Small Business CRM Cost: A Comprehensive Guide to Budgeting and ROI

Small Business CRM Cost: A Comprehensive Guide to Budgeting and ROI
Running a small business is a rollercoaster. One minute you’re celebrating a new client, the next you’re wrestling with spreadsheets and trying to remember where you put that important email. In the midst of all this chaos, you might have heard whispers about Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems. They promise to streamline your operations, boost sales, and generally make your life easier. But, the big question looms: how much does a small business CRM cost?
This guide will dive deep into the world of CRM costs, breaking down the various factors that influence pricing, helping you understand the return on investment (ROI), and ultimately, helping you choose the best CRM for your budget and business needs. We’ll explore the different pricing models, compare popular CRM solutions, and offer tips for keeping your CRM costs under control. So, buckle up, and let’s get started!
Understanding the Importance of CRM for Small Businesses
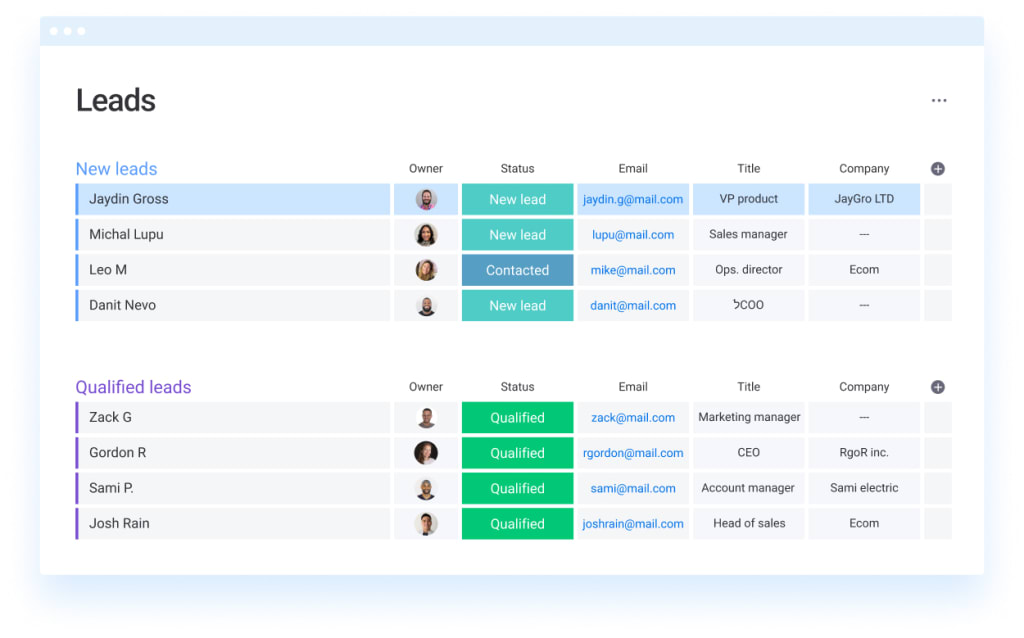
Before we get into the nitty-gritty of costs, let’s quickly recap why a CRM is so crucial for small businesses. Think of it as the central nervous system of your customer interactions. It’s where you store all your customer data – names, contact information, purchase history, communication logs, and more. This information isn’t just sitting there; it’s actively used to:
- Improve Customer Relationships: By having a 360-degree view of each customer, you can personalize interactions, anticipate their needs, and build stronger, more loyal relationships.
- Boost Sales: CRM systems help you track leads, manage the sales pipeline, and identify opportunities for upselling and cross-selling.
- Enhance Efficiency: Automate repetitive tasks, such as sending follow-up emails or scheduling appointments, freeing up your time to focus on more strategic initiatives.
- Make Data-Driven Decisions: CRM systems provide valuable insights into customer behavior, sales performance, and marketing effectiveness, enabling you to make informed decisions.
- Increase Collaboration: CRM systems centralize customer data, making it accessible to all team members, ensuring everyone is on the same page.
In short, a CRM is an investment in your business’s future. It’s about working smarter, not harder, and ultimately, driving growth.
Different CRM Pricing Models: What to Expect
The CRM landscape is vast, and so are the pricing models. Understanding these models is the first step in budgeting for your CRM.
1. Subscription-Based Pricing (SaaS – Software as a Service)
This is the most common pricing model, where you pay a recurring fee (monthly or annually) to access the CRM software. This model is popular because it offers:
- Predictable Costs: You know exactly how much you’ll be paying each month or year.
- Scalability: You can easily adjust your plan as your business grows, adding or removing users as needed.
- Reduced IT Burden: The CRM provider handles all the technical aspects, such as hosting, maintenance, and updates.
Subscription-based pricing is typically tiered, with different plans offering varying features and user limits. The cost per user per month (or year) is a key factor to consider.
2. Per-User Pricing
Within the subscription model, per-user pricing is the most prevalent. You pay a set fee for each user who accesses the CRM. This model is straightforward and easy to understand. However, it’s crucial to accurately estimate the number of users you’ll need, as adding more users can quickly increase your costs. Some vendors offer discounts for a larger number of users.
3. Tiered Pricing
Many CRM providers use a tiered pricing structure, where the price per user decreases as you move to a higher tier with more users. For example, you might pay $50 per user per month for the first 5 users, $40 per user per month for 6-10 users, and so on. This model rewards businesses that scale their CRM usage.
4. Feature-Based Pricing
Some CRM providers offer different plans based on the features included. A basic plan might include core CRM functionality, while premium plans offer advanced features such as marketing automation, advanced analytics, or integrations with third-party applications. This model allows you to pay only for the features you need, but it can become complex if you require a mix of features.
5. Usage-Based Pricing
This model is less common but can be found in some CRM solutions. You pay based on your usage of the system. This might be based on the number of contacts, the amount of data storage, or the number of emails sent. This model can be cost-effective for businesses with fluctuating needs, but it can also be unpredictable if your usage spikes unexpectedly.
6. On-Premise CRM (Less Common for Small Businesses)
In this model, you purchase a license for the CRM software and install it on your own servers. This gives you complete control over your data and infrastructure, but it also comes with significant upfront costs for the software license, hardware, and IT support. On-premise CRM is generally not recommended for small businesses due to the high costs and technical complexities.
Breaking Down CRM Costs: What You’ll Actually Pay
Now, let’s get into the specific costs you can expect to encounter when implementing a CRM for your small business. Remember that these costs can vary significantly depending on the CRM provider, the features you choose, and your business needs.
1. Subscription Fees
As discussed, the subscription fees are the core cost of your CRM. These fees are usually billed monthly or annually. The price per user per month is the most critical factor to consider. Research the pricing tiers thoroughly to understand which plan suits your business requirements best. Consider your current and projected number of users and the features you need. The more users and the more features, the higher the cost will be.
2. Implementation Costs
Setting up a CRM is not always a plug-and-play process. Implementation costs can include:
- Data Migration: Transferring your existing customer data from spreadsheets or other systems into the CRM. This can be time-consuming and may require the assistance of a consultant or the use of data migration tools. Costs depend on the volume and complexity of your data.
- Customization: Tailoring the CRM to your specific business processes. This might involve creating custom fields, workflows, or reports. Some CRM providers offer customization services, while others require you to hire a third-party consultant.
- Training: Training your team to use the CRM effectively. This can involve online tutorials, webinars, or in-person training sessions. The cost of training varies depending on the training method and the number of users.
- Integration: Connecting your CRM with other software applications, such as your email marketing platform, accounting software, or e-commerce platform. Integrations can be complex and may require the expertise of a developer.
3. Ongoing Costs
The costs don’t end after implementation. You’ll also need to budget for ongoing expenses, including:
- Support: Most CRM providers offer customer support, which can be included in your subscription fee or charged separately.
- Maintenance: CRM systems require ongoing maintenance, such as software updates, security patches, and database optimization. The provider typically handles this.
- Additional Users: If your team grows, you’ll need to add more user licenses, which will increase your subscription fees.
- Add-ons and Integrations: As your business evolves, you might need to add new features or integrate your CRM with additional applications, which can incur extra costs.
4. Hidden Costs
Be aware of potential hidden costs that may not be immediately apparent:
- Data Storage: Some CRM providers charge extra for exceeding a certain amount of data storage.
- API Usage: If you heavily use the CRM’s API (Application Programming Interface) for integrations, you might be charged based on API calls.
- Overages: Some plans have limits on the number of emails, contacts, or other metrics. Exceeding these limits can incur additional charges.
- Consulting Fees: If you need help with customization, training, or integration, you’ll likely pay consulting fees.
Comparing Popular CRM Solutions for Small Businesses
Now, let’s look at some popular CRM solutions for small businesses, providing a general overview of their pricing and key features. Note that prices are subject to change, so always check the provider’s website for the most up-to-date information.
1. HubSpot CRM
Pricing: HubSpot offers a free CRM plan with basic features, which is an excellent starting point for small businesses. Paid plans offer more advanced features, starting at a reasonable price per month. They have different hubs (Sales, Marketing, Service) and the price varies depending on the hub and features selected.
Key Features: Contact management, deal tracking, email marketing, sales automation, reporting, and integrations. HubSpot CRM is known for its user-friendliness and comprehensive features, especially for marketing and sales.
2. Zoho CRM
Pricing: Zoho CRM offers a free plan for up to three users. Paid plans are affordable, with tiered pricing based on features and user count.
Key Features: Contact management, sales automation, lead management, workflow automation, custom reporting, and extensive integrations. Zoho CRM is a robust platform with a wide range of features and integrations, making it a good choice for businesses of all sizes.
3. Pipedrive
Pricing: Pipedrive is known for its focus on sales. It offers a simple, user-friendly interface and affordable pricing, with plans tailored to different sales team sizes.
Key Features: Visual sales pipeline, deal tracking, activity management, email integration, sales automation, and reporting. Pipedrive is a great choice for sales-driven businesses that want a straightforward CRM.
4. Freshsales (Freshworks)
Pricing: Freshsales offers a free plan and competitive pricing for its paid plans. Pricing is per user, per month, with different tiers based on features.
Key Features: Contact management, lead scoring, sales automation, built-in phone and email, reporting. Freshsales is known for its ease of use and strong sales-focused features.
5. Agile CRM
Pricing: Agile CRM offers a free plan for up to 10 users, and affordable paid plans with different features and user limits.
Key Features: Contact management, sales automation, marketing automation, helpdesk, and reporting. Agile CRM is a comprehensive CRM with a strong focus on sales, marketing, and service.
Important Note: When comparing CRM solutions, always consider your specific business needs, the features you require, and your budget. Read reviews and compare pricing plans carefully before making a decision. Try out free trials whenever possible to test the platform’s functionality and user-friendliness.
Calculating the ROI of a CRM for Your Small Business
Investing in a CRM is a significant decision, and it’s essential to understand the potential return on investment (ROI). A well-implemented CRM can significantly improve your bottom line, but it’s important to measure the benefits to justify the investment.
1. Identify Key Metrics to Track
Before implementing a CRM, define the key performance indicators (KPIs) that are most important to your business. These metrics will help you measure the impact of the CRM. Some examples include:
- Sales Revenue: Track the increase in sales revenue after implementing the CRM.
- Sales Cycle Length: Measure the reduction in the time it takes to close a deal.
- Conversion Rates: Monitor the increase in conversion rates at each stage of the sales pipeline.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): Track the decrease in the cost of acquiring new customers.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV): Measure the increase in the long-term value of your customers.
- Customer Retention Rate: Monitor the improvement in customer retention.
- Customer Satisfaction: Track the improvement in customer satisfaction scores.
- Lead Generation: Measure the increase in leads generated.
2. Estimate the Benefits
Based on your chosen KPIs, estimate the potential benefits of implementing a CRM. These benefits can include:
- Increased Sales: A CRM can help you close more deals and increase sales revenue.
- Reduced Costs: Automation can reduce the time your team spends on manual tasks, which decreases operational costs.
- Improved Efficiency: A CRM streamlines workflows and improves team productivity.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: A CRM helps you provide better customer service, leading to increased customer loyalty.
Quantify these benefits as much as possible. For example, estimate the percentage increase in sales revenue or the reduction in customer acquisition cost.
3. Calculate the Costs
As discussed earlier, calculate all the costs associated with implementing and maintaining the CRM, including subscription fees, implementation costs, and ongoing costs.
4. Calculate the ROI
Use the following formula to calculate the ROI:
ROI = ((Benefits – Costs) / Costs) * 100
For example, if your CRM implementation generates $50,000 in additional revenue and the total cost of the CRM is $10,000, the ROI would be: ((50,000 – 10,000) / 10,000) * 100 = 400%. This means that for every dollar you spend on the CRM, you’re getting a return of $4.
5. Monitor and Adjust
Continuously monitor your KPIs and track the performance of your CRM. Regularly review your ROI and make adjustments as needed. If the ROI is not meeting your expectations, evaluate your CRM usage, identify areas for improvement, and consider making changes to your CRM strategy.
Tips for Keeping CRM Costs Under Control
While a CRM is a valuable investment, it’s essential to manage your costs effectively. Here are some tips to help you keep your CRM expenses under control:
- Start Small: Begin with a basic plan and add features and users as your business grows. Avoid overspending on features you don’t need.
- Choose the Right Plan: Carefully evaluate the different pricing plans and select the one that best fits your needs and budget.
- Negotiate Pricing: Don’t be afraid to negotiate with CRM providers, especially if you’re a larger business or committing to a long-term contract.
- Take Advantage of Free Trials: Test different CRM solutions before committing to a paid plan. This will help you determine which CRM is the best fit for your business and budget.
- Optimize Your CRM Usage: Make the most of the features you’re paying for. Train your team to use the CRM effectively and avoid wasting resources.
- Regularly Review Your Costs: Periodically review your CRM costs and usage to identify areas where you can save money. Consider downgrading your plan or removing unused features.
- Consider Open-Source Alternatives: If you have the technical expertise, explore open-source CRM options, which can be more cost-effective, although they often require more technical knowledge.
- Leverage Free Integrations: Many CRM providers offer free integrations with other applications. Take advantage of these integrations to streamline your workflows and avoid paying for expensive add-ons.
- Focus on Data Quality: Poor data quality can lead to wasted resources and inaccurate reporting. Invest time in data cleansing and maintenance to ensure your CRM data is accurate and up-to-date.
- Prioritize Training: Invest in training your team to use the CRM effectively. This will help you maximize the value of your investment and avoid wasting resources.
Making the Right Choice for Your Small Business
Choosing the right CRM for your small business can feel overwhelming, but by understanding the costs involved, evaluating your needs, and carefully comparing different solutions, you can make an informed decision. Remember that the best CRM is the one that meets your specific business requirements and provides a good return on investment. Do your research, compare your options, and don’t be afraid to start small and scale as your business grows. The right CRM can be a game-changer for your small business, helping you build stronger customer relationships, boost sales, and achieve sustainable growth.
Ultimately, the cost of a small business CRM is an investment, not an expense. It’s an investment in your future, your team, and your customers. By carefully considering your needs, budgeting effectively, and choosing the right CRM, you can unlock the full potential of your customer relationships and drive your business to new heights.