CRM for Small Business: Your Ultimate Guide to Choosing, Implementing, and Thriving

Introduction: Why Your Small Business Needs a CRM
Running a small business is a whirlwind. You’re juggling everything from sales and marketing to customer service and operations. It’s a constant balancing act, and sometimes, things slip through the cracks. That’s where a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system comes in. Think of it as your central hub for all things customer-related. It helps you manage interactions, track leads, and ultimately, drive sales. In today’s competitive landscape, a CRM isn’t just a nice-to-have; it’s a necessity for small businesses aiming to grow and succeed.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about CRM for small businesses. We’ll explore the benefits, the different types of CRM systems, how to choose the right one for your needs, and how to successfully implement and use it to its full potential. Get ready to transform your customer relationships and boost your bottom line!
The Core Benefits of CRM for Small Businesses
Investing in a CRM system offers a plethora of advantages for small businesses. Let’s delve into the key benefits:
Enhanced Customer Relationship Management
At its heart, a CRM is all about building stronger customer relationships. It allows you to:
- Centralize Customer Data: No more scattered spreadsheets or sticky notes. A CRM consolidates all customer information – contact details, purchase history, communication logs – into one accessible place. This 360-degree view of your customers empowers you to understand their needs and preferences better.
- Improve Communication: CRM systems often integrate with email, phone, and social media, enabling seamless communication. You can track all interactions, ensuring no customer query goes unanswered and that follow-ups are timely and relevant.
- Personalize Interactions: Armed with customer data, you can personalize your communications and tailor your offerings. Customers appreciate feeling valued and understood, and a CRM helps you deliver that experience.
Increased Sales and Revenue
A well-implemented CRM directly contributes to increased sales and revenue by:
- Streamlining Sales Processes: CRM automates many sales tasks, such as lead assignment, follow-up reminders, and quote generation. This frees up your sales team to focus on what they do best: closing deals.
- Improving Lead Management: CRM helps you track leads through the sales funnel, identify promising prospects, and nurture them with targeted content and communication. This leads to higher conversion rates.
- Identifying Upselling and Cross-selling Opportunities: By analyzing customer purchase history and behavior, a CRM can suggest relevant products or services that customers might be interested in, boosting your average order value.
Improved Efficiency and Productivity
CRM systems are designed to make your team more efficient and productive. They help you:
- Automate Tasks: Automate repetitive tasks like data entry, email marketing, and appointment scheduling. This saves time and reduces the risk of human error.
- Gain Actionable Insights: CRM provides detailed reports and analytics on sales performance, marketing campaign effectiveness, and customer behavior. This data-driven approach enables you to make informed decisions and optimize your strategies.
- Foster Collaboration: A CRM facilitates collaboration among team members by providing a shared platform for accessing and updating customer information. This ensures everyone is on the same page and working towards common goals.
Better Customer Service
Happy customers are loyal customers. A CRM empowers you to provide exceptional customer service by:
- Providing Quick Access to Customer Information: Support staff can quickly access customer data, including past interactions and purchase history, allowing them to resolve issues efficiently.
- Tracking Support Tickets: CRM systems often include support ticket management features, ensuring all customer inquiries are tracked, resolved, and followed up on.
- Offering Personalized Support: With a 360-degree view of the customer, support staff can provide personalized assistance tailored to the customer’s specific needs and preferences.
Types of CRM Systems for Small Businesses
The CRM landscape is diverse, with various types of systems catering to different business needs and budgets. Here’s a breakdown of the most common types:
Cloud-Based CRM (SaaS – Software as a Service)
Cloud-based CRM is the most popular choice for small businesses. It’s hosted on the vendor’s servers, so you don’t need to worry about installing or maintaining any software. This makes it easy to set up, access from anywhere with an internet connection, and scale as your business grows. Cloud-based CRM systems often come with subscription-based pricing, making them affordable for small businesses. They also benefit from automatic updates and regular feature enhancements.
On-Premise CRM
On-premise CRM systems are installed and managed on your own servers. This gives you more control over your data and security, but it also requires more technical expertise and upfront investment. On-premise CRM is less common for small businesses due to the associated costs and complexity.
Open-Source CRM
Open-source CRM systems offer a free, customizable platform. However, they often require technical expertise to install, configure, and maintain. While the software itself is free, you may need to pay for hosting, support, and customization services. Open-source CRM can be a good option for businesses with in-house technical capabilities or those seeking a highly tailored solution.
Industry-Specific CRM
Some CRM systems are designed specifically for certain industries, such as real estate, healthcare, or manufacturing. These systems often come with pre-built features and workflows tailored to the specific needs of that industry. If you’re in a niche industry, an industry-specific CRM can save you time and effort by providing a ready-made solution.
Choosing the Right CRM for Your Small Business
Selecting the right CRM is a crucial decision. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you make the right choice:
1. Define Your Needs and Goals
Before you start looking at CRM systems, take the time to clearly define your business needs and goals. What are you hoping to achieve with a CRM? What are your pain points? What specific features do you need? Documenting your requirements will help you narrow down your options and choose a system that aligns with your objectives.
- Identify Key Processes: Map out your sales, marketing, and customer service processes. This will help you understand how a CRM can streamline your workflows.
- Determine Your Budget: Set a realistic budget for your CRM investment, including software costs, implementation expenses, and ongoing maintenance.
- Assess Your Team’s Technical Skills: Consider your team’s technical proficiency and choose a system that is easy to use and manage.
2. Research CRM Providers
Once you have a clear understanding of your needs, start researching CRM providers. Read reviews, compare features, and explore pricing options. Look for providers that offer:
- Scalability: Choose a CRM that can grow with your business as your customer base expands and your needs evolve.
- Integration Capabilities: Ensure the CRM integrates with your existing tools, such as email marketing platforms, accounting software, and social media channels.
- User-Friendliness: Opt for a CRM with a user-friendly interface and intuitive navigation.
- Customer Support: Check the provider’s customer support options, including documentation, tutorials, and support channels.
- Security: Prioritize a CRM that offers robust security features to protect your customer data.
3. Evaluate CRM Features
Not all CRM systems are created equal. Evaluate the features of each system to determine if it meets your specific requirements. Consider these key features:
- Contact Management: The ability to store and manage customer contact information, including contact details, social media profiles, and communication history.
- Lead Management: Features for tracking leads, qualifying prospects, and nurturing them through the sales funnel.
- Sales Automation: Tools for automating sales tasks, such as lead assignment, follow-up reminders, and quote generation.
- Marketing Automation: Features for automating marketing campaigns, such as email marketing, social media posting, and lead nurturing.
- Reporting and Analytics: The ability to generate reports and analyze data on sales performance, marketing campaign effectiveness, and customer behavior.
- Mobile Access: The ability to access the CRM on mobile devices, allowing your team to stay connected and productive on the go.
- Integrations: Compatibility with other software your business uses, like email marketing platforms, accounting software, and social media channels.
4. Consider Pricing and Implementation
CRM pricing models vary. Some providers offer subscription-based pricing based on the number of users, while others offer tiered pricing with different feature sets. Consider the following:
- Pricing Structure: Understand the pricing model and any associated fees.
- Implementation Costs: Factor in the costs of implementation, including data migration, training, and customization.
- Hidden Costs: Be aware of any hidden costs, such as add-ons, support fees, or data storage charges.
5. Request Demos and Free Trials
Before making a final decision, request demos and free trials from your shortlisted CRM providers. This will allow you to:
- Get a Hands-On Experience: Test the system’s features and functionality to see if it meets your needs.
- Assess User-Friendliness: Evaluate the user interface and ease of navigation.
- Evaluate Customer Support: Test the provider’s customer support by asking questions and seeking assistance.
- Ensure Integration: Verify that the CRM integrates seamlessly with your existing tools.
6. Choose the Right CRM
Based on your research, evaluations, and trials, choose the CRM that best aligns with your needs, goals, and budget. Don’t be afraid to take your time and compare options to find the perfect fit for your small business.
Implementing Your CRM System: A Step-by-Step Guide
Once you’ve chosen your CRM, the next step is implementation. A well-planned implementation is crucial for ensuring a successful CRM adoption. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
1. Plan Your Implementation
Before you begin, create a detailed implementation plan that outlines the following:
- Goals and Objectives: Clearly define your goals for the CRM implementation and how you will measure success.
- Timeline: Set a realistic timeline for the implementation, including key milestones and deadlines.
- Team and Roles: Identify the team members involved in the implementation and assign roles and responsibilities.
- Data Migration Plan: Develop a plan for migrating your existing customer data to the new CRM system.
- Training Plan: Create a training plan to ensure your team is properly trained on how to use the CRM.
2. Data Migration
Migrating your customer data to the new CRM is a critical step. Here’s how to do it effectively:
- Clean Your Data: Before migrating your data, clean it by removing duplicates, correcting errors, and standardizing formats.
- Choose a Migration Method: Determine the best method for migrating your data, whether it’s manual entry, import using a CSV file, or a data migration tool.
- Test Your Migration: Test your data migration to ensure all data is transferred accurately.
3. Customize Your CRM
Customize your CRM to meet your specific business needs. This may involve:
- Configuring Fields and Workflows: Configure the fields and workflows to match your sales, marketing, and customer service processes.
- Integrating with Other Tools: Integrate your CRM with other tools, such as email marketing platforms, accounting software, and social media channels.
- Branding Your CRM: Customize the look and feel of your CRM to reflect your brand.
4. Train Your Team
Training your team is essential for ensuring CRM adoption. Provide comprehensive training on how to use the system, including:
- Basic Functionality: Teach your team how to navigate the system, enter data, and access information.
- Specific Features: Train your team on the specific features they will use in their roles.
- Best Practices: Provide best practices for using the CRM effectively.
- Ongoing Support: Offer ongoing support and training to help your team stay up-to-date on the latest features and best practices.
5. Roll Out and Monitor
Once your team is trained, roll out the CRM system. Monitor its performance and make adjustments as needed.
- Go Live: Officially launch the CRM system.
- Monitor Adoption: Track user adoption and identify any areas where users are struggling.
- Gather Feedback: Gather feedback from your team to identify areas for improvement.
- Make Adjustments: Make adjustments to the system or training as needed to improve performance.
Maximizing the Value of Your CRM: Best Practices
Once your CRM is implemented, the real work begins. Here are some best practices to help you maximize the value of your CRM:
1. Data Quality is Key
The accuracy and completeness of your data are crucial for the success of your CRM. Regularly update your data, remove duplicates, and ensure all information is accurate. Implement data validation rules to prevent errors and maintain data integrity. A clean database is the foundation for effective CRM usage.
2. Foster User Adoption
User adoption is essential for maximizing the value of your CRM. Encourage your team to use the system by:
- Providing Ongoing Training: Offer regular training to keep your team up-to-date on the latest features and best practices.
- Creating a Culture of Use: Encourage your team to use the CRM as part of their daily workflow.
- Providing Incentives: Offer incentives for using the CRM effectively.
- Addressing Concerns: Address any concerns or issues your team may have about using the system.
3. Automate, Automate, Automate
Leverage the automation features of your CRM to streamline your workflows and save time. Automate tasks such as lead assignment, email marketing, and appointment scheduling. Automation frees up your team to focus on more strategic tasks.
4. Regularly Analyze and Optimize
Regularly analyze your CRM data to identify areas for improvement. Use the reporting and analytics features to track your sales performance, marketing campaign effectiveness, and customer behavior. Make adjustments to your strategies based on your findings.
5. Integrate with Other Tools
Integrate your CRM with other tools, such as email marketing platforms, accounting software, and social media channels. This will streamline your workflows and provide a more complete view of your customers.
6. Stay Updated
CRM systems are constantly evolving. Stay up-to-date on the latest features and best practices by attending webinars, reading industry publications, and following CRM experts on social media. Regular updates ensure you’re making the most of your investment.
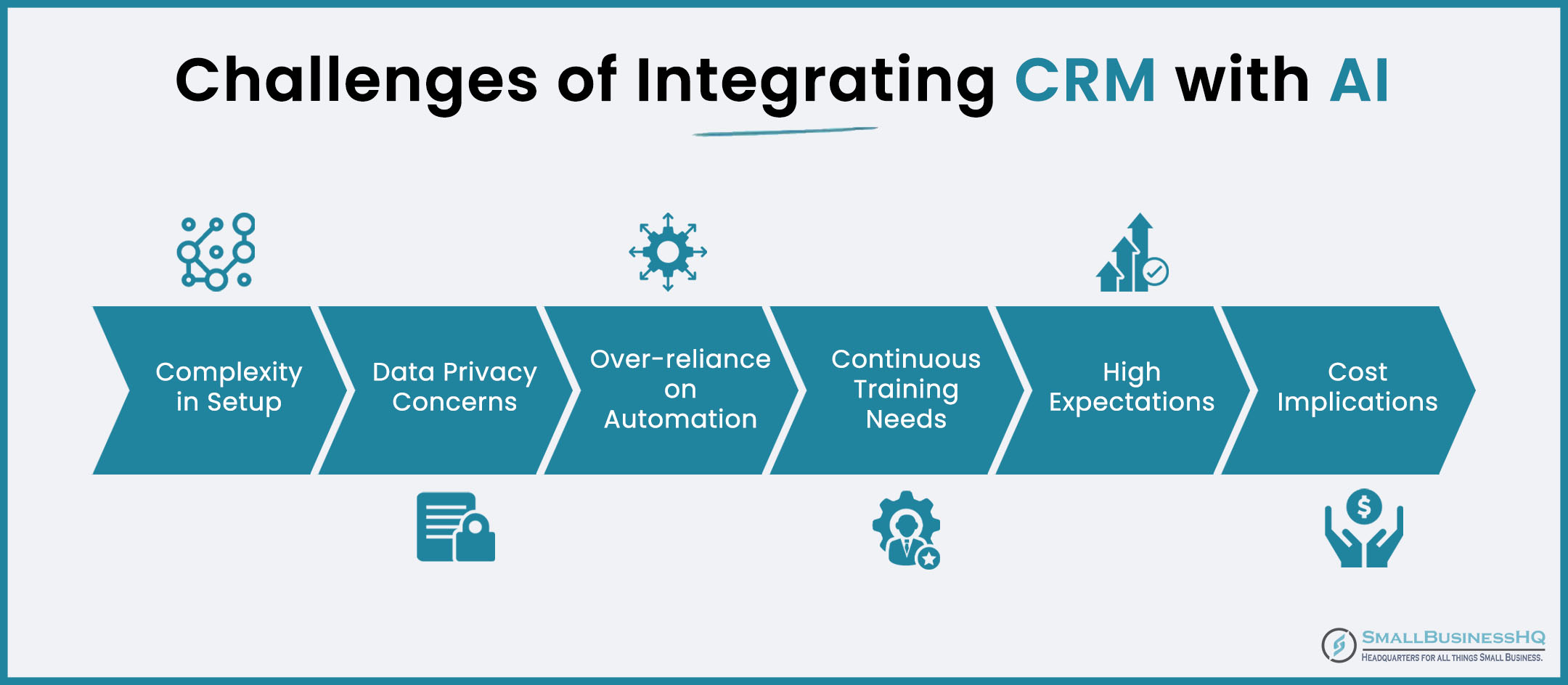
CRM for Small Business: Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
While CRM offers significant benefits, small businesses may encounter some challenges. Here’s how to overcome them:
1. Lack of User Adoption
One of the biggest challenges is getting your team to adopt the CRM. Overcome this by:
- Providing Adequate Training: Ensure your team is properly trained on how to use the system.
- Highlighting the Benefits: Explain how the CRM will make their jobs easier and more efficient.
- Making it Easy to Use: Choose a CRM that is user-friendly and intuitive.
- Leading by Example: Encourage managers and team leaders to use the CRM and demonstrate its value.
2. Data Migration Difficulties
Migrating your existing data can be time-consuming and complex. Overcome this by:
- Planning Ahead: Create a detailed data migration plan.
- Cleaning Your Data: Clean your data before migration to remove duplicates and errors.
- Testing Your Migration: Test your data migration to ensure all data is transferred accurately.
3. Customization Complexity
Customizing your CRM can be complex, especially if you don’t have technical expertise. Overcome this by:
- Choosing a User-Friendly System: Choose a CRM that offers easy customization options.
- Seeking Professional Help: Consider hiring a CRM consultant to help with customization.
- Starting Small: Start with a basic setup and gradually add customizations as needed.
4. Cost Considerations
CRM systems can be expensive. Overcome this by:
- Choosing a Budget-Friendly Option: Research CRM systems that fit your budget.
- Negotiating Pricing: Negotiate pricing with CRM providers.
- Phased Implementation: Implement the CRM in phases to spread out the costs.
Conclusion: Embracing CRM for Small Business Success
Implementing a CRM system is a game-changer for small businesses. It empowers you to build stronger customer relationships, increase sales and revenue, improve efficiency and productivity, and provide better customer service. By choosing the right CRM, implementing it effectively, and following best practices, you can transform your customer relationships and drive your business to new heights.
Don’t let the challenges of running a small business hold you back. Embrace the power of CRM and unlock your full potential. Start your CRM journey today, and watch your business thrive!