Small Business CRM Cost Guide: Unveiling the True Price Tag and Maximizing Your ROI
Small Business CRM Cost Guide: A Deep Dive
So, you’re a small business owner, juggling a million things at once. You’re the CEO, the marketing guru, the customer service rep, and maybe even the janitor (no judgment!). And somewhere in the back of your mind, you keep hearing about this magical tool called a CRM – Customer Relationship Management system. It promises to streamline your operations, boost sales, and make your life easier. But then you start looking at the cost, and your eyes glaze over. CRM pricing can feel like a labyrinth, a confusing maze of features, tiers, and hidden fees. This guide is designed to cut through the noise and give you a clear understanding of small business CRM costs.
We’ll explore the various pricing models, the factors that influence the price, and, most importantly, how to choose a CRM that fits your budget and your business needs. We’ll also look at ways to maximize your return on investment (ROI) and avoid common pitfalls. Let’s get started!
What is a CRM and Why Do You Need One?
Before we dive into the cost, let’s quickly recap what a CRM is and why it’s essential for small businesses. A CRM is essentially a centralized database that stores all your customer information. This includes contact details, purchase history, communication logs, and any other relevant data. Think of it as a digital Rolodex on steroids.
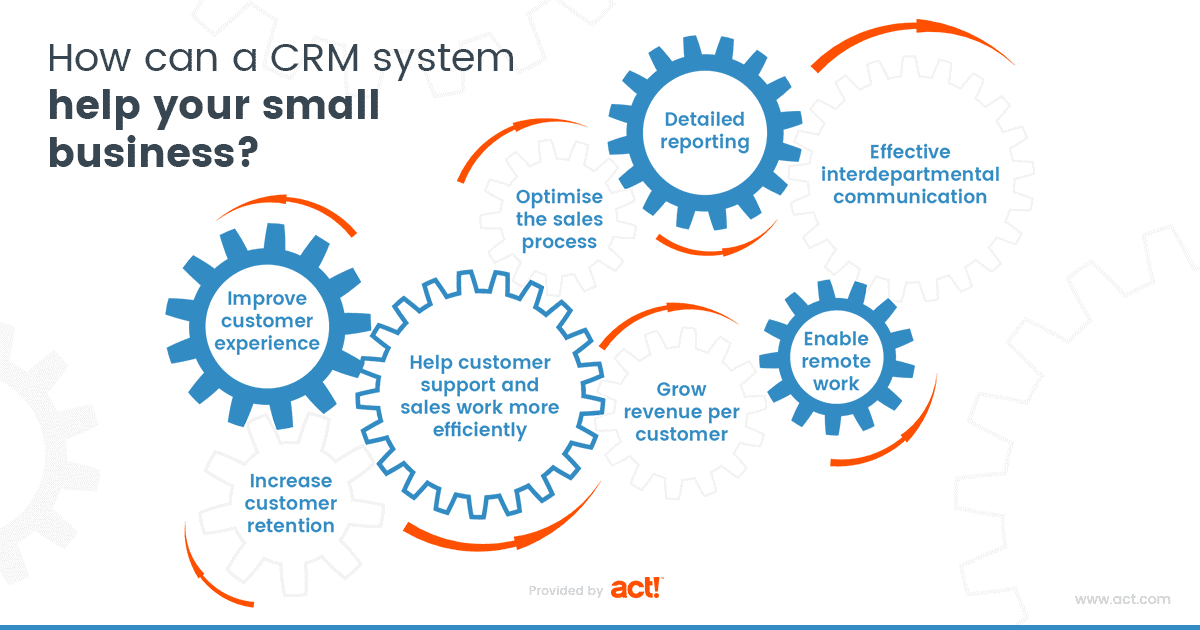
Here’s why a CRM is crucial for small businesses:
- Improved Customer Relationships: A CRM helps you understand your customers better. You can track their interactions, personalize your communication, and provide a more tailored experience.
- Increased Sales: By tracking leads, managing the sales pipeline, and automating tasks, a CRM can help you close more deals and boost revenue.
- Enhanced Efficiency: A CRM automates repetitive tasks, such as data entry and email marketing, freeing up your time to focus on more strategic activities.
- Better Data Analysis: CRM systems provide valuable insights into your customers and your sales processes, allowing you to make data-driven decisions.
- Improved Collaboration: A CRM makes it easier for your team to share information and collaborate on customer interactions.
In short, a CRM is an investment that can pay off handsomely by helping you attract, retain, and satisfy your customers. Now, let’s talk about the price tag.
Understanding CRM Pricing Models
CRM vendors typically offer a few different pricing models. Understanding these models is crucial for comparing different CRM solutions and finding one that fits your budget.
1. Subscription-Based Pricing (SaaS – Software as a Service)
This is the most common pricing model. You pay a recurring fee, usually monthly or annually, to access the CRM software. The price is often based on the number of users and the features included. This model is popular because it requires minimal upfront investment and allows you to scale your CRM usage as your business grows. It’s like renting an apartment – you pay a monthly fee for access.
2. Per-User Pricing
This is a common type of subscription-based pricing. You pay a fee for each user who has access to the CRM. For example, if you have five sales reps, you’ll pay a fee for each of those five users. This model is straightforward but can become expensive as your team grows. It’s important to consider how many users truly need access to the CRM to avoid unnecessary costs.
3. Tiered Pricing
Many CRM vendors offer tiered pricing plans. These plans typically offer different features and functionalities at different price points. The basic plan might include essential features like contact management and basic reporting. More expensive plans might include advanced features like marketing automation, sales forecasting, and custom integrations. This allows you to choose a plan that aligns with your specific needs and budget. Think of it like a menu – you choose the features you want and pay accordingly.
4. Usage-Based Pricing
Some CRM vendors charge based on usage, such as the number of contacts stored, the number of emails sent, or the amount of data storage used. This model can be beneficial if your CRM usage is variable. However, it’s essential to carefully monitor your usage to avoid unexpected charges. This is like paying for electricity – you only pay for what you use.
5. On-Premise Pricing
This model is less common, especially for small businesses. With on-premise CRM, you purchase a license to install the software on your own servers. This requires a significant upfront investment and ongoing costs for maintenance, IT support, and upgrades. It’s like buying a house – you own it, but you’re responsible for all the upkeep.
Factors That Influence CRM Costs
Several factors can influence the cost of a CRM. Understanding these factors will help you make informed decisions and choose a CRM that’s right for you.
1. Number of Users
As mentioned earlier, the number of users is a primary driver of CRM costs, especially with per-user pricing models. Consider how many team members need access to the CRM and whether they all require the same level of access and features. You might be able to reduce costs by assigning different roles and permissions to users.
2. Features and Functionality
The more features your CRM offers, the more you’ll likely pay. Basic CRM plans typically include essential features like contact management and basic reporting. More advanced plans might include marketing automation, sales force automation, customer service tools, and custom integrations. Evaluate your needs carefully and choose a plan that includes the features you require without paying for features you won’t use. Think of it like a car – do you need all the bells and whistles, or will a basic model suffice?
3. Integrations
CRM systems often integrate with other business applications, such as email marketing platforms, accounting software, and e-commerce platforms. Some integrations are free, while others require a separate subscription or involve additional costs. Consider which integrations are essential for your business and factor those costs into your budget.
4. Data Storage
Some CRM vendors charge based on the amount of data storage you use. If you have a large customer database or store a lot of files within the CRM, this can impact your costs. Consider your data storage needs and choose a CRM that offers sufficient storage capacity at a reasonable price.
5. Support and Training
CRM vendors offer varying levels of support and training. Some vendors provide free online support, while others offer premium support packages with dedicated account managers and priority support. Training options can range from free tutorials to paid training courses. Factor in the cost of support and training when evaluating different CRM solutions.
6. Customization
If you need to customize your CRM to meet your specific business needs, this can add to the cost. Customization can involve hiring a consultant, developing custom integrations, or purchasing add-ons. Consider the level of customization you require and factor those costs into your budget.
Common CRM Pricing Structures and Examples
Let’s look at some examples of CRM pricing structures to give you a better idea of what to expect.
1. Free CRM Options
Many CRM vendors offer free plans. These plans are often limited in terms of features and the number of users. They’re a great option for small businesses that are just starting and have basic CRM needs. Examples include HubSpot CRM, Zoho CRM, and Agile CRM. These free plans are typically designed to get you hooked and then entice you to upgrade to a paid plan with more features.
2. Basic Plans for Small Businesses
These plans typically offer essential features like contact management, lead tracking, and basic reporting. They’re suitable for small businesses that need a simple CRM solution. Pricing usually ranges from $10 to $50 per user per month. Examples include the basic plans from Pipedrive, Freshsales, and EngageBay.
3. Mid-Tier Plans for Growing Businesses
These plans offer more advanced features, such as marketing automation, sales force automation, and custom integrations. They’re suitable for growing businesses that need a more comprehensive CRM solution. Pricing usually ranges from $50 to $150 per user per month. Examples include the mid-tier plans from Salesforce, Microsoft Dynamics 365, and SugarCRM.
4. Enterprise Plans for Large Businesses
These plans offer the most advanced features, including custom reporting, advanced analytics, and dedicated support. They’re suitable for large businesses with complex CRM needs. Pricing can vary widely, ranging from $150 per user per month to thousands of dollars per month depending on the specific requirements. Examples include the enterprise plans from Oracle Siebel and SAP CRM.
Remember, these are just examples. The actual pricing can vary depending on the vendor, the specific features included, and any discounts or promotions available. Always check the vendor’s website for the most up-to-date pricing information.
Finding the Right CRM for Your Small Business Budget
Now that you understand the pricing models and factors that influence costs, let’s talk about how to find a CRM that fits your small business budget.
1. Define Your Needs and Goals
Before you start shopping for a CRM, take the time to define your needs and goals. What problems are you trying to solve? What features are essential? What are your must-haves and nice-to-haves? Having a clear understanding of your needs will help you narrow down your options and choose a CRM that’s a good fit.
2. Set a Budget
Determine how much you’re willing to spend on a CRM. Consider your current financial situation and your projected revenue. Remember that a CRM is an investment, and the right CRM can help you generate more revenue in the long run. However, it’s essential to set a realistic budget and stick to it.
3. Research Different CRM Vendors
Once you know your needs and budget, start researching different CRM vendors. Compare their pricing, features, and reviews. Read online reviews and testimonials to get a sense of other users’ experiences. Look for vendors that offer free trials or demos so you can try out the software before you commit.
4. Compare Pricing Plans
Carefully compare the pricing plans offered by different vendors. Pay attention to the features included in each plan and whether they meet your needs. Consider the per-user cost, any additional fees, and the overall value you’re getting. Don’t just focus on the cheapest option. Consider the long-term value and whether the CRM can grow with your business.
5. Consider Scalability
Choose a CRM that can scale with your business. As your business grows, your CRM needs will likely change. Make sure the CRM you choose offers plans that can accommodate your future growth. Consider whether you’ll need more users, more features, or more data storage in the future.
6. Look for Discounts and Promotions
Many CRM vendors offer discounts and promotions, such as annual payment discounts or discounts for non-profit organizations. Look for these opportunities to save money. You may also be able to negotiate a better price, especially if you’re a large customer or you’re committing to a long-term contract.
7. Don’t Overspend on Features You Don’t Need
Avoid the temptation to overspend on features you don’t need. Choose a plan that includes the features you require without paying for features you won’t use. You can always upgrade to a more advanced plan later if your needs change.
8. Consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
The TCO includes not only the subscription fees but also other costs, such as implementation costs, training costs, and ongoing maintenance costs. Consider the total cost of ownership when evaluating different CRM solutions.
Maximizing Your CRM ROI
Choosing the right CRM is just the first step. To maximize your ROI, you need to implement the CRM effectively and use it to its full potential.
1. Implement the CRM Properly
Proper implementation is crucial for maximizing your CRM ROI. This includes data migration, user training, and system configuration. Consider hiring a consultant to help you with the implementation process, especially if you’re new to CRM or have complex needs. Take the time to configure the system correctly to meet your specific business needs.
2. Train Your Team
Ensure that your team is properly trained on how to use the CRM. Provide ongoing training and support to help them get the most out of the system. Encourage your team to embrace the CRM and use it consistently. The more your team uses the CRM, the more value you’ll get from it.
3. Integrate with Other Systems
Integrate your CRM with other business systems, such as email marketing platforms, accounting software, and e-commerce platforms. This will streamline your workflows and improve data accuracy. Integration allows you to have a 360-degree view of your customer.
4. Use Data Effectively
Use the data in your CRM to gain insights into your customers and your sales processes. Analyze your sales pipeline, track your marketing campaigns, and identify areas for improvement. Use the data to make data-driven decisions and optimize your business processes. This is where the real power of a CRM lies.
5. Automate Tasks
Automate repetitive tasks, such as data entry and email marketing, to save time and improve efficiency. Automation can help you focus on more strategic activities and free up your team’s time. Many CRM systems offer robust automation capabilities.
6. Track Your Results
Track your results to measure the ROI of your CRM. Monitor key metrics, such as sales revenue, customer acquisition cost, and customer retention rate. Use these metrics to evaluate the effectiveness of your CRM and identify areas for improvement. This gives you concrete evidence of the CRM’s value.
7. Regularly Review and Optimize
Regularly review your CRM usage and optimize your system. Make sure you’re using the CRM to its full potential. Identify any areas where you can improve your processes or workflows. Stay up-to-date with the latest features and updates offered by your CRM vendor.
Hidden Costs to Watch Out For
Besides the obvious subscription fees, there are some hidden costs that can sneak up on you. Being aware of these can help you budget more accurately and avoid unpleasant surprises.
1. Implementation Costs
Implementing a CRM can involve costs, such as data migration, system configuration, and training. These costs can vary depending on the complexity of your CRM and the level of support you need. Factor these costs into your budget.
2. Customization Costs
If you need to customize your CRM to meet your specific business needs, this can add to the cost. Customization can involve hiring a consultant, developing custom integrations, or purchasing add-ons. Consider the level of customization you require and factor those costs into your budget.
3. Integration Costs
Integrating your CRM with other business systems can involve costs, such as integration fees or the cost of purchasing additional software. Research the integration costs before you commit to a CRM.
4. Training Costs
Training your team on how to use the CRM can involve costs, such as the cost of training courses or the time spent by your team. Factor these costs into your budget.
5. Data Migration Costs
Migrating your data from your existing systems to the CRM can involve costs, such as the cost of data migration tools or the time spent by your team. Plan for these costs, especially if you have a large amount of data.
6. Support Costs
Some CRM vendors charge for support, especially for premium support packages. Factor these costs into your budget.
7. Add-on Costs
CRM vendors often offer add-ons, such as advanced reporting tools or marketing automation features. These add-ons can add to the cost of your CRM. Consider the cost of add-ons when evaluating different CRM solutions.
Avoiding Common CRM Cost Pitfalls
Here are some common pitfalls to avoid when it comes to CRM costs.
1. Choosing a CRM That’s Too Expensive
Don’t overspend on a CRM that includes features you don’t need. Choose a plan that includes the features you require without paying for features you won’t use. Start small and scale up as your business grows.
2. Ignoring Hidden Costs
Factor in all the potential costs of a CRM, including implementation costs, customization costs, integration costs, and training costs. Don’t be surprised by hidden fees.
3. Not Training Your Team Properly
If your team isn’t properly trained on how to use the CRM, you won’t get the full value from your investment. Invest in training and provide ongoing support.
4. Not Integrating with Other Systems
If you don’t integrate your CRM with other business systems, you’ll miss out on the benefits of automation and data accuracy. Integrate your CRM with the systems that are essential for your business.
5. Not Using Data Effectively
If you don’t use the data in your CRM to gain insights into your customers and your sales processes, you’ll miss out on the opportunity to improve your business. Analyze your data and make data-driven decisions.
6. Choosing the Wrong CRM
Choosing the wrong CRM can be a costly mistake. Take the time to research different CRM vendors and choose a CRM that’s a good fit for your needs and budget.
Conclusion: Making the Right CRM Decision
Choosing a CRM is a significant decision for any small business. By understanding the various pricing models, the factors that influence costs, and how to maximize your ROI, you can make an informed decision and choose a CRM that’s right for you. Remember to define your needs, set a budget, research different vendors, compare pricing plans, and consider scalability. Don’t be afraid to start with a free or basic plan and upgrade as your needs grow. With the right CRM, you can streamline your operations, boost sales, and build stronger customer relationships. Good luck!