CRM for Small Business Security: Protecting Your Data and Your Future
CRM for Small Business Security: Safeguarding Your Valuable Assets
In today’s digital landscape, where data breaches and cyber threats are rampant, small businesses face a daunting challenge: protecting their valuable information. Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems, while essential for business growth, also introduce new vulnerabilities. This comprehensive guide delves into the critical aspects of CRM security for small businesses, offering practical advice, best practices, and actionable steps to fortify your defenses. From understanding the risks to implementing robust security measures, we’ll explore how to safeguard your data and ensure the long-term success of your business.
Understanding the Risks: Why CRM Security Matters
Before diving into solutions, it’s crucial to understand the threats that small businesses face. CRM systems store a wealth of sensitive data, including customer contact information, purchase history, financial details, and more. This information is a goldmine for cybercriminals. A successful breach can lead to:
- Financial Loss: Fines, legal fees, and the cost of recovery can cripple a small business.
- Reputational Damage: Loss of customer trust can be devastating and difficult to recover from.
- Data Breaches: Sensitive customer data can be stolen and used for fraudulent activities.
- Business Disruption: Downtime and recovery efforts can severely impact operations.
Small businesses are often targeted because they may lack the resources and expertise to implement robust security measures. This makes them an easier target for attackers. CRM security is not just about protecting data; it’s about protecting your business’s reputation, financial stability, and future.
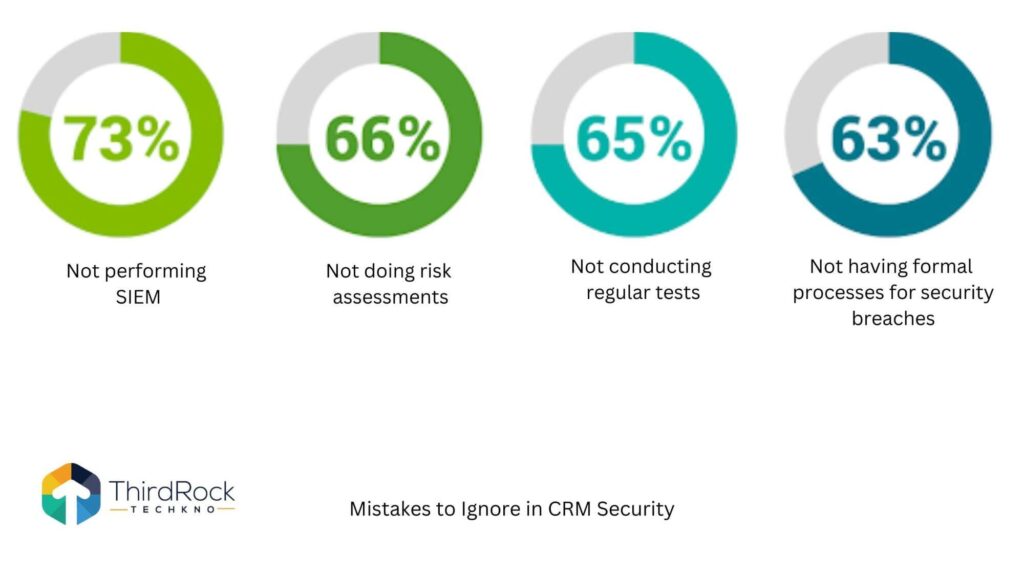
Common CRM Security Vulnerabilities
Several vulnerabilities can expose your CRM system to security risks. Understanding these vulnerabilities is the first step toward mitigating them:
Weak Passwords and Authentication
One of the most common vulnerabilities is weak passwords. Many users opt for easy-to-remember passwords, making them susceptible to brute-force attacks. Inadequate authentication methods, such as the lack of multi-factor authentication (MFA), further exacerbate the risk.
Data Breaches
Data breaches can happen due to various reasons, including phishing attacks, malware infections, and insider threats. These breaches can expose sensitive customer data to unauthorized access.
Lack of Encryption
Data encryption is crucial for protecting data in transit and at rest. Without encryption, data can be easily intercepted and read by unauthorized parties.
Outdated Software
Using outdated CRM software or failing to apply security patches can leave your system vulnerable to known exploits. Software vendors regularly release patches to address security flaws, so it’s essential to keep your software up to date.
Improper Access Controls
Granting excessive access privileges to users can increase the risk of data breaches. It’s crucial to implement role-based access control (RBAC) to limit user access to only the information they need.
Phishing Attacks
Phishing attacks are a common tactic used by cybercriminals to trick users into revealing sensitive information. These attacks often involve sending malicious emails that appear to be from legitimate sources.
Implementing Robust CRM Security Measures: A Step-by-Step Guide
Protecting your CRM system requires a multi-layered approach. Here’s a step-by-step guide to implementing robust security measures:
1. Choose a Secure CRM Provider
When selecting a CRM provider, prioritize security. Look for providers that offer:
- Strong Encryption: Data should be encrypted both in transit and at rest.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to verify their identity using multiple methods.
- Regular Security Audits: The provider should conduct regular security audits to identify and address vulnerabilities.
- Compliance Certifications: Look for providers that comply with relevant security standards, such as SOC 2.
- Data Residency Options: Consider where your data will be stored. Ensure the location aligns with your business’s needs and any compliance requirements.
Research the provider’s security track record and read reviews from other customers.
2. Implement Strong Password Policies
Enforce strong password policies to protect user accounts. These policies should include:
- Minimum Password Length: Require passwords to be at least 12 characters long.
- Password Complexity: Mandate the use of a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters.
- Regular Password Changes: Encourage or require users to change their passwords regularly.
- Password Managers: Consider using password managers to generate and store strong passwords.
- Avoid Password Reuse: Instruct users to avoid reusing passwords across different accounts.
Educate your employees about the importance of strong passwords and how to create them.
3. Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to verify their identity using multiple methods, such as a password and a code from a mobile app or a physical security key. Enable MFA for all user accounts, including administrators.
4. Implement Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
RBAC limits user access to only the information they need to perform their job duties. This reduces the risk of data breaches caused by insider threats or compromised accounts. Define user roles and assign appropriate permissions based on those roles. Regularly review and update user permissions as needed.
5. Encrypt Sensitive Data
Encrypt sensitive data, such as customer credit card information, both in transit and at rest. This ensures that even if data is intercepted or stolen, it cannot be read without the encryption key. Most reputable CRM providers offer encryption options. Utilize those and ensure that encryption is properly configured.
6. Regularly Update Software and Apply Security Patches
Keep your CRM software and all related applications up to date. Software vendors regularly release security patches to address vulnerabilities. Install these patches promptly to protect your system from known exploits. Automate the patching process if possible.
7. Conduct Regular Security Audits and Vulnerability Assessments
Conduct regular security audits and vulnerability assessments to identify and address weaknesses in your CRM system. This can be done internally or by hiring a third-party security expert. These assessments should include penetration testing to simulate real-world attacks.
8. Implement Data Backup and Recovery Procedures
Regularly back up your CRM data to protect against data loss due to hardware failures, human error, or cyberattacks. Store backups in a secure location, separate from your primary CRM system. Test your backup and recovery procedures regularly to ensure they are effective.
9. Educate Employees About Security Threats
Educate your employees about common security threats, such as phishing attacks, social engineering, and malware. Provide regular training on security best practices and how to identify and avoid potential threats. Create a culture of security awareness within your organization.
10. Monitor Your System for Suspicious Activity
Implement monitoring tools to detect suspicious activity, such as unauthorized access attempts, unusual data access patterns, and potential malware infections. Regularly review security logs and investigate any suspicious events. Consider using a Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) system to centralize log management and threat detection.
11. Develop an Incident Response Plan
Develop an incident response plan to outline the steps your business will take in the event of a security breach. This plan should include procedures for containing the breach, assessing the damage, notifying affected parties, and restoring your system. Test your incident response plan regularly to ensure it is effective.
12. Comply with Data Privacy Regulations
Familiarize yourself with relevant data privacy regulations, such as GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA, and ensure your CRM system complies with these regulations. This includes obtaining consent for data collection, providing data access and deletion rights, and implementing appropriate security measures to protect customer data.
Best Practices for CRM Security
In addition to the steps outlined above, here are some best practices to enhance your CRM security:
Regularly Review User Access
Periodically review user access privileges to ensure that users only have the necessary permissions. Revoke access for former employees or users who no longer require access to the system.
Implement Strong Network Security
Protect your network with firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and other security measures. Segment your network to isolate your CRM system from other systems.
Use a Secure Connection (HTTPS)
Ensure that your CRM system is accessed over a secure connection (HTTPS) to encrypt data in transit. This prevents eavesdropping and data tampering.
Conduct Regular Security Training
Provide regular security training to your employees to educate them about the latest threats and best practices. Conduct phishing simulations to test their awareness.
Stay Informed About Security Threats
Stay informed about the latest security threats and vulnerabilities. Subscribe to security newsletters, follow security blogs, and attend industry events to stay up-to-date.
Consider Using a Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) System
A SIEM system can help you centralize log management, detect threats, and respond to security incidents. It can also automate security tasks, such as incident response.
Implement a Data Loss Prevention (DLP) System
A DLP system can help you prevent sensitive data from leaving your organization. It can monitor data in transit, at rest, and in use, and prevent data leakage.
Regularly Test Your Security Measures
Test your security measures regularly to ensure they are effective. This includes penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, and social engineering simulations.
Review Third-Party Integrations
Review the security of any third-party integrations with your CRM system. Ensure that these integrations are secure and that they do not introduce new vulnerabilities.
Document Your Security Policies and Procedures
Document your security policies and procedures to provide guidance to your employees and to ensure consistency in your security practices.
The Role of CRM in Business Growth
While security is paramount, it’s also important to remember the core purpose of a CRM: to drive business growth. A secure CRM system allows you to:
- Enhance Customer Relationships: By securely storing and managing customer data, you can personalize interactions and build stronger relationships.
- Improve Sales Performance: A secure CRM provides sales teams with the tools and information they need to close deals and generate revenue.
- Streamline Marketing Efforts: Secure CRM systems can integrate with marketing automation tools to deliver targeted campaigns and track results.
- Increase Customer Loyalty: By providing excellent customer service and protecting customer data, you can build trust and foster customer loyalty.
- Gain a Competitive Advantage: A secure and well-managed CRM system can give you a competitive edge by helping you understand your customers better and deliver exceptional customer experiences.
Choosing the Right CRM for Your Small Business
Selecting the right CRM for your small business is a critical decision. Consider the following factors when making your choice:
- Security Features: Prioritize CRM providers that offer robust security features, such as encryption, MFA, and regular security audits.
- Scalability: Choose a CRM that can scale to meet your business’s growing needs.
- Integration Capabilities: Ensure the CRM integrates with your existing business tools, such as email marketing platforms and accounting software.
- Ease of Use: Select a CRM that is easy to use and that your employees can quickly adopt.
- Cost: Consider the cost of the CRM, including licensing fees, implementation costs, and ongoing maintenance costs.
- Customer Support: Choose a CRM provider that offers excellent customer support.
- Compliance: Ensure the CRM complies with relevant data privacy regulations.
Research different CRM providers and compare their features, pricing, and security measures. Consider a trial period to test the CRM before making a final decision.
The Future of CRM Security
The landscape of CRM security is constantly evolving. As cyber threats become more sophisticated, businesses must stay ahead of the curve. Some emerging trends in CRM security include:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML are being used to detect and prevent cyberattacks. AI can analyze data to identify suspicious activity and automate security tasks.
- Zero Trust Security: Zero trust security is a security model that assumes no user or device can be trusted by default. This approach requires continuous verification of users and devices.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain technology can be used to secure CRM data and prevent data tampering.
- Increased Automation: Automation is playing an increasingly important role in CRM security. Automated security tools can help businesses detect and respond to threats more efficiently.
- Focus on User Behavior Analytics: Analyzing user behavior can help identify suspicious activities and prevent insider threats.
Small businesses should embrace these trends to stay ahead of the evolving threat landscape.
Conclusion: Securing Your CRM for a Secure Future
CRM systems are invaluable tools for small businesses. However, they also introduce security risks. By understanding the risks, implementing robust security measures, and staying informed about the latest threats, you can protect your CRM data and ensure the long-term success of your business. Prioritize security, choose a reputable CRM provider, and educate your employees about security best practices. By taking a proactive approach to CRM security, you can safeguard your valuable assets and create a secure environment for your customers and your business.
Remember, CRM security is an ongoing process. Regularly review your security measures, stay informed about the latest threats, and adapt your security practices as needed. By investing in CRM security, you are investing in the future of your business.



