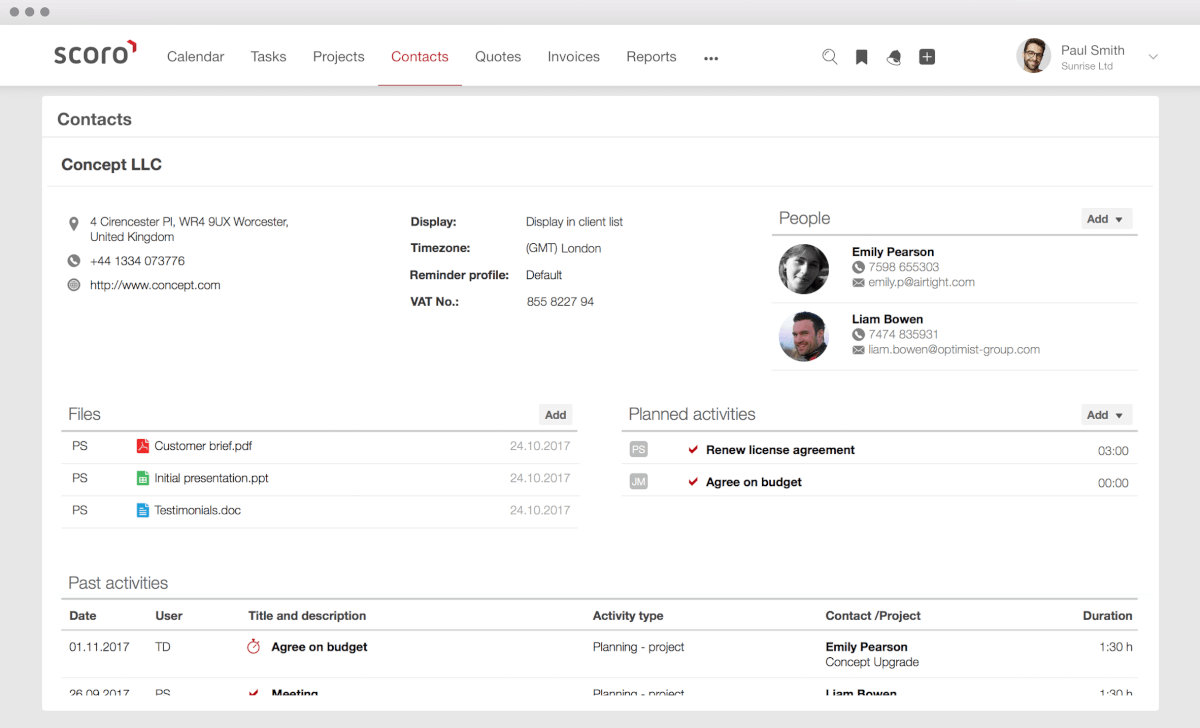
Introduction: The Small Business Revolution and the Power of CRM
In the dynamic world of small businesses, survival isn’t just about having a great product or service; it’s about building meaningful relationships. It’s about understanding your customers, anticipating their needs, and delivering experiences that keep them coming back for more. This is where a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system steps in, becoming a cornerstone for sustained growth and success. This article dives deep into the world of CRM, exploring how it can revolutionize your small business, turning potential into profit and chaos into clarity.
The landscape of small business is constantly evolving. Competition is fierce, customer expectations are higher than ever, and the tools available to entrepreneurs are more sophisticated than ever before. To thrive, small businesses need to be agile, responsive, and, above all, customer-centric. CRM systems provide the framework for achieving all of these, offering a centralized hub for managing interactions, streamlining processes, and gaining valuable insights into your customer base.
This isn’t just about big corporations anymore. Affordable and user-friendly CRM solutions are now accessible to businesses of all sizes, making it easier than ever to harness the power of customer data. From tracking leads and managing sales pipelines to providing personalized customer service and automating marketing campaigns, a CRM system can be the engine that drives your small business forward.
Understanding the Basics: What is CRM and Why Does it Matter?
At its core, a CRM system is a technology that helps you manage all your company’s relationships and interactions with customers and potential customers. Think of it as a central repository for all the information you have about your customers: their contact details, purchase history, communication logs, and any other relevant data. This information is then used to improve customer relationships, drive sales growth, and ultimately, increase profitability.
But why is CRM so critical for small businesses? The answer lies in the fundamental shift in how businesses operate. Today, customers expect personalized experiences. They want to feel valued and understood. They want businesses to remember their preferences and anticipate their needs. A CRM system empowers you to deliver on these expectations.
Here are some key benefits of implementing a CRM system:
- Improved Customer Relationships: By providing a 360-degree view of each customer, CRM helps you understand their needs, preferences, and behaviors, enabling you to build stronger, more meaningful relationships.
- Increased Sales: CRM systems streamline the sales process, helping you track leads, manage opportunities, and close deals more efficiently.
- Enhanced Customer Service: CRM enables you to provide faster, more personalized customer service, leading to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Better Data Analysis: CRM systems provide valuable insights into your customer base, allowing you to identify trends, understand customer behavior, and make data-driven decisions.
- Increased Efficiency: By automating tasks and streamlining processes, CRM systems free up your time so you can focus on more strategic initiatives.
Key Features to Look for in a CRM System
Choosing the right CRM system can feel overwhelming, but focusing on the core features that align with your business needs will simplify the process. Here are some essential features to consider:
- Contact Management: This is the foundation of any CRM system. It allows you to store and manage all your customer contact information, including names, addresses, phone numbers, email addresses, and social media profiles.
- Lead Management: This feature helps you track and nurture potential customers, from initial contact to conversion. It includes lead scoring, lead tracking, and automated follow-up capabilities.
- Sales Force Automation (SFA): SFA tools streamline the sales process by automating tasks such as lead assignment, opportunity tracking, and sales forecasting.
- Marketing Automation: Many CRM systems offer marketing automation features, such as email marketing, social media integration, and campaign management.
- Customer Service and Support: This feature enables you to manage customer inquiries, track support tickets, and provide personalized customer service.
- Reporting and Analytics: CRM systems should provide robust reporting and analytics capabilities, allowing you to track key performance indicators (KPIs), analyze trends, and make data-driven decisions.
- Integration: Look for a CRM system that integrates with other tools you use, such as email marketing platforms, accounting software, and social media channels.
- Mobile Access: In today’s mobile world, it’s crucial to have access to your CRM data on the go. Ensure your chosen system offers a mobile app or a mobile-friendly interface.
- Customization: The ability to customize the CRM system to meet your specific business needs is essential. Look for a system that allows you to add custom fields, create custom reports, and tailor the interface to your preferences.
The Benefits of CRM for Small Business: A Deep Dive
The advantages of adopting a CRM system for your small business are numerous and far-reaching. Let’s explore some of the most significant benefits in more detail:
Boosting Sales and Revenue
A CRM system can significantly boost your sales and revenue in several ways. By streamlining the sales process, CRM helps your sales team close deals more efficiently. Lead management tools allow you to track and nurture leads, ensuring that no potential customer falls through the cracks. Sales force automation features automate repetitive tasks, freeing up your sales team to focus on building relationships and closing deals. CRM also provides sales forecasting capabilities, allowing you to predict future sales and make informed decisions about resource allocation.
With a CRM, you can:
- Improve Lead Conversion Rates: By tracking leads and nurturing them through the sales pipeline, CRM helps you convert more leads into paying customers.
- Increase Sales Productivity: Automation and streamlined processes free up your sales team to focus on selling.
- Identify Upselling and Cross-selling Opportunities: By understanding your customers’ purchase history and preferences, CRM helps you identify opportunities to upsell and cross-sell products and services.
- Improve Sales Forecasting Accuracy: Accurate sales forecasts allow you to make better decisions about inventory, staffing, and other resources.
Enhancing Customer Relationships
Building strong customer relationships is the cornerstone of any successful business. A CRM system provides the tools you need to foster these relationships. By providing a 360-degree view of each customer, CRM helps you understand their needs, preferences, and behaviors. You can then use this information to personalize your interactions, provide proactive support, and build lasting loyalty. CRM enables you to track customer interactions, ensuring that every interaction is consistent and aligned with your brand values.
With a CRM, you can:
- Personalize Customer Interactions: By understanding your customers’ needs and preferences, you can tailor your communications and provide personalized experiences.
- Improve Customer Satisfaction: Faster response times, personalized service, and proactive support lead to increased customer satisfaction.
- Increase Customer Loyalty: Building strong relationships with your customers leads to increased loyalty and repeat business.
- Gather Customer Feedback: CRM systems can be used to gather customer feedback, allowing you to identify areas for improvement and better meet customer needs.
Streamlining Customer Service
Providing excellent customer service is essential for retaining customers and building a positive brand reputation. A CRM system streamlines customer service operations, making it easier to manage inquiries, track support tickets, and provide personalized support. CRM systems often include features such as a knowledge base, which allows customers to find answers to their questions quickly. Automation features, such as automated email responses and ticket routing, improve efficiency and reduce response times.
With a CRM, you can:
- Reduce Response Times: Automation and efficient ticket management reduce the time it takes to respond to customer inquiries.
- Improve Issue Resolution: CRM helps you track and manage customer issues, ensuring that they are resolved quickly and effectively.
- Provide Personalized Support: By understanding your customers’ history and preferences, you can provide personalized support that meets their individual needs.
- Improve Customer Service Efficiency: Automation and streamlined processes free up your customer service team to focus on resolving complex issues.
Improving Data Analysis and Decision-Making
Data is the lifeblood of any successful business. A CRM system provides valuable insights into your customer base, allowing you to identify trends, understand customer behavior, and make data-driven decisions. CRM systems offer robust reporting and analytics capabilities, allowing you to track key performance indicators (KPIs), analyze sales data, and measure the effectiveness of your marketing campaigns. This data can inform your business strategy, help you identify areas for improvement, and ultimately, drive growth.
With a CRM, you can:
- Track Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Monitor sales, marketing, and customer service metrics to track your progress and identify areas for improvement.
- Analyze Sales Data: Identify top-performing products, sales trends, and customer buying patterns.
- Measure Marketing Campaign Effectiveness: Track the performance of your marketing campaigns and identify which channels are driving the most leads and sales.
- Make Data-Driven Decisions: Use data to inform your business strategy, identify opportunities, and make better decisions.
Boosting Efficiency and Productivity
CRM systems automate tasks and streamline processes, freeing up your team to focus on more strategic initiatives. Automation of repetitive tasks, such as data entry and email follow-ups, saves time and reduces errors. Streamlined processes, such as sales pipeline management and customer service ticket routing, improve efficiency and reduce bottlenecks. By automating tasks and streamlining processes, CRM systems help you do more with less.
With a CRM, you can:
- Automate Repetitive Tasks: Automate data entry, email follow-ups, and other repetitive tasks to save time and reduce errors.
- Streamline Processes: Streamline sales pipeline management, customer service ticket routing, and other processes to improve efficiency.
- Improve Collaboration: CRM systems facilitate collaboration between team members, ensuring that everyone has access to the information they need.
- Increase Employee Productivity: By automating tasks and streamlining processes, CRM systems free up your employees to focus on more important tasks.
Choosing the Right CRM for Your Small Business: A Step-by-Step Guide
Selecting the right CRM system is a crucial decision. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you choose the best CRM for your small business:
1. Define Your Needs and Goals
Before you start evaluating different CRM systems, take some time to define your specific needs and goals. What are you hoping to achieve with a CRM system? What are your current pain points? What features are essential for your business? Create a list of must-have features and nice-to-have features. This will help you narrow down your options and choose a system that aligns with your business objectives.
2. Assess Your Budget
CRM systems vary in price, from free or very low-cost options to more expensive enterprise-level solutions. Determine your budget and stick to it. Consider the cost of the software, implementation, training, and ongoing maintenance. Factor in the long-term cost of ownership, including potential upgrades and add-ons.
3. Research Different CRM Systems
Once you have a clear understanding of your needs and budget, start researching different CRM systems. Read reviews, compare features, and check out pricing plans. Consider both established players and newer, more innovative solutions. Look for systems that are specifically designed for small businesses, as they often offer features and pricing that are more suitable for your needs.
4. Consider Scalability
Choose a CRM system that can grow with your business. As your business expands, you’ll need a system that can handle more users, more data, and more complex processes. Look for systems that offer scalability and flexibility, allowing you to add features and functionality as your needs evolve.
5. Evaluate Usability and User Experience
The best CRM system is one that your team will actually use. Choose a system that is easy to use, intuitive, and user-friendly. Look for a system with a clean interface, clear instructions, and helpful tutorials. Consider the learning curve and the amount of training required. A system that is difficult to use will not deliver the desired results.
6. Check for Integrations
Does the CRM integrate with the other tools you use? You’ll want a CRM that can seamlessly connect with your email marketing platform, accounting software, social media channels, and other essential tools. Integration will streamline your workflow and ensure that data flows seamlessly between your different systems.
7. Consider Mobile Access
In today’s mobile world, it’s essential to have access to your CRM data on the go. Does the CRM offer a mobile app or a mobile-friendly interface? This will allow your team to access and update customer information, manage leads, and stay connected with customers, regardless of their location.
8. Test Drive the System
Most CRM vendors offer free trials or demos. Take advantage of these opportunities to test drive the system and see if it’s a good fit for your business. Try out different features, experiment with the interface, and see how easy it is to use. This will give you a better understanding of the system’s capabilities and whether it meets your needs.
9. Consider Customer Support
What level of customer support does the vendor offer? Ensure that the vendor provides adequate support, including online documentation, tutorials, and customer service. Check the vendor’s reputation for customer support and read reviews from other users. You’ll want to choose a vendor that is responsive and helpful when you need assistance.
10. Implement and Train Your Team
Once you’ve chosen a CRM system, you’ll need to implement it and train your team. Develop an implementation plan and allocate sufficient time and resources for the process. Provide comprehensive training to your team and ensure that they understand how to use the system effectively. Ongoing training and support are essential for maximizing the value of your CRM system.
CRM Implementation Best Practices for Small Businesses
Once you’ve selected your CRM, successful implementation is key to realizing its full potential. Here are some best practices to guide you:
1. Define Clear Objectives
Before you begin, clearly define your goals for CRM implementation. What specific improvements do you want to see in sales, customer service, or marketing? Having concrete objectives will provide a roadmap for your implementation process and help you measure success.
2. Clean and Migrate Your Data
Ensure your existing customer data is accurate and up-to-date before migrating it to your new CRM. Cleanse your data by removing duplicates, correcting errors, and standardizing formatting. This will prevent inaccurate data from polluting your CRM and ensure you’re working with reliable information.
3. Customize Your CRM
Tailor your CRM to your business needs by customizing fields, workflows, and reports. Don’t try to fit your business into the CRM; make the CRM fit your business. This will enhance usability and ensure your CRM is optimized for your specific processes.
4. Train Your Team Thoroughly
Provide comprehensive training to all team members who will use the CRM. Ensure they understand how to use all the features relevant to their roles. Encourage hands-on practice and provide ongoing support to address any questions or challenges.
5. Integrate with Other Tools
Integrate your CRM with other tools you use, such as email marketing platforms, accounting software, and social media channels. This will streamline your workflows and eliminate the need for manual data entry, saving time and reducing errors.
6. Encourage User Adoption
User adoption is critical to CRM success. Encourage your team to use the CRM by highlighting its benefits, providing ongoing support, and recognizing early adopters. Make using the CRM a part of your team’s daily workflow.
7. Monitor and Evaluate Progress
Regularly monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) to track the effectiveness of your CRM implementation. Identify areas for improvement and make adjustments to your processes or training as needed. Continuously evaluate the value your CRM is providing to your business.
8. Start Small and Iterate
Don’t try to implement all features at once. Start with the core features and gradually add more functionality as your team becomes comfortable with the system. This approach allows for a smoother transition and minimizes disruption to your business.
9. Seek Expert Help When Needed
If you lack internal expertise, consider seeking help from a CRM consultant or implementation specialist. They can provide guidance, training, and support to ensure a successful implementation.
10. Stay Consistent
Ensure that all team members use the CRM consistently and adhere to established processes. This will ensure data accuracy and maximize the value of your CRM investment.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid When Implementing CRM
While CRM offers tremendous potential, implementing it successfully requires careful planning and execution. Here are some common pitfalls to avoid:
1. Lack of Clear Objectives
Without clear objectives, it’s difficult to measure success and ensure your CRM implementation is aligned with your business goals. Take the time to define your objectives before you begin.
2. Poor Data Quality
Inaccurate or incomplete data can undermine the effectiveness of your CRM. Cleanse your data before importing it and establish processes for maintaining data quality.
3. Inadequate Training
If your team isn’t properly trained, they won’t use the CRM effectively. Provide comprehensive training and ongoing support.
4. Poor User Adoption
If your team doesn’t use the CRM, you won’t realize its benefits. Encourage user adoption by highlighting the benefits, providing ongoing support, and making the CRM a part of your team’s daily workflow.
5. Over-Customization
While customization is important, avoid over-customizing your CRM. Over-customization can make the system more complex and difficult to maintain.
6. Ignoring Integration
Failing to integrate your CRM with other tools can lead to data silos and manual data entry. Integrate your CRM with the tools you use to streamline your workflows.
7. Lack of Ongoing Support
Provide ongoing support to your team to address any questions or challenges they may encounter. Continuously evaluate and improve your CRM processes.
8. Not Measuring ROI
Track your CRM’s performance and measure its return on investment (ROI). This will help you identify areas for improvement and justify your investment in the system.
9. Choosing the Wrong System
Selecting a CRM that doesn’t fit your business needs can be a costly mistake. Thoroughly research and evaluate different CRM systems before making a decision.
10. Not Adapting to Change
Your business will evolve, and your CRM needs to adapt with it. Be prepared to make changes to your CRM as your business grows and your needs change.
The Future of CRM for Small Businesses
The future of CRM for small businesses is bright, with ongoing advancements in technology and a growing focus on customer-centricity. Here are some trends to watch:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML are revolutionizing CRM, enabling businesses to automate tasks, personalize customer experiences, and gain deeper insights into customer behavior. AI-powered CRM systems can predict customer needs, recommend products, and automate marketing campaigns. ML algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to identify trends and patterns that would be impossible for humans to detect.
Mobile CRM
Mobile CRM is becoming increasingly important, as businesses need to access customer data and manage interactions on the go. Mobile CRM apps provide access to critical customer information, enabling sales teams to close deals faster and customer service teams to provide support from anywhere.
Cloud-Based CRM
Cloud-based CRM solutions are becoming increasingly popular, as they offer numerous benefits, including lower costs, increased scalability, and improved accessibility. Cloud-based CRM systems are easy to implement and maintain, and they can be accessed from any device with an internet connection.
Personalized Customer Experiences
Customers expect personalized experiences, and CRM systems are essential for delivering them. CRM systems enable businesses to personalize their communications, products, and services based on customer data and preferences. This leads to increased customer satisfaction, loyalty, and revenue.
Integration with Social Media
Social media is an important channel for customer engagement, and CRM systems are increasingly integrating with social media platforms. Integration with social media allows businesses to monitor social media activity, engage with customers, and gather customer feedback.
Focus on Customer Journey Mapping
Businesses are increasingly focusing on customer journey mapping, which involves understanding the different stages of the customer journey and optimizing the customer experience at each stage. CRM systems can be used to track customer interactions and map the customer journey, enabling businesses to identify areas for improvement.
Conclusion: Embracing CRM for Small Business Success
In the ever-evolving landscape of small business, embracing a CRM system is no longer a luxury but a necessity. By implementing a well-chosen and effectively utilized CRM, you equip your business with the tools to build stronger customer relationships, streamline operations, and drive sustainable growth. From boosting sales and enhancing customer service to improving data analysis and increasing efficiency, the benefits of CRM are undeniable.
Remember, the key to success lies not just in implementing a CRM, but in choosing the right system for your specific needs, implementing it effectively, and ensuring that your team embraces it. By following the best practices outlined in this article, you can avoid common pitfalls and maximize the return on your CRM investment.
The future of small business is customer-centric, and CRM is the key to unlocking that future. Embrace the power of CRM, and watch your small business thrive.