Unlocking Growth: A Deep Dive into CRM Marketing Performance and How to Maximize It
In today’s hyper-competitive business landscape, understanding and optimizing your Customer Relationship Management (CRM) marketing performance isn’t just beneficial; it’s essential for survival and sustained growth. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the world of CRM marketing, exploring its intricacies, benefits, and, most importantly, how to leverage it to achieve remarkable results. We’ll cover everything from the fundamentals of CRM and its role in marketing to advanced strategies for data analysis, personalization, and campaign optimization. Get ready to transform your marketing efforts and unlock your full potential.
What is CRM Marketing? A Foundation for Success
At its core, CRM marketing is a strategic approach that uses customer relationship management systems to improve customer interactions and boost sales. It’s about more than just collecting customer data; it’s about using that data to understand your customers, personalize your interactions, and build lasting relationships. Think of it as the engine that drives customer-centricity within your marketing strategy.
A robust CRM system acts as the central nervous system, storing and organizing all customer-related information, including contact details, purchase history, communication logs, and preferences. This 360-degree view of your customers enables you to make informed decisions, tailor your marketing messages, and deliver exceptional customer experiences. Without a well-integrated CRM system, your marketing efforts are like shooting in the dark – relying on guesswork rather than data-driven insights.
The Key Benefits of CRM Marketing
Implementing a CRM marketing strategy offers a multitude of advantages for businesses of all sizes:
- Improved Customer Retention: By understanding customer behavior and preferences, you can proactively address their needs and build stronger relationships, leading to increased loyalty and reduced churn.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Personalized interactions and proactive communication contribute to a more positive customer experience, resulting in higher satisfaction levels.
- Increased Sales and Revenue: Targeted marketing campaigns and personalized offers drive conversions and generate more sales.
- Greater Marketing Efficiency: Automating marketing tasks and streamlining workflows frees up time and resources, allowing your team to focus on strategic initiatives.
- Better Data Analysis and Reporting: CRM systems provide valuable insights into customer behavior, campaign performance, and overall marketing effectiveness, enabling data-driven decision-making.
- Improved Lead Management: CRM systems help you track and nurture leads, ensuring that no potential customer falls through the cracks.
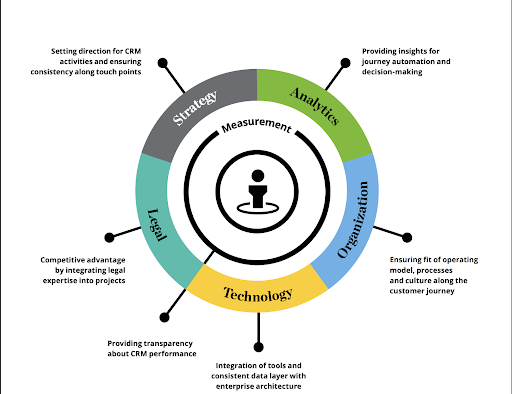
Building Blocks of CRM Marketing Performance
To achieve optimal CRM marketing performance, it’s crucial to understand the key components that contribute to its success. These include:
1. Data Collection and Management
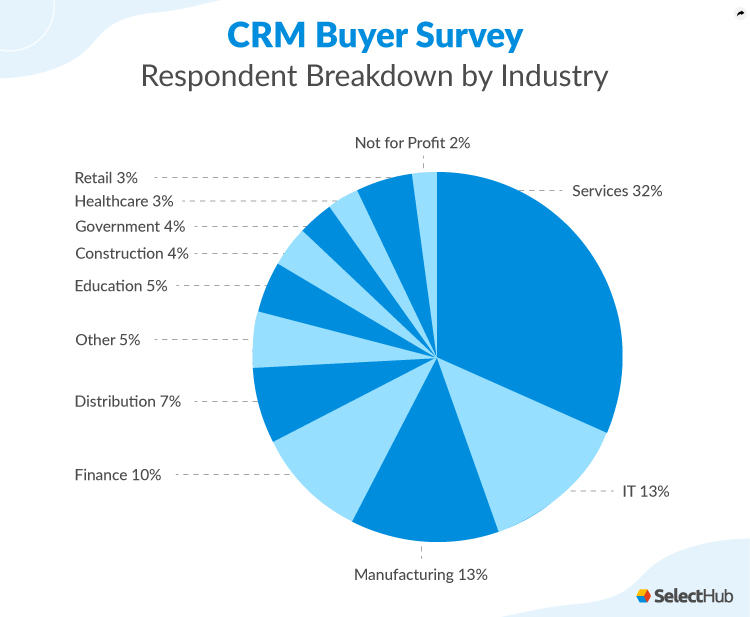
Data is the lifeblood of any successful CRM marketing strategy. The more comprehensive and accurate your data, the better you’ll understand your customers and tailor your marketing efforts. Key aspects of data collection and management include:
- Data Sources: Identify all potential data sources, including your website, social media channels, email marketing platforms, sales interactions, and customer surveys.
- Data Quality: Implement processes to ensure data accuracy and completeness. Regularly cleanse and update your data to remove duplicates and outdated information.
- Data Segmentation: Divide your customer base into segments based on demographics, behaviors, and preferences. This allows you to create targeted marketing campaigns that resonate with specific groups.
- Data Security and Privacy: Adhere to all relevant data privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA, and implement robust security measures to protect customer data.
2. Segmentation and Targeting
Once you have collected and organized your customer data, the next step is to segment your audience and target specific groups with tailored marketing messages. Effective segmentation and targeting involve:
- Defining Target Personas: Create detailed profiles of your ideal customers, including their demographics, interests, behaviors, and pain points.
- Segmenting Your Audience: Divide your customer base into meaningful segments based on shared characteristics. Common segmentation criteria include demographics, purchase history, website activity, and engagement levels.
- Developing Targeted Campaigns: Create marketing campaigns that are specifically designed to appeal to each segment. This includes tailoring your messaging, offers, and channels to resonate with their unique needs and preferences.
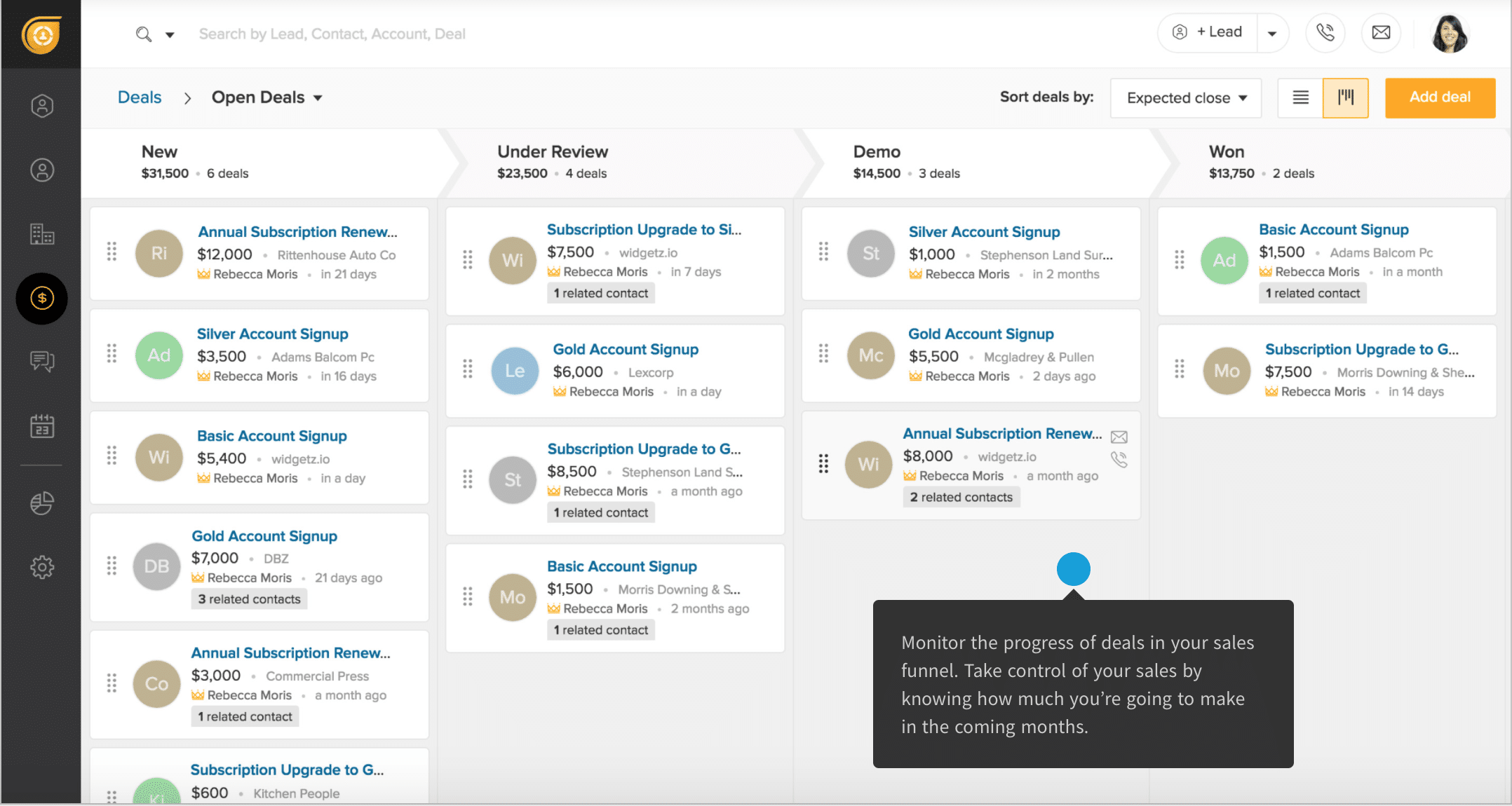
3. Campaign Management
Campaign management is the process of planning, executing, and monitoring your marketing campaigns. Effective campaign management involves:
- Defining Campaign Goals: Clearly define the objectives of each campaign, such as generating leads, increasing sales, or improving customer retention.
- Selecting Channels: Choose the most appropriate marketing channels for each campaign, such as email, social media, SMS, or paid advertising.
- Creating Compelling Content: Develop engaging and relevant content that resonates with your target audience.
- Setting Up Automation Workflows: Automate repetitive tasks, such as sending welcome emails, nurturing leads, and following up with customers.
- Tracking and Analyzing Results: Monitor the performance of your campaigns and analyze the results to identify areas for improvement.
4. Personalization
Personalization is the art of tailoring your marketing messages and experiences to individual customers. It’s about making each customer feel valued and understood. Effective personalization involves:
- Personalizing Email Marketing: Use customer data to personalize email subject lines, content, and offers.
- Personalizing Website Experiences: Customize your website content and design based on customer behavior and preferences.
- Personalizing Product Recommendations: Suggest relevant products and services based on customer purchase history and browsing activity.
- Personalizing Customer Service: Provide personalized customer service interactions based on customer history and needs.
5. Automation
Marketing automation streamlines repetitive tasks, freeing up your team to focus on more strategic initiatives. Key areas for automation include:
- Email Marketing Automation: Automate email sequences for lead nurturing, onboarding, and customer retention.
- Social Media Automation: Schedule social media posts and automate engagement activities.
- Lead Scoring and Routing: Automatically score leads based on their behavior and route them to the appropriate sales representatives.
- Workflow Automation: Automate various marketing processes, such as campaign setup, reporting, and data updates.
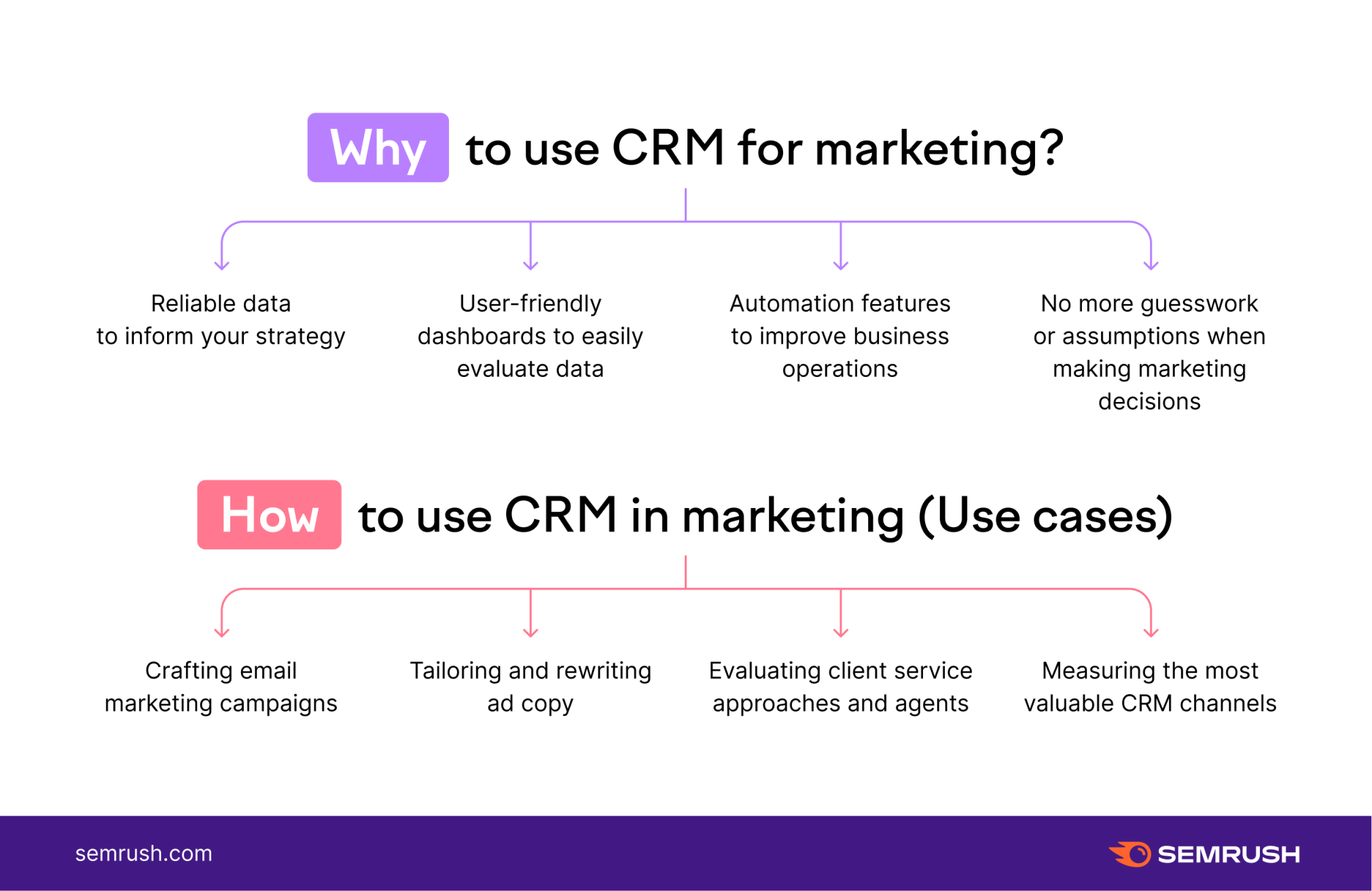
Measuring and Analyzing CRM Marketing Performance
To truly understand the effectiveness of your CRM marketing efforts, you need to track and analyze key performance indicators (KPIs). This data-driven approach allows you to identify what’s working, what’s not, and make informed decisions to optimize your campaigns.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to Track
Here are some of the most important KPIs to monitor:
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): The cost of acquiring a new customer.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV): The predicted revenue a customer will generate over their relationship with your business.
- Conversion Rates: The percentage of customers who complete a desired action, such as making a purchase or filling out a form.
- Click-Through Rates (CTR): The percentage of people who click on a link in your email or ad.
- Open Rates: The percentage of people who open your emails.
- Customer Retention Rate: The percentage of customers who remain customers over a specific period.
- Churn Rate: The percentage of customers who stop doing business with you.
- Return on Investment (ROI): The profitability of your marketing campaigns.
- Lead Generation: The number of new leads generated through your marketing efforts.
- Website Traffic: The number of visitors to your website.
- Social Media Engagement: The level of interaction with your content on social media.
Data Analysis and Reporting
Regularly analyze your CRM marketing data to identify trends, patterns, and areas for improvement. Create reports that summarize your key findings and provide actionable insights. Key aspects of data analysis and reporting include:
- Data Visualization: Use charts and graphs to visualize your data and make it easier to understand.
- Cohort Analysis: Analyze the behavior of customer cohorts over time to identify trends and patterns.
- A/B Testing: Experiment with different variations of your marketing campaigns to determine which ones perform best.
- Reporting Tools: Utilize CRM reporting tools to generate automated reports and track your progress.
- Regular Reviews: Conduct regular reviews of your marketing performance to identify areas for improvement and make adjustments to your strategy.
Strategies for Optimizing CRM Marketing Performance
Once you have a solid understanding of your CRM marketing performance, you can implement strategies to optimize your campaigns and achieve better results. Here are some key strategies to consider:
1. Enhance Data Quality
As mentioned earlier, data is the foundation of successful CRM marketing. Regularly review and cleanse your data to ensure its accuracy, completeness, and relevance. This includes:
- Data Cleansing: Remove duplicate records, correct errors, and update outdated information.
- Data Enrichment: Supplement your existing data with additional information, such as demographic details and purchase history.
- Data Governance: Implement processes and policies to ensure data quality and consistency.
2. Refine Segmentation and Targeting
Continuously refine your segmentation and targeting strategies to ensure that your marketing messages are reaching the right people. This includes:
- Regularly Reviewing Personas: Update your customer personas to reflect changes in customer behavior and preferences.
- Testing Different Segments: Experiment with different segmentation criteria to identify the most effective segments.
- Personalizing Messaging: Tailor your messaging to the specific needs and interests of each segment.
3. Improve Campaign Performance
Continuously monitor and optimize your marketing campaigns to improve their performance. This includes:
- A/B Testing: Test different variations of your campaigns to identify what works best.
- Optimizing Email Subject Lines: Experiment with different subject lines to improve open rates.
- Improving Landing Page Conversions: Optimize your landing pages to increase conversions.
- Testing Different Channels: Experiment with different marketing channels to reach your target audience.
4. Leverage Marketing Automation
Marketing automation can significantly improve your efficiency and effectiveness. Implement automation workflows for:
- Lead Nurturing: Automate the process of nurturing leads through the sales funnel.
- Onboarding: Automate the onboarding process for new customers.
- Customer Retention: Automate the process of retaining existing customers.
- Personalized Communication: Use automation to send personalized communications to your customers.
5. Enhance Personalization
Personalization is key to creating a positive customer experience. Implement personalization strategies for:
- Personalized Email Marketing: Use customer data to personalize email subject lines, content, and offers.
- Personalized Website Experiences: Customize your website content and design based on customer behavior and preferences.
- Personalized Product Recommendations: Suggest relevant products and services based on customer purchase history and browsing activity.
- Personalized Customer Service: Provide personalized customer service interactions based on customer history and needs.
6. Integrate Your CRM with Other Systems
Integrate your CRM system with other systems, such as your website, e-commerce platform, and social media channels, to create a seamless customer experience. This integration will allow you to:
- Track Customer Behavior: Track customer behavior across all touchpoints.
- Personalize Interactions: Personalize interactions based on customer behavior.
- Automate Workflows: Automate workflows across different systems.
- Gain a Holistic View of the Customer: Gain a holistic view of the customer.
Choosing the Right CRM System
Selecting the right CRM system is crucial for the success of your CRM marketing efforts. Consider the following factors when choosing a CRM system:
- Features and Functionality: Choose a CRM system that offers the features and functionality you need to manage your customer relationships effectively.
- Scalability: Select a CRM system that can scale to meet your growing needs.
- Integration Capabilities: Ensure that the CRM system can integrate with your existing systems.
- Ease of Use: Choose a CRM system that is easy to use and navigate.
- Cost: Consider the cost of the CRM system, including licensing fees, implementation costs, and ongoing maintenance costs.
- Vendor Reputation: Research the vendor’s reputation and customer reviews.
- Support and Training: Ensure that the vendor offers adequate support and training.
The Future of CRM Marketing
CRM marketing is constantly evolving, and several trends are shaping its future. These include:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is being used to automate tasks, personalize customer interactions, and provide data-driven insights.
- Machine Learning (ML): ML is being used to predict customer behavior and personalize marketing campaigns.
- Omnichannel Marketing: Businesses are using multiple channels to interact with customers, creating a seamless customer experience.
- Customer Data Platforms (CDPs): CDPs are being used to collect and manage customer data from multiple sources.
- Privacy and Data Security: Businesses are prioritizing data privacy and security to protect customer data.
Conclusion: Embracing CRM Marketing for Sustainable Growth
CRM marketing is a powerful strategy that can transform your marketing efforts and drive sustainable growth. By understanding the fundamentals, implementing effective strategies, and continuously optimizing your performance, you can build stronger customer relationships, increase sales, and achieve your business goals. Embrace the power of CRM marketing and unlock your full potential. It’s not just about technology; it’s about understanding your customers, building relationships, and providing exceptional experiences. That is the essence of truly successful CRM marketing.
By consistently refining your strategies, embracing new technologies, and focusing on the customer, you can stay ahead of the curve and thrive in today’s dynamic market.