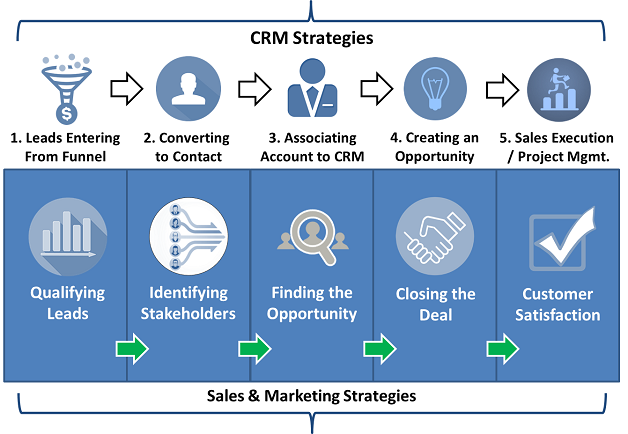
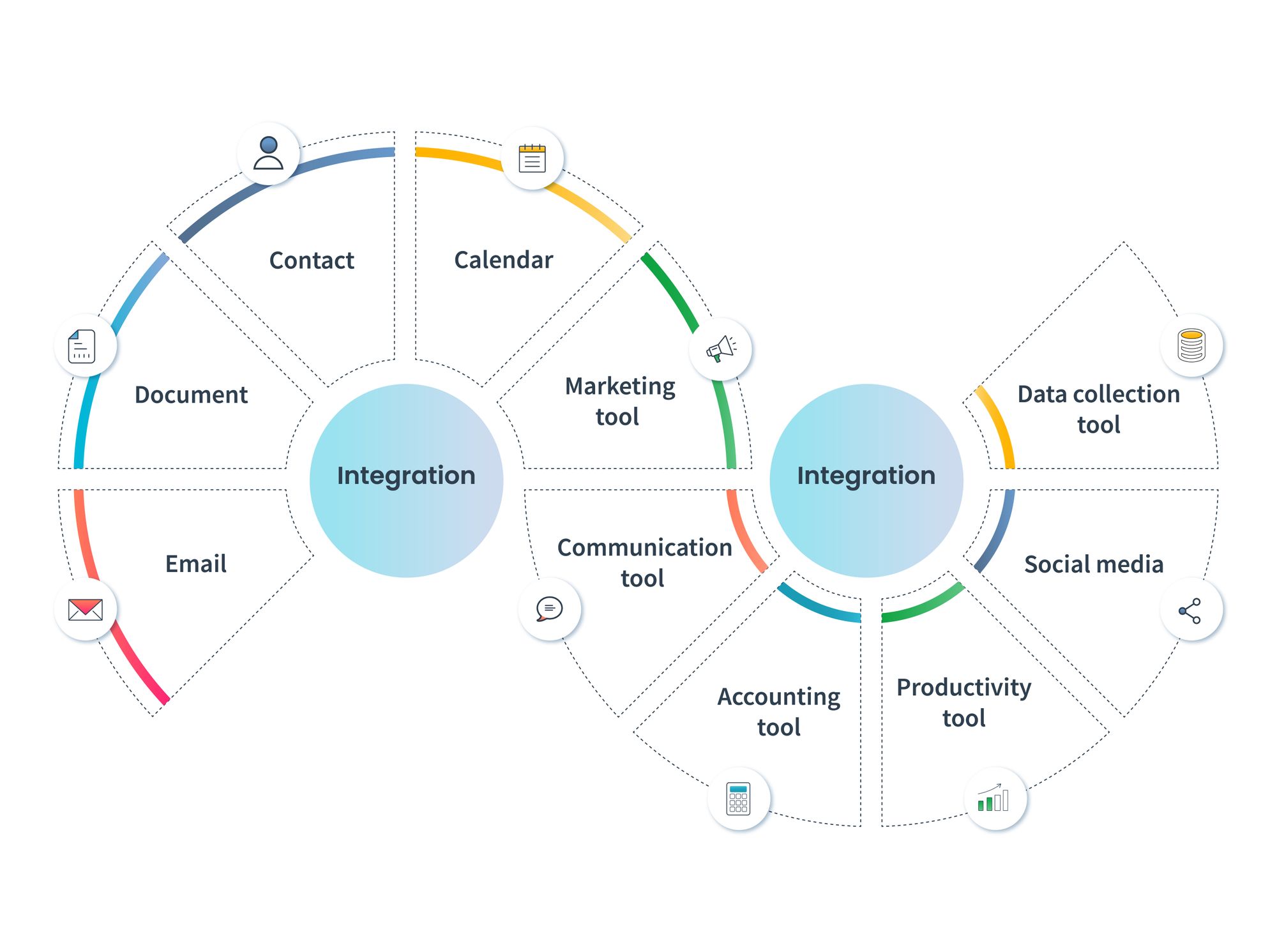
Small Business CRM Cost Guide: Unveiling the True Price Tag & Maximizing Your ROI

Introduction: Decoding the CRM Cost Conundrum for Small Businesses
So, you’re a small business owner, juggling a million things at once. You’re wearing multiple hats, from CEO to janitor, and the thought of implementing a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system has crossed your mind. It makes sense, right? CRM promises to streamline your operations, boost sales, and help you build stronger customer relationships. But then comes the dreaded question: How much is this going to cost?
The truth is, the cost of a CRM for small businesses can vary wildly. It’s not a one-size-fits-all situation. Factors like the features you need, the size of your team, and the provider you choose all play a significant role in determining the final price tag. This comprehensive guide will break down everything you need to know about small business CRM costs, helping you navigate the landscape and make an informed decision that aligns with your budget and business goals. We’ll cover everything from the initial investment to the ongoing expenses, and, importantly, we’ll explore how to maximize your return on investment (ROI).
Understanding the Different CRM Pricing Models
Before we dive into specific costs, it’s crucial to understand the different pricing models that CRM providers use. This knowledge will help you compare options and choose the model that best suits your business needs and financial situation.
1. Subscription-Based Pricing (SaaS – Software as a Service)
This is the most common pricing model for CRM systems, especially for small businesses. With SaaS, you pay a recurring fee, usually monthly or annually, to access the software. The fee is typically based on the number of users (employees) who will be using the system and the features included in your chosen plan. This model offers several advantages:
- Predictable Costs: You know exactly how much you’ll be paying each month or year.
- Scalability: You can easily add or remove users as your business grows or shrinks.
- Automatic Updates: The CRM provider handles all software updates and maintenance.
- Accessibility: You and your team can access the CRM from anywhere with an internet connection.
However, be mindful of potential limitations:
- Recurring Costs: You’ll need to budget for these ongoing expenses.
- Feature Limitations: Some plans may have limited features, requiring you to upgrade to a more expensive plan as your needs evolve.
2. Per-User Pricing
Within the subscription-based model, many CRM providers use per-user pricing. This means you pay a specific fee for each user who has access to the CRM system. This is a straightforward model, making it easy to calculate your costs. The price per user can vary significantly depending on the features included and the provider. Consider these points:
- Scalability: Easily add or remove users as your team changes.
- Control: You only pay for the users who need access.
- Cost Fluctuations: Your monthly costs will fluctuate based on the number of users.
3. Tiered Pricing
Many CRM providers offer tiered pricing plans. These plans typically offer different levels of features and functionality at different price points. The higher the tier, the more features you get. This allows you to choose a plan that aligns with your specific needs and budget. This model provides flexibility but demands careful evaluation:
- Customization: Choose a plan that matches your specific needs.
- Scalability: Upgrade as your business grows.
- Complexity: Comparing plans can be complex.
4. Freemium Models
Some CRM providers offer a freemium model, which includes a free version with limited features. This can be a great way to get started with CRM without any upfront costs. However, the free version often has limitations, such as a limited number of users, contacts, or features. This is a great starting point, but consider these points:
- No Upfront Cost: Test out the CRM before committing.
- Limited Features: May not meet all your business needs.
- Upgrade Paths: Be prepared to upgrade to a paid plan as your needs grow.
5. On-Premise CRM (Less Common for Small Businesses)
In the past, on-premise CRM systems were more prevalent. This model involves purchasing a license for the software and installing it on your own servers. You are responsible for all aspects of the software, including installation, maintenance, security, and updates. This model is less common for small businesses due to its high upfront costs and ongoing maintenance requirements. Key points to consider:
- High Upfront Costs: Requires significant investment in software licenses, hardware, and IT infrastructure.
- Ongoing Maintenance: You are responsible for all maintenance, security, and updates.
- Customization: Offers more flexibility in customization.
Breaking Down the Costs: What to Expect
Now, let’s delve into the specific costs you can anticipate when implementing a CRM system for your small business. Remember that these are estimates, and the actual costs will vary depending on the factors we discussed earlier.
1. Software Subscription Fees
This is the most significant ongoing cost. As we’ve established, most CRM systems use a subscription-based model. The price per user, per month, can range from as little as $10 to over $200, depending on the features and provider. Key considerations:
- Number of Users: The more users, the higher the cost.
- Feature Tier: More advanced features equal higher costs.
- Provider: Different providers have different pricing structures.
Example: A CRM with per-user pricing at $25 per user, per month. If you have 5 users, your monthly cost would be $125.
2. Implementation Costs
Implementing a CRM isn’t as simple as just signing up and logging in. There are often implementation costs involved, which can include:
- Data Migration: Transferring your existing customer data from spreadsheets, other systems, or even from paper records. This can be time-consuming and may require specialized tools or services.
- Customization: Tailoring the CRM to your specific business needs. This might involve configuring workflows, creating custom fields, or integrating with other software you use.
- Training: Training your team on how to use the CRM effectively. This can be done through online tutorials, in-person training sessions, or a combination of both.
- Consulting Services: Some businesses hire CRM consultants to help with the implementation process. Consultants can provide expert guidance and ensure a smooth transition.
These costs can vary widely depending on the complexity of your implementation. For a simple implementation, you might be able to handle it yourself with minimal costs. However, a more complex implementation could involve significant expenses.
3. Training Costs
Investing in training is crucial for ensuring your team can use the CRM effectively. Training costs can include:
- Online Tutorials and Documentation: Many CRM providers offer free or low-cost online resources.
- In-Person Training: Hiring a CRM trainer to come to your office to provide in-person training.
- Train-the-Trainer Programs: Training one or more employees to become internal CRM experts.
The cost of training will depend on the method you choose and the level of training required. Effective training will significantly reduce the time it takes for your team to adopt the new system and maximize its benefits.
4. Integration Costs
Most businesses use multiple software applications. Integrating your CRM with other software, such as your email marketing platform, accounting software, or e-commerce platform, can streamline your workflows and improve efficiency. Integration costs can include:
- Pre-built Integrations: Many CRM providers offer pre-built integrations with popular software. These integrations are typically easy to set up and often free.
- Custom Integrations: If you need to integrate with a less common or custom-built application, you may need to hire a developer.
- API Access: Some CRM providers offer API (Application Programming Interface) access, allowing you to build custom integrations.
The cost of integration will depend on the complexity of the integration and whether you can use pre-built integrations or need to develop custom ones.
5. Ongoing Maintenance and Support Costs
Even after your CRM is up and running, there will be ongoing maintenance and support costs. These costs can include:
- Technical Support: Most CRM providers offer technical support to help you with any issues you encounter. The level of support included in your subscription plan can vary.
- Software Updates: CRM providers regularly release software updates to fix bugs, add new features, and improve security. These updates are typically included in your subscription.
- Data Backup and Security: CRM providers are responsible for backing up your data and maintaining the security of their systems. However, it’s a good idea to have your own backup plan as well.
- Additional Features and Add-ons: You may need to purchase additional features or add-ons as your business grows.
These ongoing costs are generally included in your subscription fee, but it’s important to understand what’s included and what’s not.
Choosing the Right CRM for Your Small Business: Key Considerations
With a clear understanding of the costs involved, you’re now ready to choose the right CRM for your small business. Here are some key considerations to guide your decision-making process:
1. Define Your Needs
Before you start evaluating CRM systems, take the time to define your specific needs. What problems are you trying to solve? What features are essential? What are your sales, marketing, and customer service goals? This will help you narrow down your options and choose a CRM that aligns with your business objectives.
- Sales Automation: Do you need features to automate sales tasks, such as lead tracking, email marketing, and sales reporting?
- Marketing Automation: Do you need features to automate marketing tasks, such as email campaigns, social media management, and lead nurturing?
- Customer Service: Do you need features to manage customer inquiries, track support tickets, and provide self-service options?
- Reporting and Analytics: Do you need to track key performance indicators (KPIs) and generate reports on your sales, marketing, and customer service efforts?
- Integrations: Which other software applications do you need to integrate with?
2. Set a Budget
Determine how much you’re willing to spend on a CRM system. This will help you narrow down your options and avoid overspending. Consider both the initial investment and the ongoing costs. Be realistic about your budget and don’t be afraid to start with a more basic plan and upgrade as your needs grow.
3. Research and Compare Providers
Once you have a clear understanding of your needs and budget, start researching different CRM providers. Compare their features, pricing, and reviews. Look for providers that offer a free trial or a freemium plan so you can test out their software before committing. Read reviews from other small businesses to get insights into their experiences.
4. Consider Scalability
Choose a CRM system that can grow with your business. As your business expands, you’ll need a CRM that can handle more users, contacts, and data. Look for a system that offers flexible pricing plans and the ability to add features as needed.
5. Evaluate Ease of Use
The CRM system should be easy to use and intuitive. If your team struggles to use the system, they won’t use it effectively, and you won’t see the benefits. Look for a system with a user-friendly interface and good documentation. Consider the learning curve and how much training will be required.
6. Prioritize Data Security and Privacy
Your CRM system will store sensitive customer data. Ensure the provider has robust security measures in place to protect your data from unauthorized access and breaches. Look for providers that comply with data privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA.
7. Seek Customer Support
When selecting a CRM, consider the level of customer support offered. Is support available via phone, email, or live chat? Is the support team responsive and helpful? Good customer support can be invaluable when you encounter problems or have questions.
Top CRM Solutions for Small Businesses: A Quick Glance
Here’s a brief overview of some popular CRM solutions suitable for small businesses, along with a general idea of their pricing (remember to check the provider’s website for the most up-to-date pricing):
1. HubSpot CRM
HubSpot offers a free CRM with a robust set of features, making it an excellent starting point for small businesses. It’s known for its ease of use and comprehensive marketing and sales tools. Paid plans offer advanced features and increased limits.
- Pricing: Free plan available. Paid plans range from around $45/month to significantly higher depending on the features and number of users.
- Key Features: Contact management, deal tracking, email marketing, sales automation, reporting.
- Pros: User-friendly, free plan, comprehensive features, strong marketing automation.
- Cons: Limited features in the free plan, pricing can become expensive as you scale.
2. Zoho CRM
Zoho CRM is a feature-rich CRM with a competitive pricing structure. It offers a free plan for a limited number of users, and its paid plans are affordable. Zoho CRM is known for its extensive integrations and customization options.
- Pricing: Free plan for up to 3 users. Paid plans range from around $14/user/month to $52/user/month.
- Key Features: Contact management, lead management, sales automation, workflow automation, reporting, integrations.
- Pros: Affordable, feature-rich, extensive integrations, good customization options.
- Cons: Interface can be overwhelming for beginners, some advanced features require higher-tier plans.
3. Freshsales
Freshsales is a sales-focused CRM known for its ease of use and intuitive interface. It offers a free plan and affordable paid plans, making it a good option for small businesses focused on sales. Freshsales is known for its built-in phone and email features.
- Pricing: Free plan available. Paid plans range from around $15/user/month to $69/user/month.
- Key Features: Contact management, lead management, sales automation, built-in phone, email tracking, reporting.
- Pros: User-friendly, affordable, strong sales-focused features.
- Cons: Limited features in the free plan, may not be suitable for businesses with complex needs.
4. Pipedrive
Pipedrive is a sales-focused CRM designed for salespeople. It offers a visual and intuitive interface, making it easy to manage sales pipelines. Pipedrive’s pricing is straightforward and predictable.
- Pricing: Plans start from around $14.90/user/month.
- Key Features: Sales pipeline management, contact management, deal tracking, sales automation, reporting.
- Pros: User-friendly, excellent for pipeline management, straightforward pricing.
- Cons: Limited marketing automation features, not as feature-rich as some other CRMs.
5. Agile CRM
Agile CRM offers a comprehensive suite of features for sales, marketing, and customer service. It offers a free plan and affordable paid plans. Agile CRM is a good option for businesses looking for an all-in-one solution.
- Pricing: Free plan available. Paid plans start from around $14.99/user/month.
- Key Features: Contact management, lead management, sales automation, marketing automation, customer service, reporting.
- Pros: All-in-one solution, affordable, comprehensive features.
- Cons: Interface can be clunky, some features may be less polished than those of specialized CRMs.
Maximizing Your CRM ROI: Making the Most of Your Investment
Investing in a CRM is only the first step. To truly realize the benefits and maximize your ROI, you need to implement the CRM effectively and use it strategically. Here’s how:
1. Implement a Strong Implementation Plan
Don’t rush the implementation process. Take the time to plan your implementation carefully. This includes data migration, customization, and training. A well-planned implementation will ensure a smooth transition and reduce the likelihood of problems down the road. Consider these key elements:
- Data Migration Strategy: Plan how you will migrate your data. Clean and organize your data before importing it into the CRM.
- Customization Requirements: Determine what customizations are needed, and prioritize them.
- Training Schedule: Develop a training schedule and ensure all users are adequately trained.
- Testing Phase: Test the system thoroughly before going live.
2. Train Your Team Effectively
Proper training is essential for ensuring your team can use the CRM effectively. Provide comprehensive training that covers all aspects of the system, from basic navigation to advanced features. Offer ongoing training and support to help your team stay up-to-date on the latest features and best practices. Consider these training strategies:
- Role-Based Training: Tailor training to the specific roles of your team members.
- Hands-On Practice: Provide opportunities for hands-on practice and real-world scenarios.
- Ongoing Support: Offer ongoing support and resources, such as documentation and tutorials.
- Feedback and Refinement: Gather feedback from your team and make adjustments to your training program as needed.
3. Encourage User Adoption
User adoption is critical for the success of your CRM. Encourage your team to use the system regularly by making it easy to use and demonstrating its value. Show them how the CRM can help them improve their productivity and achieve their goals. Address any concerns or resistance to change promptly. Consider these techniques:
- Lead by Example: Demonstrate how you use the CRM yourself.
- Highlight Benefits: Show your team how the CRM will benefit them.
- Provide Support: Offer ongoing support and answer questions.
- Recognize Success: Acknowledge and reward team members who are using the CRM effectively.
4. Clean and Maintain Your Data
Keep your data clean and up-to-date. Inaccurate or outdated data can lead to wasted time, missed opportunities, and poor decision-making. Regularly review your data and correct any errors. Implement processes to ensure data accuracy. Consider these steps:
- Data Entry Standards: Establish data entry standards and guidelines.
- Regular Data Cleansing: Regularly review and clean your data.
- Data Validation: Implement data validation rules to ensure data accuracy.
- Data Governance: Establish data governance policies to ensure data quality.
5. Automate Your Workflows
Use the CRM’s automation features to streamline your workflows and free up your team’s time. Automate repetitive tasks, such as sending emails, creating tasks, and updating records. Automation will help you improve efficiency and reduce errors. Explore these automation opportunities:
- Sales Automation: Automate lead nurturing, follow-up emails, and sales reporting.
- Marketing Automation: Automate email campaigns, social media posting, and lead scoring.
- Customer Service Automation: Automate ticket routing, self-service options, and customer feedback surveys.
6. Analyze Your Data and Track KPIs
Regularly analyze your CRM data to gain insights into your sales, marketing, and customer service efforts. Track key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure your progress and identify areas for improvement. Use your CRM reporting tools to generate reports and dashboards that provide valuable insights. Consider these KPIs:
- Sales KPIs: Sales revenue, conversion rates, deal size, sales cycle length.
- Marketing KPIs: Lead generation, website traffic, conversion rates, marketing ROI.
- Customer Service KPIs: Customer satisfaction, resolution time, first contact resolution.
- Regular Reporting: Generate regular reports and review them with your team.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Use the insights you gain to make data-driven decisions.
7. Integrate with Other Tools
Integrate your CRM with other software applications, such as your email marketing platform, accounting software, and e-commerce platform. Integrations will streamline your workflows and provide a more complete view of your customers. Explore these integration opportunities:
- Email Marketing: Integrate with your email marketing platform to sync contacts and track email campaigns.
- Accounting Software: Integrate with your accounting software to track sales and manage invoices.
- E-commerce Platform: Integrate with your e-commerce platform to track customer orders and manage customer data.
- Collaboration Tools: Integrate with your collaboration tools to improve team communication.
Conclusion: Making the Right CRM Investment for Your Small Business
Choosing and implementing a CRM system is a significant decision for any small business. By understanding the various CRM cost models, carefully evaluating your needs, and selecting the right provider, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your budget and business goals. Remember to prioritize user adoption, data quality, and effective implementation to maximize your ROI. With the right CRM in place, your small business can build stronger customer relationships, streamline its operations, and achieve sustainable growth.
Don’t be intimidated by the initial investment. View it as an investment in your future. The right CRM can empower your team, improve your efficiency, and ultimately help you achieve your business goals. Take your time, do your research, and choose the CRM that’s right for you. Your customers, and your bottom line, will thank you for it.
Good luck on your CRM journey!