Unlocking Growth: A Deep Dive into CRM Marketing Performance and How to Skyrocket Your Results
Unlocking Growth: A Deep Dive into CRM Marketing Performance and How to Skyrocket Your Results
In today’s hyper-competitive landscape, businesses are constantly searching for an edge. They need a way to not only attract customers but also to nurture those relationships, understand their needs, and ultimately, drive revenue. This is where the power of CRM marketing performance comes into play. It’s no longer enough to simply have a CRM system; you need to understand how to leverage it to its full potential. This comprehensive guide will delve deep into the intricacies of CRM marketing performance, providing you with the knowledge and strategies you need to achieve remarkable results.
What is CRM Marketing Performance? A Foundation for Success
At its core, CRM marketing performance refers to the effectiveness of your customer relationship management (CRM) system in supporting your marketing efforts. It’s about how well you’re using your CRM to manage customer interactions, personalize marketing campaigns, track performance, and ultimately, drive business growth. Think of it as the engine that powers your marketing machine. Without a well-tuned engine, your marketing efforts will sputter and stall.
CRM marketing performance is not just about the software itself; it’s about the strategies, processes, and people involved. It’s about using the data within your CRM to gain a 360-degree view of your customers, enabling you to make informed decisions and create highly targeted campaigns. It’s also about measuring and analyzing the results of your marketing efforts to identify what’s working and what’s not, and then making adjustments accordingly.
Key Components of CRM Marketing Performance
Several key components contribute to strong CRM marketing performance:
- Data Quality: The foundation of any successful CRM strategy is the quality of your data. Accurate, complete, and up-to-date data is essential for understanding your customers and making informed decisions.
- Segmentation: Dividing your customer base into distinct segments based on demographics, behavior, or other relevant factors allows you to tailor your marketing messages and increase their relevance.
- Personalization: Delivering personalized experiences is crucial for engaging customers and building loyalty. This includes personalizing email content, website content, and even product recommendations.
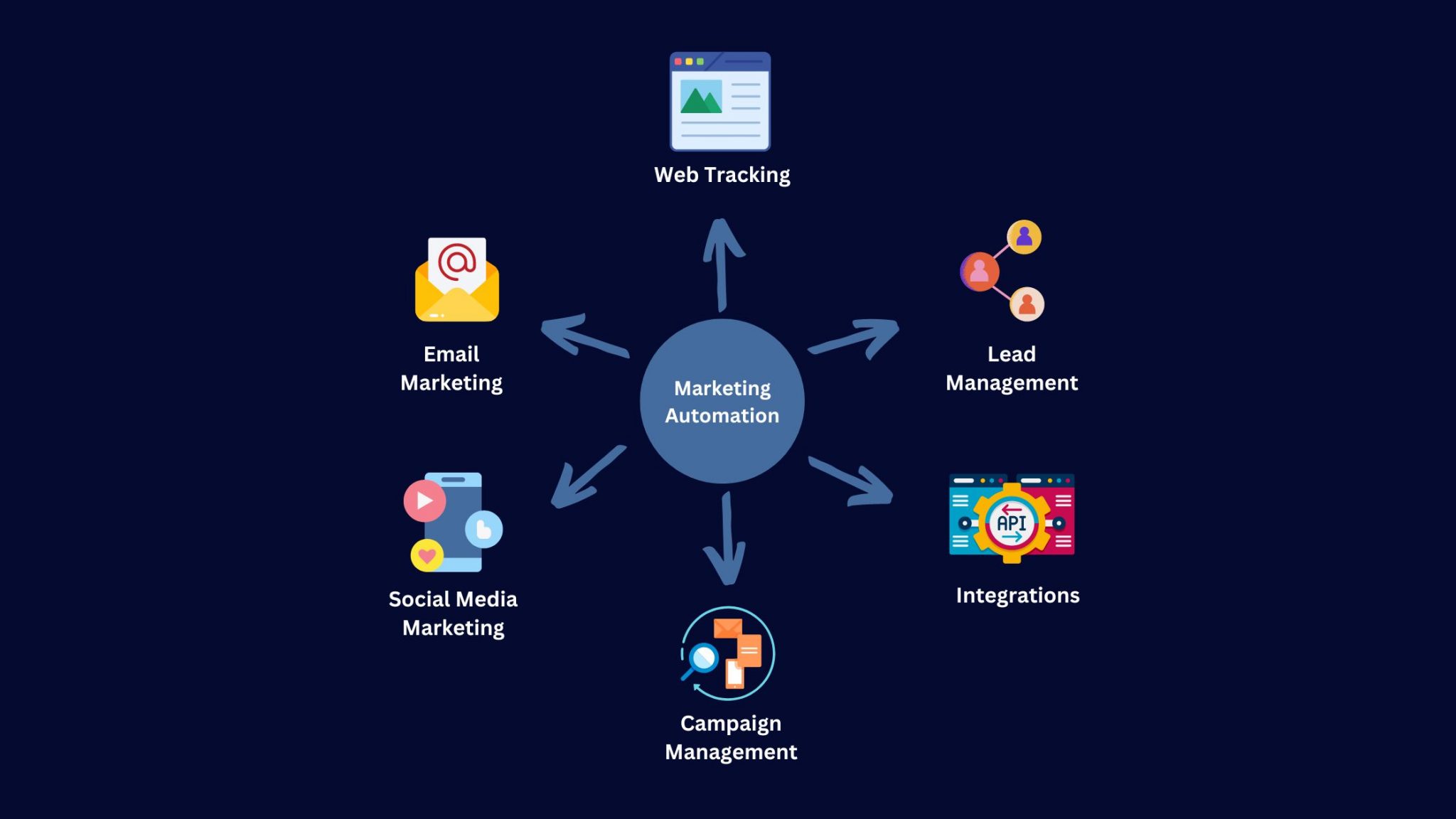
- Automation: Automating marketing tasks, such as email campaigns, lead nurturing, and social media posts, frees up your marketing team to focus on more strategic initiatives.
- Analytics and Reporting: Tracking and analyzing key performance indicators (KPIs) is essential for measuring the effectiveness of your CRM marketing efforts and identifying areas for improvement.
The Benefits of Effective CRM Marketing Performance
Investing in CRM marketing performance can yield a multitude of benefits for your business. These include:
- Increased Revenue: By targeting the right customers with the right messages at the right time, you can significantly increase your sales and revenue.
- Improved Customer Loyalty: Personalized experiences and proactive customer service build stronger relationships and increase customer loyalty.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: By understanding your customers’ needs and preferences, you can deliver products and services that meet their expectations, leading to higher satisfaction levels.
- Reduced Marketing Costs: By automating tasks and targeting your marketing efforts more effectively, you can reduce your marketing costs and improve your return on investment (ROI).
- Better Decision-Making: Data-driven insights from your CRM provide a more comprehensive understanding of your customers and the market, enabling you to make more informed decisions.
- Streamlined Processes: Automating tasks and integrating your CRM with other business systems streamlines your marketing processes and improves efficiency.
How to Improve Your CRM Marketing Performance
Improving your CRM marketing performance is an ongoing process that requires a strategic approach. Here are some key steps you can take:
1. Define Your Goals and Objectives
Before you can improve your CRM marketing performance, you need to define your goals and objectives. What do you want to achieve? Do you want to increase sales, improve customer loyalty, or reduce marketing costs? Once you have clearly defined goals, you can develop a strategy to achieve them.
2. Clean and Organize Your Data
As mentioned earlier, data quality is critical. Take the time to clean and organize your data. This includes removing duplicate records, correcting errors, and ensuring that all data fields are complete and accurate. This may seem like a tedious task, but it’s essential for getting the most out of your CRM.
3. Segment Your Customer Base
Segmenting your customer base allows you to tailor your marketing messages to specific groups of customers. This increases the relevance of your messages and improves your chances of success. Consider segmenting your customers based on demographics, behavior, purchase history, or any other relevant factors.
4. Personalize Your Marketing Campaigns
Personalization is key to engaging customers and building loyalty. Use the data in your CRM to personalize your email content, website content, and even product recommendations. Address customers by name, mention their past purchases, and offer relevant products or services.
5. Automate Your Marketing Tasks
Automation can save you time and money while improving your marketing efficiency. Automate tasks such as email campaigns, lead nurturing, and social media posts. This frees up your marketing team to focus on more strategic initiatives.
6. Integrate Your CRM with Other Systems
Integrating your CRM with other business systems, such as your website, e-commerce platform, and social media accounts, can streamline your processes and improve data accuracy. This integration allows data to flow seamlessly between systems, eliminating the need for manual data entry.
7. Track and Analyze Your Results
Tracking and analyzing key performance indicators (KPIs) is essential for measuring the effectiveness of your CRM marketing efforts. Identify the KPIs that are most important to your business, such as sales, customer acquisition cost, and customer lifetime value. Regularly review your results and make adjustments to your strategy as needed.
8. Provide Ongoing Training and Support
Your CRM system is only as effective as the people who use it. Provide ongoing training and support to your marketing team to ensure they know how to use the system effectively. This training should cover all aspects of the CRM, from data entry to campaign creation to reporting and analysis.
9. Embrace Continuous Improvement
CRM marketing performance is not a one-time project; it’s an ongoing process. Continuously evaluate your efforts, identify areas for improvement, and make adjustments to your strategy as needed. Stay up-to-date on the latest CRM marketing trends and best practices to ensure you’re getting the most out of your system.
10. Choose the Right CRM System
Selecting the right CRM system is crucial for your success. Consider your specific needs and requirements when choosing a system. Look for a system that is user-friendly, scalable, and integrates with other systems you use. Research various CRM platforms, compare their features and pricing, and read reviews from other users. Make sure the system aligns with your business goals and offers the capabilities you need to effectively manage your customer relationships and drive marketing performance.
Key Metrics to Measure CRM Marketing Performance
To accurately assess your CRM marketing performance, you must track a variety of key metrics. These metrics provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of your campaigns and overall marketing strategy. Here are some essential metrics to monitor:
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): This metric measures the total cost of acquiring a new customer, including marketing and sales expenses. A lower CAC indicates greater efficiency in your customer acquisition efforts.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV): CLTV estimates the total revenue a customer is expected to generate throughout their relationship with your business. A higher CLTV signifies greater profitability and customer loyalty.
- Conversion Rate: This metric tracks the percentage of leads or prospects that convert into paying customers. Monitoring conversion rates helps you identify bottlenecks in your sales funnel and optimize your marketing campaigns.
- Click-Through Rate (CTR): CTR measures the percentage of users who click on a link in your email campaigns or online advertisements. A higher CTR indicates that your content is engaging and relevant to your target audience.
- Open Rate: Open rate measures the percentage of recipients who open your email campaigns. This metric helps assess the effectiveness of your subject lines and email content.
- Lead Conversion Rate: This metric tracks the percentage of leads who convert into qualified opportunities or sales. It indicates the effectiveness of your lead nurturing and sales processes.
- Return on Investment (ROI): ROI measures the profitability of your marketing campaigns, comparing the revenue generated to the marketing costs incurred. A positive ROI indicates a successful marketing investment.
- Customer Retention Rate: This metric tracks the percentage of customers who remain loyal to your business over a specific period. A higher retention rate reflects customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Churn Rate: Churn rate measures the percentage of customers who stop doing business with your company over a certain period. A lower churn rate indicates greater customer satisfaction and retention.
- Website Traffic and Engagement: Monitor website traffic, bounce rate, time on page, and other engagement metrics to assess the effectiveness of your online marketing efforts.
Tools and Technologies for Enhancing CRM Marketing Performance
Several tools and technologies can significantly enhance your CRM marketing performance. Implementing these tools can streamline your processes, improve data accuracy, and provide valuable insights. Here are some essential tools to consider:
- CRM Software: The foundation of your CRM marketing efforts. Choose a robust CRM platform that meets your specific needs, such as Salesforce, HubSpot, Zoho CRM, or Microsoft Dynamics 365.
- Marketing Automation Platforms: Automate repetitive marketing tasks, such as email campaigns, lead nurturing, and social media posting. Popular platforms include Marketo, Pardot, and ActiveCampaign.
- Email Marketing Software: Design and send engaging email campaigns. Consider platforms such as Mailchimp, Constant Contact, or GetResponse.
- Lead Scoring Tools: Qualify leads based on their behavior and demographics. These tools help prioritize leads and optimize your sales efforts.
- Analytics and Reporting Tools: Track and analyze key performance indicators (KPIs). Tools like Google Analytics, Tableau, and Power BI provide valuable insights into your marketing performance.
- Social Media Management Tools: Schedule and manage your social media posts. Platforms like Hootsuite, Buffer, and Sprout Social help streamline your social media efforts.
- Data Enrichment Tools: Enhance your customer data with additional information, such as demographics, job titles, and social media profiles.
- A/B Testing Tools: Test different versions of your marketing materials to optimize their performance.
- Customer Feedback Tools: Collect customer feedback through surveys, polls, and reviews.
Best Practices for Maximizing CRM Marketing Performance
To achieve optimal CRM marketing performance, adopt these best practices:
- Prioritize Data Quality: Ensure your data is accurate, complete, and up-to-date. Regularly clean and update your data to maintain its integrity.
- Develop a Customer-Centric Strategy: Focus on understanding your customers’ needs and preferences. Tailor your marketing efforts to provide value and build strong relationships.
- Personalize Your Marketing Messages: Use customer data to personalize your email content, website content, and product recommendations.
- Automate Repetitive Tasks: Automate tasks such as email campaigns, lead nurturing, and social media posting to free up your marketing team.
- Segment Your Customer Base: Divide your customer base into distinct segments based on demographics, behavior, or other relevant factors.
- Integrate Your CRM with Other Systems: Integrate your CRM with other business systems to streamline your processes and improve data accuracy.
- Track and Analyze Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Regularly monitor your KPIs to measure the effectiveness of your marketing efforts.
- Provide Ongoing Training and Support: Ensure your marketing team is well-trained and supported in using the CRM system.
- Embrace Continuous Improvement: Continuously evaluate your efforts, identify areas for improvement, and make adjustments to your strategy.
- Stay Up-to-Date on the Latest Trends: Keep abreast of the latest CRM marketing trends and best practices to stay ahead of the competition.
- Foster Collaboration Between Sales and Marketing: Align your sales and marketing teams to ensure a seamless customer experience.
- Use Mobile Optimization: Ensure your marketing materials are optimized for mobile devices.
- Focus on Customer Experience: Make sure your customer experience is positive.
The Future of CRM Marketing Performance
The future of CRM marketing performance is bright, with exciting developments on the horizon. Here are some key trends to watch:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is transforming CRM marketing, enabling personalized experiences, predictive analytics, and automated decision-making.
- Machine Learning (ML): ML algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and predict customer behavior, allowing for more targeted marketing efforts.
- Hyper-Personalization: Customers expect highly personalized experiences. CRM marketing will continue to evolve to deliver hyper-personalized content and offers.
- Data Privacy and Security: Data privacy and security are becoming increasingly important. CRM marketing strategies will need to prioritize data protection and compliance with regulations.
- Omnichannel Marketing: Customers interact with businesses across multiple channels. CRM marketing will integrate these channels to provide a seamless customer experience.
- Voice Search Optimization: Voice search is growing in popularity. CRM marketing will need to optimize content for voice search.
- The Rise of Customer Data Platforms (CDPs): CDPs are emerging as powerful tools for unifying customer data and providing a 360-degree view of the customer.
By embracing these trends, businesses can stay ahead of the curve and unlock the full potential of CRM marketing performance.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of CRM Marketing
CRM marketing performance is not just a buzzword; it’s a critical component of any successful marketing strategy. By leveraging the power of your CRM system, you can build stronger customer relationships, drive revenue, and achieve sustainable growth. This guide has provided you with the knowledge and strategies you need to improve your CRM marketing performance. Remember to focus on data quality, personalization, automation, and continuous improvement. Embrace the latest trends and technologies to stay ahead of the competition. With a well-defined strategy and a commitment to excellence, you can transform your CRM into a powerful engine for marketing success. The journey to exceptional CRM marketing performance is ongoing, requiring dedication, adaptation, and a relentless focus on the customer. Embrace the challenge, and watch your business thrive!