Small Business CRM Checklist: Your Ultimate Guide to Choosing, Implementing, and Thriving
Small Business CRM Checklist: Your Ultimate Guide to Choosing, Implementing, and Thriving
Running a small business is a whirlwind of activity. You’re juggling everything from product development and marketing to customer service and sales. In the midst of all this, it’s easy for things to fall through the cracks, especially when it comes to managing your customer relationships. That’s where a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system comes in. A CRM is more than just a contact list; it’s a powerful tool that can streamline your operations, boost sales, and help you build lasting relationships with your customers. This comprehensive checklist will guide you through every step of the process, from selecting the right CRM to successfully implementing it and reaping the rewards.
What is a CRM and Why Does Your Small Business Need One?
Before we dive into the checklist, let’s briefly touch on what a CRM is and why it’s essential for small businesses. A CRM system is a software solution that helps you manage all your interactions with current and potential customers. It centralizes customer data, tracks sales activities, automates tasks, and provides valuable insights into your business performance. Think of it as the central nervous system of your customer-facing operations.
Here’s why your small business needs a CRM:
- Improved Customer Relationships: A CRM allows you to understand your customers better, personalize interactions, and provide exceptional service, leading to increased customer loyalty and retention.
- Increased Sales: By tracking leads, managing the sales pipeline, and automating sales tasks, a CRM can help you close more deals and boost revenue.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Automate repetitive tasks, such as email follow-ups and data entry, freeing up your time to focus on more strategic initiatives.
- Better Data Analysis: Gain valuable insights into your sales performance, customer behavior, and marketing effectiveness, enabling you to make data-driven decisions.
- Centralized Data: Keep all customer information in one place, ensuring everyone in your team has access to the most up-to-date information.
Phase 1: Choosing the Right CRM for Your Small Business
Choosing the right CRM is the most crucial first step. The market is flooded with options, each boasting different features and functionalities. This section will guide you through the key considerations to ensure you select a CRM that aligns with your business needs and goals.
1. Define Your Needs and Goals
Before you start shopping, take the time to clearly define your needs and goals. Ask yourself the following questions:
- What are your primary business objectives? Are you focused on increasing sales, improving customer service, or streamlining marketing efforts?
- What are your current pain points? What challenges are you facing in managing your customer relationships?
- What features are essential? Make a list of must-have features, such as contact management, sales pipeline management, email marketing integration, or reporting capabilities.
- What is your budget? Determine how much you’re willing to spend on a CRM, considering both the initial setup costs and ongoing subscription fees.
- Who will be using the CRM? Consider the needs of different team members, such as sales representatives, customer service agents, and marketing professionals.
Answering these questions will help you narrow down your options and identify the CRMs that best fit your specific requirements.
2. Research CRM Options
Once you have a clear understanding of your needs, it’s time to research available CRM options. Here’s how to approach this:
- Online Reviews and Comparisons: Read reviews from other small business owners to get insights into the pros and cons of different CRM systems. Compare features, pricing, and customer support options.
- Software Directories: Explore software directories, such as G2, Capterra, and TrustRadius, to browse CRM options and filter by features, pricing, and user ratings.
- Vendor Websites: Visit the websites of potential CRM providers to learn more about their products, features, and pricing plans.
- Free Trials and Demos: Take advantage of free trials and demos to test out different CRM systems and see how they work in practice.
Take your time to explore various options and create a shortlist of CRMs that seem promising.
3. Evaluate Key Features
As you evaluate different CRM systems, pay close attention to the following key features:
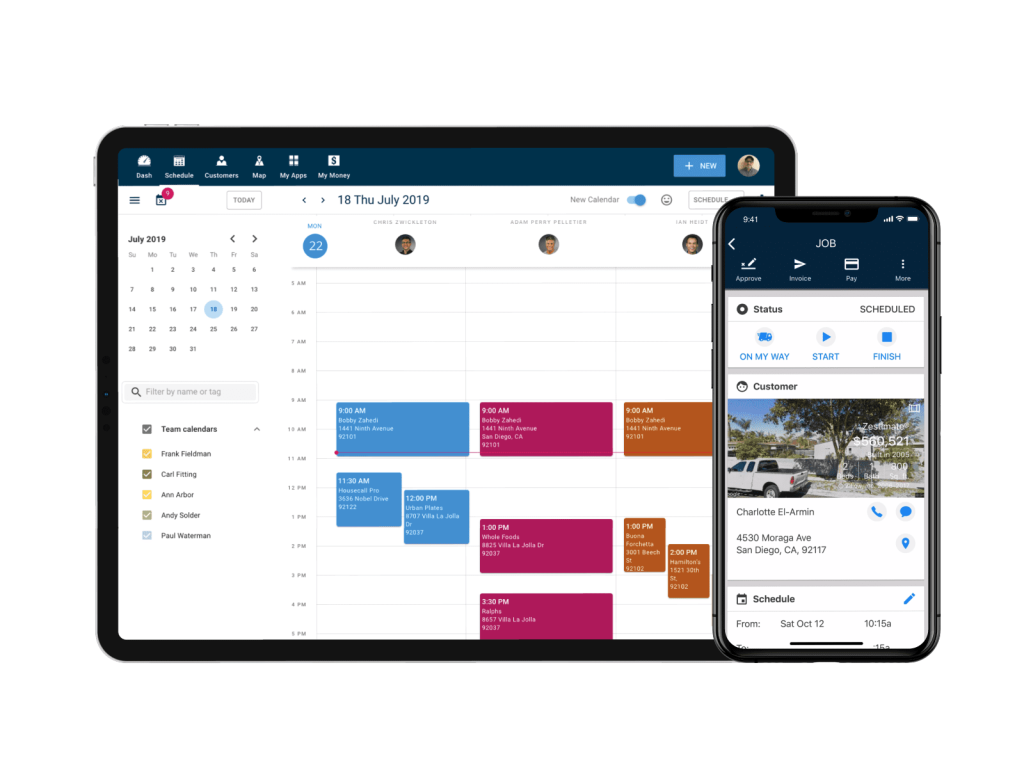
- Contact Management: The ability to store and manage customer contact information, including names, addresses, phone numbers, email addresses, and social media profiles.
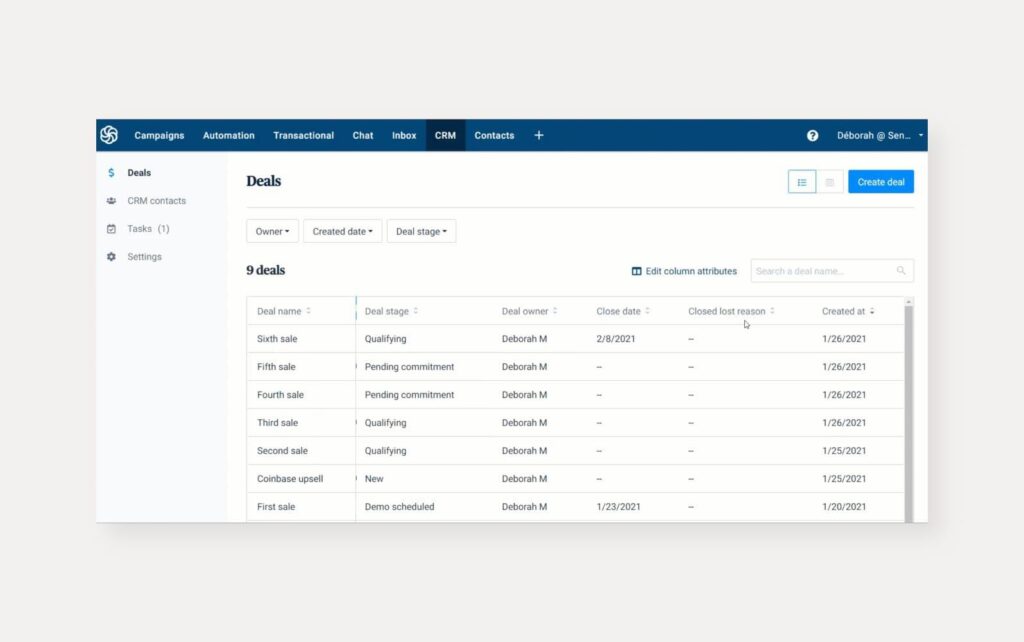
- Sales Pipeline Management: A visual representation of your sales process, allowing you to track leads, manage opportunities, and monitor the progress of deals.
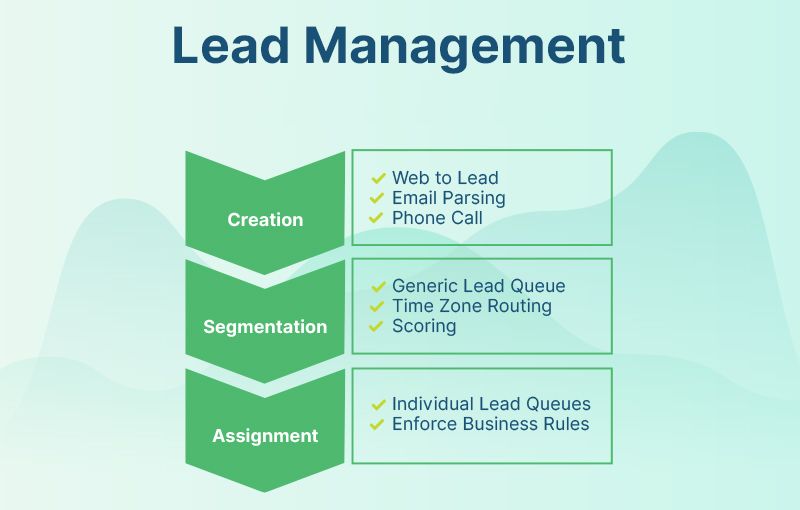
- Lead Management: Features for capturing, qualifying, and nurturing leads, such as lead scoring, lead segmentation, and lead routing.
- Email Marketing Integration: The ability to integrate with your email marketing platform, allowing you to send targeted email campaigns and track their performance.
- Reporting and Analytics: Tools for generating reports and analyzing data to gain insights into your sales performance, customer behavior, and marketing effectiveness.
- Automation: Features for automating repetitive tasks, such as email follow-ups, data entry, and task assignment.
- Integration with Other Tools: The ability to integrate with other tools you use, such as your accounting software, e-commerce platform, and social media channels.
- Mobile Accessibility: The ability to access your CRM data and functionality on mobile devices.
- Customer Support: The availability of customer support, including documentation, tutorials, and live chat or phone support.
- Scalability: The ability of the CRM to scale as your business grows.
Prioritize the features that are most important to your business needs.
4. Consider Pricing and Implementation Costs
CRM pricing varies widely, ranging from free options for basic features to enterprise-level solutions with advanced functionality. When evaluating pricing, consider the following:
- Subscription Fees: Most CRM systems operate on a subscription basis, with monthly or annual fees.
- User Licenses: Some CRMs charge per user, while others offer unlimited user licenses.
- Setup Costs: Consider any initial setup costs, such as data migration fees or training costs.
- Hidden Costs: Be aware of any hidden costs, such as add-on fees or charges for exceeding storage limits.
- Long-Term Value: Evaluate the long-term value of the CRM, considering its ability to improve your sales, customer service, and overall business performance.
Choose a CRM that fits within your budget and offers a good return on investment.
5. Select Your CRM and Sign Up
After careful consideration, select the CRM that best meets your needs and sign up for a plan that aligns with your budget and requirements. Before you commit, make sure you understand the terms and conditions of your subscription, including the cancellation policy and data security measures.
Phase 2: Implementing Your CRM System
Once you’ve chosen your CRM, the next step is to implement it successfully. This involves migrating your data, configuring the system, training your team, and establishing best practices. This section will guide you through the implementation process.
1. Data Migration
Migrating your existing data to the new CRM is a critical step. Here’s how to approach data migration:
- Data Audit: Review your existing data to identify any duplicates, errors, or inconsistencies.
- Data Cleaning: Clean and standardize your data to ensure accuracy and consistency.
- Data Export: Export your data from your existing systems in a compatible format, such as CSV or Excel.
- Data Import: Import your data into the new CRM, following the instructions provided by the vendor.
- Data Validation: Verify that your data has been imported correctly and that all fields are populated as expected.
Data migration can be time-consuming, so plan accordingly and allocate sufficient time for this process.
2. System Configuration
Configure your CRM to meet your specific business needs. This includes:
- Customization: Customize the CRM to match your branding, workflows, and processes.
- User Roles and Permissions: Define user roles and permissions to control access to data and functionality.
- Workflow Automation: Set up automated workflows to streamline your sales, marketing, and customer service processes.
- Integrations: Integrate your CRM with other tools you use, such as your email marketing platform, accounting software, and social media channels.
- Data Fields: Configure custom fields to capture specific information relevant to your business.
Take the time to configure your CRM thoroughly to ensure it meets your unique requirements.
3. Training Your Team
Training your team is essential for the successful adoption of your new CRM. Here’s how to approach training:
- Training Plan: Develop a training plan that outlines the training objectives, content, and schedule.
- Training Materials: Create training materials, such as user manuals, tutorials, and video guides.
- Training Sessions: Conduct training sessions for your team members, covering the key features and functionality of the CRM.
- Hands-on Practice: Provide opportunities for hands-on practice to reinforce learning.
- Ongoing Support: Provide ongoing support and assistance to your team members as they use the CRM.
Invest in comprehensive training to ensure your team is comfortable and proficient in using the CRM.
4. Setting Up Best Practices
Establish best practices to ensure your team uses the CRM consistently and effectively. This includes:
- Data Entry Standards: Define data entry standards to ensure data accuracy and consistency.
- Workflow Guidelines: Establish guidelines for using workflows to automate tasks and processes.
- Reporting and Analysis: Define reporting and analysis requirements to track key metrics and monitor performance.
- Regular Data Audits: Conduct regular data audits to identify and correct any errors or inconsistencies.
- Communication: Encourage open communication and collaboration among team members regarding the CRM.
Implementing best practices will help you maximize the benefits of your CRM.
Phase 3: Optimizing and Maintaining Your CRM
Implementing a CRM is not a one-time event. It’s an ongoing process that requires continuous optimization and maintenance. This section will guide you through the steps to ensure your CRM remains effective and aligned with your evolving business needs.
1. Monitor and Analyze Data
Regularly monitor and analyze your CRM data to gain insights into your sales performance, customer behavior, and marketing effectiveness. Use the CRM’s reporting and analytics tools to track key metrics, such as:
- Sales Revenue: Track your sales revenue to measure your overall sales performance.
- Lead Conversion Rates: Analyze your lead conversion rates to identify areas for improvement.
- Customer Acquisition Cost: Calculate your customer acquisition cost to optimize your marketing spend.
- Customer Retention Rate: Monitor your customer retention rate to measure customer loyalty.
- Customer Satisfaction: Track customer satisfaction to identify areas for improvement in your customer service.
Use the data to identify trends, patterns, and areas for improvement.
2. Refine Workflows and Processes
Regularly review and refine your workflows and processes to ensure they are efficient and effective. Identify any bottlenecks or inefficiencies and make adjustments as needed. Consider:
- Automating Tasks: Automate repetitive tasks to save time and improve efficiency.
- Optimizing Sales Pipeline: Optimize your sales pipeline to improve lead conversion rates.
- Streamlining Customer Service: Streamline your customer service processes to improve customer satisfaction.
Continuously refine your workflows and processes to maximize the benefits of your CRM.
3. Update Data and Keep It Clean
Keeping your CRM data up-to-date and clean is essential for data accuracy and reliability. Regularly update your data to ensure it reflects the latest information. Consider:
- Data Validation: Implement data validation rules to prevent errors and inconsistencies.
- Data Cleansing: Regularly clean your data to remove duplicates, correct errors, and standardize information.
- Data Enrichment: Enrich your data by adding relevant information, such as social media profiles and industry data.
- Data Backup: Back up your data regularly to protect against data loss.
Maintaining clean and accurate data will improve the effectiveness of your CRM.
4. User Adoption and Feedback
Encourage user adoption and gather feedback from your team members to ensure they are using the CRM effectively and to identify areas for improvement. Consider:
- User Training: Provide ongoing training and support to ensure your team members are comfortable and proficient in using the CRM.
- Feedback Collection: Collect feedback from your team members to identify areas for improvement.
- User Engagement: Encourage user engagement by recognizing and rewarding users who are actively using the CRM.
- Regular Reviews: Conduct regular reviews of your CRM usage to identify areas for improvement.
By encouraging user adoption and gathering feedback, you can ensure your CRM is meeting your team’s needs.
5. Integration and Customization
As your business grows, your CRM needs may change. Regularly review your integrations and customizations to ensure they are still meeting your needs. Consider:
- New Integrations: Integrate your CRM with new tools and applications as needed.
- Customization Updates: Update your customizations to reflect changes in your business processes.
- API Access: Utilize the CRM’s API to integrate with custom applications and services.
Keeping your CRM up-to-date with the latest integrations and customizations will help you maximize its benefits.
Conclusion: Maximizing Your CRM Investment
Implementing and maintaining a CRM is a strategic investment that can significantly improve your small business’s performance. By following this checklist, you can choose the right CRM, implement it successfully, and optimize it for long-term success. Remember that a CRM is not a magic bullet; it’s a tool that, when used effectively, can help you build stronger customer relationships, boost sales, and streamline your operations. Embrace the process, stay adaptable, and continuously seek ways to leverage your CRM to achieve your business goals.
The journey doesn’t end with implementation. It’s an ongoing process of learning, adapting, and refining. By staying proactive and engaged, you can ensure your CRM remains a valuable asset for your small business for years to come. Good luck, and may your customer relationships thrive!