Small Business CRM Checklist: Your Ultimate Guide to Choosing, Implementing, and Mastering Customer Relationship Management
Small Business CRM Checklist: Your Path to Customer Relationship Mastery
Running a small business is a juggling act. You’re wearing multiple hats, from sales and marketing to customer service and operations. Amidst this whirlwind, keeping track of your customers, their needs, and your interactions with them can feel like an impossible task. That’s where a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system steps in, offering a lifeline of organization and efficiency. But with so many options available, choosing the right CRM for your small business can feel overwhelming. This checklist is designed to guide you through every step, ensuring you select, implement, and master a CRM that truly empowers your business.
This comprehensive checklist goes beyond a simple list; it’s a roadmap. It covers the critical aspects of CRM selection, implementation, and ongoing optimization. We’ll delve into understanding your needs, evaluating CRM solutions, planning your implementation, training your team, and ultimately, measuring your success. By following this checklist, you’ll be equipped to make informed decisions, avoid common pitfalls, and unlock the full potential of CRM for your small business. Prepare to transform your customer relationships and drive sustainable growth.
Phase 1: Needs Assessment – Understanding Your CRM Requirements
Before diving into CRM options, take a step back and assess your business’s unique needs. This crucial phase ensures you choose a system that aligns perfectly with your goals and operational requirements. Consider this the foundation upon which you’ll build your CRM strategy.
1. Define Your Business Objectives
What do you hope to achieve with a CRM? Are you aiming to:
- Increase Sales: Track leads, manage the sales pipeline, and close deals more efficiently.
- Improve Customer Retention: Provide better customer service, personalize interactions, and build loyalty.
- Enhance Marketing Efforts: Segment your audience, automate marketing campaigns, and track campaign performance.
- Streamline Operations: Automate tasks, improve communication, and centralize customer data.
Clearly defined objectives will guide your CRM selection and implementation.
2. Identify Your Key Business Processes
Map out your current customer-related processes. How do you:
- Generate Leads: Where do leads come from (website, social media, referrals, etc.)?
- Qualify Leads: What criteria do you use to determine if a lead is a good fit?
- Manage Sales Opportunities: How do you track the progress of deals through the sales pipeline?
- Provide Customer Service: How do you handle customer inquiries, complaints, and support requests?
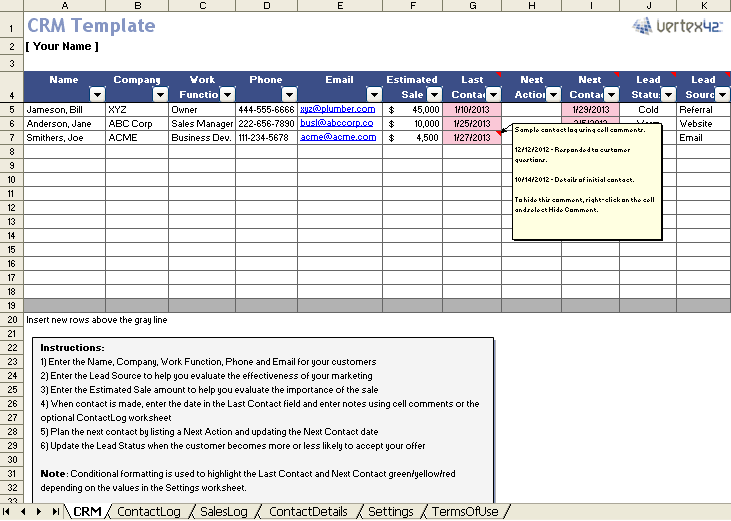
- Manage Customer Data: Where is customer information currently stored (spreadsheets, email, etc.)?
Understanding these processes will help you identify areas where CRM can provide the most value.
3. Determine Your Budget and Resources
CRM systems vary significantly in cost. Consider:
- Software Costs: Subscription fees (monthly or annual), per-user pricing.
- Implementation Costs: Data migration, customization, and integration with other systems.
- Training Costs: Training your team on how to use the CRM.
- Ongoing Maintenance Costs: Technical support, updates, and upgrades.
Assess your available resources, including staff time and technical expertise, to determine what you can realistically afford.
4. Evaluate Your Current Technology Stack
Identify the systems you already use, such as:
- Email Marketing Software: Mailchimp, Constant Contact, etc.
- Accounting Software: QuickBooks, Xero, etc.
- Website Platform: WordPress, Shopify, etc.
Ensure the CRM you choose can integrate seamlessly with your existing tools. Integration is crucial for data synchronization and automation.
5. Define Your User Roles and Permissions
Who will be using the CRM, and what level of access will they need? Consider:
- Sales Representatives: Access to lead and opportunity data, sales pipeline management.
- Marketing Team: Access to contact data, campaign management tools.
- Customer Service Representatives: Access to customer history, support ticket management.
- Administrators: Full access to all features, system configuration, and user management.
Defining user roles ensures data security and efficient workflow management.
Phase 2: CRM Selection – Choosing the Right Solution
With a clear understanding of your needs, it’s time to evaluate CRM options. This involves researching vendors, comparing features, and conducting demos to find the perfect fit.
1. Research CRM Vendors
Explore the market and identify potential CRM solutions. Consider:
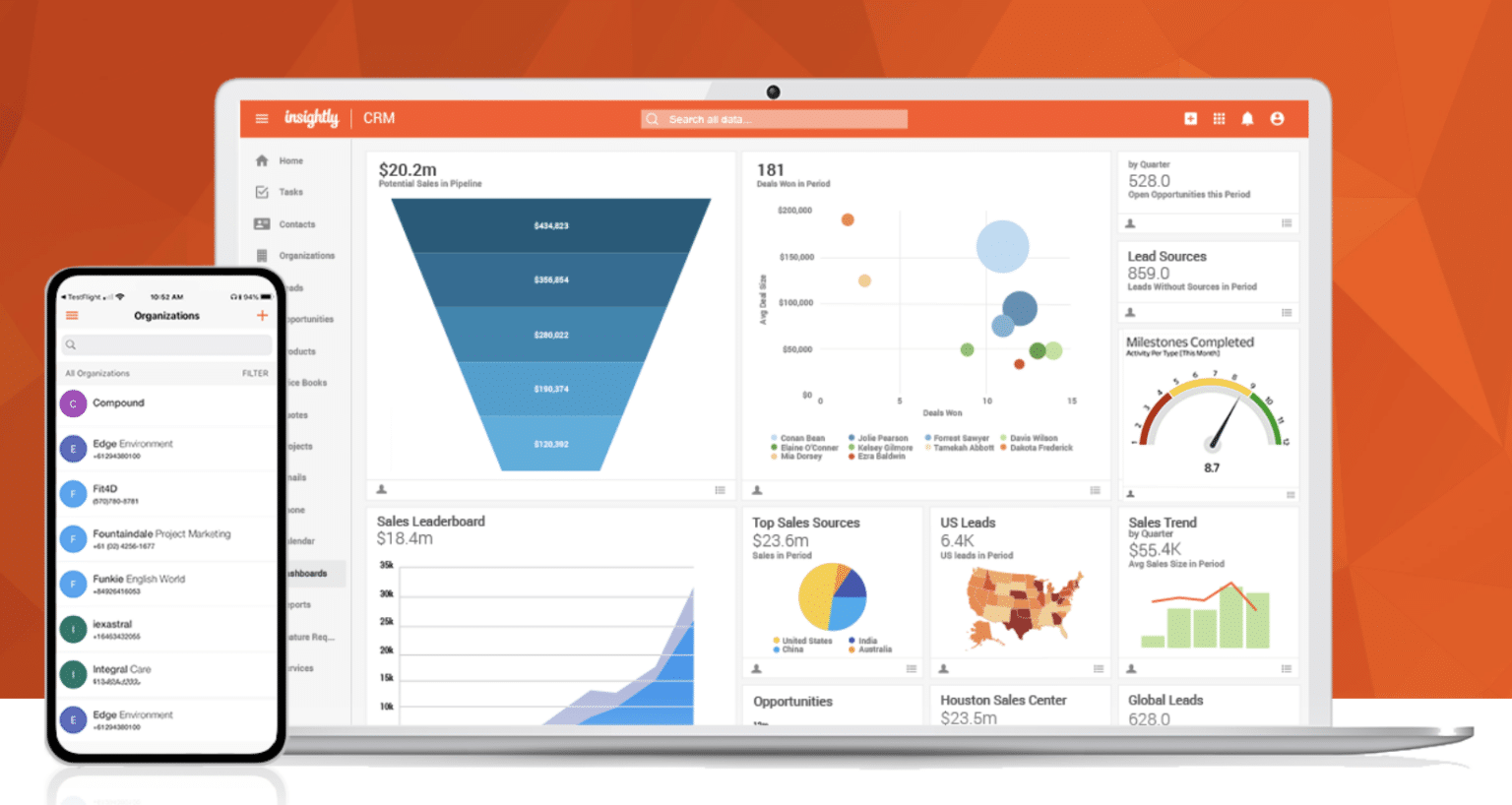
- Popular CRM Platforms: Salesforce, HubSpot CRM, Zoho CRM, Pipedrive, Microsoft Dynamics 365, Freshsales, and Agile CRM.
- Industry-Specific CRMs: Some CRMs are designed for specific industries (e.g., real estate, healthcare).
- Reviews and Ratings: Read online reviews from other small businesses. Websites like G2, Capterra, and TrustRadius are great resources.
- Vendor Reputation: Research the vendor’s history, customer support, and long-term stability.
2. Create a Feature Checklist
Based on your needs assessment, create a detailed checklist of required features. Prioritize features that are essential for your business. Consider the following categories:
- Contact Management: Contact storage, segmentation, and organization.
- Lead Management: Lead capture, scoring, and nurturing.
- Sales Automation: Sales pipeline management, deal tracking, and automated tasks.
- Marketing Automation: Email marketing, campaign management, and lead nurturing.
- Customer Service: Ticket management, knowledge base, and self-service portals.
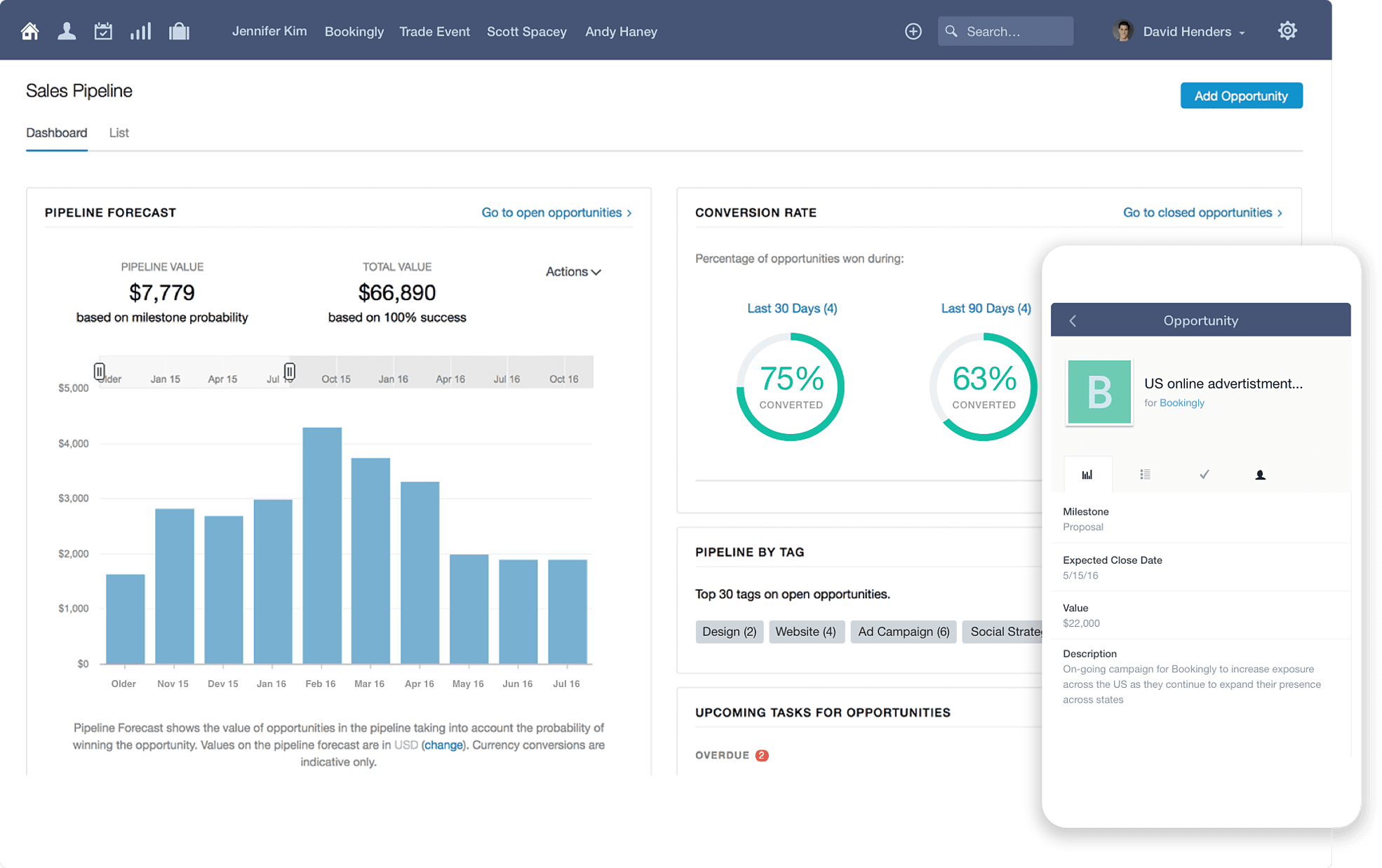
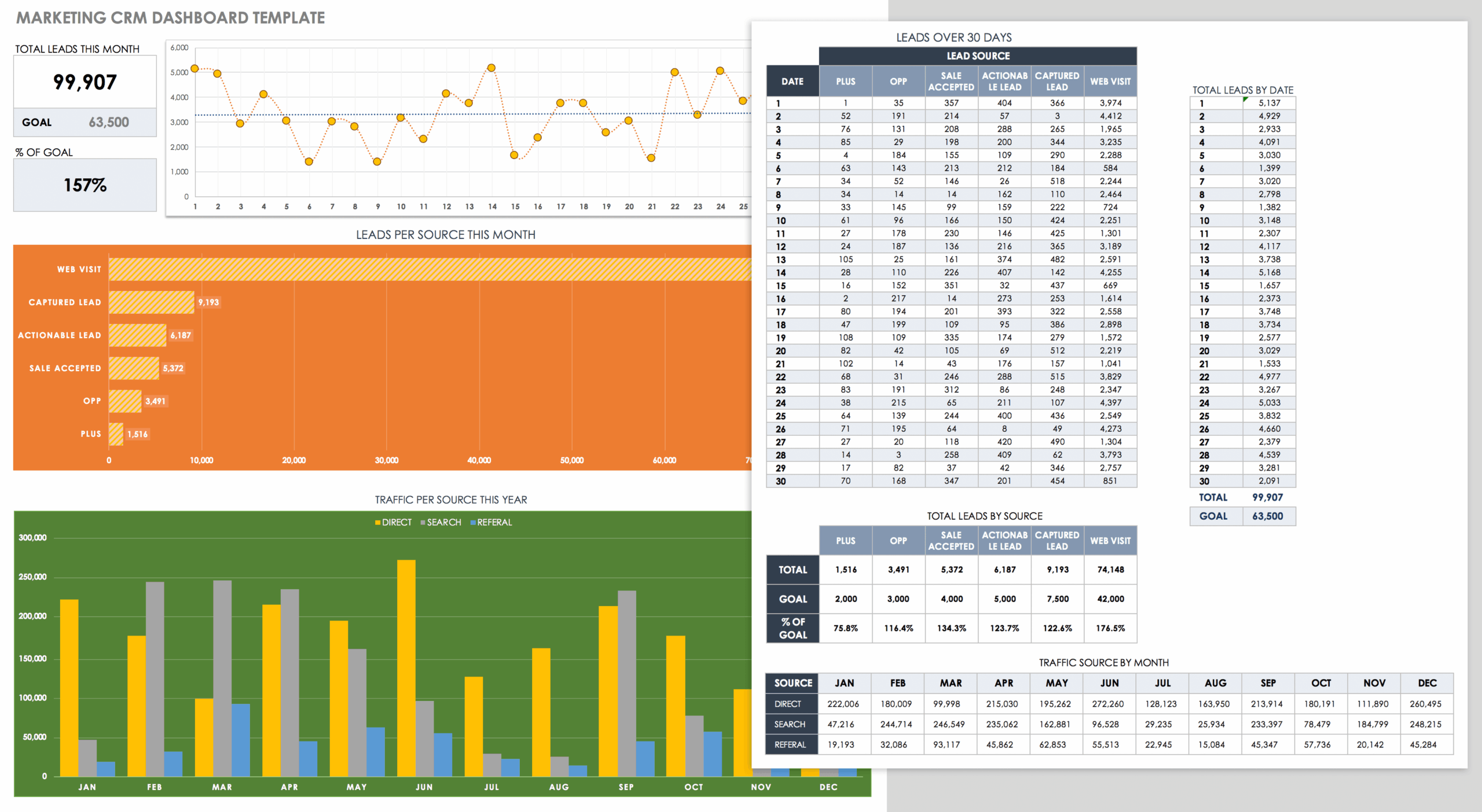
- Reporting and Analytics: Sales reports, customer behavior analysis, and performance dashboards.
- Integrations: Integration with existing tools (email, marketing automation, accounting software, etc.).
- Mobile Accessibility: Mobile apps or responsive design for on-the-go access.
- Customization: Ability to customize fields, workflows, and reports to fit your specific needs.
3. Evaluate Pricing and Licensing Options
Compare pricing plans from different vendors. Consider:
- Free Plans: Many CRMs offer free plans with limited features.
- Paid Plans: Subscription-based plans with varying features and user limits.
- User-Based Pricing: Per-user pricing is common, so factor in the number of users.
- Feature-Based Pricing: Some plans offer different features based on the price point.
- Hidden Costs: Be aware of potential add-on costs for integrations, training, and support.
4. Request Demos and Free Trials
Schedule demos with potential vendors to see the CRM in action. Ask specific questions about features and functionality. Take advantage of free trials to test the CRM with your data and workflows. This is a crucial step to ensure the CRM is user-friendly and meets your requirements.
5. Consider Scalability
Choose a CRM that can grow with your business. Consider:
- Scalability of Features: Can the CRM handle increased data volume and user activity?
- Scalability of Pricing: Can the pricing plan accommodate your business growth?
- Scalability of Integrations: Can the CRM integrate with new tools as your needs evolve?
6. Check for Data Security and Compliance
Ensure the CRM offers robust security features and complies with relevant data privacy regulations (e.g., GDPR, CCPA). Prioritize security to protect customer data.
Phase 3: CRM Implementation – Setting Up for Success
Once you’ve chosen a CRM, the implementation phase begins. This involves data migration, system configuration, and user training. A well-planned implementation is crucial for a smooth transition and maximum return on investment.
1. Plan Your Implementation Strategy
Create a detailed implementation plan that outlines the steps, timeline, and resources required. Break down the implementation process into manageable phases. Consider:
- Data Migration: How will you migrate data from existing systems to the CRM?
- System Configuration: How will you customize the CRM to fit your business processes?
- User Training: How will you train your team on how to use the CRM?
- Testing and Validation: How will you test the CRM to ensure it’s working correctly?
2. Prepare Your Data for Migration
Clean and organize your data before migrating it to the CRM. This includes:
- Data Cleaning: Remove duplicates, correct errors, and standardize formatting.
- Data Formatting: Ensure data is in a format that is compatible with the CRM.
- Data Mapping: Map your existing data fields to the corresponding fields in the CRM.
3. Configure the CRM
Customize the CRM to match your business processes. This includes:
- Adding Custom Fields: Create custom fields to store specific data relevant to your business.
- Setting Up Workflows: Automate tasks and processes, such as lead assignment and email notifications.
- Configuring Sales Pipelines: Define your sales stages and customize the pipeline to match your sales process.
- Setting Up Integrations: Connect the CRM with your existing tools.
- Personalizing Dashboards: Customize dashboards to display key performance indicators (KPIs) and reports.
4. Import Your Data
Import your cleaned and formatted data into the CRM. Test the data import process to ensure accuracy. Verify that all data has been imported correctly and is accessible.
5. Train Your Team
Provide comprehensive training to your team on how to use the CRM. This includes:
- Training Materials: Create training manuals, videos, and other resources.
- Training Sessions: Conduct training sessions for different user roles.
- Hands-on Practice: Provide opportunities for users to practice using the CRM.
- Ongoing Support: Offer ongoing support and resources to address user questions and issues.
6. Test and Validate
Thoroughly test the CRM to ensure it’s working correctly. Conduct user acceptance testing (UAT) to validate that the system meets your requirements. Identify and resolve any issues before going live.
7. Go Live and Monitor
Once you’re confident the system is ready, launch the CRM. Monitor the system for performance and address any issues that arise. Provide ongoing support and training to users.
Phase 4: CRM Optimization – Maximizing Your CRM Investment
Implementation is just the beginning. Ongoing optimization is essential to ensure you’re getting the most out of your CRM. This involves analyzing data, refining processes, and continuously improving your CRM strategy.
1. Track Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Identify and track KPIs to measure the success of your CRM implementation. Examples include:
- Sales Conversion Rates: Track the percentage of leads that convert into customers.
- Sales Cycle Length: Measure the time it takes to close a deal.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): Calculate the cost of acquiring a new customer.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV): Estimate the revenue a customer will generate over their relationship with your business.
- Customer Retention Rate: Measure the percentage of customers who remain loyal.
- Lead Response Time: Track the time it takes to respond to leads.
- Customer Satisfaction Scores: Measure customer satisfaction through surveys and feedback.
2. Analyze Data and Generate Reports
Use the CRM’s reporting features to analyze data and gain insights into your business performance. Generate reports on sales, marketing, and customer service activities. Identify trends and patterns to inform decision-making.
3. Refine Your Processes
Continuously review and refine your business processes based on data analysis and user feedback. Identify areas for improvement and optimize your workflows. Make adjustments to the CRM configuration as needed.
4. Provide Ongoing Training and Support
Provide ongoing training and support to your team to ensure they are using the CRM effectively. Offer refresher courses and provide documentation and resources. Address user questions and issues promptly.
5. Stay Up-to-Date
Keep abreast of new features and updates released by your CRM vendor. Implement new features and functionality to improve your CRM performance. Stay informed about industry best practices and trends.
6. Integrate with Emerging Technologies
Explore integrating your CRM with emerging technologies, such as:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Use AI-powered tools for lead scoring, sales forecasting, and customer service automation.
- Chatbots: Implement chatbots to provide instant customer support and gather leads.
- Social Media Integration: Integrate your CRM with social media platforms to track customer interactions and manage social media campaigns.
7. Regularly Review and Audit Your CRM
Conduct regular reviews and audits of your CRM to ensure it’s meeting your needs. Assess the effectiveness of your CRM strategy and identify areas for improvement. Make adjustments to your CRM configuration as needed.
Key Considerations for Small Businesses
Choosing and implementing a CRM is a significant undertaking, especially for small businesses with limited resources. Here are some key considerations to keep in mind:
- Simplicity is Key: Start with a CRM that is easy to use and has a clean interface. Avoid complex systems that can overwhelm your team.
- User Adoption: User adoption is crucial for CRM success. Get buy-in from your team and provide adequate training and support.
- Start Small and Scale Up: Begin with the core features that address your most pressing needs. Gradually add more features as your business grows.
- Focus on the Customer: Always prioritize the customer experience. Use your CRM to personalize interactions and build strong customer relationships.
- Data Security: Prioritize data security and ensure your CRM provider has robust security measures in place.
- Integration is Important: Choose a CRM that integrates with your existing tools to streamline your workflow.
- Flexibility and Customization: Choose a CRM that offers flexibility and customization options to meet your unique needs.
- Mobile Accessibility: Ensure your CRM has mobile accessibility so you can access it from anywhere.
- Regular Backups: Implement regular backups of your CRM data to protect against data loss.
- Seek Expert Advice: If needed, consider seeking advice from a CRM consultant or expert to help you with the selection, implementation, and optimization process.
Conclusion: CRM – Your Partner in Growth
Implementing a CRM is an investment in your business’s future. By following this checklist, you’ll be well-equipped to choose, implement, and master a CRM that empowers your small business. Remember that a CRM is not just a piece of software; it’s a strategic tool that can transform your customer relationships, streamline your operations, and drive sustainable growth. Embrace the power of CRM, and watch your business thrive.