CRM Marketing Segmentation: Your Key to Unlocking Personalized Customer Experiences
In today’s hyper-competitive marketplace, simply having a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system isn’t enough. To truly thrive, businesses need to leverage the power of their CRM data to understand their customers on a deeper level and deliver personalized experiences. This is where CRM marketing segmentation comes in. It’s the art and science of dividing your customer base into distinct groups based on shared characteristics, enabling you to tailor your marketing efforts and create more meaningful interactions. Think of it as crafting individual messages for different groups of people rather than shouting the same message to everyone.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of CRM marketing segmentation, equipping you with the knowledge and tools to implement effective strategies that drive results. We’ll explore the ‘why’ behind segmentation, the different types of segments you can create, and the practical steps to get started. Get ready to transform your marketing from generic blasts into personalized customer journeys that resonate and convert.
Why CRM Marketing Segmentation Matters
Let’s be honest, nobody likes feeling like a number. Customers crave personalized experiences, and they’re more likely to engage with brands that understand their needs and preferences. CRM marketing segmentation allows you to deliver precisely that. Here’s why it’s a crucial component of any successful marketing strategy:
- Enhanced Customer Engagement: By tailoring your messaging to specific customer segments, you increase the likelihood of capturing their attention and fostering a deeper connection. It’s about showing them that you ‘get’ them.
- Improved Conversion Rates: Targeted marketing campaigns are inherently more effective. When you speak directly to a customer’s needs and interests, they’re more likely to take the desired action, whether it’s making a purchase, signing up for a newsletter, or requesting a demo.
- Increased ROI: Segmentation allows you to allocate your marketing budget more efficiently. Instead of wasting resources on campaigns that aren’t relevant to everyone, you can focus on the segments most likely to convert, maximizing your return on investment.
- Better Customer Retention: Personalized experiences build loyalty. When customers feel understood and valued, they’re more likely to stick around. Segmentation helps you create these lasting relationships.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Segmentation provides valuable insights into your customer base. By analyzing the behavior and characteristics of different segments, you can gain a deeper understanding of your customers and make more informed marketing decisions.
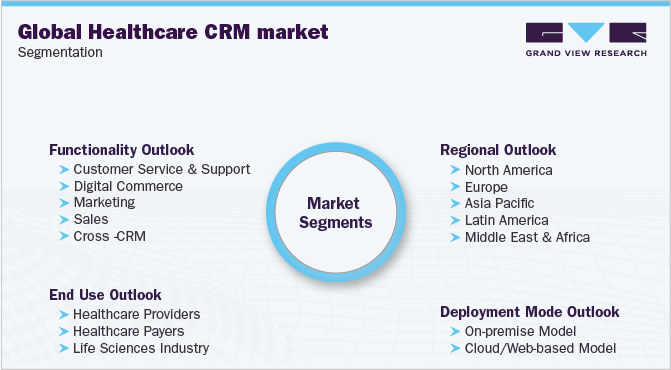
Types of CRM Marketing Segmentation
The beauty of CRM marketing segmentation is its flexibility. You can segment your customer base in countless ways, depending on your business goals and the data you have available. Here are some of the most common and effective segmentation approaches:
1. Demographic Segmentation
This is perhaps the most basic form of segmentation, but it’s still incredibly valuable. Demographic segmentation involves grouping customers based on readily available characteristics such as:
- Age: Different age groups have different needs, preferences, and purchasing behaviors. A teenager is likely to have different interests than a senior citizen.
- Gender: Tailoring your messaging and product offerings to specific genders can significantly improve engagement.
- Income: Understanding your customers’ income levels helps you determine their purchasing power and tailor your pricing and product offerings accordingly.
- Education: Educational background can provide insights into a customer’s interests, values, and communication preferences.
- Occupation: Knowing a customer’s profession can help you understand their industry, their needs, and the challenges they face.
- Family Status: Are they single, married, do they have children? This information can inform your product recommendations and marketing messages.
Example: A clothing retailer might segment its customer base by age and gender, creating separate campaigns for young women, men over 40, and so on.
2. Geographic Segmentation
This type of segmentation focuses on the location of your customers. It can be as broad as country or region, or as granular as zip code or neighborhood. Geographic segmentation is particularly useful for businesses with a local presence or those that operate in specific geographic markets.
- Location: Country, state, city, or even neighborhood.
- Climate: Tailor your product offerings based on the local climate (e.g., selling winter coats in colder regions).
- Urban vs. Rural: Urban customers may have different needs and preferences than rural customers.
- Language: If you operate in multilingual regions, tailor your marketing materials to the appropriate languages.
Example: A restaurant chain might use geographic segmentation to target customers within a specific radius of its locations, offering special promotions or discounts to drive foot traffic.
3. Psychographic Segmentation
This goes beyond demographics and focuses on the psychological aspects of your customers. It involves understanding their lifestyles, values, attitudes, interests, and personalities. This type of segmentation provides a deeper understanding of why your customers make the choices they do.
- Lifestyle: Are they health-conscious, adventurous, or homebodies?
- Values: What are their core beliefs and principles?
- Attitudes: What are their opinions on various topics?
- Interests: What are their hobbies and passions?
- Personality: Are they introverted or extroverted, risk-averse or risk-taking?
Example: A fitness brand might segment its customer base based on their lifestyle, targeting health-conscious individuals with marketing messages about healthy eating and workout routines.
4. Behavioral Segmentation
This is arguably one of the most powerful forms of segmentation. It focuses on how customers interact with your brand, including their purchasing behavior, website activity, and engagement with your marketing campaigns.
- Purchase History: What products or services have they bought in the past?
- Frequency of Purchases: How often do they buy from you?
- Average Order Value: How much do they typically spend?
- Website Activity: What pages do they visit? How long do they stay on your site?
- Engagement with Marketing Campaigns: Do they open your emails? Do they click on your links? Do they respond to your calls to action?
- Customer Loyalty: Are they repeat customers? Do they participate in your loyalty program?
Example: An e-commerce store might segment its customer base based on purchase history, targeting customers who have previously bought a specific product with related product recommendations or exclusive offers.
5. Needs-Based Segmentation
This type of segmentation focuses on the specific needs that customers are trying to fulfill when they purchase your products or services. It requires a deep understanding of your customer’s pain points and motivations.
- Problem Solving: What problems are they trying to solve with your products or services?
- Desired Outcomes: What are they hoping to achieve?
- Benefits Sought: What specific benefits are they looking for?
Example: A software company might segment its customer base based on the specific problems they are trying to solve, targeting small business owners with solutions that help them manage their finances, and targeting larger enterprises with solutions that help them streamline their operations.
6. Value-Based Segmentation
This segmentation approach categorizes customers based on their economic value to your business. It helps you prioritize your marketing efforts and allocate resources effectively.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV): How much revenue do they generate over their relationship with your business?
- Profitability: How profitable are they?
- Cost to Serve: How much does it cost to serve their needs?
Example: A subscription service might identify its high-value customers and offer them exclusive perks and benefits to increase their loyalty and lifetime value.
How to Implement CRM Marketing Segmentation: A Step-by-Step Guide
Now that you understand the ‘why’ and ‘what’ of CRM marketing segmentation, let’s dive into the ‘how’. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you implement effective segmentation strategies:
1. Define Your Objectives
Before you start segmenting, it’s crucial to define your objectives. What do you hope to achieve with segmentation? Are you trying to increase sales, improve customer retention, or drive website traffic? Having clear objectives will guide your segmentation strategy and help you measure your success.
2. Gather Data
Data is the lifeblood of segmentation. You need to gather as much relevant data as possible about your customers. This data can come from various sources, including:
- Your CRM System: This is the primary source of customer data.
- Website Analytics: Track customer behavior on your website.
- Social Media Analytics: Understand your audience’s demographics and interests.
- Surveys: Collect feedback directly from your customers.
- Customer Service Interactions: Learn about customer needs and pain points.
- Purchase History: Analyze past purchases to identify patterns and preferences.
Ensure you have a robust data collection strategy in place, and that you are compliant with all relevant data privacy regulations like GDPR or CCPA.
3. Choose Your Segmentation Criteria
Based on your objectives and the data you have available, choose the segmentation criteria that are most relevant to your business. Consider the different types of segmentation we discussed earlier (demographic, geographic, psychographic, behavioral, needs-based, and value-based) and select the ones that align with your goals.
4. Segment Your Customer Base
Use your CRM system or other data analysis tools to segment your customer base based on the criteria you’ve chosen. Create distinct groups of customers that share common characteristics.
5. Analyze Your Segments
Once you’ve created your segments, analyze them to gain a deeper understanding of each group. What are their needs, preferences, and behaviors? What are their pain points? This analysis will inform your marketing strategies and help you create more effective campaigns.
6. Develop Targeted Marketing Campaigns
Now it’s time to put your segmentation strategy into action. Develop marketing campaigns that are tailored to each segment. This includes:
- Personalized Messaging: Craft messaging that resonates with each segment’s specific needs and interests.
- Targeted Offers: Create offers and promotions that are relevant to each segment.
- Channel Selection: Choose the marketing channels that are most effective for reaching each segment (e.g., email, social media, direct mail).
- Content Creation: Develop content that addresses the specific needs and interests of each segment.
7. Implement and Test Your Campaigns
Launch your targeted marketing campaigns and monitor their performance. Use A/B testing to experiment with different messaging, offers, and channels to optimize your results. Track key metrics such as conversion rates, click-through rates, and customer engagement to measure the effectiveness of your campaigns.
8. Measure and Optimize
Continuously monitor the performance of your segmented marketing campaigns and make adjustments as needed. Analyze your data to identify areas for improvement and refine your segmentation strategy over time. Segmentation is an ongoing process, not a one-time event.
Tools and Technologies for CRM Marketing Segmentation
Several tools and technologies can help you implement and manage your CRM marketing segmentation strategy:
- CRM Systems: (e.g., Salesforce, HubSpot, Zoho CRM) Provide the foundation for storing and managing customer data and segmenting your customer base.
- Marketing Automation Platforms: (e.g., Marketo, Pardot, ActiveCampaign) Automate your marketing campaigns and personalize your customer communications.
- Data Analytics Tools: (e.g., Google Analytics, Tableau, Power BI) Analyze your customer data and gain insights into their behavior and preferences.
- Email Marketing Platforms: (e.g., Mailchimp, Constant Contact, Sendinblue) Deliver targeted email campaigns to your customer segments.
- Customer Data Platforms (CDPs): (e.g., Segment, Tealium, mParticle) Centralize and unify customer data from various sources, providing a single view of your customers.
Best Practices for CRM Marketing Segmentation
To maximize the effectiveness of your CRM marketing segmentation efforts, keep these best practices in mind:
- Start Small: Don’t try to segment your entire customer base at once. Start with a few key segments and gradually expand your efforts.
- Keep it Simple: Avoid over-segmenting your customer base. Too many segments can make it difficult to manage your campaigns.
- Focus on Actionable Insights: Ensure that your segmentation criteria provide actionable insights that you can use to improve your marketing efforts.
- Be Data-Driven: Base your segmentation decisions on data, not gut feelings.
- Personalize, Personalize, Personalize: The more personalized your messaging, the better.
- Test and Iterate: Continuously test and optimize your segmentation strategy to improve its effectiveness.
- Review and Update Regularly: Customer needs and preferences change over time. Regularly review and update your segmentation strategy to ensure it remains relevant.
- Prioritize Privacy: Always respect customer privacy and comply with all relevant data privacy regulations.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
While CRM marketing segmentation offers significant benefits, businesses can encounter challenges along the way. Here are some common hurdles and how to address them:
- Data Quality Issues: Inaccurate or incomplete data can undermine your segmentation efforts. Regularly clean and update your data to ensure its accuracy. Implement data validation rules and use data enrichment tools to improve data quality.
- Lack of Data: If you don’t have enough data to segment your customer base effectively, focus on collecting more data. Implement surveys, track website activity, and integrate with other data sources.
- Complexity: Overly complex segmentation can be difficult to manage and maintain. Start with a simple segmentation strategy and gradually add complexity as needed.
- Resistance to Change: Some team members may be resistant to adopting a new segmentation strategy. Educate your team on the benefits of segmentation and provide training on how to use the new tools and processes.
- Integration Challenges: Integrating your CRM system with other marketing tools can be challenging. Choose tools that integrate seamlessly with your CRM system and provide technical support.
The Future of CRM Marketing Segmentation
The landscape of CRM marketing segmentation is constantly evolving. Here are some trends to watch:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI and machine learning are increasingly being used to automate segmentation, personalize customer experiences, and predict customer behavior.
- Hyper-Personalization: Businesses are moving towards hyper-personalization, tailoring their marketing messages to individual customers.
- Real-Time Segmentation: Segmentation is becoming more dynamic, with businesses adapting their segmentation strategies in real-time based on customer behavior.
- Focus on Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV): Businesses are increasingly focusing on segmenting customers based on their CLTV to identify and nurture their most valuable customers.
- Privacy-First Approach: With growing concerns about data privacy, businesses are adopting a privacy-first approach to segmentation, prioritizing customer privacy and data security.
By embracing these trends, businesses can stay ahead of the curve and create even more effective and personalized customer experiences.
Conclusion: Embrace the Power of Segmentation
CRM marketing segmentation is no longer a luxury; it’s a necessity for businesses that want to thrive in today’s customer-centric world. By understanding your customers on a deeper level, you can deliver personalized experiences that resonate, drive engagement, and boost your bottom line. Implement the strategies and best practices outlined in this guide, and you’ll be well on your way to transforming your marketing efforts and building lasting customer relationships. Don’t just sell to your customers; connect with them. Segment, personalize, and watch your business flourish.