Small Business CRM Cost Guide: Decoding the Price and Boosting Your ROI
Running a small business is a whirlwind, isn’t it? You’re juggling a thousand things – from securing new clients to keeping existing ones happy, all while trying to stay ahead of the competition. In this chaotic landscape, a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system can be a game-changer. It’s like having a super-powered assistant that helps you manage your interactions with customers and potential leads.
But here’s the million-dollar question (or maybe the several-hundred-dollar question): How much does a CRM system *really* cost? The answer, as with most things in life, is: it depends. This comprehensive guide will break down the costs associated with CRM systems for small businesses, helping you navigate the pricing landscape and make an informed decision that aligns with your budget and business goals. We’ll delve into the various pricing models, hidden costs, and factors that influence the overall expense. By the end of this guide, you’ll be equipped to choose a CRM that not only fits your budget but also delivers a solid return on investment (ROI).
What is a CRM and Why Does Your Small Business Need One?
Before we dive into the cost, let’s quickly recap what a CRM system actually *is* and why it’s crucial for small businesses. At its core, a CRM is a software solution designed to manage and analyze all your customer interactions and data throughout the customer lifecycle. Think of it as a central hub for all things customer-related.
Here’s a glimpse of what a CRM can do for your business:
- Centralized Customer Data: Store all customer information, from contact details to purchase history, in one accessible location.
- Improved Customer Service: Provide personalized and efficient customer service by having instant access to customer data.
- Enhanced Sales Efficiency: Automate sales processes, track leads, and manage the sales pipeline more effectively.
- Streamlined Marketing Campaigns: Segment your audience, personalize marketing messages, and track campaign performance.
- Better Reporting and Analytics: Gain valuable insights into customer behavior, sales performance, and marketing effectiveness.
- Increased Sales and Revenue: By improving customer relationships and streamlining processes, CRM systems can boost sales and revenue.
In essence, a CRM helps you understand your customers better, nurture relationships, and ultimately, drive business growth. Even if you’re a solopreneur or a small team, the benefits of a CRM are undeniable.
Understanding CRM Pricing Models: The Key to Budgeting
The pricing structure of CRM systems can vary widely, making it essential to understand the different models available. This knowledge will empower you to compare options effectively and choose a plan that suits your financial situation.
1. Subscription-Based Pricing (SaaS – Software as a Service)
This is the most prevalent pricing model for CRM systems. You pay a recurring fee (typically monthly or annually) to access the software. The cost is often based on the number of users, features, and storage capacity. SaaS models are popular because they eliminate the need for upfront hardware or IT infrastructure investments. Here’s a breakdown:
- Pros:
- Predictable costs: You know exactly how much you’ll be paying each month or year.
- Scalability: Easily add or remove users as your business grows or shrinks.
- Automatic updates: The vendor handles software updates and maintenance.
- Accessibility: Access the CRM from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Cons:
- Recurring costs: You’re always paying, even if you’re not actively using the system.
- Limited customization: Customization options may be restricted depending on the plan.
- Vendor lock-in: Switching to a different CRM can be complex.
Examples of CRM systems with subscription-based pricing: HubSpot CRM, Salesforce Sales Cloud, Zoho CRM, Pipedrive.
2. On-Premise Pricing
With this model, you purchase a license to install the CRM software on your own servers. You’re responsible for the hardware, IT infrastructure, and maintenance. This option offers more control and customization but comes with higher upfront costs and ongoing IT expenses. Here’s a breakdown:
- Pros:
- Greater control: You have complete control over the software and data.
- Customization: You can customize the CRM to meet your specific needs.
- Data security: Data is stored on your own servers, which can be an advantage for security-conscious businesses.
- Cons:
- High upfront costs: You need to purchase hardware, software licenses, and potentially hire IT staff.
- Ongoing maintenance: You’re responsible for software updates, backups, and security.
- Limited scalability: Scaling the system can be complex and expensive.
Examples of CRM systems with on-premise pricing: Microsoft Dynamics 365 (can be deployed on-premise), SugarCRM (offers on-premise options).
3. Hybrid Pricing
Some CRM vendors offer a hybrid approach, combining elements of both SaaS and on-premise models. This might involve a subscription for core features and additional fees for add-ons or customization. This approach offers a balance between cost-effectiveness and control.
4. Open-Source Pricing
Open-source CRM systems are available for free, but you’ll likely need to pay for hosting, implementation, and customization. This option can be cost-effective for businesses with technical expertise or the willingness to invest in development.
Examples of Open-Source CRM: SuiteCRM, Vtiger CRM.
Breaking Down the Costs: What Factors Influence CRM Pricing?
Now that you understand the different pricing models, let’s delve into the specific factors that impact the overall cost of a CRM system. Knowing these factors will help you make a more informed decision and avoid unexpected expenses.
1. Number of Users
This is a primary driver of cost, especially for subscription-based models. Most vendors charge per user, per month, or per year. The more users you have, the higher your monthly or annual bill will be. Consider your current team size and any anticipated growth when estimating user costs.
2. Features and Functionality
CRM systems offer a wide range of features, from basic contact management to advanced sales automation, marketing automation, and analytics. The more features you need, the more you’ll likely pay. Tiered pricing plans often offer different feature sets at different price points. Carefully evaluate your business needs and choose a plan that includes the features you require without paying for unnecessary functionality.
3. Storage Capacity
CRM systems store a significant amount of data, including customer information, documents, and attachments. Some vendors charge extra for storage capacity beyond a certain limit. Consider your data storage needs and choose a plan that provides sufficient storage space.
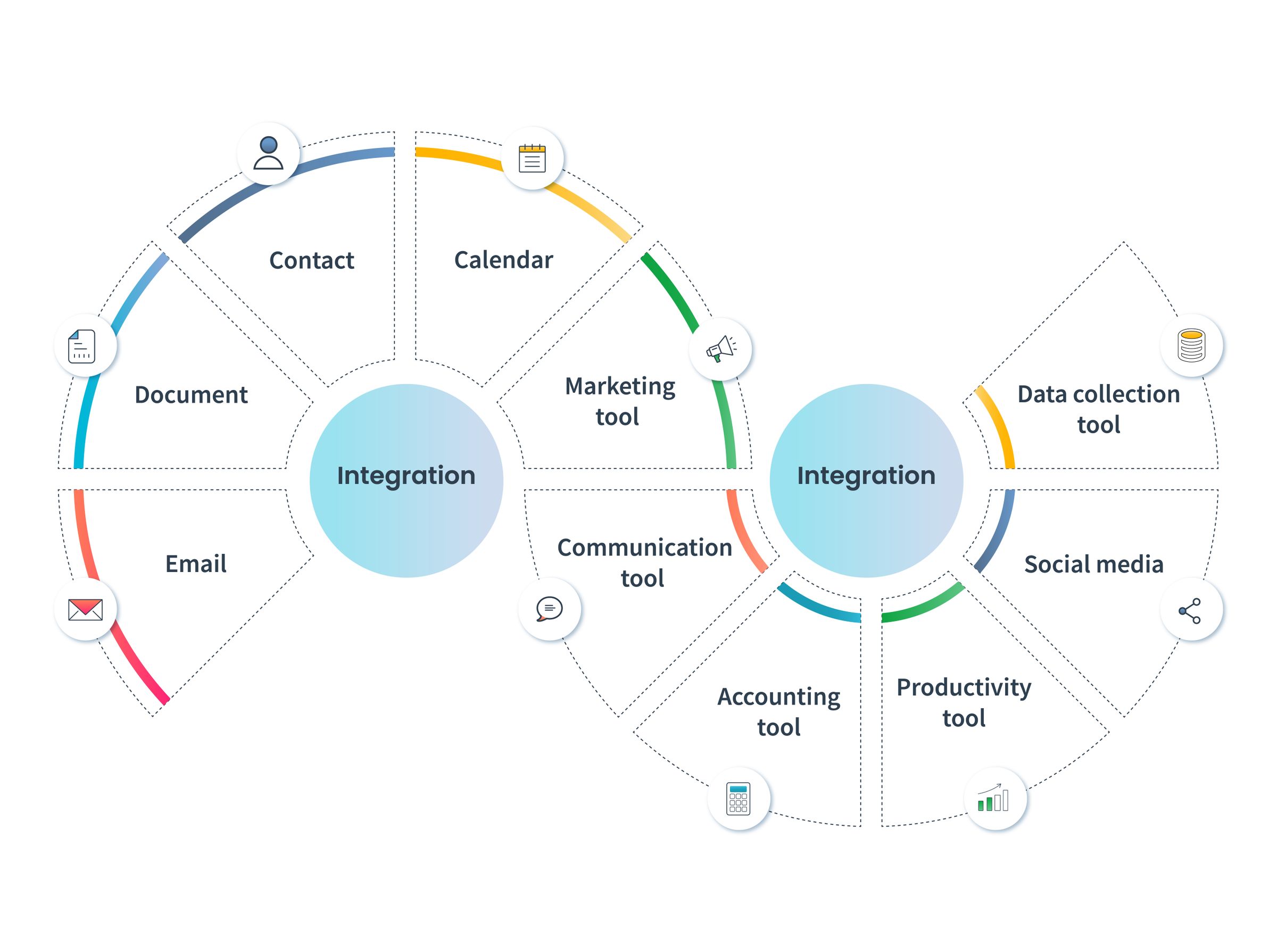
4. Integrations
CRM systems often integrate with other business applications, such as email marketing platforms, accounting software, and social media channels. Integrations can enhance the functionality of your CRM but may come with additional costs. Some integrations are free, while others require a separate subscription or fee.
5. Customization
If you need to customize the CRM to meet your specific business requirements, you may incur additional costs for development and implementation. Customization can involve modifying existing features, creating custom fields, or developing custom integrations. Consider the level of customization you need and factor in the associated costs.
6. Implementation and Training
Implementing a CRM system can be a complex process, especially if you’re new to CRM. You may need to hire a consultant or vendor to help with implementation, data migration, and training. These services can add to the overall cost of the CRM. Factor in the cost of implementation and training when budgeting for your CRM system.
7. Support and Maintenance
Vendors typically offer different levels of support, from basic online support to premium support with dedicated account managers. The level of support you choose will impact the overall cost. Ensure the support provided meets your needs. Ongoing maintenance, including software updates and security patches, is typically included in subscription fees, but on-premise systems require you to handle maintenance or pay for it.
8. Add-ons and Extensions
Many CRM systems offer add-ons and extensions that provide additional functionality. These add-ons may come with additional costs, either as a one-time purchase or a recurring subscription. Evaluate the value of each add-on and determine whether it’s worth the investment.
Hidden Costs to Watch Out For
Beyond the obvious costs, several hidden expenses can inflate the overall cost of your CRM system. Being aware of these hidden costs can help you avoid budget overruns and make a more informed decision.
- Data Migration Costs: Transferring your existing customer data into the new CRM can be time-consuming and may require specialized tools or services.
- Integration Costs: Integrating your CRM with other business applications may involve development work or additional subscriptions.
- Customization Costs: Customizing the CRM to meet your specific needs can add to the overall cost.
- Training Costs: Providing training to your team can involve internal resources or external consultants.
- Downtime Costs: Any downtime during implementation or maintenance can impact your business operations and revenue.
- Upgrade Costs: As your business grows, you may need to upgrade to a more expensive plan with more features and capacity.
- Hidden Fees: Be aware of any hidden fees, such as setup fees, cancellation fees, or overage charges.
Comparing CRM Systems: A Practical Approach
With a plethora of CRM systems available, comparing your options can feel daunting. Here’s a practical approach to help you evaluate and compare CRM systems:
1. Define Your Needs
Before starting your search, clearly define your business needs and goals. What do you want to achieve with a CRM system? What features are essential? What integrations do you need? Having a clear understanding of your requirements will help you narrow down your options.
2. Set Your Budget
Determine your budget for a CRM system. Consider both the upfront costs and the ongoing expenses. This will help you eliminate options that are outside your financial reach.
3. Research CRM Systems
Research different CRM systems and identify those that meet your needs and budget. Read reviews, compare features, and assess pricing models.
4. Request Demos and Trials
Request demos and free trials from the CRM vendors you’re considering. This will allow you to test the software, evaluate its features, and see if it meets your needs.
5. Evaluate Pricing Plans
Compare the pricing plans offered by each vendor. Consider the number of users, features, storage capacity, and support options. Calculate the total cost of ownership for each plan.
6. Assess Implementation and Training
Evaluate the implementation process and training options offered by each vendor. Consider the level of support you’ll need to get the system up and running and train your team.
7. Consider Long-Term Costs
Don’t just focus on the initial cost. Consider the long-term costs, such as ongoing subscription fees, maintenance costs, and potential upgrade costs.
8. Read Reviews and Testimonials
Read reviews and testimonials from other small businesses to get insights into their experiences with different CRM systems. This can help you identify potential challenges and benefits.
9. Ask Questions
Don’t hesitate to ask the vendors questions about pricing, features, implementation, and support. Get all the information you need to make an informed decision.
10. Choose the Right CRM
Based on your research, evaluation, and comparison, choose the CRM system that best meets your needs and budget. Consider the long-term value and ROI of the system.
Maximizing ROI: Getting the Most Out of Your CRM Investment
Investing in a CRM system is only the first step. To maximize your ROI, you need to implement the system effectively and use it to its full potential.
- Data Migration: Migrate all your existing customer data into the CRM accurately and completely.
- User Training: Provide adequate training to your team to ensure they understand how to use the system effectively.
- Process Automation: Automate repetitive tasks, such as lead assignment and email marketing, to save time and improve efficiency.
- Data Analysis: Analyze your customer data to gain insights into customer behavior, sales performance, and marketing effectiveness.
- Regular Updates: Regularly update your customer data to keep it accurate and up-to-date.
- Integration: Integrate your CRM with other business applications to streamline your workflows and improve data sharing.
- Feedback: Gather feedback from your team and customers to continuously improve your CRM usage.
- Set Goals: Set clear goals and track your progress to measure the ROI of your CRM investment.
Top CRM Systems for Small Businesses: A Quick Glance
Choosing the right CRM is a very individual process, but some systems consistently rank highly for small businesses. Here’s a brief overview of some popular options:
- HubSpot CRM: A popular, free CRM with robust features and excellent ease of use. Offers paid plans for advanced functionality.
- Zoho CRM: A comprehensive and affordable CRM with a wide range of features and customization options.
- Pipedrive: A sales-focused CRM designed for small businesses, known for its user-friendly interface and intuitive features.
- Salesforce Sales Cloud: A powerful and scalable CRM that offers a wide range of features and customization options. More expensive than other options, but can be a good long-term investment.
- Freshsales: An easy-to-use CRM with a focus on sales, offering features like lead scoring and sales automation.
Remember to research these and other options thoroughly to find the perfect fit for *your* business needs and budget.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice for Your Business
Choosing a CRM system is a significant decision for any small business. By understanding the different pricing models, factors that influence cost, and hidden expenses, you can navigate the CRM landscape and make an informed decision. Remember to define your needs, set your budget, and compare your options carefully. Ultimately, the right CRM system can streamline your operations, improve customer relationships, and drive business growth. Don’t be afraid to invest the time and effort to find the perfect CRM solution for your small business – the rewards are well worth it!