Small Business CRM Checklist 2025: Your Ultimate Guide to Choosing, Implementing, and Thriving

Small Business CRM Checklist 2025: Your Ultimate Guide to Choosing, Implementing, and Thriving
Running a small business is a whirlwind. You’re juggling everything – from sales and marketing to customer service and operations. In this chaotic landscape, a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system isn’t just a luxury; it’s a necessity. Think of it as your central hub, your organizational brain, and your key to unlocking sustainable growth. This comprehensive small business CRM checklist for 2025 will guide you through every stage, from understanding your needs to maximizing the value of your chosen CRM. We’ll cover everything, ensuring you’re not just surviving, but thriving in the competitive market.
Why a CRM is Crucial for Your Small Business in 2025
Before we dive into the checklist, let’s solidify the ‘why.’ Why should you even bother with a CRM? The answer is multifaceted, but here are the core benefits:
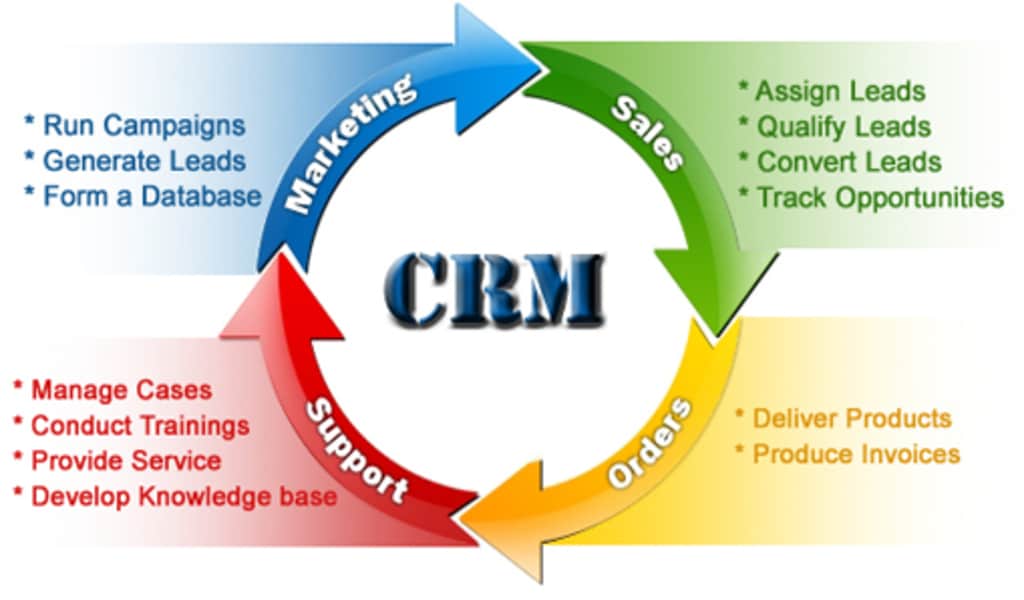
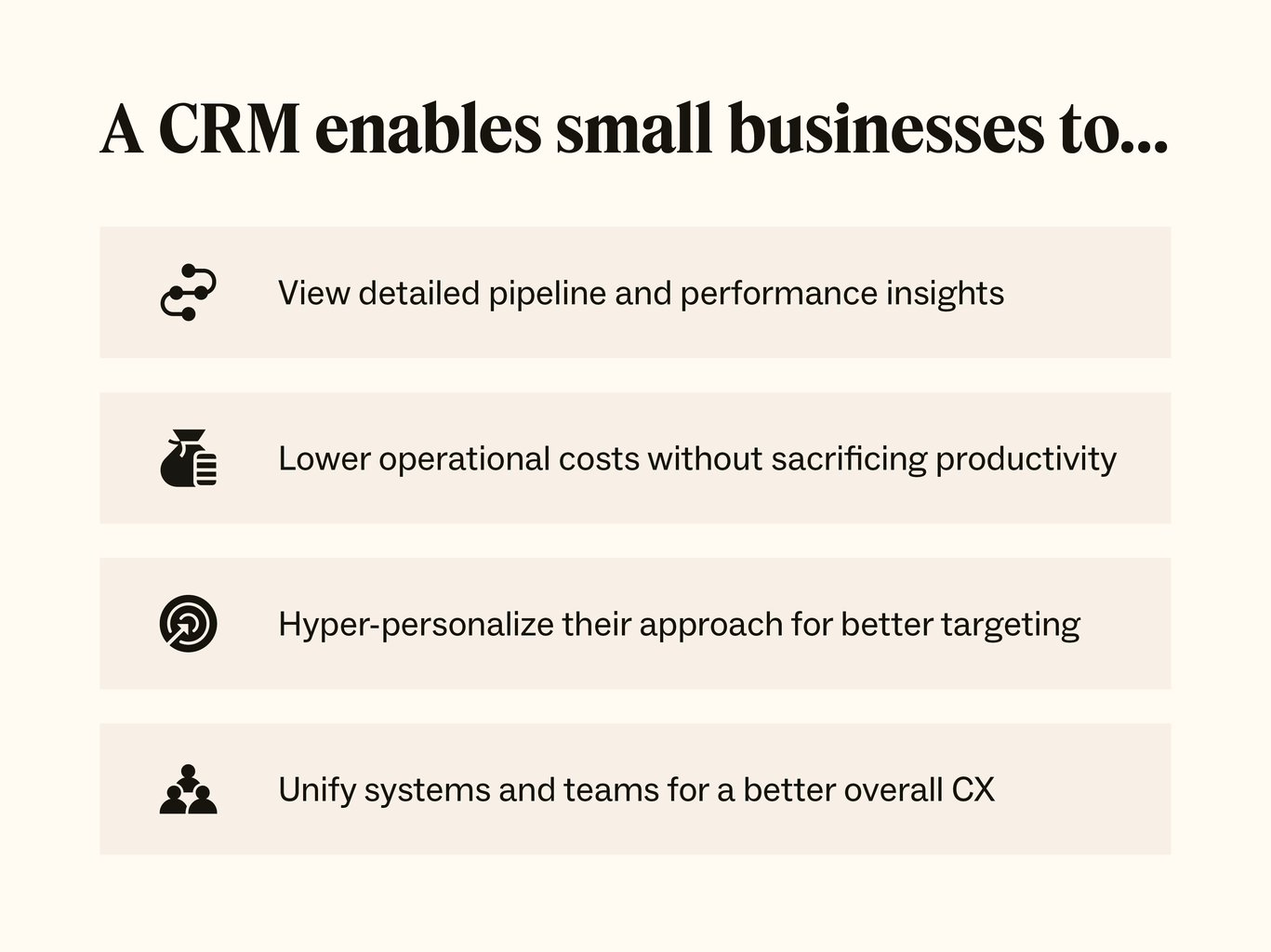
- Improved Customer Relationships: A CRM centralizes all customer interactions, providing a 360-degree view. You’ll know their purchase history, preferences, and communication history, enabling personalized interactions.
- Increased Sales: By streamlining the sales process, a CRM helps your team close deals faster. Automated workflows, lead scoring, and sales pipeline management are just a few ways it boosts efficiency.
- Enhanced Customer Service: Quick access to customer information and issue history empowers your support team to resolve issues promptly and effectively, leading to higher customer satisfaction.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: CRMs offer robust reporting and analytics. You can track key performance indicators (KPIs), identify trends, and make informed decisions about your business strategy.
- Improved Team Collaboration: A CRM facilitates seamless communication and collaboration across departments. Everyone has access to the same information, reducing silos and improving efficiency.
- Automation and Efficiency: Automate repetitive tasks, freeing up your team to focus on more strategic initiatives. This leads to significant time savings and increased productivity.
In 2025, the businesses that excel are those that leverage technology to build strong customer relationships, optimize their processes, and make data-driven decisions. A CRM is the cornerstone of achieving these goals.
Phase 1: Assessing Your Needs and Defining Your CRM Goals
Before you even start looking at CRM solutions, you need a clear understanding of your business needs and goals. This is the foundation upon which you’ll build your CRM strategy.
1. Identify Your Key Business Objectives
What are you hoping to achieve with a CRM? Are you primarily focused on increasing sales, improving customer service, streamlining marketing efforts, or a combination of these? Defining your objectives will guide your CRM selection process.
- Sales Growth: Set specific sales targets, such as increasing revenue by a certain percentage or closing a specific number of deals.
- Customer Retention: Define metrics like customer churn rate and customer lifetime value (CLTV). Aim to reduce churn and increase CLTV.
- Customer Satisfaction: Track customer satisfaction scores (CSAT) and net promoter scores (NPS). Set targets for improving these scores.
- Marketing Efficiency: Measure the effectiveness of your marketing campaigns and aim to improve lead generation and conversion rates.
2. Analyze Your Current Processes
Document your existing workflows for sales, marketing, and customer service. Identify pain points, inefficiencies, and areas where automation can improve your processes. This will help you determine which CRM features are most important.
- Sales Process: Map out your sales pipeline, from lead generation to deal closure. Identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement.
- Marketing Process: Analyze your lead generation, nurturing, and conversion processes. Determine how a CRM can help you automate and optimize these processes.
- Customer Service Process: Document how you handle customer inquiries, support tickets, and issue resolution. Identify ways to improve response times and customer satisfaction.
3. Define Your CRM User Roles and Permissions
Determine who will be using the CRM and what level of access each user will need. This will help you configure user roles and permissions within the CRM.
- Sales Team: Sales representatives will need access to leads, contacts, and sales pipelines.
- Marketing Team: Marketing professionals will need access to lead data, campaign management tools, and analytics.
- Customer Service Team: Customer service representatives will need access to customer information, support tickets, and issue history.
- Management: Managers will need access to reports, dashboards, and analytics to monitor performance.
4. Determine Your Data Requirements
Identify the data you need to store in your CRM, such as contact information, purchase history, communication logs, and custom fields. This will help you choose a CRM that supports your data requirements.
- Contact Information: Name, email address, phone number, job title, company name, and other relevant contact details.
- Company Information: Company size, industry, location, and other relevant company details.
- Sales Data: Deal stage, sales value, close date, and other relevant sales information.
- Customer Service Data: Support tickets, issue history, and customer feedback.
- Marketing Data: Campaign performance, lead source, and customer behavior data.
5. Set a Budget
Determine how much you’re willing to spend on a CRM. Consider the costs of software licenses, implementation, training, and ongoing maintenance. Small businesses often have budget constraints, so finding a cost-effective solution is crucial. There are a variety of pricing models, from free options to enterprise-level subscriptions.
Phase 2: Researching and Selecting the Right CRM
Now that you’ve defined your needs, it’s time to research and select the CRM that best fits your business. This is a crucial step, so take your time and do your homework.
1. Identify Potential CRM Vendors
Research the leading CRM vendors in the market. Consider factors like features, pricing, integrations, and customer reviews. Some popular options for small businesses include:
- HubSpot CRM: Known for its user-friendly interface and free plan.
- Zoho CRM: Offers a wide range of features and affordable pricing.
- Salesforce Sales Cloud: A more robust and scalable option, suitable for growing businesses.
- Pipedrive: Focuses on sales pipeline management and ease of use.
- Freshsales: Offers a modern interface and features like integrated phone and email.
2. Evaluate CRM Features
Compare the features of different CRM solutions and determine which ones align with your business needs. Focus on the features that are most important to your objectives.
- Contact Management: Ability to store and manage contact information, including lead and customer details.
- Sales Automation: Features like automated workflows, lead scoring, and sales pipeline management.
- Marketing Automation: Email marketing, campaign management, and lead nurturing capabilities.
- Customer Service Tools: Support ticket management, knowledge base, and live chat functionality.
- Reporting and Analytics: Ability to track key performance indicators (KPIs) and generate reports.
- Integrations: Compatibility with other tools you use, such as email marketing platforms, accounting software, and social media platforms.
- Mobile Access: The ability to access the CRM from mobile devices is increasingly important for on-the-go teams.
3. Consider Pricing and Scalability
Evaluate the pricing models of different CRM solutions. Consider the cost of software licenses, add-ons, and support. Also, consider scalability. Will the CRM be able to grow with your business as it expands?
- Pricing Models: Subscription-based, per-user pricing, and tiered pricing plans are common.
- Hidden Costs: Be aware of potential hidden costs, such as implementation fees, training costs, and add-on fees.
- Scalability: Choose a CRM that can accommodate your future growth and evolving business needs.
4. Read Reviews and Get Recommendations
Read online reviews from other small businesses to get insights into the strengths and weaknesses of different CRM solutions. Ask for recommendations from other business owners or industry experts.
- Online Reviews: Read reviews on websites like G2, Capterra, and TrustRadius.
- Industry Forums: Participate in online forums and communities to get recommendations from other small business owners.
- Ask for Referrals: Ask other business owners for referrals and recommendations.
5. Request Demos and Free Trials
Request demos and free trials from your top CRM contenders. This will allow you to test the software, evaluate its features, and determine if it’s a good fit for your business.
- Demos: Schedule demos with CRM vendors to see the software in action.
- Free Trials: Take advantage of free trials to test the software yourself.
- Ask Questions: Ask questions during the demo or trial to clarify any doubts.
Phase 3: Implementing Your CRM
Once you’ve chosen your CRM, the next step is implementation. This involves setting up the system, migrating your data, and training your team.
1. Plan Your Implementation
Develop a detailed implementation plan that outlines the steps involved, the timeline, and the resources required. This will help you stay organized and on track.
- Project Timeline: Create a timeline for each stage of the implementation process.
- Resource Allocation: Assign resources to each task, including staff members, budget, and time.
- Data Migration Plan: Plan how you will migrate your existing data into the new CRM.
2. Configure Your CRM
Customize your CRM to meet your specific business needs. This may involve configuring user roles, creating custom fields, and setting up workflows.
- User Roles and Permissions: Configure user roles and permissions to control access to different features and data.
- Custom Fields: Create custom fields to store data specific to your business.
- Workflows: Set up automated workflows to streamline your processes.
3. Migrate Your Data
Migrate your existing data into the new CRM. This may involve importing data from spreadsheets, databases, or other systems.
- Data Cleansing: Clean and organize your data before migrating it.
- Data Mapping: Map your existing data fields to the corresponding fields in the CRM.
- Data Import: Import your data into the CRM.
4. Train Your Team
Provide training to your team on how to use the CRM. This will ensure that everyone is familiar with the system and can use it effectively.
- Training Materials: Provide training materials, such as user manuals, videos, and online tutorials.
- Hands-on Training: Provide hands-on training to help your team learn how to use the CRM.
- Ongoing Support: Provide ongoing support to help your team troubleshoot issues and answer questions.
5. Test and Refine
Test the CRM to ensure that it’s working correctly. Identify any issues and make adjustments as needed. Refine your processes based on feedback from your team.
- Testing: Test the CRM to ensure that all features are working correctly.
- Feedback: Gather feedback from your team on their experience using the CRM.
- Refinement: Make adjustments to your processes and CRM configuration based on feedback.
Phase 4: Maximizing Your CRM’s Value
Implementation is just the beginning. To truly realize the value of your CRM, you need to continuously monitor, optimize, and adapt.
1. Track Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Identify and track key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the success of your CRM implementation. These KPIs will help you identify areas for improvement.
- Sales KPIs: Revenue, sales cycle length, conversion rates, and customer acquisition cost (CAC).
- Customer Service KPIs: Customer satisfaction scores (CSAT), net promoter scores (NPS), and average resolution time.
- Marketing KPIs: Lead generation, conversion rates, and return on investment (ROI) of marketing campaigns.
2. Monitor CRM Usage
Monitor how your team is using the CRM. Identify any areas where they may need additional training or support.
- User Activity: Track user logins, feature usage, and data entry.
- Identify Gaps: Identify any gaps in CRM usage and provide additional training or support.
3. Analyze Data and Generate Reports
Regularly analyze the data in your CRM and generate reports to gain insights into your business performance. Use these insights to make data-driven decisions.
- Sales Reports: Track sales performance, identify top-performing products, and forecast future sales.
- Customer Service Reports: Track customer satisfaction, identify common issues, and improve customer service processes.
- Marketing Reports: Track the performance of your marketing campaigns, identify top-performing channels, and optimize your marketing spend.
4. Integrate with Other Tools
Integrate your CRM with other tools you use, such as email marketing platforms, accounting software, and social media platforms. This will streamline your processes and improve efficiency.
- Email Marketing: Integrate your CRM with your email marketing platform to automate email campaigns and track results.
- Accounting Software: Integrate your CRM with your accounting software to streamline invoicing and payment processing.
- Social Media: Integrate your CRM with your social media platforms to track social media interactions and engage with customers.
5. Continuously Optimize and Adapt
Continuously optimize your CRM configuration and processes to meet your evolving business needs. Adapt to changes in the market and customer preferences.
- Regular Reviews: Regularly review your CRM configuration and processes to identify areas for improvement.
- Feedback: Gather feedback from your team on their experience using the CRM and make adjustments as needed.
- Stay Updated: Stay updated on the latest CRM features and best practices.
Advanced CRM Strategies for 2025
As technology evolves, so too will the capabilities and strategic importance of your CRM. Here are some advanced strategies to consider for 2025 and beyond:
1. AI-Powered CRM
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming the CRM landscape. Explore AI-powered features such as:
- Predictive Analytics: AI can analyze customer data to predict future behavior, such as churn risk or purchase likelihood.
- Chatbots: AI-powered chatbots can provide instant customer support and answer frequently asked questions.
- Automated Insights: AI can analyze data and provide automated insights into customer behavior, sales trends, and marketing performance.
2. Hyper-Personalization
Customers expect personalized experiences. Use your CRM to deliver hyper-personalized interactions.
- Personalized Content: Tailor your website content, email campaigns, and other marketing materials to individual customer preferences.
- Personalized Recommendations: Recommend products or services based on a customer’s past purchases, browsing history, and other data.
- Personalized Offers: Offer personalized discounts and promotions based on a customer’s individual needs and preferences.
3. Omnichannel CRM
Provide a seamless customer experience across all channels, including email, phone, chat, social media, and in-person interactions. A truly omnichannel CRM integrates data from all channels into a single view.
- Unified Customer View: Ensure that all customer interactions are tracked in a single location.
- Consistent Messaging: Deliver consistent messaging across all channels.
- Seamless Handoffs: Enable seamless handoffs between different channels.
4. CRM and the Metaverse
As the metaverse evolves, consider how your CRM can be integrated into this new digital space.
- Virtual Customer Service: Provide customer support in the metaverse.
- Virtual Sales: Conduct sales meetings and product demonstrations in the metaverse.
- Immersive Experiences: Create immersive experiences for customers in the metaverse.
5. Focus on Data Privacy and Security
Data privacy and security are paramount. Ensure your CRM complies with all relevant regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA. Implement robust security measures to protect customer data.
- Data Encryption: Encrypt customer data to protect it from unauthorized access.
- Access Controls: Implement access controls to restrict access to sensitive data.
- Regular Audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify and address vulnerabilities.
Key Takeaways: Your CRM Success Blueprint
Let’s recap the essential components of a successful CRM implementation and ongoing use for your small business:
- Start with Strategy: Define your objectives, analyze your processes, and choose the right CRM for your needs.
- Prioritize Data: Clean, accurate, and well-managed data is the lifeblood of your CRM.
- Train and Empower: Equip your team with the knowledge and skills they need to use the CRM effectively.
- Measure and Iterate: Track your KPIs, analyze your data, and continuously improve your CRM processes.
- Embrace Innovation: Stay ahead of the curve by leveraging AI, hyper-personalization, and other advanced CRM strategies.
By following this comprehensive checklist, you’ll be well-equipped to choose, implement, and leverage a CRM to drive growth, enhance customer relationships, and achieve lasting success for your small business in 2025 and beyond. Remember, a CRM is not just software; it’s a strategic investment in your future.