.
- Workflow Automation: Automating repetitive tasks, such as sending follow-up emails.
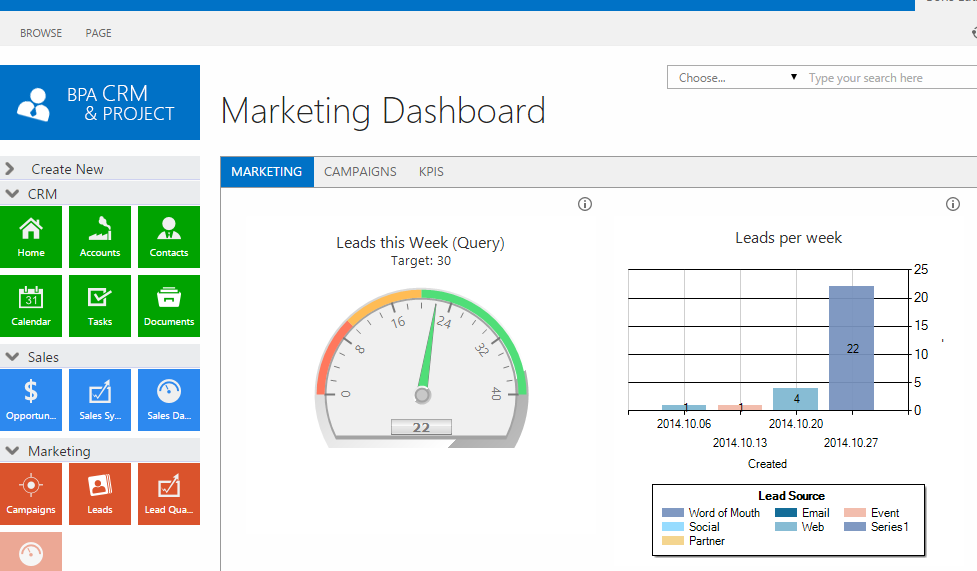
Reporting and Analytics
This provides insights into your sales and marketing performance. Key features include:
- Sales Reports: Tracking sales metrics, such as revenue, deal size, and conversion rates.
- Marketing Reports: Analyzing the performance of your marketing campaigns.
- Customizable Dashboards: Creating dashboards to visualize key metrics and track progress.
Integration with Other Tools
Consider how the CRM integrates with other tools you use, such as:
- Email Marketing Platforms: Integration with platforms like Mailchimp or Constant Contact.
- Social Media: Connecting your CRM to social media channels for social listening and engagement.
- Accounting Software: Integration with accounting software for seamless data transfer.
Top CRM Systems for Small Businesses: A Comparative Look
Now that you know what to look for, let’s explore some of the top CRM systems specifically designed for small businesses. Each has its strengths and weaknesses, so consider your specific needs when making your choice.
1. HubSpot CRM
Overview: HubSpot CRM is a popular choice for small businesses, particularly because it offers a free version with powerful features. It’s known for its user-friendly interface and comprehensive suite of tools.
Key Features:
- Free Forever Plan: Includes contact management, deal tracking, task management, and email marketing features.
- User-Friendly Interface: Easy to navigate and use, even for beginners.
- Sales Automation: Automate tasks and follow-ups to streamline your sales process.
- Marketing Tools: Integrates with HubSpot’s marketing platform for email marketing, landing pages, and more.
- Reporting and Analytics: Provides valuable insights into your sales and marketing performance.
Pros: Free plan, user-friendly, comprehensive features, strong marketing capabilities.
Cons: Limited features in the free plan, some advanced features require paid upgrades.
2. Zoho CRM
Overview: Zoho CRM is a versatile and affordable CRM system with a wide range of features. It’s a good choice for businesses that need a customizable and scalable solution.
Key Features:
- Customization: Highly customizable to fit your specific business needs.
- Sales Automation: Automate your sales process with workflows and triggers.
- Lead Management: Capture and nurture leads effectively.
- Reporting and Analytics: Provides detailed reports and analytics to track your sales performance.
- Integration: Integrates with various Zoho apps and third-party applications.
Pros: Highly customizable, affordable, extensive features, good integration options.
Cons: Can be complex to set up and configure, user interface may take some getting used to.
3. Pipedrive
Overview: Pipedrive is a sales-focused CRM designed to help sales teams manage their pipelines and close deals. It’s known for its visual interface and ease of use.
Key Features:
- Visual Sales Pipeline: Clear and intuitive view of your sales pipeline.
- Activity Tracking: Tracks all your sales activities, such as calls, emails, and meetings.
- Deal Management: Easily manage deals and track their progress.
- Automation: Automate repetitive tasks to save time.
- Reporting: Provides sales reports and analytics to track your performance.
Pros: User-friendly, sales-focused, visual pipeline, easy to set up and use.
Cons: Limited marketing automation features, may not be suitable for businesses with complex marketing needs.
4. Freshsales (Freshworks CRM)
Overview: Freshsales is a sales CRM that offers a good balance of features and affordability. It’s known for its conversational interface and integrated phone system.
Key Features:
- Built-in Phone System: Make and receive calls directly from the CRM.
- Email Integration: Integrate with your email provider for seamless communication.
- Sales Automation: Automate tasks and follow-ups to streamline your sales process.
- Lead Scoring: Automatically score leads based on their behavior and engagement.
- Reporting and Analytics: Provides detailed reports and analytics to track your sales performance.
Pros: Built-in phone system, user-friendly, affordable, good sales automation features.
Cons: Limited features in the free plan, may not be suitable for businesses with complex marketing needs.
5. Insightly
Overview: Insightly is a CRM and project management tool that’s well-suited for businesses that need to manage both customer relationships and projects. It’s known for its ease of use and project management capabilities.
Key Features:
- Contact Management: Store and manage customer contact information.
- Sales Pipeline Management: Track leads through the sales process.
- Project Management: Manage projects and tasks related to your customer relationships.
- Reporting: Provides sales and project reports to track your performance.
- Integration: Integrates with various third-party applications.
Pros: Project management capabilities, user-friendly, good for businesses that need both CRM and project management features.
Cons: Limited features in the free plan, may not be suitable for businesses with complex sales needs.
Getting Started with CRM: A Step-by-Step Guide
Now that you have a better understanding of CRM and some popular options, let’s walk through the steps to get started:
1. Assess Your Needs
Before you dive into choosing a CRM, take the time to assess your business needs. Consider the following questions:
- What are your business goals? What do you want to achieve with a CRM? (e.g., increase sales, improve customer satisfaction, streamline processes)
- What are your current challenges? What problems are you facing in managing your customer relationships?
- What features do you need? Identify the key features that are essential for your business.
- What is your budget? Determine how much you are willing to spend on a CRM.
- Who will be using the CRM? Consider the size of your team and their technical skills.
Answering these questions will help you narrow down your options and choose the right CRM for your business.
2. Research and Compare CRM Systems
Once you have a clear understanding of your needs, research different CRM systems. Read reviews, compare features, and consider pricing. Take advantage of free trials to test the systems and see which one best fits your needs. Consider the following when comparing:
- Features: Does the CRM offer the features you need?
- Ease of Use: Is the CRM user-friendly and easy to learn?
- Pricing: Is the CRM affordable for your budget?
- Customer Support: Does the CRM offer good customer support?
- Integrations: Does the CRM integrate with other tools you use?
Comparing different CRM systems will help you make an informed decision.
3. Choose and Implement Your CRM
After researching and comparing, choose the CRM that best fits your needs. Then, begin the implementation process. This typically involves:
- Data Migration: Importing your existing customer data into the CRM.
- Customization: Configuring the CRM to match your business processes.
- Training: Training your team on how to use the CRM.
- Testing: Testing the CRM to ensure it’s working correctly.
Implementation can take time, so be patient and plan accordingly.
4. Train Your Team
Proper training is essential for the successful adoption of a CRM. Make sure your team understands how to use the CRM and its features. Provide training materials, such as user manuals, videos, and online tutorials. Encourage your team to ask questions and provide support as they learn. Regular training sessions can also help your team stay up-to-date on new features and best practices.
5. Integrate Your CRM with Other Tools
To maximize the benefits of your CRM, integrate it with other tools you use, such as your email marketing platform, social media channels, and accounting software. Integration streamlines your workflow and ensures data consistency across all your systems. Most CRM systems offer integrations with popular tools, so check the available options and configure the integrations that are relevant to your business.
6. Start Using the CRM and Track Your Progress
Once your team is trained and the CRM is set up, start using it! Encourage your team to actively use the CRM for all customer interactions. Track your progress by monitoring key metrics, such as sales, customer satisfaction, and lead conversion rates. Regularly review your data and make adjustments to your CRM usage as needed. This will help you optimize your CRM and achieve your business goals.
7. Continuously Refine and Optimize
CRM implementation is an ongoing process. Continuously refine and optimize your CRM usage to maximize its effectiveness. Regularly review your CRM data, identify areas for improvement, and make adjustments to your processes. As your business grows and evolves, your CRM needs may change. Stay up-to-date on new features and best practices, and consider upgrading your CRM plan as needed. This will help you ensure that your CRM continues to meet your business needs.
Tips for CRM Success in Your Small Business
Implementing a CRM can be a game-changer for your small business. Here are some tips to ensure success:
- Start Small: Don’t try to implement everything at once. Start with the core features and gradually add more as you become comfortable.
- Get Buy-In: Ensure your team understands the benefits of CRM and is on board with using it.
- Clean Data: Ensure your data is accurate and up-to-date. This is crucial for getting accurate insights from the CRM.
- Set Clear Goals: Define your goals for using the CRM and track your progress.
- Be Consistent: Encourage your team to consistently use the CRM for all customer interactions.
- Provide Ongoing Training: Offer ongoing training and support to help your team use the CRM effectively.
- Regularly Review and Analyze: Regularly review your data and make adjustments as needed.
- Choose the Right CRM: Select a CRM system that is a good fit for your business needs and budget.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
While CRM systems offer significant benefits, small businesses can encounter challenges during implementation and usage. Being aware of these common obstacles and how to address them can help you avoid pitfalls and maximize your CRM’s effectiveness.
1. Lack of User Adoption
Challenge: Team members resist using the CRM, leading to incomplete data and missed opportunities. This often stems from a lack of understanding of the CRM’s value, fear of change, or a perception that it adds extra work.
Solution:
- Communicate the Benefits: Clearly explain how the CRM will benefit each team member and the business as a whole. Highlight how it can simplify tasks, improve efficiency, and enhance customer relationships.
- Provide Training and Support: Offer comprehensive training on the CRM’s features and functionalities. Provide ongoing support and address any questions or concerns promptly.
- Make it Easy to Use: Choose a CRM that is user-friendly and intuitive. Customize the system to align with your team’s workflows and make it as easy as possible to enter and access information.
- Lead by Example: Encourage managers and team leaders to actively use the CRM and demonstrate its value.
- Incentivize Usage: Consider implementing incentives for team members who consistently use the CRM and achieve positive results.
2. Poor Data Quality
Challenge: Inaccurate, incomplete, or outdated data within the CRM can lead to incorrect insights, ineffective marketing campaigns, and a poor customer experience. This can result from data entry errors, lack of standardization, or failure to update information regularly.
Solution:
- Establish Data Entry Standards: Define clear guidelines for data entry, including required fields, formatting conventions, and data validation rules.
- Automate Data Entry Where Possible: Use integrations and automation features to automatically populate data from other sources, reducing the risk of manual errors.
- Regularly Clean and Update Data: Implement a process for regularly reviewing and updating data. This may involve removing duplicates, correcting errors, and ensuring information is current.
- Train Your Team: Educate your team on the importance of data quality and provide training on best practices for data entry and maintenance.
- Use Data Validation Tools: Utilize data validation tools within your CRM to ensure data accuracy and consistency.
3. Integration Issues
Challenge: Problems integrating the CRM with other business systems, such as email marketing platforms, accounting software, or e-commerce platforms, can lead to data silos and inefficiencies.
Solution:
- Choose a CRM with Robust Integration Capabilities: Select a CRM that offers seamless integrations with the tools you already use.
- Plan Your Integrations Carefully: Identify the systems you need to integrate and plan the integration process in advance.
- Test Your Integrations Thoroughly: Before fully implementing integrations, test them to ensure data flows correctly and functions as expected.
- Seek Expert Help: If you encounter difficulties with integrations, consider seeking assistance from your CRM provider or a qualified IT professional.
- Monitor Your Integrations: Regularly monitor your integrations to ensure they are functioning correctly and address any issues promptly.
4. Lack of Customization
Challenge: The CRM doesn’t align with your specific business processes, leading to inefficiencies and a lack of user adoption. This can result from choosing a CRM that is not flexible enough or failing to customize the system to meet your needs.
Solution:
- Choose a Customizable CRM: Select a CRM that allows you to customize fields, workflows, and reports to match your unique business requirements.
- Define Your Processes: Before implementing the CRM, clearly define your sales, marketing, and customer service processes.
- Customize the CRM to Match Your Processes: Configure the CRM to support your processes, including creating custom fields, designing custom workflows, and building custom reports.
- Regularly Review and Adjust Your Customizations: As your business evolves, regularly review your CRM customizations and make adjustments as needed to ensure they continue to meet your needs.
5. Not Defining Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Challenge: Failing to track the right metrics, leading to a lack of insights into the CRM’s effectiveness and the business’s overall performance.
Solution:
- Identify Key Metrics: Determine the most important metrics to track, such as sales revenue, customer acquisition cost, customer lifetime value, and customer satisfaction.
- Set Up Reporting: Configure your CRM to track these metrics and generate reports.
- Regularly Analyze Your Data: Review your reports regularly to identify trends, measure progress, and make data-driven decisions.
- Adjust Your KPIs as Needed: As your business evolves, regularly review your KPIs and make adjustments as needed to ensure they remain relevant.
The Future of CRM for Small Businesses
The CRM landscape is constantly evolving, with new technologies and trends emerging regularly. Staying informed about these advancements can help small businesses leverage CRM to its full potential.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML are transforming the CRM industry. These technologies can automate tasks, provide predictive analytics, and personalize customer interactions. For small businesses, AI-powered CRM can offer:
- Automated Lead Scoring: Automatically identify and prioritize high-potential leads.
- Predictive Sales Forecasting: Forecast sales with greater accuracy.
- Personalized Customer Recommendations: Provide personalized product or service recommendations.
- Chatbots: Offer 24/7 customer support through chatbots.
Mobile CRM
Mobile CRM allows users to access and manage customer data from anywhere, anytime. This is especially valuable for small businesses with field sales teams or remote workers. Mobile CRM features include:
- Access to Customer Data: Access contact information, sales history, and other relevant data on the go.
- Task Management: Manage tasks, appointments, and follow-ups from your mobile device.
- Real-Time Updates: Receive real-time updates on sales activities and customer interactions.
- Offline Access: Access data even without an internet connection.
Social CRM
Social CRM integrates social media with your CRM system. This allows you to monitor social media conversations, engage with customers, and gain insights into their preferences and behaviors. Social CRM features include:
- Social Listening: Monitor social media for mentions of your brand or industry.
- Social Engagement: Engage with customers on social media.
- Social Analytics: Analyze social media data to understand customer sentiment and preferences.
- Social Media Integration: Integrate social media profiles with customer profiles.
Focus on Customer Experience
In today’s competitive market, customer experience is more important than ever. CRM systems are evolving to provide a more seamless and personalized customer experience. This includes:
- Personalized Communication: Tailor your communications to individual customer preferences.
- Omnichannel Support: Provide customer support across multiple channels, such as email, phone, chat, and social media.
- Proactive Customer Service: Anticipate customer needs and proactively offer solutions.
- Customer Feedback Integration: Integrate customer feedback into your CRM to improve your products and services.
Conclusion: Embracing CRM for Small Business Success
Implementing a CRM system is a strategic move that can significantly benefit your small business. By centralizing customer data, streamlining processes, and providing valuable insights, a CRM empowers you to build stronger customer relationships, increase sales, and drive growth. While the initial setup may require some effort, the long-term benefits far outweigh the investment. Remember to assess your needs, choose the right CRM for your business, train your team, and continuously refine your approach. By embracing CRM, you’ll be well-equipped to navigate the complexities of customer relationship management and achieve lasting success. Start today, and watch your business thrive!