Mastering Small Business CRM: A Comprehensive Tutorial to Boost Your Sales and Customer Relationships

Introduction: Why Your Small Business Needs a CRM
In today’s competitive landscape, small businesses face the constant challenge of attracting and retaining customers. One of the most effective tools for achieving this is a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system. Think of a CRM as the central nervous system of your customer interactions. It’s where you store, organize, and analyze all the information related to your customers, enabling you to build stronger relationships and drive sales growth. This tutorial will guide you through everything you need to know to implement and utilize a CRM for your small business effectively.
Before diving into the specifics, let’s address a common misconception: that CRMs are only for large corporations with vast budgets. This couldn’t be further from the truth. In fact, small businesses can derive even greater benefits from a CRM because they often have more direct interactions with their customers. A well-implemented CRM can help you personalize those interactions, understand your customers’ needs better, and ultimately, provide a superior customer experience that fosters loyalty.
This tutorial covers everything from choosing the right CRM to setting it up, using its core features, and measuring your success. We’ll explore the benefits in detail and provide practical tips and examples to help you get started. Get ready to transform how you manage your customer relationships and take your small business to the next level!
Understanding the Benefits of a CRM for Small Businesses
Investing in a CRM for your small business is a strategic move that can yield significant returns. Let’s explore the key advantages:
- Improved Customer Relationships: At its core, a CRM helps you build better relationships. By centralizing customer data, you gain a 360-degree view of each customer, including their purchase history, communication logs, and preferences. This allows you to personalize your interactions, anticipate their needs, and provide tailored solutions.
- Increased Sales: A CRM streamlines the sales process, making it easier to manage leads, track opportunities, and close deals. Features like automated follow-ups, sales pipeline management, and sales forecasting empower your sales team to work more efficiently and effectively, leading to higher conversion rates and increased revenue.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Automate repetitive tasks, such as data entry, email marketing, and appointment scheduling. This frees up your team to focus on more strategic activities, such as building relationships and closing deals. A CRM can also integrate with other business tools, further streamlining workflows and saving time.
- Better Data Organization: Say goodbye to scattered spreadsheets and disorganized contact information. A CRM provides a centralized repository for all your customer data, making it easy to find the information you need when you need it. This improves collaboration among team members and ensures everyone is on the same page.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: CRM systems provide valuable insights into your customer behavior and sales performance. By analyzing the data within your CRM, you can identify trends, understand what’s working and what’s not, and make data-driven decisions to improve your sales and marketing strategies.
- Improved Customer Service: With a CRM, your customer service team can access a complete history of customer interactions, allowing them to provide faster and more effective support. This leads to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Choosing the Right CRM for Your Small Business
Selecting the right CRM is crucial for its successful implementation and adoption within your small business. The market offers a wide array of options, each with its own features, pricing models, and target audience. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you choose the best CRM for your needs:
- Assess Your Needs: Before you start comparing CRM systems, take the time to understand your specific requirements. What are your primary goals for implementing a CRM? What are your current pain points in managing customer relationships, sales, and marketing? Consider the following questions:
- What are your key customer touchpoints?
- What data do you need to track about your customers?
- What processes do you want to automate?
- What reports and insights do you need to generate?
- Define Your Budget: CRM systems come in various pricing tiers, from free options to enterprise-level solutions. Determine a realistic budget that aligns with your financial resources and the value you expect to receive from the CRM. Consider the following costs:
- Subscription fees (monthly or annual)
- Implementation costs (if you need professional assistance)
- Training costs for your team
- Potential add-ons or integrations
- Research CRM Options: Once you have a clear understanding of your needs and budget, start researching different CRM systems. Some popular choices for small businesses include:
- HubSpot CRM: A free, user-friendly CRM with powerful features for sales, marketing, and customer service.
- Zoho CRM: A comprehensive CRM with a wide range of features and affordable pricing plans.
- Salesforce Sales Cloud: A robust CRM with advanced features, suitable for growing businesses. However, it can be more complex and expensive.
- Pipedrive: A sales-focused CRM designed to streamline the sales process.
- Freshsales: A CRM with built-in features for sales, marketing, and customer support, known for its ease of use.
- Evaluate Key Features: Consider the features that are most important to your business. Look for a CRM that offers the following capabilities:
- Contact Management: Store and organize customer contact information, including names, addresses, phone numbers, and email addresses.
- Lead Management: Track and nurture leads throughout the sales pipeline.
- Sales Automation: Automate repetitive sales tasks, such as email follow-ups and task assignments.
- Sales Pipeline Management: Visualize and manage your sales pipeline, tracking deals through each stage.
- Reporting and Analytics: Generate reports and analyze key performance indicators (KPIs).
- Integration Capabilities: Ensure the CRM integrates with your existing business tools, such as email marketing platforms, accounting software, and social media.
- Mobile Accessibility: Access your CRM data on the go with a mobile app.
- Read Reviews and Compare Pricing: Before making a decision, read reviews from other small businesses to understand their experiences with different CRM systems. Compare pricing plans and ensure the CRM offers the features you need within your budget.
- Consider Scalability: Choose a CRM that can grow with your business. As your company expands, you’ll want a CRM that can accommodate your increasing needs and data volume.
- Free Trials and Demos: Take advantage of free trials and demos offered by CRM vendors to test the platform and see if it’s a good fit for your business.
Setting Up Your CRM: A Step-by-Step Guide
Once you’ve chosen the right CRM, the next step is to set it up and configure it to meet your specific needs. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you get started:
- Create Your Account and Choose Your Plan: Sign up for an account with your chosen CRM provider and select the pricing plan that aligns with your business needs.
- Customize Your Settings: Configure your CRM settings to match your company’s branding and preferences. This may include setting your company logo, customizing the user interface, and defining your sales pipeline stages.
- Import Your Data: Import your existing customer data into the CRM. Most CRM systems allow you to import data from spreadsheets or other databases. Ensure your data is clean and well-organized before importing it. You can also manually add customer contacts.
- Set Up Users and Permissions: Create user accounts for each member of your team and assign appropriate permissions. This ensures that each user has access to the information and features they need while maintaining data security.
- Integrate with Other Tools: Integrate your CRM with other business tools, such as your email marketing platform, accounting software, and social media accounts. This will streamline your workflows and improve data accuracy.
- Customize Your Sales Pipeline: Define your sales pipeline stages and customize them to match your sales process. This will help you track deals through each stage and identify potential bottlenecks.
- Set Up Automation Rules: Automate repetitive tasks, such as sending email follow-ups, assigning leads, and creating tasks. This will save you time and improve efficiency.
- Train Your Team: Provide training to your team on how to use the CRM. This will help them understand the features, functionality, and best practices for using the system effectively.
- Test and Refine: After setting up your CRM, test it thoroughly to ensure everything is working as expected. Refine your settings and configurations as needed based on your team’s feedback and your business needs.
Using Your CRM: Core Features and Best Practices
With your CRM set up, it’s time to start using it to manage your customer relationships and drive sales. Here are some core features and best practices to help you get the most out of your CRM:
Contact Management
Contact management is the foundation of any CRM. Use your CRM to:
- Store and Organize Contact Information: Keep all your customer contact information in one central location, including names, addresses, phone numbers, email addresses, and social media profiles.
- Segment Your Contacts: Group your contacts into segments based on demographics, behavior, or other criteria. This allows you to personalize your marketing and sales efforts.
- Add Notes and Activities: Track all interactions with your customers, including phone calls, emails, meetings, and notes. This provides a complete history of your customer relationships.
- Manage Your Contacts Effectively: Regularly update your contact information, remove duplicates, and ensure the accuracy of your data.
Lead Management
Lead management is critical for converting leads into customers. Use your CRM to:
- Capture Leads: Capture leads from various sources, such as your website, social media, and marketing campaigns.
- Qualify Leads: Identify and qualify leads based on their needs and interest.
- Nurture Leads: Nurture leads through automated email campaigns and personalized follow-ups.
- Track Lead Activity: Track lead activity, such as website visits, email opens, and clicks.
- Assign Leads to Sales Reps: Assign qualified leads to your sales team for follow-up.
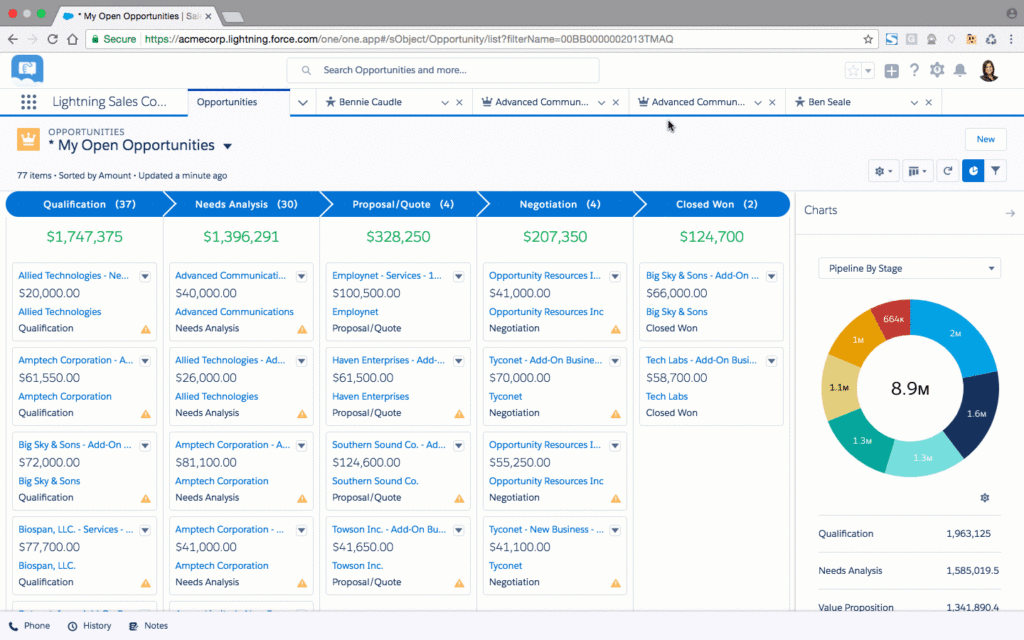
Sales Pipeline Management
Sales pipeline management helps you visualize and manage your sales process.
- Create a Sales Pipeline: Define the stages of your sales pipeline, from lead to close.
- Track Deals: Track deals through each stage of your sales pipeline.
- Monitor Progress: Monitor the progress of your deals and identify potential bottlenecks.
- Forecast Sales: Forecast your sales based on the deals in your pipeline.
- Analyze Sales Performance: Analyze your sales performance to identify areas for improvement.
Sales Automation
Sales automation streamlines your sales process and improves efficiency.
- Automate Repetitive Tasks: Automate repetitive tasks, such as sending email follow-ups, creating tasks, and updating deal stages.
- Set Up Automated Workflows: Set up automated workflows to trigger actions based on specific events, such as a lead submitting a form.
- Personalize Your Communications: Personalize your communications using data from your CRM.
- Improve Sales Efficiency: Automate your sales process to improve efficiency and save time.
Reporting and Analytics
Reporting and analytics provide valuable insights into your customer behavior and sales performance.
- Generate Reports: Generate reports on key performance indicators (KPIs), such as sales revenue, conversion rates, and customer satisfaction.
- Analyze Your Data: Analyze your data to identify trends, understand what’s working and what’s not, and make data-driven decisions.
- Track Key Metrics: Track key metrics, such as customer acquisition cost (CAC), customer lifetime value (CLTV), and churn rate.
- Make Data-Driven Decisions: Use your data to make data-driven decisions to improve your sales and marketing strategies.
Integrating Your CRM with Other Business Tools
To maximize the value of your CRM, integrate it with other business tools. This will streamline your workflows and improve data accuracy. Here are some common integrations:
- Email Marketing Platforms: Integrate your CRM with your email marketing platform to automate email campaigns, personalize communications, and track email performance.
- Accounting Software: Integrate your CRM with your accounting software to track sales revenue, manage invoices, and generate financial reports.
- Social Media: Integrate your CRM with your social media accounts to track social media interactions, manage social media leads, and personalize your social media marketing efforts.
- Website Analytics: Integrate your CRM with your website analytics platform to track website visits, user behavior, and lead generation.
- Help Desk Software: Integrate your CRM with your help desk software to provide faster and more effective customer support.
Measuring Your CRM Success
It’s essential to measure the success of your CRM implementation to ensure you’re getting the desired results. Here are some key metrics to track:
- Sales Revenue: Track your sales revenue to measure the impact of your CRM on your sales performance.
- Conversion Rates: Track your conversion rates to measure the effectiveness of your sales and marketing efforts.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): Track your CAC to measure the cost of acquiring new customers.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV): Track your CLTV to measure the long-term value of your customers.
- Customer Satisfaction: Track customer satisfaction to measure the quality of your customer service.
- Customer Retention Rate: Track your customer retention rate to measure the ability to retain your customers.
- Number of Leads Generated: Track the number of leads generated to measure the effectiveness of your lead generation efforts.
- Number of Deals Closed: Track the number of deals closed to measure the success of your sales team.
- Sales Cycle Length: Track the length of your sales cycle to measure the efficiency of your sales process.
- Employee Adoption Rate: Measure how well your team has adopted and is utilizing the CRM.
Regularly review these metrics to identify areas for improvement and make data-driven decisions to optimize your CRM usage. Don’t be afraid to adjust your strategies based on the insights you gain. The goal is to continually refine your approach to customer relationship management and drive better business outcomes.
Troubleshooting Common CRM Issues
Even with the best planning, you may encounter issues with your CRM. Here are some common problems and solutions:
- Data Entry Errors: Implement data validation rules to minimize errors. Train your team on proper data entry procedures and regularly review data for accuracy.
- Low User Adoption: Provide adequate training and ongoing support. Make the CRM user-friendly and address any concerns promptly. Show the team the benefits of using the CRM and how it can simplify their tasks.
- Integration Problems: Test integrations thoroughly before implementation. If problems arise, consult the CRM provider’s documentation or support team. Ensure your integrated systems are compatible and up-to-date.
- Slow Performance: Optimize your CRM settings and ensure your hardware meets the system requirements. Clear out unnecessary data and regularly back up your system. Consider upgrading to a more powerful plan if needed.
- Lack of Customization: If the CRM doesn’t meet your specific needs, explore customization options or consider a different CRM. Evaluate your business requirements and see if the CRM can be tailored to fit them.
- Data Security Concerns: Implement strong security measures, such as user permissions and data encryption. Regularly back up your data and follow the CRM provider’s security recommendations. Review your security settings to ensure they align with your business’s needs.
Conclusion: The Future of CRM for Small Businesses
Implementing and utilizing a CRM is no longer a luxury, but a necessity for small businesses that want to thrive. As technology continues to evolve, so will the capabilities of CRM systems. The future of CRM for small businesses is likely to include:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI-powered CRM systems will offer more advanced features, such as predictive analytics, automated lead scoring, and personalized customer interactions.
- Improved Automation: CRM systems will offer more sophisticated automation capabilities, allowing businesses to streamline their workflows and save even more time.
- Enhanced Mobile Accessibility: CRM systems will become even more mobile-friendly, allowing businesses to access their data and manage their customer relationships from anywhere.
- Greater Integration: CRM systems will integrate with a wider range of business tools, providing a more seamless and integrated experience.
- Focus on Customer Experience: CRM systems will focus on improving the customer experience, offering features that help businesses personalize their interactions and build stronger relationships.
By staying informed about the latest trends and technologies, small businesses can ensure they are making the most of their CRM investments and building lasting relationships with their customers. This tutorial has provided you with a comprehensive guide to help you get started. Embrace the power of CRM, and watch your small business flourish!