Unlocking Growth: How CRM, Marketing, and Customer Feedback Forge Unbreakable Bonds
Unlocking Growth: How CRM, Marketing, and Customer Feedback Forge Unbreakable Bonds
In the dynamic world of business, where customer loyalty is the ultimate prize, understanding the intricate dance between Customer Relationship Management (CRM), marketing strategies, and customer feedback is not just advantageous—it’s essential. This comprehensive guide delves deep into how these three pillars work in harmony to fuel sustainable growth, improve customer satisfaction, and ultimately, boost your bottom line. We’ll explore the nuances of each element, providing actionable insights and real-world examples to help you navigate this complex landscape.
The Foundation: Understanding CRM
At its core, CRM is more than just a software; it’s a philosophy centered around building and nurturing relationships with your customers. It’s about understanding their needs, preferences, and behaviors to deliver personalized experiences that keep them coming back for more. Implementing a robust CRM system can revolutionize how you interact with your customers, transforming your approach from a transactional model to a relationship-driven one.
What is CRM?
CRM, or Customer Relationship Management, is a technology and strategy for managing all your company’s relationships and interactions with customers and potential customers. The goal is simple: improve business relationships. A CRM system helps companies stay connected to customers, streamline processes, and improve profitability.
Think of it as the central nervous system of your customer interactions. It collects, organizes, and analyzes vast amounts of data about your customers, providing a 360-degree view that empowers you to make informed decisions. This comprehensive understanding allows you to:
- Personalize your marketing efforts.
- Improve customer service.
- Identify and target your most valuable customers.
- Streamline your sales processes.
- Increase customer retention.
Key Benefits of CRM
The advantages of implementing a well-designed CRM system are numerous and far-reaching. Here are some of the most significant benefits:
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: By providing a personalized experience, CRM helps you meet and exceed customer expectations, leading to higher satisfaction levels.
- Enhanced Sales Performance: CRM streamlines the sales process, providing sales teams with the tools and information they need to close deals more efficiently.
- Increased Efficiency: Automation features within CRM systems automate repetitive tasks, freeing up your team to focus on more strategic initiatives.
- Better Data Management: CRM centralizes customer data, making it easy to access, analyze, and utilize for better decision-making.
- Reduced Costs: By streamlining processes and improving efficiency, CRM can help you reduce operational costs.
The Marketing Magic: Leveraging CRM for Targeted Campaigns
Marketing is the engine that drives customer acquisition and engagement. When integrated with a robust CRM system, marketing campaigns become laser-focused, personalized, and significantly more effective. This synergy allows you to move beyond generic messaging and deliver tailored content that resonates with individual customer segments.
Segmenting Your Audience
One of the most powerful capabilities of CRM-integrated marketing is the ability to segment your audience based on various criteria. This could include:
- Demographics: Age, gender, location, income, etc.
- Behavior: Purchase history, website activity, engagement with past campaigns, etc.
- Interests: Product preferences, content consumption, etc.
- Lifecycle Stage: New leads, existing customers, churned customers, etc.
By segmenting your audience, you can create highly targeted campaigns that speak directly to their specific needs and interests. For example, you could send a promotional email to customers who have previously purchased a specific product, offering them a discount on a related item. Or, you could create a series of educational emails for new leads, nurturing them through the sales funnel.
Personalization: The Key to Engagement
Personalization is no longer a luxury; it’s an expectation. Customers want to feel valued and understood. CRM enables you to personalize your marketing efforts in several ways:
- Personalized Email Marketing: Use the customer’s name, reference their past purchases, and recommend products based on their interests.
- Targeted Website Content: Display different content to different customer segments based on their behavior and preferences.
- Personalized Advertising: Utilize CRM data to target specific customer segments with relevant ads on social media and other platforms.
By personalizing your marketing, you increase engagement, build stronger relationships, and ultimately drive conversions.
Automating Your Marketing Efforts
Marketing automation is a game-changer. CRM systems often include automation features that allow you to streamline your marketing workflows, saving time and resources. This could include:
- Automated Email Sequences: Set up triggered emails that are sent automatically based on customer behavior, such as welcome emails, abandoned cart emails, and follow-up emails after a purchase.
- Lead Nurturing Campaigns: Create a series of emails and other content designed to nurture leads through the sales funnel.
- Social Media Scheduling: Schedule social media posts in advance to ensure consistent engagement.
Automation allows you to scale your marketing efforts and reach a wider audience with less manual effort.
The Voice of the Customer: The Power of Customer Feedback
Customer feedback is the lifeblood of any successful business. It provides invaluable insights into what your customers love, what they dislike, and what they want. When integrated with CRM and marketing, customer feedback becomes a powerful tool for continuous improvement and innovation.
Collecting Customer Feedback
There are several ways to collect customer feedback:
- Surveys: Send out surveys after a purchase, after a customer service interaction, or periodically to gauge customer satisfaction.
- Feedback Forms: Include feedback forms on your website, in your products, or in your marketing materials.
- Social Media Monitoring: Monitor social media channels for mentions of your brand and products.
- Customer Reviews: Encourage customers to leave reviews on your website and on third-party review sites.
- Direct Communication: Encourage your customer service team to actively solicit feedback during interactions.
The more channels you use to collect feedback, the more comprehensive your understanding of your customers will be.
Analyzing Customer Feedback
Collecting feedback is only the first step. The next step is to analyze the data to identify trends, patterns, and areas for improvement. This could involve:
- Sentiment Analysis: Use software to analyze the sentiment of customer feedback, determining whether it is positive, negative, or neutral.
- Keyword Analysis: Identify the most frequently mentioned keywords and topics in customer feedback.
- Trend Analysis: Track changes in customer sentiment and feedback over time.
- Data Visualization: Use charts and graphs to visualize your data and identify key insights.
By analyzing customer feedback, you can gain a deeper understanding of your customers’ needs and preferences.
Acting on Customer Feedback
The ultimate goal of collecting and analyzing customer feedback is to take action. This could involve:
- Improving Your Products and Services: Use feedback to identify areas where you can improve your products and services.
- Enhancing the Customer Experience: Use feedback to identify pain points in the customer journey and make improvements.
- Training Your Employees: Use feedback to identify areas where your employees need additional training.
- Communicating with Customers: Let your customers know that you are listening to their feedback and taking action.
By taking action on customer feedback, you demonstrate that you value your customers and are committed to providing them with the best possible experience.
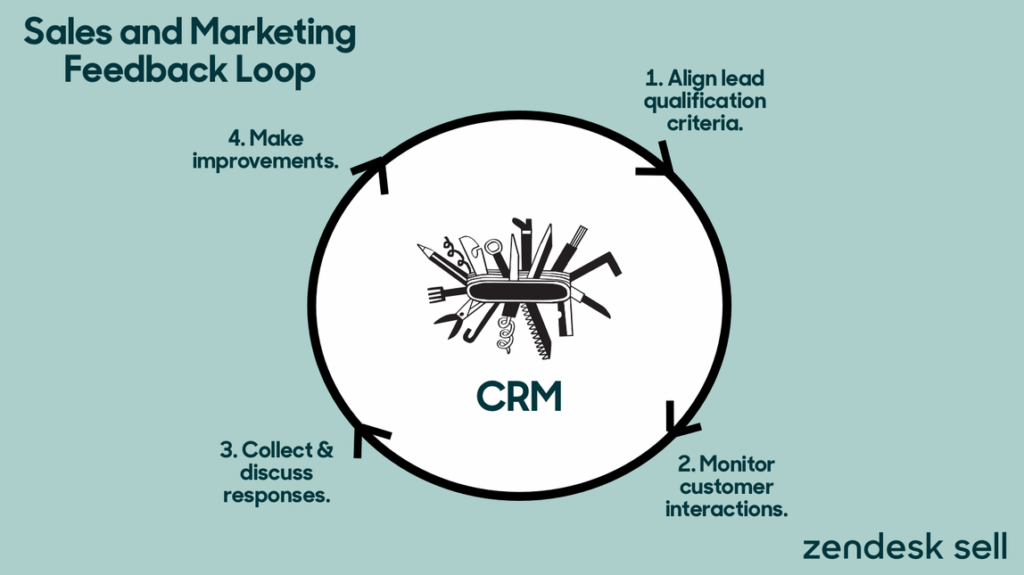
The Synergy: CRM, Marketing, and Customer Feedback in Action
The true power of CRM, marketing, and customer feedback lies in their synergy. When these three elements work together, they create a powerful feedback loop that drives continuous improvement and growth. Here’s how it works:
- CRM Provides the Foundation: Your CRM system provides the foundation for collecting and organizing customer data.
- Marketing Leverages CRM Data: Your marketing team uses CRM data to segment your audience, personalize your campaigns, and target the right customers with the right message.
- Customer Feedback Informs Marketing and CRM: Customer feedback provides insights into what’s working and what’s not. This feedback is used to refine your marketing campaigns, improve your CRM data, and ultimately, improve the customer experience.
- Continuous Improvement: The feedback loop is continuous. As you implement changes based on customer feedback, you collect more feedback to evaluate the effectiveness of those changes. This iterative process drives continuous improvement and growth.
Examples of Synergy in Action
- Example 1: E-commerce Website
An e-commerce website uses its CRM to track customer purchase history. Based on this data, the marketing team sends personalized emails recommending related products. After a purchase, the customer receives a survey asking for feedback on their experience. The feedback is analyzed, and any negative experiences are addressed by the customer service team. The website uses the feedback to improve its product descriptions, shipping processes, and customer service protocols.
- Example 2: SaaS Company
A SaaS company uses its CRM to track customer usage data. The marketing team uses this data to identify customers who are not fully utilizing the product. They then send these customers targeted emails with helpful tips and tutorials. The company also uses customer feedback from surveys and in-app feedback forms to improve the product’s features and usability. This feedback is then used to update the CRM data, further refining the customer profiles.
Choosing the Right CRM System
Selecting the right CRM system is crucial for your success. Consider the following factors when making your choice:
- Your Business Needs: What are your specific goals and objectives? What features do you need?
- Your Budget: How much are you willing to spend? Consider the cost of the software, implementation, and ongoing maintenance.
- Ease of Use: Is the system user-friendly and easy to learn?
- Integration Capabilities: Does the system integrate with your existing marketing and sales tools?
- Scalability: Can the system grow with your business?
- Customer Support: Does the vendor offer adequate customer support?
Research different CRM systems and compare their features, pricing, and reviews. Consider requesting demos and free trials to get a feel for the system before making a commitment.
Best Practices for Success
To maximize the impact of CRM, marketing, and customer feedback, follow these best practices:
- Invest in Training: Provide your team with adequate training on how to use the CRM system and marketing tools.
- Integrate Your Systems: Ensure that your CRM system is integrated with your marketing automation tools, your website, and your other business systems.
- Set Clear Goals: Define your goals and objectives for using CRM, marketing, and customer feedback.
- Track Your Results: Monitor your key metrics, such as customer satisfaction, sales performance, and customer retention.
- Continuously Improve: Regularly review your processes and make adjustments based on your results and customer feedback.
- Prioritize Data Privacy: Ensure you are compliant with all relevant data privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA. Be transparent with customers about how you collect and use their data.
The Future of CRM, Marketing, and Customer Feedback
The landscape of CRM, marketing, and customer feedback is constantly evolving. Here are some trends to watch:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is being used to automate tasks, personalize marketing campaigns, and improve customer service.
- Machine Learning (ML): ML is being used to analyze customer data and predict customer behavior.
- Mobile CRM: Mobile CRM apps are becoming increasingly popular, allowing businesses to access and manage customer data on the go.
- Voice Assistants: Voice assistants are being integrated with CRM systems, making it easier for sales and marketing teams to access information and complete tasks.
- Focus on Customer Experience (CX): Businesses are increasingly focused on providing a seamless and personalized customer experience across all touchpoints.
By staying up-to-date on these trends, you can ensure that your business remains competitive and continues to meet the evolving needs of your customers.
Conclusion: Building Lasting Customer Bonds
In conclusion, the strategic integration of CRM, marketing, and customer feedback is a powerful formula for building lasting customer relationships and driving sustainable growth. By understanding the nuances of each element, leveraging their synergistic potential, and implementing best practices, businesses can create a customer-centric ecosystem that fosters loyalty, increases profitability, and positions them for long-term success. This journey isn’t a one-time project; it’s a continuous cycle of learning, adapting, and striving to better understand and serve your customers. Embrace the power of these interconnected strategies, and watch your business flourish.