Seamless Harmony: Mastering CRM Integration with Flow for Unprecedented Efficiency
Seamless Harmony: Mastering CRM Integration with Flow for Unprecedented Efficiency
In today’s fast-paced business environment, the ability to streamline operations and maximize productivity is paramount. Businesses are constantly seeking innovative solutions to optimize their workflows, reduce manual tasks, and improve overall efficiency. One of the most effective ways to achieve this is through the seamless integration of Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems with workflow automation tools, often referred to as “Flow.” This article delves into the intricacies of CRM integration with Flow, exploring the benefits, implementation strategies, and best practices for achieving unprecedented efficiency.
Understanding the Power of CRM and Flow
Before we dive into the specifics of integration, it’s essential to understand the core functionalities of both CRM systems and Flow automation tools.
What is a CRM?
A Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system is a software solution designed to manage and analyze customer interactions and data throughout the customer lifecycle. It serves as a central hub for all customer-related information, including contact details, communication history, sales opportunities, and more. CRM systems empower businesses to:
- Enhance customer relationships by providing a 360-degree view of each customer.
- Improve sales performance by tracking leads, managing opportunities, and automating sales processes.
- Boost customer service by providing agents with easy access to customer information and enabling efficient issue resolution.
- Gain valuable insights into customer behavior and preferences through data analysis and reporting.
What is Flow?
Flow, often referred to as workflow automation or business process automation (BPA), is a technology that enables businesses to automate repetitive tasks and streamline complex processes. Flow tools use a visual interface to create automated workflows, which can trigger actions based on specific events or conditions. This allows businesses to:
- Reduce manual effort by automating tasks such as data entry, email notifications, and task assignments.
- Improve accuracy by minimizing human error and ensuring consistent execution of processes.
- Increase efficiency by accelerating workflows and reducing processing times.
- Free up employees’ time to focus on more strategic and value-added activities.
The Benefits of CRM Integration with Flow
Integrating CRM systems with Flow tools offers a multitude of benefits that can significantly improve business performance. Here are some key advantages:
Enhanced Data Synchronization
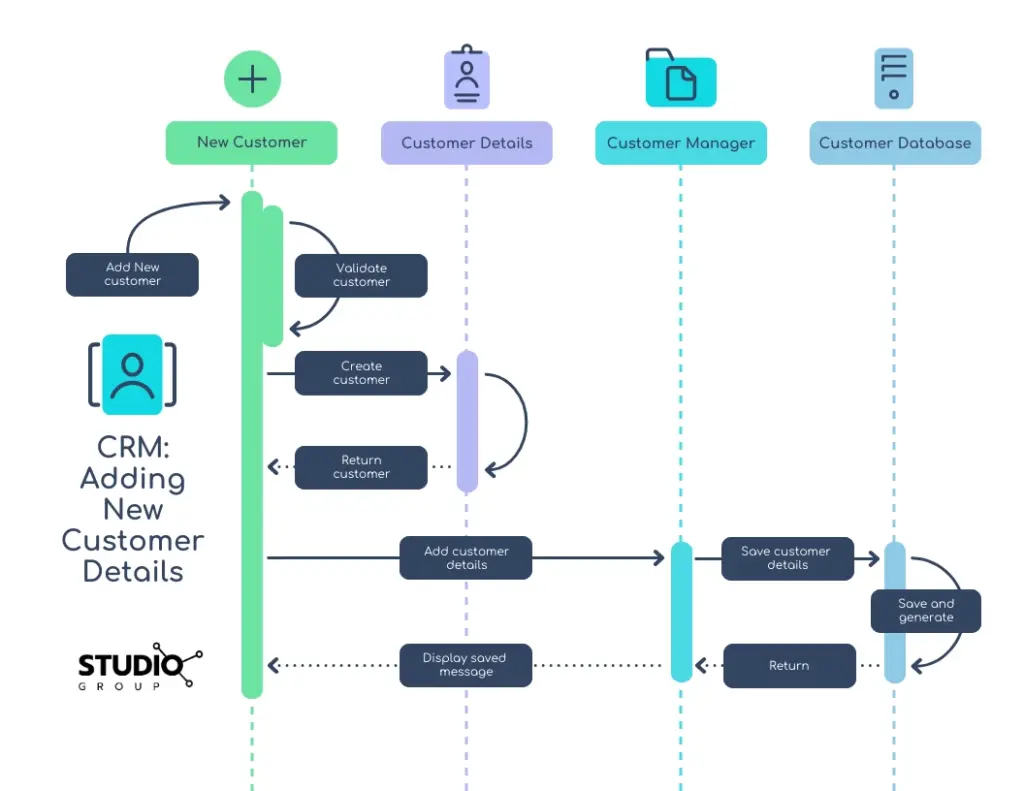
One of the primary benefits of integration is the seamless synchronization of data between CRM and Flow. This ensures that information is consistent and up-to-date across both systems. For example, when a new lead is created in the CRM, a workflow can automatically trigger the creation of a corresponding task in the Flow tool to assign the lead to a sales representative. This eliminates the need for manual data entry and reduces the risk of errors.
Automated Sales Processes
CRM integration with Flow can significantly streamline sales processes. Workflows can be designed to automate various tasks, such as lead qualification, opportunity management, and quote generation. For instance, when a sales opportunity reaches a certain stage in the CRM, a workflow can automatically trigger the generation of a quote or the assignment of a task to the appropriate team member. This automation frees up sales representatives to focus on closing deals and building relationships with customers.
Improved Customer Service
Integrating CRM with Flow can also enhance customer service operations. Workflows can be used to automate tasks such as case assignment, escalation, and follow-up. For example, when a customer submits a support ticket, a workflow can automatically assign the ticket to the appropriate agent and send an automated acknowledgment email. This ensures that customer inquiries are addressed promptly and efficiently, leading to improved customer satisfaction.
Increased Efficiency and Productivity
By automating repetitive tasks and streamlining workflows, CRM integration with Flow can significantly increase efficiency and productivity across various departments. Employees can focus on more strategic and value-added activities, leading to improved business outcomes. For instance, a marketing team can automate lead nurturing campaigns, freeing up their time to focus on creating engaging content and analyzing marketing performance.
Reduced Manual Errors
Manual data entry and processing are prone to human error. By automating these tasks through CRM integration with Flow, businesses can reduce the risk of errors and ensure data accuracy. This leads to improved decision-making and more reliable business operations.
Cost Savings
The increased efficiency and productivity resulting from CRM integration with Flow can lead to significant cost savings. By automating tasks and reducing manual effort, businesses can reduce labor costs, improve resource utilization, and optimize overall operational expenses.
Implementing CRM Integration with Flow: A Step-by-Step Guide
Successfully integrating CRM with Flow requires careful planning and execution. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you through the process:
1. Define Your Objectives and Requirements
Before you begin the integration process, it’s essential to define your objectives and requirements. What specific business processes do you want to automate? What data needs to be synchronized between the CRM and Flow tools? Clearly defining your goals will help you choose the right integration approach and ensure that the integration meets your specific needs.
2. Choose the Right Integration Method
There are several methods for integrating CRM with Flow, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Some common integration methods include:
- Native Integrations: Many CRM and Flow tools offer pre-built integrations that allow you to connect the two systems with minimal configuration. This is often the easiest and most straightforward approach.
- API Integrations: Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) allow you to create custom integrations between the CRM and Flow tools. This provides more flexibility and control over the integration process but requires more technical expertise.
- Third-Party Integration Platforms: Several third-party platforms specialize in connecting CRM and Flow tools. These platforms offer pre-built connectors and a user-friendly interface for managing integrations.
Choose the integration method that best suits your technical capabilities and business requirements.
3. Select the Right Tools
Choosing the right CRM and Flow tools is crucial for a successful integration. Consider factors such as:
- Features and Functionality: Ensure that the CRM and Flow tools offer the features and functionality you need to meet your business requirements.
- Scalability: Choose tools that can scale to accommodate your future growth.
- Ease of Use: Opt for user-friendly tools that are easy to learn and use.
- Integration Capabilities: Verify that the CRM and Flow tools can be integrated with each other using your chosen integration method.
- Cost: Consider the cost of the tools and the integration process.
4. Plan Your Data Mapping
Data mapping is the process of defining how data will be synchronized between the CRM and Flow tools. Carefully plan how data fields will be mapped to ensure that data is accurately transferred between the two systems. Consider the following:
- Data Fields: Identify the data fields that need to be synchronized.
- Data Transformation: Determine if any data transformation is required, such as converting data formats or cleaning data.
- Data Synchronization Frequency: Decide how often data should be synchronized (e.g., real-time, hourly, daily).
5. Configure the Integration
Once you’ve chosen your integration method, selected your tools, and planned your data mapping, it’s time to configure the integration. Follow the instructions provided by your CRM and Flow tools to set up the integration. This may involve entering API keys, configuring data mapping rules, and testing the integration.
6. Test the Integration
Thoroughly test the integration to ensure that data is being synchronized correctly and that workflows are functioning as expected. Test different scenarios and data flows to identify any potential issues. Make any necessary adjustments to the configuration based on your testing results.
7. Train Your Employees
Provide training to your employees on how to use the integrated CRM and Flow tools. Ensure that they understand how data is synchronized, how workflows work, and how to use the tools to perform their tasks effectively.
8. Monitor and Optimize
After the integration is live, continuously monitor its performance to ensure that it’s working as expected. Identify any bottlenecks or areas for improvement and make adjustments as needed. Regularly review your workflows and data mapping to ensure that they continue to meet your business requirements.
Best Practices for CRM Integration with Flow
To maximize the benefits of CRM integration with Flow, consider these best practices:
Start Small and Iterate
Don’t try to integrate everything at once. Start with a small set of processes and data and gradually expand the integration as you gain experience and confidence. This allows you to identify and address any issues early on and minimize disruption to your business operations.
Prioritize Data Accuracy
Ensure that data accuracy is a top priority. Implement data validation rules and cleansing processes to maintain the integrity of your data. This will ensure that your workflows are based on reliable information and that your business decisions are well-informed.
Automate Repetitive Tasks
Identify and automate repetitive tasks to free up employees’ time and improve efficiency. Focus on tasks that are time-consuming, error-prone, or manual. This will allow your employees to focus on more strategic and value-added activities.
Use Clear and Concise Workflows
Design workflows that are clear, concise, and easy to understand. Avoid overly complex workflows that can be difficult to manage and troubleshoot. Use visual aids, such as flowcharts, to illustrate your workflows and make them easier to follow.
Document Your Integration
Document your integration, including your objectives, requirements, integration method, data mapping, and workflows. This documentation will be invaluable for troubleshooting, training, and making future changes to your integration.
Regularly Review and Update Your Integration
Regularly review your integration to ensure that it continues to meet your business requirements. As your business evolves, your needs may change, and you may need to update your workflows or data mapping. Stay up-to-date with the latest features and updates of your CRM and Flow tools to take advantage of new capabilities and improve your integration.
Prioritize Security
Security should be a paramount concern when integrating CRM with Flow. Protect sensitive customer data by implementing appropriate security measures, such as data encryption, access controls, and regular security audits. Ensure that your integration complies with all relevant data privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA.
Real-World Examples of CRM Integration with Flow
To further illustrate the power of CRM integration with Flow, let’s explore some real-world examples:
Example 1: Sales Lead Nurturing
A company uses a CRM to manage its sales leads. When a new lead is created in the CRM, a workflow is triggered in the Flow tool. The workflow automatically sends a welcome email to the lead, assigns the lead to a sales representative, and creates a follow-up task for the representative. Over the next few weeks, the workflow sends a series of automated emails to the lead, providing valuable information and nurturing the lead until it’s ready to make a purchase. This automation helps the sales team to qualify leads more efficiently and increase conversion rates.
Example 2: Customer Support Ticket Management
A customer submits a support ticket through the company’s website. The CRM system receives the ticket and a Flow workflow is initiated. The workflow automatically assigns the ticket to the appropriate support agent based on the nature of the issue. It also sends an automated acknowledgment email to the customer and tracks the progress of the ticket. As the agent updates the ticket status in the CRM, the workflow triggers automated notifications to the customer, keeping them informed of the progress. Once the issue is resolved, the workflow automatically sends a satisfaction survey to the customer. This automation streamlines the support process, improves response times, and enhances customer satisfaction.
Example 3: Order Processing and Fulfillment
When a customer places an order through the company’s e-commerce platform, the order information is automatically synced to the CRM. A Flow workflow is then triggered to automate the order processing and fulfillment steps. The workflow automatically checks inventory levels, generates shipping labels, and sends order confirmation emails to the customer. It also updates the order status in the CRM as the order progresses through the fulfillment process. This automation speeds up order processing, reduces manual errors, and improves the customer experience.
Example 4: Marketing Campaign Automation
A marketing team uses the CRM to manage customer data and segment audiences for marketing campaigns. When a new marketing campaign is launched, a Flow workflow is triggered to automate the campaign execution. The workflow sends targeted email campaigns to specific customer segments, tracks email opens and clicks, and updates the CRM with the results. Based on customer engagement, the workflow can automatically adjust the campaign strategy, such as sending follow-up emails or assigning leads to sales representatives. This automation helps the marketing team to improve campaign performance and generate more leads.
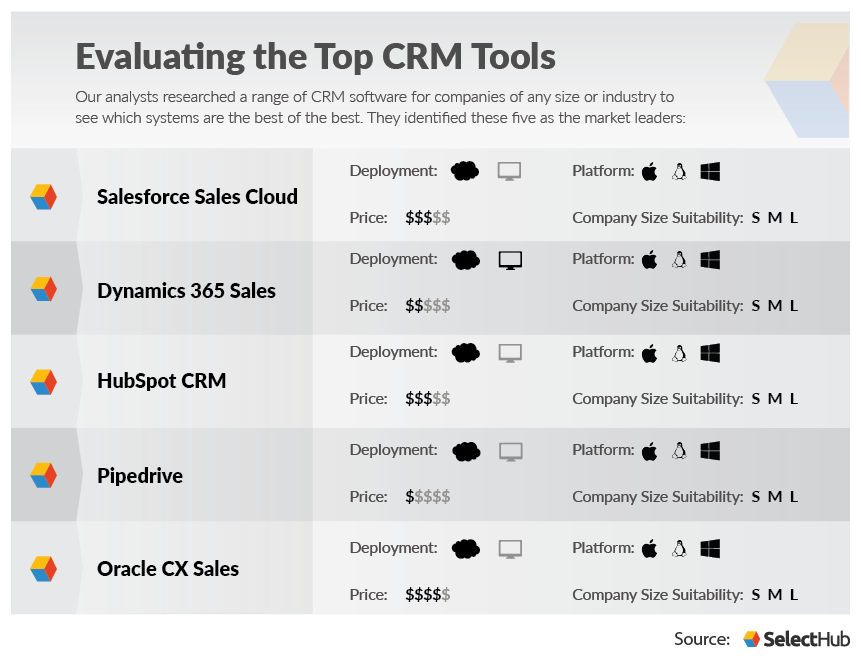
Choosing the Right CRM and Flow Tools
Selecting the appropriate CRM and Flow tools is critical for successful integration. Here are some popular options and what to consider when making your choice:
CRM Systems:
- Salesforce: A leading CRM platform known for its robust features, scalability, and extensive integration capabilities. It’s a great choice for large businesses with complex needs.
- HubSpot CRM: A free and user-friendly CRM that’s ideal for small to medium-sized businesses. It offers a comprehensive suite of marketing, sales, and customer service tools.
- Zoho CRM: A versatile CRM platform with a wide range of features and integrations. It’s a good option for businesses of all sizes.
- Microsoft Dynamics 365: A comprehensive CRM and ERP solution that integrates seamlessly with other Microsoft products. It’s a good choice for businesses that use the Microsoft ecosystem.
- Pipedrive: A sales-focused CRM that’s designed to help sales teams manage leads and close deals. It’s known for its ease of use and intuitive interface.
Flow/Workflow Automation Tools:
- Zapier: A popular integration platform that connects thousands of apps and services. It’s easy to use and offers a wide range of pre-built integrations.
- Microsoft Power Automate (formerly Microsoft Flow): A powerful workflow automation tool that integrates seamlessly with Microsoft products. It’s a good choice for businesses that use the Microsoft ecosystem.
- Integromat: A visual automation platform that allows you to connect apps and automate workflows. It offers a flexible and user-friendly interface.
- Make (formerly Integromat): Similar to Integromat, Make is a visual automation platform offering robust features and integrations. It’s a great alternative for complex automation needs.
- UiPath: A leading Robotic Process Automation (RPA) platform that can automate complex business processes. It’s a good choice for businesses that want to automate highly repetitive tasks.
When choosing your tools, consider the following:
- Integration Capabilities: Ensure that the CRM and Flow tools can be integrated with each other or with a third-party integration platform.
- Features and Functionality: Choose tools that offer the features and functionality you need to meet your business requirements.
- Ease of Use: Opt for user-friendly tools that are easy to learn and use.
- Scalability: Select tools that can scale to accommodate your future growth.
- Cost: Consider the cost of the tools and the integration process.
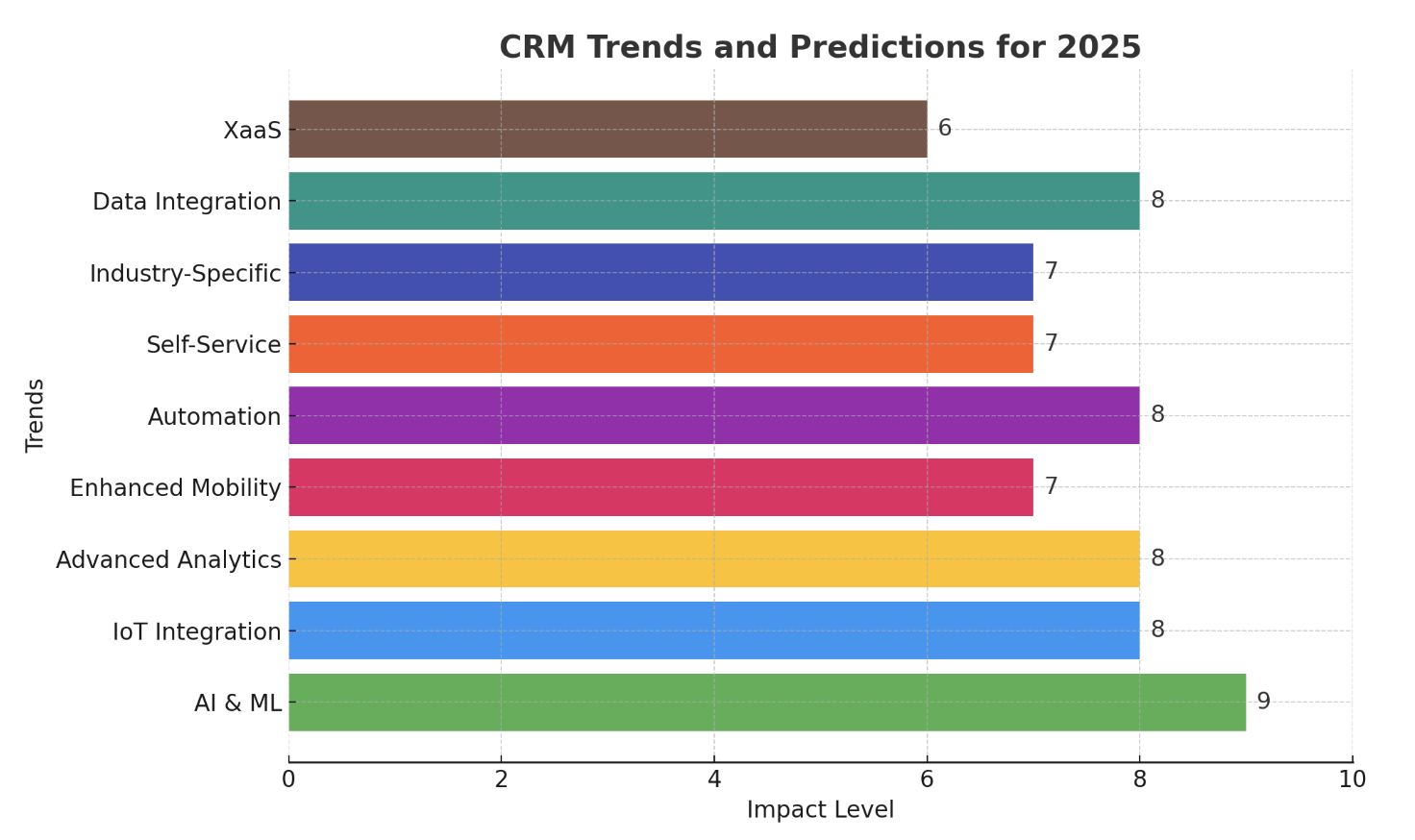
The Future of CRM Integration with Flow
The integration of CRM with Flow is constantly evolving, and new technologies are emerging to further enhance the capabilities of these systems. Some trends to watch out for include:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML are increasingly being used to automate more complex processes and provide insights into customer behavior. AI-powered workflows can analyze customer data to identify patterns, predict customer needs, and personalize customer interactions. For example, AI can be used to automate lead scoring, predict churn risk, and recommend personalized products or services.
Low-Code/No-Code Automation
Low-code/no-code platforms are making it easier for businesses to create and manage workflows without requiring extensive coding knowledge. These platforms offer a user-friendly interface and pre-built connectors that allow business users to automate processes quickly and easily. This empowers business users to take control of their workflows and make changes as needed.
Hyperautomation
Hyperautomation is the application of AI, ML, RPA, and other technologies to automate as many business processes as possible. This approach aims to create end-to-end automation across the entire organization, leading to significant improvements in efficiency and productivity. CRM integration with Flow is a key component of hyperautomation strategies.
Integration with Emerging Technologies
CRM and Flow tools are increasingly integrating with emerging technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT), blockchain, and virtual reality (VR). These integrations will enable businesses to create new customer experiences, automate new processes, and gain valuable insights from new data sources. For example, IoT devices can be integrated with CRM to track customer behavior in real-time, and blockchain can be used to secure customer data and transactions.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Integration
CRM integration with Flow is a powerful strategy for businesses looking to optimize their operations, enhance customer relationships, and drive growth. By seamlessly connecting these two essential systems, businesses can automate repetitive tasks, streamline workflows, improve data accuracy, and gain valuable insights into customer behavior. Implementing CRM integration with Flow requires careful planning, execution, and ongoing monitoring. However, the benefits are well worth the effort. By embracing the power of integration, businesses can unlock unprecedented levels of efficiency, productivity, and customer satisfaction, paving the way for long-term success in today’s competitive market.