Small Business CRM Cost: A Comprehensive Guide to Affordability and ROI
Introduction: Navigating the CRM Landscape for Small Businesses
Starting a small business is an exciting journey, filled with challenges and rewards. One of the critical aspects of running a successful small business is managing customer relationships. This is where a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system comes into play. A CRM helps you organize customer data, streamline communication, and ultimately, boost sales. However, the idea of implementing a CRM can sometimes feel daunting, especially when considering the cost. This comprehensive guide delves into the world of small business CRM costs, breaking down the factors that influence pricing, exploring various options, and helping you make an informed decision that aligns with your budget and business goals.
What is a CRM and Why Does Your Small Business Need One?
Before we dive into the financial aspects, let’s clarify what a CRM is and why it’s essential for small businesses. A CRM is a technology solution designed to manage all your company’s relationships and interactions with current and potential customers. Think of it as your central hub for all customer-related information. It’s more than just a contact list; it’s a powerful tool that can:
- Centralize Customer Data: Store all customer information, including contact details, purchase history, communication logs, and more, in one accessible location.
- Improve Communication: Facilitate personalized and timely communication through email, phone, and other channels.
- Automate Tasks: Automate repetitive tasks, such as follow-up emails and appointment scheduling, freeing up your time for more strategic activities.
- Enhance Sales and Marketing: Provide insights into customer behavior, enabling you to target your marketing efforts and personalize sales interactions.
- Boost Customer Satisfaction: Improve customer service by providing quick access to customer information and a seamless experience.
For small businesses, these benefits can be transformative. In the early stages, every customer interaction counts. A CRM helps you build stronger relationships, nurture leads, and ultimately, drive revenue growth. Without a CRM, you might be relying on spreadsheets, sticky notes, or a scattered collection of emails – all of which can lead to missed opportunities and frustrated customers.
Key Factors Influencing Small Business CRM Cost
The cost of a CRM for a small business can vary significantly, depending on several factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for making a budget-conscious decision. Here are the primary elements that affect the price tag:
1. Pricing Models
CRM vendors offer various pricing models. The most common are:
- Per-User, Per-Month: This is a popular model where you pay a monthly fee for each user who accesses the CRM. The price per user can range from a few dollars to hundreds, depending on the features and the vendor.
- Tiered Pricing: Some vendors offer tiered pricing based on the number of users or the features included. As your business grows and your needs evolve, you can upgrade to a higher tier.
- Free Plans: Many CRM providers offer free plans with limited features. These can be a good starting point for very small businesses or those with basic CRM needs.
- One-Time Fee: In some cases, you might encounter a one-time fee for the software or implementation. This model is less common nowadays, especially for cloud-based CRMs.
- Usage-Based Pricing: Certain CRM systems charge based on usage, such as the number of emails sent, contacts stored, or features utilized.
2. Features and Functionality
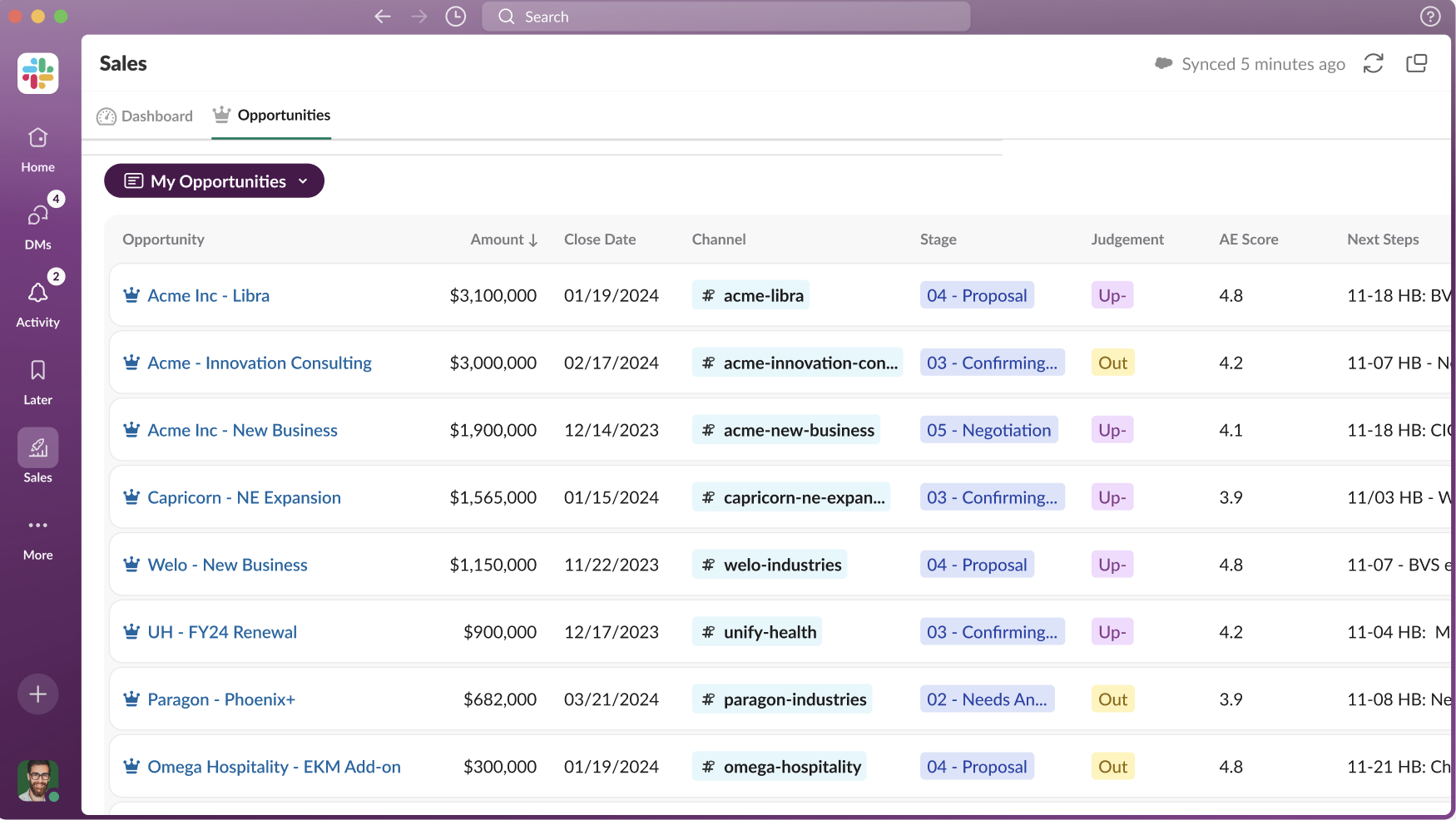
The features you need will significantly impact the cost. Basic CRM systems offer core functionalities like contact management, lead tracking, and basic reporting. More advanced systems include features like:
- Sales Automation: Automating sales processes, such as lead scoring, deal tracking, and quote generation.
- Marketing Automation: Automating email campaigns, social media posting, and lead nurturing.
- Customer Service Tools: Help desk features, live chat, and knowledge base integration.
- Customization and Integration: The ability to customize the CRM to your specific needs and integrate with other business applications.
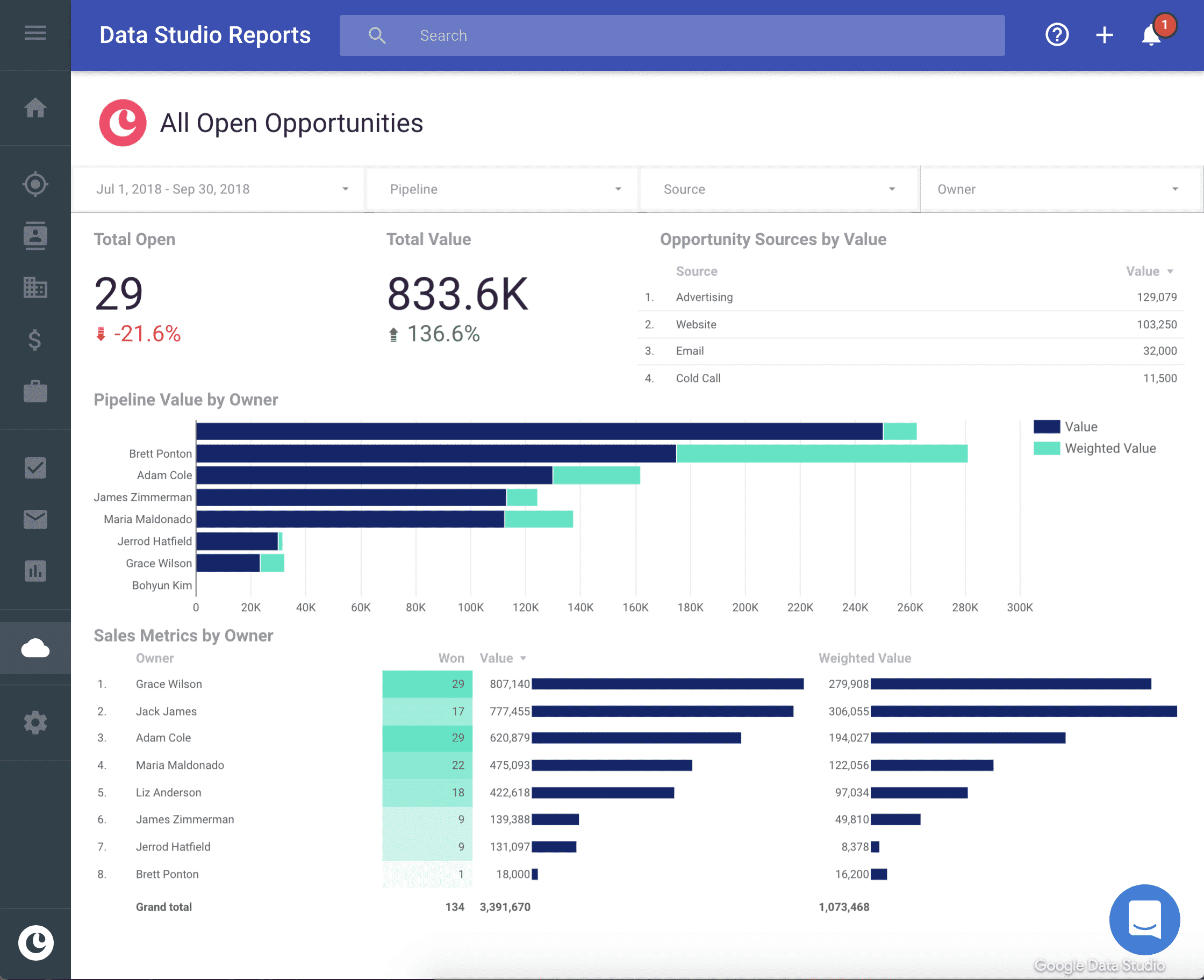
- Reporting and Analytics: Advanced reporting and analytics capabilities to gain insights into your sales and marketing performance.
The more features you need, the higher the price is likely to be.
3. Number of Users
As mentioned earlier, many CRM vendors use a per-user pricing model. The more users who need access to the CRM, the higher your monthly cost will be. Consider how many employees will actively use the CRM and whether you need to provide access to external parties, such as consultants or partners.
4. Implementation and Training
Implementing a CRM is not always a plug-and-play process. Some vendors offer implementation services, which can include data migration, system configuration, and user training. These services often come with an additional cost. Consider the level of support you’ll need during the implementation phase and factor those costs into your budget.
5. Customization and Integration
If you need to customize the CRM to fit your specific business processes or integrate it with other software applications, such as your accounting system or e-commerce platform, you might incur additional costs. Customization often involves professional services, and integrations can require specialized connectors or development work.
6. Vendor Reputation and Support
The reputation of the CRM vendor and the level of support they offer can also influence the cost. Vendors with a strong reputation and excellent customer support might charge a premium for their services. However, investing in a reliable vendor with good support can save you time and headaches in the long run.
Cost Comparison: Popular CRM Options for Small Businesses
Let’s take a look at some popular CRM options for small businesses and compare their pricing models and key features. Please note that pricing can change, so it’s always best to check the vendor’s website for the most up-to-date information.
1. HubSpot CRM
Pricing: HubSpot offers a free CRM plan with basic features. Paid plans start at a reasonable price per month and scale up based on the features you need. They offer a range of products beyond just CRM, including marketing, sales, and customer service hubs, each with its own pricing tiers.
Key Features: Contact management, deal tracking, email marketing, sales automation, reporting, and integration with other HubSpot tools. The free version is surprisingly powerful for small businesses.
Pros: User-friendly interface, excellent free plan, strong integration capabilities, comprehensive marketing and sales tools.
Cons: Advanced features can become expensive as your business grows.
2. Zoho CRM
Pricing: Zoho CRM offers a free plan for up to three users. Paid plans are competitively priced and offer a wide range of features. Zoho also provides a suite of business applications, including email, project management, and more.
Key Features: Contact management, lead management, sales force automation, workflow automation, reporting, and integration with other Zoho apps.
Pros: Affordable, feature-rich, excellent integration with other Zoho apps, customization options.
Cons: The user interface can be slightly less intuitive than some competitors.
3. Pipedrive
Pricing: Pipedrive is a sales-focused CRM with straightforward pricing plans based on the number of users and features. It is designed to be intuitive for salespeople.
Key Features: Sales pipeline management, deal tracking, email integration, activity reminders, and reporting.
Pros: User-friendly, sales-focused, visual pipeline management, easy to get started.
Cons: Less emphasis on marketing automation compared to some other options.
4. Freshsales (Freshworks CRM)
Pricing: Freshsales offers a free plan and several paid plans with different feature sets. They have a focus on customer service.
Key Features: Contact management, lead scoring, sales automation, email integration, and phone integration.
Pros: User-friendly, good for sales and customer service, offers a free plan.
Cons: Can become expensive with advanced features and a large number of users.
5. Agile CRM
Pricing: Agile CRM offers a free plan for up to 10 users. Paid plans are competitively priced and offer a comprehensive set of features.
Key Features: Contact management, sales automation, marketing automation, helpdesk, and project management.
Pros: All-in-one platform, affordable, good for small businesses with diverse needs.
Cons: Interface can seem a bit cluttered compared to some other options.
Calculating the True Cost: Beyond the Monthly Fee
When evaluating CRM costs, it’s essential to look beyond the monthly subscription fee. The total cost of ownership (TCO) includes several factors that can significantly impact your budget. Consider these additional expenses:
- Implementation Costs: If you choose a CRM that requires professional implementation, factor in the associated costs. These can include data migration, system configuration, and training.
- Training Costs: Even if you don’t use implementation services, you’ll likely need to train your employees on how to use the CRM. This can involve internal training, online courses, or external consultants.
- Customization Costs: If you require custom features or integrations, factor in the development costs.
- Integration Costs: Integrating your CRM with other business applications, such as your accounting software or e-commerce platform, can incur costs for connectors, APIs, or professional services.
- Ongoing Maintenance and Support: Factor in the cost of ongoing maintenance, support, and potential upgrades.
By considering the TCO, you can get a more accurate picture of the true cost of a CRM and make a more informed decision.
Free CRM Options: Is Free Always the Best Option?
Free CRM plans can be attractive for small businesses with limited budgets. They often provide basic features like contact management, lead tracking, and basic reporting. However, it’s crucial to understand the limitations of free plans:
- Limited Features: Free plans often have limited features compared to paid plans. You might miss out on essential functionalities like advanced automation, integration with other apps, or robust reporting capabilities.
- Storage Limits: Free plans may have restrictions on the number of contacts, data storage, or email sends.
- User Limits: Free plans might limit the number of users who can access the CRM.
- Support Limitations: Free plans typically offer limited support, which can be a problem if you encounter technical issues or need assistance.
- Branding: Some free plans display the vendor’s branding within the CRM, which can be undesirable.
While free CRM plans can be a good starting point, carefully evaluate your business needs and the limitations of the free plan. If your business has complex requirements or you anticipate rapid growth, a paid plan might be a better long-term investment.
Maximizing ROI: Getting the Most Value from Your CRM Investment
Implementing a CRM is an investment. To ensure you get a good return on your investment (ROI), consider these strategies:
- Define Your Goals: Before choosing a CRM, clearly define your business goals. What do you want to achieve with a CRM? Increase sales? Improve customer satisfaction? Streamline your marketing efforts? Having clear goals will help you choose the right CRM and measure its success.
- Choose the Right Features: Select a CRM with the features you need to achieve your goals. Don’t pay for features you won’t use.
- Implement Properly: Proper implementation is critical for the success of your CRM. Ensure your data is migrated correctly, and your employees are trained on how to use the system.
- Encourage User Adoption: Encourage your employees to use the CRM consistently. Provide training, support, and incentives to promote user adoption.
- Integrate with Other Tools: Integrate your CRM with other business applications, such as your email marketing platform or accounting software, to streamline your workflows.
- Analyze Your Data: Regularly analyze the data in your CRM to gain insights into your sales and marketing performance. Use these insights to optimize your processes and improve your results.
- Measure Your ROI: Track key metrics, such as sales growth, customer satisfaction, and lead conversion rates, to measure the ROI of your CRM investment.
By following these strategies, you can maximize the value of your CRM investment and drive significant improvements in your business performance.
Hidden Costs and Potential Pitfalls to Avoid
While the monthly subscription fee is the most visible cost, there are hidden costs and potential pitfalls to be aware of. Here are some things to watch out for:
- Unexpected Implementation Fees: Carefully review the implementation process and any associated fees. Some vendors might charge extra for data migration, system configuration, or training.
- Over-Customization: Avoid over-customizing your CRM. Customization can be expensive and time-consuming, and it can also make it harder to upgrade your system in the future.
- Integration Challenges: Integrating your CRM with other systems can be complex. Ensure the CRM has good integration capabilities and that you understand the potential costs involved.
- Data Migration Issues: Data migration can be a challenging process. Ensure your data is clean and organized before you migrate it to the CRM. Otherwise, you might encounter data quality issues and data loss.
- Lack of User Adoption: If your employees don’t use the CRM, you won’t see the benefits. Invest in training and support to ensure user adoption.
- Vendor Lock-in: Be aware of vendor lock-in. Some CRMs make it difficult to switch to another vendor. Research the vendor’s reputation and ensure they offer flexible contracts.
By being aware of these potential pitfalls, you can avoid unexpected costs and ensure a smooth CRM implementation process.
Making the Right Choice: A Step-by-Step Guide
Choosing the right CRM for your small business is a crucial decision. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you navigate the process:
- Assess Your Needs: Identify your business goals and the specific needs you have for a CRM. What problems are you trying to solve? What features do you need?
- Set Your Budget: Determine how much you can afford to spend on a CRM. Consider both the monthly subscription fee and the total cost of ownership.
- Research CRM Options: Research different CRM vendors and compare their features, pricing, and reviews.
- Create a Shortlist: Create a shortlist of potential CRM options that meet your needs and budget.
- Request Demos: Request demos from the vendors on your shortlist. Evaluate the user interface, features, and ease of use.
- Get Quotes: Get quotes from the vendors on your shortlist. Compare the pricing plans and the services included.
- Consider Implementation and Training: Factor in the cost of implementation and training.
- Check Reviews and References: Read reviews and check references from other small businesses that use the CRM.
- Make a Decision: Choose the CRM that best meets your needs and budget.
- Implement and Train: Implement the CRM and train your employees on how to use it.
By following these steps, you can make an informed decision and choose the right CRM for your small business.
Conclusion: Investing in Your Future
Choosing a CRM for your small business is more than just a technology decision; it’s an investment in your future. By understanding the costs involved, evaluating your options carefully, and implementing the CRM effectively, you can build stronger customer relationships, streamline your sales and marketing efforts, and drive sustainable growth. Remember to focus on the value the CRM brings, considering the long-term benefits it provides. While the initial investment might seem significant, the improvements in efficiency, customer satisfaction, and revenue generation can far outweigh the cost. Take the time to research, plan, and choose wisely, and your CRM will become a valuable asset for your small business for years to come.