Boost Your Small Retail Business: Why You Need a CRM and How to Choose the Best One

Boost Your Small Retail Business: Why You Need a CRM and How to Choose the Best One
Running a small retail business is a whirlwind. You’re juggling inventory, managing staff, keeping an eye on sales, and, oh yeah, trying to build relationships with your customers. In this fast-paced environment, it’s easy for customer interactions to fall through the cracks. That’s where a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system comes in. It’s not just for big corporations; a CRM can be a game-changer for small retail businesses, helping you understand your customers better, personalize their experiences, and ultimately, drive more sales. This article will dive deep into the world of CRM for small retail businesses, exploring its benefits, key features, and how to choose the right one for your specific needs.
What is CRM and Why Does Your Small Retail Business Need It?
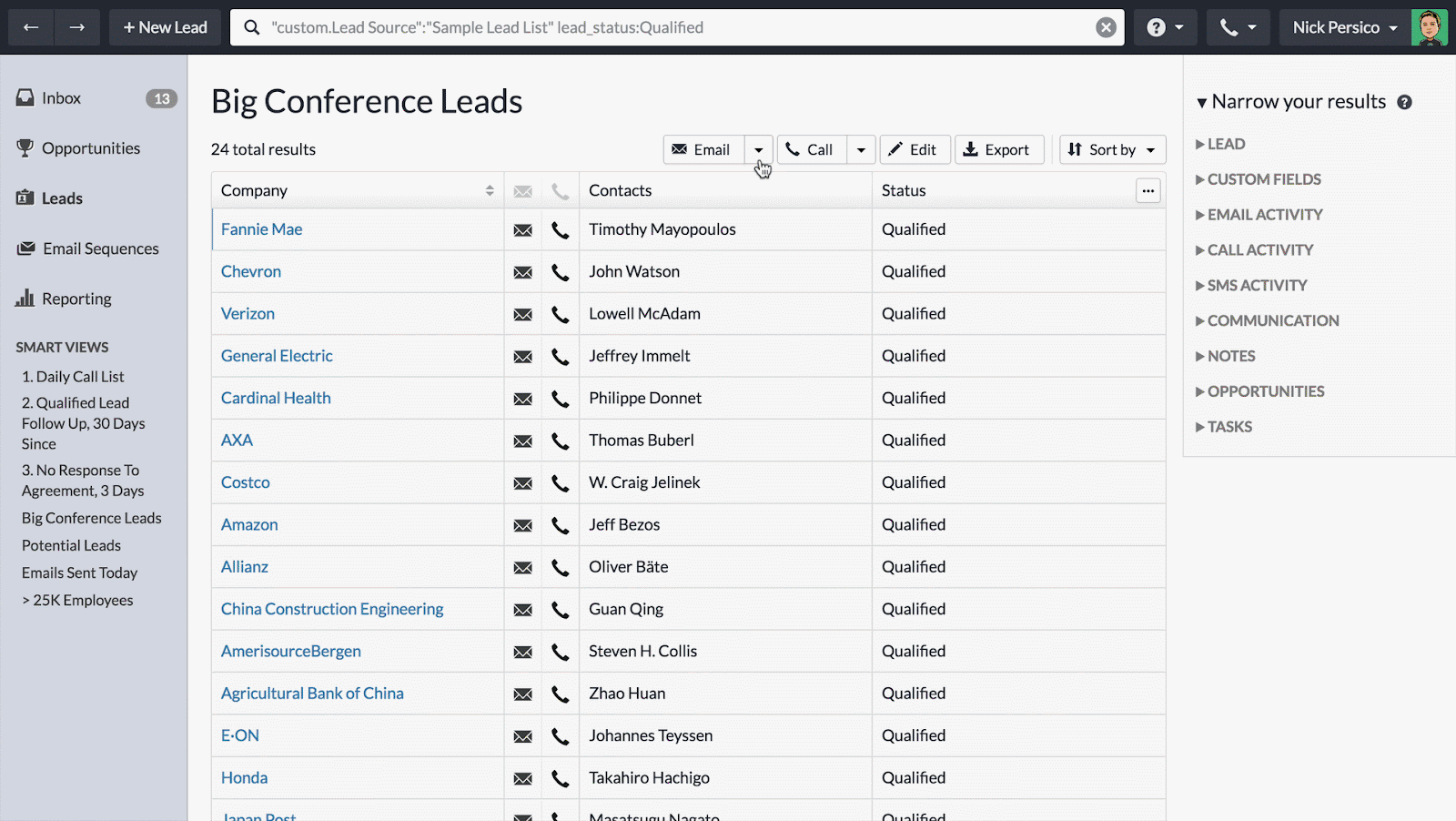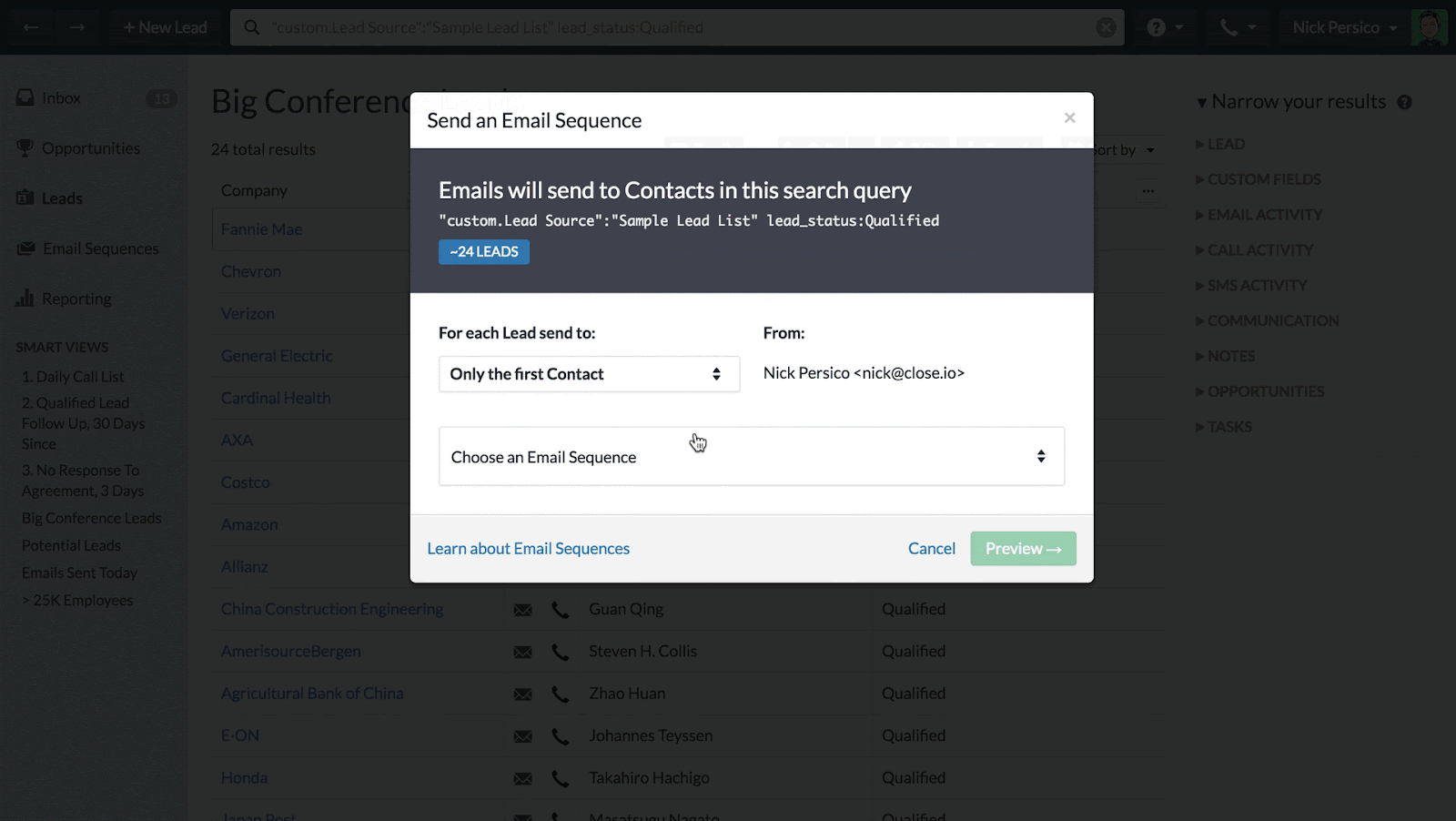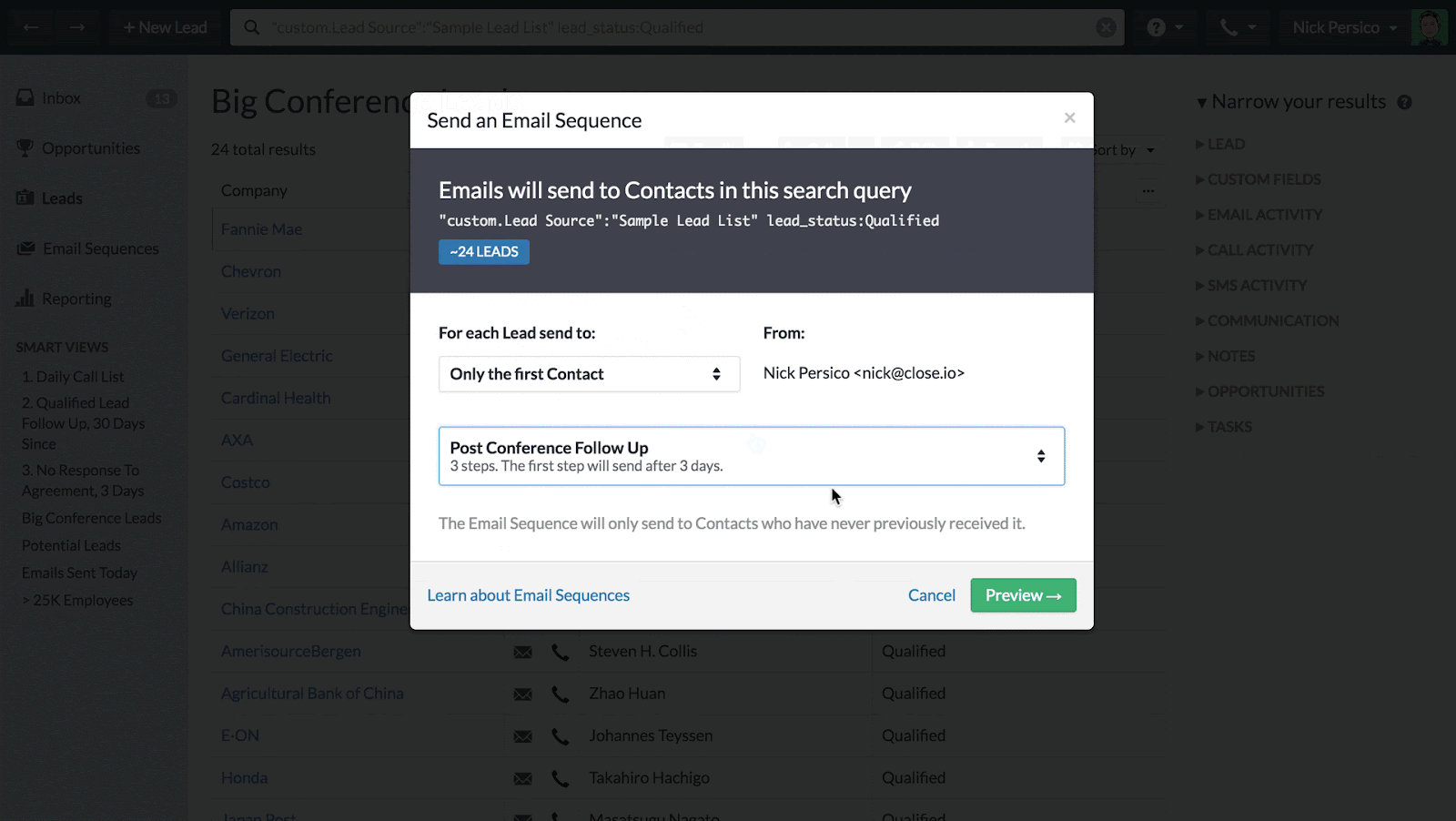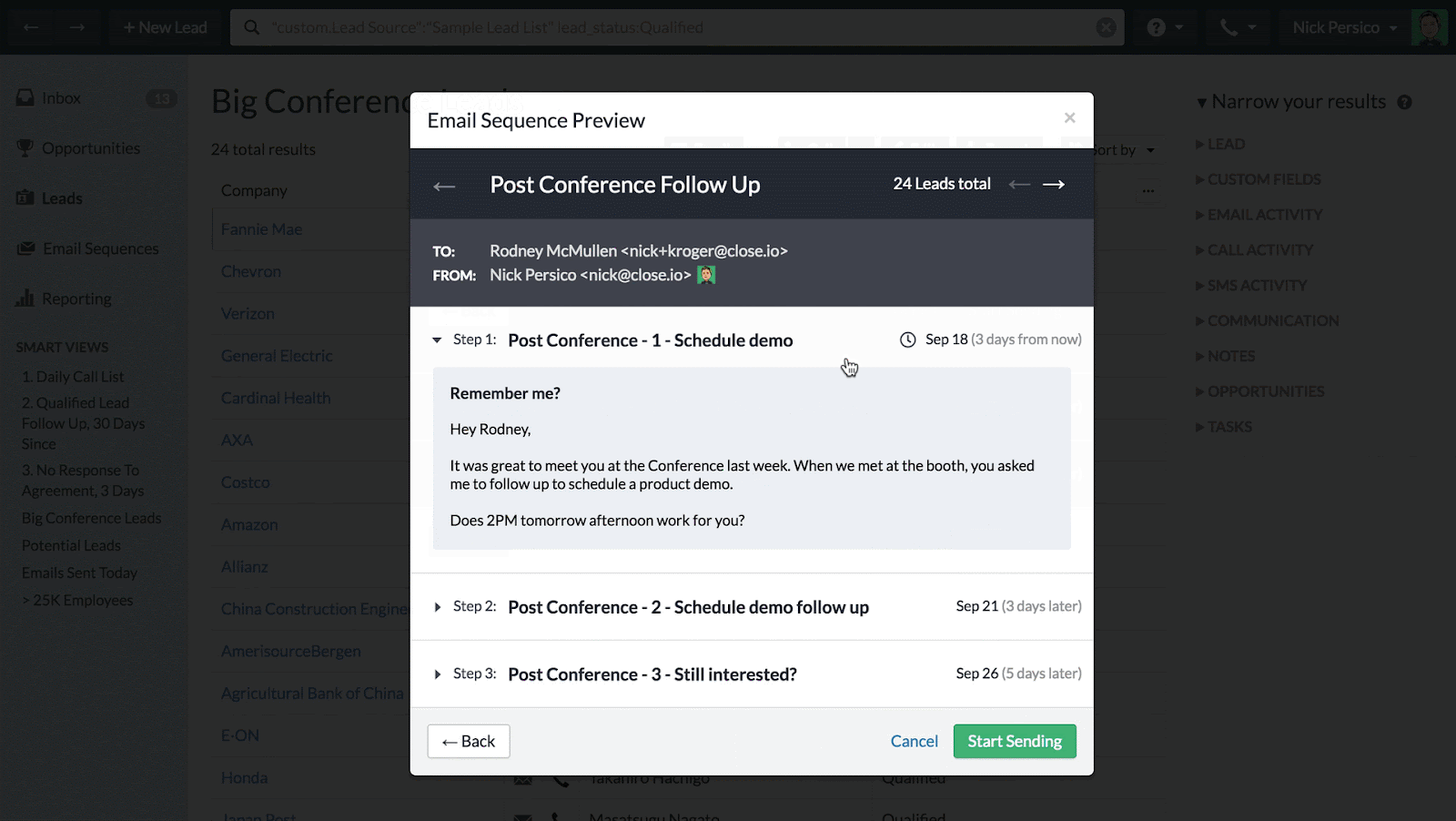
At its core, a CRM is a system that helps you manage and analyze customer interactions and data throughout the customer lifecycle. Think of it as a central hub for all things customer-related. It allows you to store customer information, track interactions, and automate tasks, freeing up your time to focus on what matters most: growing your business.
Why is this so crucial for small retail businesses? Here’s why:
- Improved Customer Relationships: A CRM helps you build stronger relationships with your customers by providing a complete view of their interactions with your business. You can personalize your communication, remember their preferences, and offer tailored recommendations.
- Increased Sales and Revenue: By understanding your customers better, you can identify opportunities to upsell and cross-sell, leading to increased sales and revenue.
- Enhanced Customer Loyalty: When customers feel valued and understood, they’re more likely to become loyal customers. A CRM helps you create a positive customer experience that keeps them coming back.
- Streamlined Operations: CRM systems automate many of the manual tasks involved in managing customer relationships, such as sending emails, scheduling appointments, and tracking leads. This frees up your time and resources, allowing you to focus on other important aspects of your business.
- Better Data Analysis: CRM systems provide valuable insights into your customer base, sales trends, and marketing performance. You can use this data to make informed decisions and optimize your business strategies.
In essence, a CRM empowers you to transform your customer interactions from fragmented and reactive to organized and proactive. It helps you move from simply selling products to building lasting relationships that drive growth.
Key Features to Look for in a CRM for Small Retail Businesses
Not all CRM systems are created equal. When choosing a CRM for your small retail business, it’s essential to consider the features that are most relevant to your specific needs. Here are some key features to look for:
Contact Management
This is the foundation of any CRM system. It allows you to store and manage customer contact information, including names, addresses, phone numbers, email addresses, and social media profiles. Look for a CRM that allows you to easily import and export contact data, search and filter contacts, and add custom fields to capture specific information relevant to your business.
Sales Tracking
A good CRM should allow you to track sales opportunities, manage leads, and monitor the sales pipeline. This feature helps you identify potential customers, track their progress through the sales process, and close deals more effectively. Look for features like sales forecasting, deal tracking, and sales reports.
Marketing Automation
Marketing automation features can help you automate repetitive marketing tasks, such as sending email campaigns, creating social media posts, and segmenting your customer base. This saves you time and allows you to reach your customers with targeted messages. Look for features like email marketing, social media integration, and lead scoring.
Customer Service and Support
A CRM can help you provide excellent customer service by tracking customer inquiries, managing support tickets, and providing a centralized location for customer interactions. This ensures that your customers receive prompt and efficient support. Look for features like help desk integration, live chat, and knowledge base functionality.
Reporting and Analytics
Reporting and analytics features provide valuable insights into your customer base, sales trends, and marketing performance. This data helps you make informed decisions and optimize your business strategies. Look for features like sales reports, customer segmentation, and marketing performance dashboards.
Integration with Other Tools
Your CRM should integrate seamlessly with other tools you use, such as your point of sale (POS) system, e-commerce platform, and accounting software. This allows you to streamline your operations and avoid data silos. Look for integrations with popular platforms like Shopify, WooCommerce, and Quickbooks.
Mobile Access
In today’s fast-paced world, it’s essential to have access to your CRM data on the go. Look for a CRM that offers a mobile app or a mobile-friendly interface, so you can access customer information, track sales, and manage your business from anywhere.
User-Friendly Interface
The CRM should be easy to use and intuitive, even for users with limited technical skills. Look for a CRM with a clean and modern interface, clear instructions, and helpful tutorials.
Choosing the Right CRM: A Step-by-Step Guide
Choosing the right CRM can feel overwhelming, but by following a systematic approach, you can make an informed decision. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
1. Define Your Needs and Goals
Before you start evaluating CRM systems, take the time to define your specific needs and goals. What are you hoping to achieve with a CRM? What are the biggest challenges you’re facing in managing customer relationships? Identify the key features that are essential for your business.
2. Research CRM Options
Once you know your needs, start researching CRM options. There are many different CRM systems available, ranging from simple, affordable solutions to more complex, feature-rich platforms. Consider factors like pricing, features, ease of use, and integration capabilities.
3. Create a Shortlist
Narrow down your options to a shortlist of 3-5 CRM systems that seem like a good fit for your business. Based on your research, eliminate any options that are clearly not a good fit based on your requirements.
4. Request Demos and Trials
Request demos or free trials of the CRM systems on your shortlist. This will allow you to see the CRM in action and get a feel for its features and usability. Pay close attention to the user interface, ease of navigation, and the availability of support resources.
5. Evaluate and Compare
During the demo or trial period, evaluate each CRM based on your needs and goals. Compare the features, pricing, and ease of use of each system. Consider factors like customer support, training resources, and integration capabilities.
6. Get Feedback from Your Team
Involve your team in the decision-making process. Get their feedback on the CRM systems they have tried and their opinions on which system is the best fit for your business. Their input is important as they will be the ones using the system daily.
7. Make Your Decision and Implement
Based on your evaluation and feedback, make your final decision and choose the CRM that best meets your needs. Once you’ve selected a CRM, it’s time to implement it. Develop an implementation plan, train your team, and start using the CRM to manage your customer relationships.
Top CRM Systems for Small Retail Businesses
Here are some of the top CRM systems for small retail businesses, each with its own strengths and weaknesses:
Zoho CRM
Zoho CRM is a popular choice for small businesses due to its affordability, ease of use, and comprehensive features. It offers a wide range of features, including contact management, sales tracking, marketing automation, and customer service tools. Zoho CRM integrates with a variety of third-party apps and offers a free plan for up to three users.
HubSpot CRM
HubSpot CRM is a free, user-friendly CRM that’s ideal for small businesses that are new to CRM. It offers a range of features, including contact management, sales tracking, and marketing automation tools. HubSpot CRM integrates with a variety of third-party apps and offers a paid version with more advanced features.
Salesforce Sales Cloud Essentials
Salesforce Sales Cloud Essentials is a more advanced CRM platform that’s suitable for small businesses that are looking for a robust and scalable solution. It offers a wide range of features, including contact management, sales tracking, marketing automation, and customer service tools. Salesforce Sales Cloud Essentials integrates with a vast ecosystem of third-party apps and offers a paid version with more advanced features.
Pipedrive
Pipedrive is a sales-focused CRM that’s designed to help small businesses manage their sales pipeline and close deals more effectively. It offers a range of features, including contact management, sales tracking, and sales automation tools. Pipedrive integrates with a variety of third-party apps and offers a paid version with more advanced features.
Freshsales
Freshsales is a CRM that is part of the Freshworks suite of products. It is known for its ease of use and intuitive interface. It offers features like contact management, sales tracking, and built-in telephony. Freshsales is a good option for businesses looking for a CRM that is easy to set up and use.
Tips for Successful CRM Implementation
Implementing a CRM is an investment, and to ensure its success, keep these tips in mind:
- Get Buy-In from Your Team: Involve your team in the CRM selection and implementation process. Make sure they understand the benefits of the CRM and how it will help them do their jobs more effectively.
- Provide Training and Support: Provide your team with adequate training on how to use the CRM. Offer ongoing support and resources to help them get the most out of the system.
- Start Small and Scale Up: Don’t try to implement all the features of your CRM at once. Start with the core features and gradually add more features as your team becomes more comfortable with the system.
- Clean Up Your Data: Before you import your customer data into the CRM, take the time to clean it up. Remove duplicates, correct errors, and ensure that your data is accurate and complete.
- Set Clear Goals and Metrics: Define your goals for using the CRM and track your progress. Use metrics to measure the success of your CRM implementation and identify areas for improvement.
- Customize Your CRM: Tailor your CRM to meet the specific needs of your business. Customize fields, workflows, and reports to ensure that the CRM is aligned with your business processes.
- Regularly Review and Optimize: Regularly review your CRM usage and make adjustments as needed. Identify areas for improvement and optimize your CRM configuration to ensure that it’s meeting your evolving needs.
The Future of CRM in Retail
The world of CRM is constantly evolving, and there are several trends that are shaping the future of CRM in retail:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is being used to automate tasks, personalize customer experiences, and provide valuable insights into customer behavior.
- Mobile CRM: Mobile CRM solutions are becoming increasingly important, as they allow retailers to access customer data and manage their businesses from anywhere.
- Omnichannel CRM: Omnichannel CRM systems integrate data from all customer touchpoints, providing a unified view of the customer journey.
- Customer Data Platforms (CDPs): CDPs are becoming increasingly popular, as they help retailers collect, manage, and analyze customer data from multiple sources.
- Focus on Customer Experience: The customer experience is becoming more important than ever, and CRM systems are playing a key role in helping retailers create positive and memorable customer experiences.
As these trends continue to evolve, CRM systems will become even more powerful and essential for small retail businesses.
Final Thoughts
Implementing a CRM might seem daunting, but the benefits for your small retail business are undeniable. By choosing the right system and following these tips, you can transform your customer interactions, boost sales, and build lasting relationships. Take the time to assess your needs, research the options, and make the investment in a CRM that will empower your business to thrive in today’s competitive retail landscape. The payoff – happier customers, increased sales, and a thriving business – is well worth the effort.