Small Business CRM Cost: A Comprehensive Guide to Budgeting and Maximizing ROI
Small Business CRM Cost: A Comprehensive Guide to Budgeting and Maximizing ROI
Running a small business is a rollercoaster. One minute you’re celebrating a new client, the next you’re wrestling with spreadsheets and struggling to keep track of everything. That’s where a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system comes in. It’s like having a super-organized assistant who remembers every detail about your customers, helping you nurture leads, close deals, and build lasting relationships. But before you dive in, a crucial question looms: How much does a small business CRM cost?
This isn’t a simple question with a one-size-fits-all answer. CRM costs vary widely depending on the features you need, the size of your business, and the provider you choose. This comprehensive guide will break down all aspects of small business CRM costs, helping you understand the different pricing models, hidden fees, and factors that influence the overall expense. We’ll also explore how to maximize your return on investment (ROI) and choose the right CRM for your specific needs, so you can make an informed decision and take your business to the next level.
Understanding the Basics of CRM and Its Value
Before we get into the nitty-gritty of costs, let’s quickly recap what a CRM system actually *does* and why it’s so valuable for small businesses. Essentially, a CRM is a centralized hub for all your customer-related data. It helps you:
- Manage contacts: Store and organize contact information, including names, phone numbers, email addresses, and more.
- Track interactions: Log every interaction you have with a customer, from emails and phone calls to meetings and social media interactions.
- Automate tasks: Automate repetitive tasks like sending follow-up emails, scheduling appointments, and generating reports.
- Improve sales processes: Streamline your sales pipeline, track leads, and close deals more efficiently.
- Enhance customer service: Provide better customer service by having all the information you need at your fingertips.
- Gain insights: Analyze your customer data to identify trends, understand customer behavior, and make data-driven decisions.
The benefits of a CRM are numerous. It can help you increase sales, improve customer satisfaction, reduce costs, and boost overall productivity. For a small business, these benefits can be transformative, allowing you to compete more effectively and achieve sustainable growth. But how much does all this goodness cost?
CRM Pricing Models: A Breakdown
CRM providers offer various pricing models, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these models is crucial for budgeting and comparing different CRM solutions. Here’s a breakdown of the most common pricing models:
1. Subscription-Based Pricing (SaaS – Software as a Service)
This is the most popular pricing model, especially for small businesses. You pay a recurring fee (usually monthly or annually) to access the CRM software. The fee is typically based on the number of users, the features included, and the level of support provided. SaaS CRM solutions are often the most affordable option for small businesses, as they eliminate the need for expensive hardware and IT staff. The costs are often predictable, making budgeting easier.
Pros:
- Predictable costs
- Easy to implement
- Regular updates and maintenance included
- Scalable – you can easily add or remove users as your business grows
Cons:
- Recurring costs
- Reliance on the provider for security and data storage
- Limited customization options compared to on-premise solutions
2. Per-User Pricing
This is a common variation of subscription-based pricing. You pay a fixed fee for each user who has access to the CRM system. The price per user can vary depending on the features included in the plan. This model is ideal for businesses with a predictable number of users. This option is usually flexible and can be scaled as the company grows. It’s important to consider how many users you truly need. Do you need every employee to have full access, or can you limit access to specific departments or roles?
Pros:
- Simple to understand
- Easy to budget for
- Scalable
Cons:
- Costs can add up quickly as your team grows
- May not be the most cost-effective option if you have a large team
3. Tiered Pricing
Many CRM providers offer tiered pricing plans, with different features and price points for each tier. The basic tier typically includes essential CRM features, while higher tiers offer more advanced features such as marketing automation, advanced reporting, and integrations with other business applications. This model allows you to choose the plan that best fits your needs and budget. Often, the tiers are based on the number of contacts, storage space, or advanced features you need.
Pros:
- Flexibility to choose the right features for your needs
- Scalability – you can upgrade to a higher tier as your business grows
- Often offers a cost-effective solution for businesses of all sizes
Cons:
- Can be complex to compare different plans
- May need to upgrade to a higher tier as your business needs evolve
4. On-Premise Licensing (Less Common for Small Businesses)
With on-premise CRM, you purchase a license to use the software and install it on your own servers. This model typically involves a significant upfront investment for the software license, as well as ongoing costs for hardware, IT staff, and maintenance. This option is less common for small businesses due to the high initial cost and the ongoing technical expertise required. However, on-premise solutions offer greater control over your data and security.
Pros:
- Greater control over data and security
- Customization options
- Potentially lower long-term costs for large businesses
Cons:
- High upfront costs
- Requires IT staff and expertise
- Ongoing maintenance and upgrade costs
5. Open-Source CRM (Free or Low-Cost)
Open-source CRM solutions are available for free or at a very low cost. You can download and install the software yourself, or you can pay for a hosted solution. Open-source CRM solutions often offer a high degree of customization and flexibility, but they may require technical expertise to set up and maintain. They can be a good option for businesses with limited budgets and technical capabilities. While the software itself might be free, you’ll likely need to invest in hosting, support, and potential customization.
Pros:
- Low or no upfront costs
- Highly customizable
- Large community support
Cons:
- Requires technical expertise
- May require you to pay for hosting, support, and customization
- Can be challenging to integrate with other business applications
Factors Influencing CRM Costs
Several factors can influence the overall cost of a CRM system. Understanding these factors will help you make informed decisions and choose a CRM solution that fits your budget. Here are the key factors to consider:
1. Number of Users
As mentioned earlier, many CRM providers charge based on the number of users. The more users you have, the higher the cost. Carefully assess how many users actually need access to the CRM. Do all of your employees need a license, or can you limit access to specific departments or roles? Consider the roles and responsibilities within your company to determine the optimal number of users. For example, your sales team will likely need full access, while your accounting department might only need limited access to certain customer data.
2. Features and Functionality
The more features you need, the higher the cost. Basic CRM systems typically include contact management, sales pipeline management, and basic reporting. More advanced systems offer features like marketing automation, lead scoring, advanced analytics, and integration with other business applications. Determine which features are essential for your business and which ones are nice-to-haves. Prioritize the features that will have the biggest impact on your sales, customer service, and overall productivity. Think about your long-term goals and whether the CRM can scale with your business as your needs evolve.
3. CRM Provider
Different CRM providers have different pricing models and pricing levels. Research and compare different providers to find the one that offers the best value for your money. Consider factors like the provider’s reputation, customer support, ease of use, and integration capabilities. Some popular CRM providers for small businesses include:
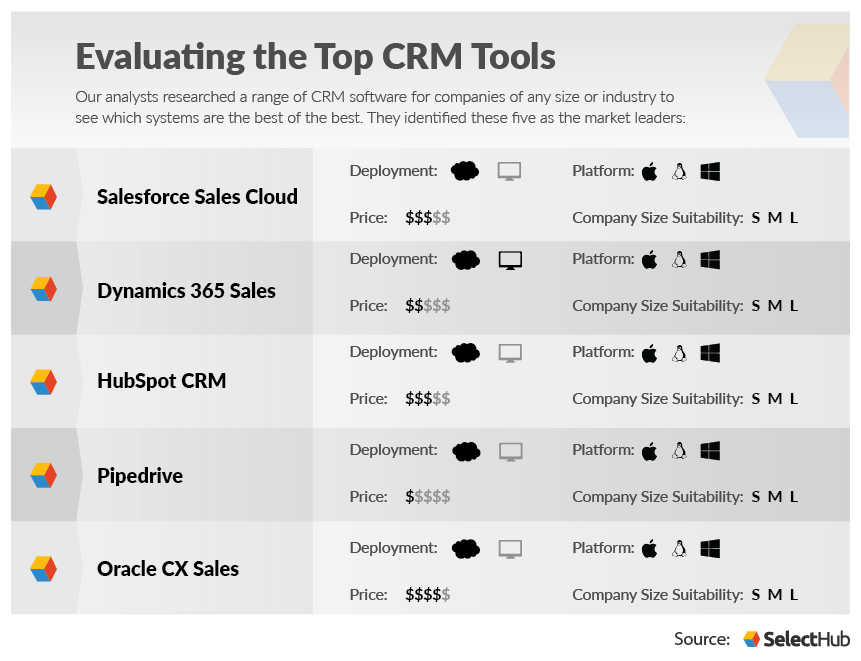
- Zoho CRM: A popular and affordable option with a wide range of features.
- HubSpot CRM: A free CRM with powerful features and excellent integration capabilities.
- Pipedrive: A sales-focused CRM designed for small businesses.
- Salesforce Essentials: A scaled-down version of Salesforce designed for small businesses.
- Freshsales: A sales CRM with built-in phone, email, and chat features.
Each provider has its strengths and weaknesses, so it’s crucial to find the one that aligns with your business needs and budget.
4. Implementation and Training
Implementing a CRM system can involve costs for data migration, customization, and training. Some CRM providers offer implementation services, while others rely on partners or require you to handle the implementation yourself. Training is essential to ensure that your team can effectively use the CRM system. Consider the time and resources required for implementation and training when budgeting for a CRM solution. Factor in the time it takes for your team to learn the system, as well as any potential disruption to your workflow during the implementation process.
5. Customization and Integrations
If you need to customize the CRM system to meet your specific business needs, you may incur additional costs. Customization can involve developing custom fields, workflows, and reports. Integrating the CRM with other business applications, such as your accounting software or email marketing platform, can also involve additional costs. The more complex your integrations, the higher the cost. Consider the potential need for customization and integrations when selecting a CRM provider and budget accordingly.
6. Support and Maintenance
Most CRM providers offer support and maintenance as part of their subscription plans. However, the level of support and the response times can vary. Some providers offer premium support options for an additional fee. Ensure that the CRM provider offers the level of support you need. Consider the costs associated with ongoing maintenance, such as software updates and bug fixes.
Hidden CRM Costs to Watch Out For
Beyond the obvious costs, there are often hidden costs associated with CRM systems that you should be aware of. These hidden costs can significantly impact your overall budget. Here are some common hidden costs to consider:
1. Data Migration Costs
Migrating your existing data from spreadsheets or other systems to the CRM can be time-consuming and may require professional assistance. Some CRM providers offer data migration services, but they often come with an additional cost. Even if you handle the data migration yourself, you’ll need to factor in the time and resources required. Make sure to assess the quality and format of your existing data. Inconsistent or incomplete data can make the migration process more challenging and time-consuming.
2. Customization Costs
If you need to customize the CRM system to meet your specific business needs, you may incur additional costs. Customization can involve developing custom fields, workflows, and reports. Some CRM providers offer customization services, while others require you to work with a third-party developer. The cost of customization can vary depending on the complexity of the project. Define your customization requirements clearly before selecting a CRM provider. Identify the features that are essential and those that are nice-to-haves.
3. Integration Costs
Integrating the CRM with other business applications, such as your accounting software or email marketing platform, can also involve additional costs. Some CRM providers offer integrations with popular applications, while others require you to use third-party integration tools or custom development. The cost of integrations can vary depending on the complexity of the integration. Research the integration capabilities of different CRM providers. Consider the costs associated with maintaining and updating your integrations. Choose a CRM provider that offers seamless integrations with the other business applications you use.
4. Training Costs
Training your team to use the CRM system effectively is essential to ensure that you get the most out of your investment. Some CRM providers offer training resources, such as online tutorials and webinars. However, you may need to invest in additional training, such as in-person training or custom training programs. Training costs can vary depending on the type of training and the number of users. Factor in the time your team will spend learning the system. Provide ongoing training and support to ensure that your team stays up-to-date on the latest features and best practices.
5. Data Storage Costs
Some CRM providers offer limited data storage as part of their subscription plans. If you need more storage space, you may have to pay extra. Data storage costs can vary depending on the amount of storage you need. Consider the amount of data you’ll be storing in the CRM, including contact information, documents, and attachments. Regularly review your data storage needs to ensure that you’re not overpaying for storage space. Delete any unnecessary data to free up storage space.
6. Add-on Costs
CRM providers often offer add-ons that provide additional features and functionality. Add-ons can include features like advanced analytics, marketing automation tools, and sales intelligence tools. Add-on costs can vary depending on the add-on. Carefully evaluate the value of each add-on before purchasing it. Consider whether the add-on will improve your sales, customer service, or overall productivity. Prioritize the add-ons that will have the biggest impact on your business.
How to Choose the Right CRM for Your Small Business
Choosing the right CRM system can be a daunting task. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you find the perfect CRM for your small business:
1. Define Your Needs and Goals
Before you start shopping for a CRM, take the time to define your needs and goals. What are your business objectives? What are your biggest challenges? What are you hoping to achieve with a CRM? Identify the specific features and functionality you need. Determine your budget and the number of users you’ll need. Think about your long-term goals and whether the CRM can scale with your business as your needs evolve. Consider your sales, marketing, and customer service processes. Identify the areas where a CRM can provide the most value.
2. Research and Compare Different CRM Providers
Once you know your needs and goals, start researching different CRM providers. Compare their features, pricing models, and reviews. Read online reviews and testimonials to get insights from other small businesses. Look for providers that offer a free trial or a free plan. Create a shortlist of potential CRM providers. Visit the providers’ websites and gather information about their products and services. Consider factors like customer support, ease of use, and integration capabilities.
3. Evaluate Features and Functionality
Evaluate the features and functionality of each CRM provider. Does the CRM offer the features you need? Does it integrate with the other business applications you use? Consider the ease of use and the user interface. Look for a CRM that is intuitive and easy to navigate. Assess the reporting and analytics capabilities. Make sure the CRM provides the insights you need to make data-driven decisions. Consider the security features and data privacy policies.
4. Consider Pricing and Budget
Compare the pricing models of different CRM providers. Choose the pricing model that best fits your budget and business needs. Consider the total cost of ownership, including the subscription fees, implementation costs, and ongoing maintenance costs. Look for a CRM that offers a free trial or a free plan. Factor in the potential for future growth and the need for additional features. Ensure the pricing is transparent and easy to understand. Avoid hidden fees and unexpected costs.
5. Try Before You Buy
Take advantage of free trials or free plans to test out different CRM systems. This will give you a hands-on experience and allow you to evaluate the user interface, features, and functionality. Test the CRM with your own data and workflows. Get feedback from your team on the usability and effectiveness of the CRM. Ensure that the CRM meets your specific needs and goals. Do not hesitate to reach out to the provider’s customer support team to ask any questions you have.
6. Plan for Implementation and Training
Develop a plan for implementing the CRM system and training your team. Consider the time and resources required for implementation and training. Determine who will be responsible for the implementation and training. Create a training schedule and provide ongoing support. Ensure that your team is comfortable using the CRM system. Provide regular training sessions and refreshers to keep your team up-to-date on the latest features and best practices. Plan for data migration and customization. Back up your data before migrating it to the CRM system.
Maximizing ROI on Your CRM Investment
Investing in a CRM system is a significant decision. To ensure you get the most out of your investment, it’s crucial to focus on maximizing your ROI. Here are some tips to help you achieve that:
1. Define Clear Goals and Metrics
Before you start using the CRM, define clear goals and metrics. What do you want to achieve with the CRM? How will you measure your success? Track key metrics, such as sales leads, conversion rates, customer satisfaction, and customer retention. Regularly review your metrics and track your progress towards your goals. Use the CRM’s reporting and analytics features to gain insights into your performance.
2. Implement Best Practices
Follow best practices for using the CRM system. Train your team on how to use the CRM effectively. Create standardized processes for data entry and lead management. Ensure that your team is using the CRM consistently. Regularly review your processes and make improvements as needed. Leverage the CRM’s automation features to streamline your workflows. Set up automated email campaigns, task reminders, and other automated processes to save time and improve efficiency.
3. Integrate with Other Business Applications
Integrate the CRM with other business applications, such as your accounting software, email marketing platform, and social media channels. This will streamline your workflows and improve data accuracy. Ensure that your data is consistent across all your business applications. Use the CRM’s integration capabilities to automate data transfer between different applications. Choose a CRM that offers seamless integrations with the other business applications you use.
4. Clean and Maintain Your Data
Keep your CRM data clean and up-to-date. Regularly review your data and remove any duplicates or outdated information. Implement a data cleansing process to ensure that your data is accurate and consistent. Encourage your team to maintain the data regularly. Develop a data governance policy to ensure that data is handled responsibly. Clean data is essential for accurate reporting and effective decision-making.
5. Provide Ongoing Training and Support
Provide ongoing training and support to your team. Ensure that your team is comfortable using the CRM system. Offer regular training sessions and refreshers. Encourage your team to ask questions and seek help when needed. Stay up-to-date on the latest features and best practices. Provide ongoing support to ensure that your team can effectively use the CRM system. Make sure that your team understands the importance of using the CRM consistently.
6. Analyze and Optimize Your CRM Usage
Regularly analyze your CRM usage and identify areas for improvement. Review your reports and analytics to track your progress. Identify any bottlenecks or inefficiencies in your processes. Make adjustments to your CRM configuration or workflows as needed. Continuously optimize your CRM usage to ensure that you’re getting the most out of your investment. Use the CRM’s reporting and analytics features to identify areas for improvement.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice for Your Business
Choosing the right CRM system is a critical decision for any small business. By understanding the different pricing models, factors that influence costs, and how to maximize your ROI, you can make an informed decision and choose the CRM that’s right for your needs. Remember to define your goals, research and compare different providers, evaluate features and functionality, consider pricing and budget, try before you buy, and plan for implementation and training. By following these steps, you can unlock the power of CRM and take your business to the next level. Don’t be afraid to invest in a CRM. It’s an investment that will pay off in the long run by helping you build stronger customer relationships, streamline your sales processes, and achieve sustainable growth.
The journey to selecting the right CRM might seem daunting, but by approaching it strategically, you can find a solution that fits your budget and empowers your business. Take the time to explore your options, ask the right questions, and ultimately, choose a CRM that aligns with your vision for the future.