Unlocking Growth: How CRM, Marketing, and Customer Feedback Orchestrate Success

In the ever-evolving landscape of business, the customer reigns supreme. Their needs, desires, and experiences dictate the trajectory of a company’s success. This is where the powerful synergy of CRM (Customer Relationship Management), marketing, and customer feedback comes into play. They are not merely isolated components but rather interconnected threads that, when woven together skillfully, create a tapestry of growth, loyalty, and sustained profitability. This article delves deep into the intricacies of this dynamic relationship, exploring how these three elements can be leveraged to build a thriving business.
The Cornerstone: CRM and Its Role in Customer-Centricity
At the heart of this strategic alliance lies CRM. It’s more than just software; it’s a philosophy, a commitment to understanding and nurturing customer relationships. CRM systems serve as the central nervous system of a business, collecting, organizing, and analyzing vast amounts of customer data. This data provides invaluable insights into customer behavior, preferences, and pain points.
What is CRM? A Comprehensive Overview
CRM is a technology that allows businesses to manage and analyze customer interactions and data throughout the customer lifecycle. It encompasses a wide range of functions, from sales and marketing automation to customer service and support. The primary goal of CRM is to improve business relationships, retain customers, and drive sales growth. It helps to:
- Centralize Customer Data: Consolidate all customer information in one place, providing a 360-degree view of each customer.
- Improve Communication: Facilitate seamless communication across different departments, ensuring consistent messaging.
- Automate Tasks: Streamline repetitive tasks, freeing up employees to focus on more strategic activities.
- Enhance Sales Performance: Provide sales teams with the tools and insights they need to close deals more effectively.
- Personalize Customer Experiences: Tailor interactions and offers to meet individual customer needs and preferences.
Implementing a CRM system is a crucial first step in fostering a customer-centric approach. It provides the foundation for building strong relationships and delivering exceptional customer experiences.
The Benefits of a Robust CRM System
The advantages of a well-implemented CRM system are numerous and far-reaching. They include:
- Increased Sales: By providing sales teams with better leads, improved follow-up capabilities, and a deeper understanding of customer needs, CRM can significantly boost sales performance.
- Improved Customer Retention: CRM helps businesses understand customer behavior and identify potential churn risks. By proactively addressing customer concerns and providing exceptional service, CRM can significantly improve customer retention rates.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Personalizing interactions and providing prompt, efficient service leads to higher customer satisfaction levels.
- Improved Efficiency: Automating tasks and streamlining workflows saves time and resources, allowing employees to focus on more strategic initiatives.
- Better Decision-Making: CRM provides valuable data and analytics that enable businesses to make informed decisions based on real-time customer insights.
- Increased Profitability: By increasing sales, reducing costs, and improving customer retention, CRM ultimately contributes to higher profitability.
Marketing’s Strategic Dance with CRM
Marketing and CRM are natural partners, working in tandem to attract, engage, and retain customers. CRM provides the data and insights that inform marketing strategies, while marketing channels deliver the messages and experiences that drive customer engagement.
CRM as the Engine of Marketing Strategy
CRM data is the lifeblood of effective marketing. It allows marketers to:
- Segment Audiences: Divide customers into targeted groups based on demographics, behaviors, and preferences.
- Personalize Campaigns: Tailor marketing messages and offers to resonate with specific customer segments.
- Optimize Campaigns: Track the performance of marketing campaigns and make data-driven adjustments to improve results.
- Improve Lead Generation: Identify and nurture potential customers through targeted marketing efforts.
- Measure ROI: Track the return on investment for marketing campaigns and demonstrate their impact on business growth.
By leveraging CRM data, marketers can move beyond generic, one-size-fits-all campaigns and create highly targeted, personalized experiences that drive engagement and conversions.
Marketing Automation: A CRM-Powered Advantage
Marketing automation, often integrated with CRM, allows businesses to streamline and automate repetitive marketing tasks. This includes:
- Email Marketing: Sending targeted email campaigns based on customer behavior and preferences.
- Social Media Marketing: Scheduling and managing social media posts to engage with customers.
- Lead Nurturing: Guiding potential customers through the sales funnel with automated email sequences and personalized content.
- Workflow Automation: Automating tasks such as lead assignment, follow-up reminders, and data entry.
Marketing automation frees up marketers to focus on more strategic activities, such as campaign planning and content creation, while ensuring that customers receive timely and relevant communications.
The Power of Customer Feedback: A Continuous Improvement Loop
Customer feedback is the invaluable fuel that drives continuous improvement. It provides direct insights into customer experiences, allowing businesses to identify areas of strength and weakness. By actively soliciting and analyzing customer feedback, businesses can refine their products, services, and overall customer experience.
Collecting Customer Feedback: The Methods
There are various methods for collecting customer feedback, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Some of the most common methods include:
- Surveys: Conducting online, email, or in-person surveys to gather feedback on specific products, services, or experiences.
- Customer Interviews: Conducting one-on-one interviews to gain in-depth insights into customer needs and preferences.
- Focus Groups: Bringing together a group of customers to discuss their experiences and provide feedback.
- Social Media Monitoring: Monitoring social media channels for mentions of the brand and analyzing customer sentiment.
- Review Platforms: Monitoring online review platforms, such as Google My Business, Yelp, and TripAdvisor, to gather feedback.
- Customer Service Interactions: Analyzing customer service interactions, such as phone calls, emails, and chat logs, to identify common issues and areas for improvement.
The choice of method depends on the specific goals of the feedback initiative and the target audience. A combination of methods often provides the most comprehensive insights.
Analyzing and Acting on Customer Feedback
Collecting customer feedback is only the first step. The real value lies in analyzing the data and taking action based on the insights gained. This involves:
- Identifying Trends: Looking for patterns and trends in customer feedback, such as recurring complaints or positive comments.
- Segmenting Feedback: Analyzing feedback by customer segment to identify specific needs and preferences.
- Prioritizing Issues: Determining which issues are most critical to address based on their impact on customer satisfaction and business goals.
- Developing Solutions: Creating action plans to address customer concerns and improve the customer experience.
- Measuring Results: Tracking the impact of implemented solutions to ensure that they are effective.
By actively listening to customer feedback and taking action to address their concerns, businesses can demonstrate their commitment to customer satisfaction and build stronger relationships.
Integrating CRM, Marketing, and Customer Feedback: A Winning Formula
The true power of these three elements is unleashed when they are integrated and work in harmony. This integration creates a virtuous cycle of continuous improvement, where customer data informs marketing strategies, marketing efforts drive customer engagement, and customer feedback provides insights for further refinement.
Creating a Unified Customer View
The first step in integration is to create a unified customer view. This involves:
- Centralizing Data: Consolidating customer data from CRM, marketing automation platforms, and customer feedback channels into a single, accessible repository.
- Connecting Systems: Integrating CRM with marketing automation platforms, customer service systems, and other relevant tools.
- Using Unique Identifiers: Using unique identifiers, such as email addresses or customer IDs, to link customer data across different systems.
A unified customer view provides a 360-degree understanding of each customer, enabling businesses to personalize interactions and deliver exceptional experiences.
Personalization: The Key to Customer Engagement
Personalization is the cornerstone of effective marketing in the modern era. By using CRM data and customer feedback, businesses can tailor their interactions and offers to meet individual customer needs and preferences. This includes:
- Personalized Email Campaigns: Sending targeted email campaigns based on customer behavior, demographics, and purchase history.
- Personalized Website Experiences: Customizing website content and offers based on customer preferences and browsing history.
- Personalized Product Recommendations: Recommending products based on customer purchase history and browsing behavior.
- Personalized Customer Service: Providing customer service representatives with access to customer data to personalize interactions and resolve issues efficiently.
Personalization increases customer engagement, improves conversion rates, and builds stronger customer relationships.
The Feedback Loop: A Cycle of Continuous Improvement
The integration of CRM, marketing, and customer feedback creates a powerful feedback loop. This loop works as follows:
- CRM Provides Data: CRM provides the data and insights that inform marketing strategies and customer service efforts.
- Marketing Drives Engagement: Marketing campaigns and customer service interactions drive customer engagement and collect valuable data.
- Customer Feedback Provides Insights: Customer feedback provides insights into customer experiences, identifying areas of strength and weakness.
- Insights Drive Improvements: The insights gained from customer feedback are used to refine products, services, and marketing strategies.
- The Cycle Repeats: The improved products, services, and marketing strategies lead to higher customer satisfaction and further data collection, perpetuating the cycle.
This continuous improvement loop is essential for long-term success. It allows businesses to adapt to changing customer needs and preferences, stay ahead of the competition, and build lasting customer relationships.
Real-World Examples: CRM, Marketing, and Customer Feedback in Action
Let’s look at some real-world examples of how businesses are successfully leveraging the power of CRM, marketing, and customer feedback.
Example 1: E-commerce Retailer
An e-commerce retailer uses CRM to track customer purchase history, browsing behavior, and customer service interactions. They use this data to:
- Segment Customers: Segment customers based on their purchase history, such as frequent buyers, first-time buyers, and customers who have abandoned their carts.
- Personalize Email Campaigns: Send targeted email campaigns to each segment, offering personalized product recommendations, discounts, and promotions.
- Gather Customer Feedback: Send post-purchase surveys to gather feedback on the customer experience.
- Improve Customer Service: Use customer feedback to identify and address common customer service issues.
As a result, the retailer sees an increase in sales, customer retention, and customer satisfaction.
Example 2: Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) Company
A SaaS company uses CRM to manage leads, track customer usage, and provide customer support. They use this data to:
- Nurture Leads: Nurture leads through the sales funnel with automated email sequences and personalized content.
- Identify At-Risk Customers: Identify customers who are at risk of churn based on their usage patterns.
- Provide Proactive Support: Provide proactive support to at-risk customers to prevent churn.
- Gather Customer Feedback: Conduct in-app surveys and gather feedback through customer service interactions.
- Improve Product Development: Use customer feedback to inform product development and prioritize new features.
The SaaS company experiences improved customer retention and product development.
Example 3: Healthcare Provider
A healthcare provider uses CRM to manage patient data, track appointments, and provide personalized care. They use this data to:
- Schedule Appointments: Schedule appointments efficiently and remind patients of upcoming appointments.
- Personalize Patient Communications: Send personalized communications to patients based on their medical history and care plans.
- Gather Patient Feedback: Send patient satisfaction surveys to gather feedback on the care experience.
- Improve Patient Outcomes: Use patient feedback to improve the quality of care and patient outcomes.
The healthcare provider sees improvements in patient satisfaction and care quality.
Choosing the Right CRM, Marketing, and Feedback Tools
Selecting the right tools is crucial for success. The best CRM, marketing automation, and customer feedback tools will depend on the specific needs and goals of the business. Some popular options include:
CRM Platforms
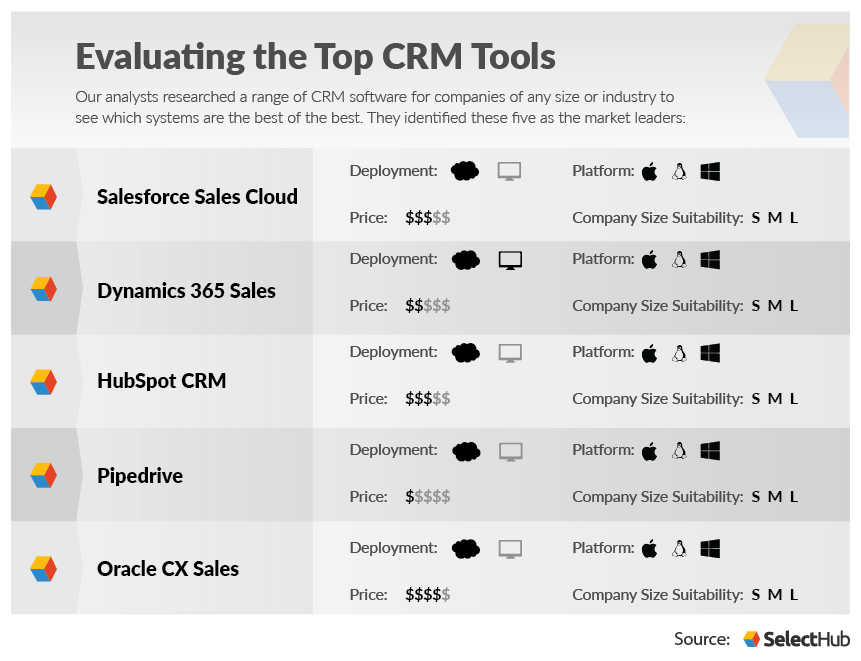
- Salesforce: A comprehensive CRM platform that offers a wide range of features and integrations.
- HubSpot CRM: A free CRM platform that is easy to use and integrates seamlessly with HubSpot’s marketing and sales tools.
- Zoho CRM: A CRM platform that offers a wide range of features at an affordable price.
- Microsoft Dynamics 365: A CRM platform that integrates with other Microsoft products.
- Pipedrive: A sales-focused CRM platform.
Marketing Automation Platforms
- HubSpot Marketing Hub: A comprehensive marketing automation platform that integrates seamlessly with HubSpot CRM.
- Marketo: A powerful marketing automation platform that is designed for enterprise-level businesses.
- Pardot: A marketing automation platform from Salesforce.
- ActiveCampaign: A user-friendly marketing automation platform that is suitable for small and medium-sized businesses.
- Mailchimp: Best for email marketing, but also offers marketing automation features.
Customer Feedback Tools
- SurveyMonkey: A popular online survey platform.
- Qualtrics: A comprehensive experience management platform.
- Typeform: A survey platform with a conversational design.
- Hotjar: A tool for website heatmaps and user behavior analysis.
- Google Forms: A free and easy-to-use survey platform.
When choosing tools, consider the following factors:
- Features: Ensure that the tools offer the features that are needed to meet business requirements.
- Integrations: Choose tools that integrate seamlessly with existing systems.
- Ease of Use: Select tools that are easy to use and require minimal training.
- Scalability: Choose tools that can scale to accommodate business growth.
- Cost: Consider the cost of the tools and ensure that they fit within the budget.
Best Practices for Success
To maximize the effectiveness of CRM, marketing, and customer feedback, consider the following best practices:
- Start with a Clear Strategy: Define clear goals and objectives before implementing any CRM, marketing, or feedback initiatives.
- Invest in Training: Provide employees with the training they need to use the tools effectively.
- Prioritize Data Quality: Ensure that customer data is accurate, complete, and up-to-date.
- Personalize Everything: Tailor interactions and offers to meet individual customer needs and preferences.
- Be Consistent: Maintain consistent messaging and branding across all channels.
- Be Responsive: Respond to customer feedback promptly and address their concerns.
- Measure Results: Track the performance of CRM, marketing, and feedback initiatives and make data-driven adjustments.
- Continuously Improve: Regularly review and refine processes to ensure that they are aligned with business goals.
- Foster a Customer-Centric Culture: Make customer satisfaction a top priority throughout the organization.
By adhering to these best practices, businesses can create a customer-centric culture and unlock the full potential of CRM, marketing, and customer feedback.
The Future: Trends and Innovations
The landscape of CRM, marketing, and customer feedback is constantly evolving. Staying ahead of the curve requires businesses to embrace new trends and innovations. Some of the key trends to watch include:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is being used to automate tasks, personalize customer experiences, and provide more accurate insights.
- Machine Learning (ML): ML is being used to predict customer behavior, identify potential churn risks, and optimize marketing campaigns.
- Big Data Analytics: Businesses are using big data analytics to gain a deeper understanding of customer behavior and preferences.
- Mobile-First Strategies: Businesses are focusing on mobile-first strategies to reach customers on their preferred devices.
- Voice Search Optimization: Businesses are optimizing their content for voice search to improve their visibility in search results.
- Personalized Video Marketing: Personalized video marketing is becoming increasingly popular as a way to engage customers.
- Customer Data Platforms (CDPs): CDPs are becoming increasingly popular as a way to centralize customer data from multiple sources.
By embracing these trends, businesses can stay ahead of the competition and deliver exceptional customer experiences.
Conclusion: A Symphony of Success
In conclusion, the harmonious integration of CRM, marketing, and customer feedback is a powerful recipe for business success. CRM provides the foundation for understanding and managing customer relationships, marketing drives customer engagement and generates leads, and customer feedback provides the insights needed for continuous improvement. When these three elements work together, they create a virtuous cycle of growth, loyalty, and sustained profitability.
By embracing a customer-centric approach, investing in the right tools, and adhering to best practices, businesses can unlock the full potential of this powerful synergy. The future of business is customer-centric, and those who master the art of CRM, marketing, and customer feedback will be best positioned to thrive in the years to come. The journey towards customer-centricity is an ongoing one, a continuous quest to understand and exceed customer expectations. It’s a symphony, a complex interplay of data, strategy, and human connection, and the businesses that master this composition will undoubtedly achieve lasting success.