Small Business CRM Cost: A Comprehensive Guide to Budgeting, Pricing, and ROI
Small Business CRM Cost: A Comprehensive Guide to Budgeting, Pricing, and ROI
Starting a small business is an exciting journey, filled with potential and challenges. One of the most crucial decisions you’ll make is how to manage your customer relationships. This is where a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system comes into play. But, before you jump in, a key question arises: What is the small business CRM cost, and how can you make the right investment?
This comprehensive guide will delve deep into the world of CRM costs for small businesses. We’ll explore the various pricing models, the factors that influence the overall expense, and how to calculate the return on investment (ROI). Whether you’re a startup or an established small business, understanding the financial implications of a CRM system is paramount.
Understanding the Importance of CRM for Small Businesses
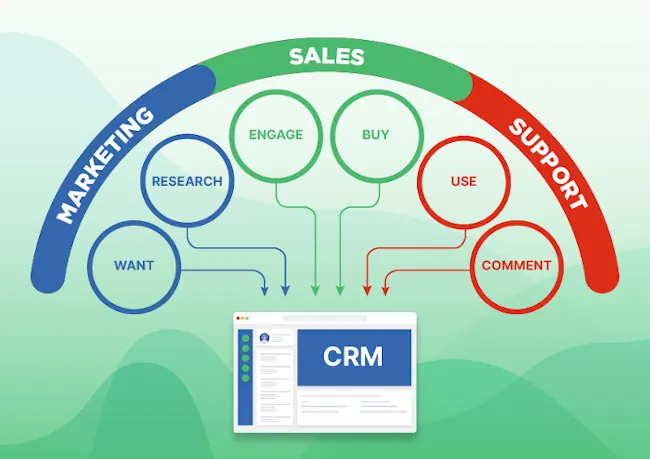
Before we dive into the numbers, let’s briefly discuss why a CRM is essential for small businesses. In today’s competitive landscape, building and maintaining strong customer relationships is critical for success. A CRM system helps you:
- Centralize Customer Data: Store all customer information in one accessible location, eliminating data silos.
- Improve Customer Service: Provide faster, more personalized support.
- Automate Sales Processes: Streamline your sales pipeline and close deals more efficiently.
- Enhance Marketing Efforts: Target your marketing campaigns with precision.
- Boost Sales and Revenue: Ultimately, drive more sales and increase profitability.
Without a CRM, small businesses often struggle with disorganized data, missed opportunities, and inefficient processes. Investing in the right CRM can be a game-changer.
Decoding Small Business CRM Pricing Models
The cost of a CRM isn’t a one-size-fits-all figure. It varies based on the pricing model the vendor uses. Here are the most common pricing models you’ll encounter:
1. Per-User, Per-Month Pricing
This is the most prevalent model. You pay a monthly fee for each user who accesses the CRM. The price per user can range from a few dollars to over a hundred, depending on the features included and the vendor. This model is often scalable, allowing you to add or remove users as your business grows or shrinks.
Pros: Predictable costs, easy to scale, often includes support and updates.
Cons: Costs can add up quickly as your team grows, might not be cost-effective if only a few users need full access.
2. Tiered Pricing
Tiered pricing offers different packages or tiers with varying features and user limits. Each tier has a different price point. This model allows you to choose the plan that best fits your needs and budget.
Pros: Flexibility, can choose a plan that matches your specific requirements, often offers a range of features.
Cons: May need to upgrade to a more expensive tier as your needs evolve, might not always offer all the features you need in the most affordable tier.
3. Usage-Based Pricing
Some CRM systems charge based on usage. This could be the number of contacts stored, the number of emails sent, or the amount of data used. This model is often suitable for businesses with fluctuating needs.
Pros: Pay only for what you use, can be cost-effective if usage is low or variable.
Cons: Costs can be unpredictable, might be difficult to budget accurately, can become expensive if usage increases significantly.
4. One-Time Purchase or Perpetual License
Less common nowadays, this model involves a one-time fee for the software license. You own the software and can use it indefinitely. However, you might need to pay extra for updates and support.
Pros: No recurring costs, potentially lower long-term costs.
Cons: High upfront cost, might not include updates or support, can become outdated quickly.
5. Freemium Model
Some CRM providers offer a free version with limited features. This can be a great option for very small businesses or startups that are just starting out. You can then upgrade to a paid plan as your needs grow.
Pros: Free to start, allows you to test the software before committing to a paid plan.
Cons: Limited features, might not be suitable for all business needs, might require upgrading to a paid plan as your business grows.
Factors Influencing Small Business CRM Cost
Several factors influence the final cost of a CRM system. Understanding these factors will help you make an informed decision and choose a CRM that fits your budget.
1. Features and Functionality
The more features a CRM offers, the more it will typically cost. Basic CRM systems often include contact management, sales pipeline tracking, and basic reporting. More advanced systems might offer marketing automation, lead scoring, project management, and integrations with other business tools. Consider which features are essential for your business and which ones are “nice to have.” Prioritize the features that will provide the most value.
2. Number of Users
As mentioned earlier, the number of users is a significant factor in per-user pricing models. The more users you have, the higher your monthly or annual cost will be. Carefully assess how many users need access to the CRM and consider whether you need to provide full access to every employee. Perhaps some employees only need limited access to specific features.
3. Customization and Integrations
If you need to customize the CRM to fit your specific business processes or integrate it with other software (e.g., accounting software, email marketing platforms), this can add to the cost. Some CRM providers offer customization options at an additional fee, while others might require you to hire a third-party developer.
4. Data Storage and Usage
Some CRM systems have limitations on data storage or usage. If you have a large database of contacts or send a high volume of emails, you might need to upgrade to a higher-tier plan with more storage or usage allowances. Ensure you understand the limitations and associated costs.
5. Support and Training
The level of support and training provided by the CRM vendor can also impact the cost. Some vendors offer premium support plans with dedicated account managers and priority support. Others provide self-service resources like online documentation and tutorials. Consider the level of support you need and factor it into your budget.
6. Implementation Costs
Implementing a CRM system can involve costs beyond the software itself. This might include data migration, training, and consulting services. Factor in these costs when calculating your total investment.
7. Add-ons and Third-Party Apps
Many CRM systems integrate with third-party apps and add-ons to extend their functionality. While these add-ons can be valuable, they can also add to your monthly expenses. Evaluate the cost of any add-ons you plan to use.
Calculating the Return on Investment (ROI) of a CRM
Investing in a CRM is a business decision, and like any investment, you need to understand the potential return. Calculating the ROI can help you justify the cost and ensure you’re getting the most value from your investment.
Here’s how to calculate the ROI of a CRM:
- Identify the Benefits: Determine the key benefits you expect to gain from the CRM. This could include increased sales, improved customer retention, reduced operational costs, and increased efficiency.
- Quantify the Benefits: Assign a monetary value to each benefit. For example, if you expect to increase sales by 10%, calculate the dollar amount of that increase. If you expect to reduce operational costs, estimate the savings.
- Calculate the Costs: Determine the total cost of the CRM, including the software cost, implementation costs, and ongoing expenses.
- Calculate the ROI: Use the following formula:
ROI = ((Benefits - Costs) / Costs) * 100
For example, if your CRM investment costs $5,000 per year and generates $10,000 in benefits, your ROI would be:
ROI = (($10,000 - $5,000) / $5,000) * 100 = 100%
A positive ROI indicates that the CRM is generating a return on your investment. The higher the ROI, the better.
Tips for Reducing Small Business CRM Cost
While a CRM is a worthwhile investment, there are ways to reduce the overall cost. Here are some tips:
- Choose the Right Plan: Carefully evaluate your needs and choose a plan that offers the features you require without overspending. Don’t pay for features you won’t use.
- Negotiate Pricing: Don’t be afraid to negotiate with CRM vendors. Ask for discounts or special offers, especially if you’re signing up for a long-term contract.
- Start Small and Scale: Begin with a basic plan and add features or users as your business grows. This allows you to control costs and avoid overspending.
- Utilize Free Trials: Take advantage of free trials to test different CRM systems before committing to a paid plan. This allows you to evaluate the features and usability.
- Consider Open-Source CRM: Open-source CRM systems are often free to use, but you might need to pay for hosting, customization, and support.
- Train Your Team: Proper training can help your team use the CRM effectively and maximize its value. This can lead to a better ROI.
- Look for Bundled Deals: Some CRM providers offer bundled deals that include other services, such as marketing automation or email marketing.
- Review Your Usage Regularly: Periodically review your CRM usage to ensure you’re making the most of your investment. Identify areas where you can improve efficiency and reduce costs.
Top CRM Systems for Small Businesses
Here are some popular CRM systems that are often well-suited for small businesses, along with a brief overview of their pricing and features:
(Note: Pricing and features are subject to change. Always check the vendor’s website for the most up-to-date information.)
1. HubSpot CRM
Overview: HubSpot CRM is a popular choice for small businesses, especially those focused on marketing. It offers a free version with basic features and a range of paid plans with more advanced functionality.
Pricing: Free plan available. Paid plans start at a reasonable price point and scale up based on the features needed.
Key Features: Contact management, deal tracking, sales pipeline, email marketing, and marketing automation.
2. Zoho CRM
Overview: Zoho CRM is a versatile CRM system that caters to a wide range of business needs. It offers a free plan for a limited number of users and several paid plans with varying features.
Pricing: Free plan available. Paid plans are competitively priced and offer a range of features for different business sizes.
Key Features: Contact management, sales force automation, marketing automation, analytics, and integrations.
3. Pipedrive
Overview: Pipedrive is a sales-focused CRM designed to help sales teams manage their pipelines and close deals. It is known for its user-friendly interface and focus on sales activities.
Pricing: Per-user, per-month pricing. Offers various plans with different features.
Key Features: Sales pipeline management, deal tracking, email integration, and reporting.
4. Freshsales
Overview: Freshsales, by Freshworks, is a CRM that emphasizes ease of use and a focus on sales. It provides features for sales automation, lead management, and communication.
Pricing: Offers a free plan and several paid plans with different feature sets.
Key Features: Contact management, sales automation, lead scoring, and integrated phone and email.
5. Agile CRM
Overview: Agile CRM is a comprehensive CRM that offers sales, marketing, and customer service features in a single platform. It is suitable for small and medium-sized businesses.
Pricing: Offers a free plan and various paid plans with different features and user limits.
Key Features: Contact management, sales automation, marketing automation, and helpdesk features.
Making the Right Choice for Your Small Business
Choosing the right CRM for your small business is a significant decision. It requires careful consideration of your needs, budget, and business goals. By understanding the different pricing models, the factors that influence cost, and how to calculate ROI, you can make an informed decision and choose a CRM that will help your business thrive.
Here’s a quick recap of the key steps:
- Assess Your Needs: Identify your business requirements and the features you need from a CRM.
- Set a Budget: Determine how much you can afford to spend on a CRM.
- Research Vendors: Explore different CRM vendors and compare their pricing and features.
- Evaluate Pricing Models: Understand the different pricing models and choose the one that best fits your needs.
- Consider Scalability: Choose a CRM that can scale with your business.
- Read Reviews: Read reviews from other small businesses to get insights into the pros and cons of each CRM.
- Take Advantage of Free Trials: Test out different CRM systems before making a final decision.
- Implement and Train: Implement the CRM and train your team on how to use it effectively.
By following these steps, you can find a CRM that meets your needs, fits your budget, and helps you build stronger customer relationships. Remember, the right CRM is an investment that can drive significant growth and success for your small business.
Don’t be afraid to experiment and find the perfect fit for your unique business needs. The right CRM can empower your team, streamline your processes, and ultimately, help you achieve your business goals. Good luck!