CRM for Small Business Security: Protecting Your Data and Building Trust

CRM for Small Business Security: Safeguarding Your Data and Fostering Trust
In today’s digital landscape, data is the lifeblood of any business, and for small businesses, the stakes are particularly high. A data breach can be crippling, leading to financial losses, reputational damage, and even legal repercussions. That’s where Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems come in. While primarily designed to manage customer interactions, CRM systems also play a crucial role in enhancing small business security. This article delves into the multifaceted aspects of CRM security, exploring how small businesses can leverage these platforms to protect their valuable data, build customer trust, and ensure long-term success.
The Importance of CRM Security for Small Businesses
Small businesses often operate with limited resources and may not have dedicated IT security teams. This makes them particularly vulnerable to cyber threats. CRM systems, which store sensitive customer information, become prime targets for attackers. Protecting this data is not just a matter of compliance; it’s a fundamental requirement for survival. When data is compromised, it can lead to a cascade of negative consequences:
- Financial Loss: Data breaches can result in direct financial losses due to remediation costs, legal fees, and potential fines.
- Reputational Damage: A breach can severely damage a company’s reputation, eroding customer trust and leading to lost business.
- Legal and Compliance Issues: Businesses must comply with data privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA, and breaches can lead to significant penalties.
- Operational Disruptions: A security incident can disrupt business operations, leading to downtime and lost productivity.
Implementing robust CRM security measures is therefore essential for small businesses to mitigate these risks and ensure their long-term viability. It’s about more than just protecting data; it’s about building a secure and trustworthy environment for your customers and employees.
Key Security Features to Look for in a CRM System
When selecting a CRM system, security should be a top priority. Here are some key security features to consider:
1. Data Encryption
Data encryption is the process of converting data into an unreadable format, protecting it from unauthorized access. Look for CRM systems that offer encryption both in transit (when data is being transmitted over a network) and at rest (when data is stored on servers). This is a critical layer of defense, ensuring that even if data is intercepted or stolen, it remains unreadable without the proper decryption key.
2. Access Controls and Permissions
Role-based access control (RBAC) allows you to define user roles and assign specific permissions based on those roles. This ensures that employees only have access to the data they need to perform their jobs, minimizing the risk of accidental or malicious data breaches. Implement a least-privilege access model, granting users only the minimum necessary permissions.
3. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to verify their identity using multiple factors, such as a password and a one-time code from a mobile device. This significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, even if a user’s password is compromised. Ensure your CRM system supports MFA for all user accounts.
4. Regular Backups
Regular data backups are essential for disaster recovery. In the event of a data breach, system failure, or other unforeseen circumstances, backups allow you to restore your data and minimize downtime. Choose a CRM system that offers automated, secure backups and a clear recovery plan.
5. Security Audits and Compliance
Look for CRM systems that undergo regular security audits and certifications, such as SOC 2 or ISO 27001. These certifications demonstrate that the vendor has implemented robust security measures and adheres to industry best practices. Choose a CRM system that complies with relevant data privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA, to avoid potential legal issues.
6. Activity Logging and Monitoring
Activity logging tracks user actions within the CRM system, providing an audit trail of who accessed what data and when. This is crucial for identifying suspicious activity and investigating security incidents. Implement real-time monitoring to detect and respond to potential threats promptly.
7. Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
DLP tools prevent sensitive data from leaving your organization’s control. This can include features such as preventing users from copying or printing sensitive data, or blocking the transfer of data to unauthorized locations. While not all CRM systems offer built-in DLP, some integrate with third-party DLP solutions.
Best Practices for Implementing CRM Security
Implementing a secure CRM system is not just about choosing the right platform; it’s also about following best practices to ensure its effectiveness:
1. Strong Password Policies
Enforce strong password policies for all user accounts. This includes requiring complex passwords, regularly changing passwords, and avoiding the use of easily guessable passwords. Educate employees about the importance of password security and encourage them to use unique passwords for their CRM accounts.
2. User Training and Awareness
Train your employees on security best practices, including how to identify and avoid phishing attacks, social engineering attempts, and other threats. Conduct regular security awareness training to keep employees informed about the latest threats and vulnerabilities. Create a culture of security awareness within your organization.
3. Data Minimization
Collect and store only the data that is necessary for your business operations. Avoid collecting unnecessary personal information, as this increases your attack surface and potential liability. Regularly review your data retention policies and delete data that is no longer needed.
4. Regular Software Updates
Keep your CRM system and all related software up to date with the latest security patches. Software updates often include critical security fixes that address known vulnerabilities. Automate the update process whenever possible to ensure that your systems are always protected.
5. Incident Response Plan
Develop a comprehensive incident response plan that outlines the steps to take in the event of a data breach or other security incident. This plan should include procedures for detecting, containing, and recovering from a breach, as well as communication protocols for notifying customers and relevant authorities. Regularly test your incident response plan to ensure its effectiveness.
6. Vendor Due Diligence
When selecting a CRM vendor, conduct thorough due diligence to assess their security practices. Review their security policies, certifications, and incident response plan. Ask questions about their data encryption, access controls, and other security measures. Choose a vendor that prioritizes security and has a proven track record of protecting customer data.
7. Regular Security Assessments
Conduct regular security assessments, such as vulnerability scans and penetration tests, to identify and address potential weaknesses in your CRM system. This can help you proactively identify and mitigate security risks before they can be exploited by attackers. Consider hiring a third-party security expert to conduct these assessments.
Choosing the Right CRM for Enhanced Security
Selecting a CRM system is a crucial decision, and security should be a primary factor in your evaluation process. Consider the following factors when choosing a CRM:
- Security Features: Evaluate the security features offered by each CRM vendor, including data encryption, access controls, MFA, and activity logging.
- Vendor Reputation: Research the vendor’s reputation and track record for security. Look for reviews and testimonials from other customers.
- Compliance: Ensure that the CRM system complies with relevant data privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA.
- Scalability: Choose a CRM system that can scale to meet your business’s future needs, including security requirements.
- Integration: Consider how the CRM system integrates with your existing security tools and infrastructure.
- Support and Training: Ensure that the vendor provides adequate support and training to help you implement and manage the CRM system securely.
Some CRM systems that are known for their strong security features include Salesforce, HubSpot, Zoho CRM, and Microsoft Dynamics 365. However, it is crucial to evaluate each CRM system based on your specific security needs and requirements.
The Human Element of CRM Security
While technology plays a vital role in CRM security, the human element is equally important. Even the most secure CRM system can be compromised if employees are not properly trained or if they engage in risky behaviors. Here are some ways to address the human element:
- Security Awareness Training: Regularly train your employees on security best practices, including how to identify and avoid phishing attacks, social engineering attempts, and other threats.
- Phishing Simulations: Conduct phishing simulations to test employees’ ability to recognize and avoid phishing emails.
- Password Management: Educate employees about the importance of strong passwords and password management best practices. Encourage them to use password managers.
- Access Control: Implement role-based access control (RBAC) to ensure that employees only have access to the data they need to perform their jobs.
- Data Handling Policies: Develop clear policies and procedures for handling sensitive customer data, including how to store, transmit, and dispose of data securely.
- Employee Screening: Conduct background checks on employees who will have access to sensitive customer data.
Building Trust Through Secure CRM Practices
Implementing robust CRM security measures is not just about protecting data; it’s also about building trust with your customers. When customers know that their data is safe and secure, they are more likely to trust your business and remain loyal. Here’s how to foster trust through secure CRM practices:
- Transparency: Be transparent with your customers about your security practices. Clearly communicate how you protect their data and what steps you take to prevent data breaches.
- Data Privacy Policy: Have a clear and concise data privacy policy that explains how you collect, use, and protect customer data. Make this policy easily accessible on your website.
- Compliance with Regulations: Demonstrate your commitment to data privacy by complying with relevant regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA.
- Prompt Response to Breaches: In the event of a data breach, respond promptly and transparently. Notify affected customers and provide them with information about the incident and the steps you are taking to address it.
- Regular Communication: Keep your customers informed about your security efforts and any changes you make to your security practices.
- Security Certifications: Display security certifications, such as SOC 2 or ISO 27001, on your website and marketing materials to demonstrate your commitment to security.
The Future of CRM Security
The threat landscape is constantly evolving, and CRM security must adapt to stay ahead of emerging threats. Here are some trends to watch:
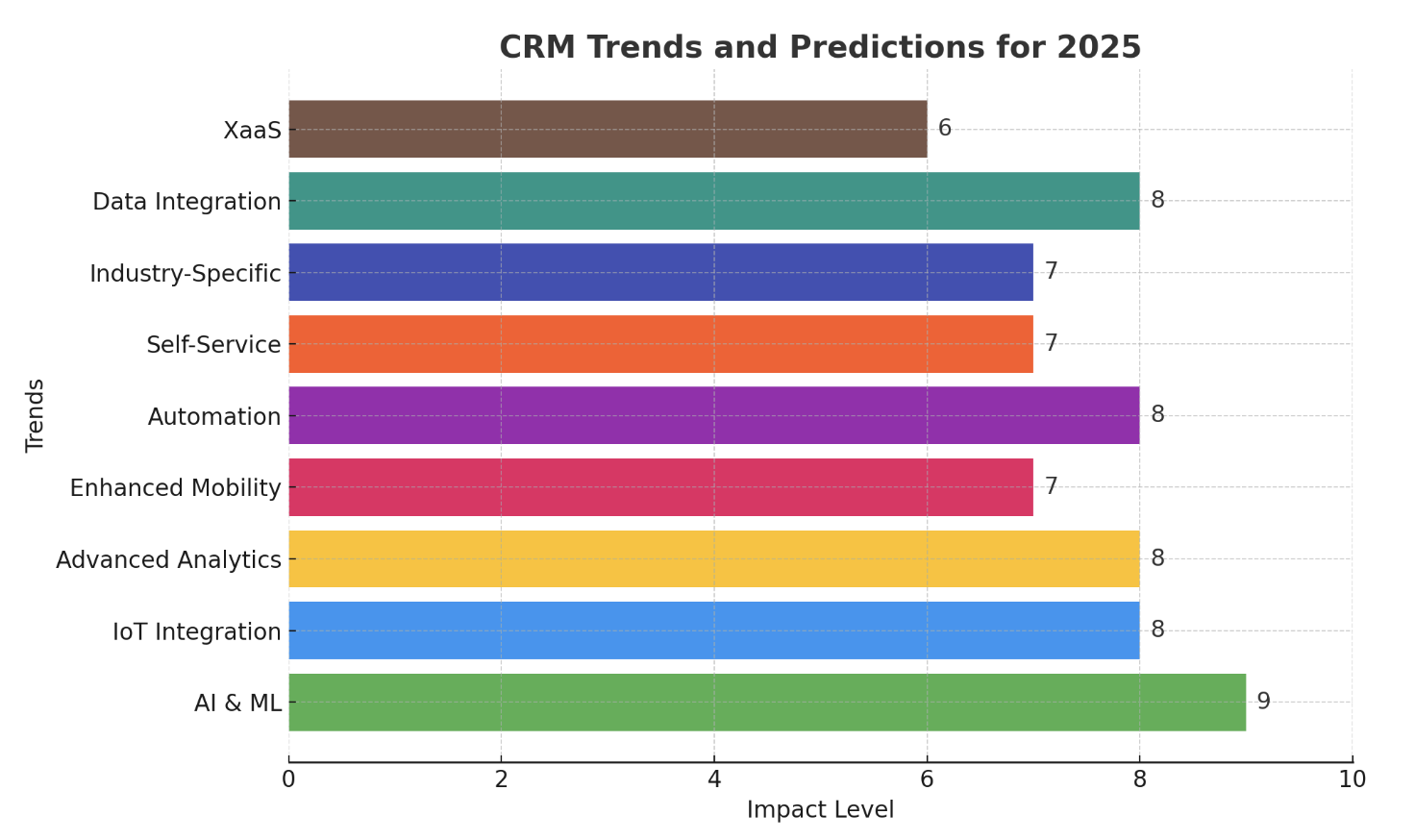
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML are being used to enhance CRM security by detecting and responding to threats in real-time, automating security tasks, and improving threat intelligence.
- Zero Trust Security: Zero trust security models assume that no user or device can be trusted by default. This approach requires continuous verification and authorization, which can significantly enhance CRM security.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain technology can be used to secure data and improve transparency in CRM systems.
- Increased Focus on Data Privacy: Data privacy regulations are becoming stricter, and businesses must prioritize data privacy compliance.
- Integration with Security Ecosystems: CRM systems are increasingly integrating with other security tools and platforms, such as security information and event management (SIEM) systems and threat intelligence platforms.
Conclusion
CRM security is not an afterthought; it’s a fundamental component of a successful small business. By implementing robust security measures, educating employees, and building trust with customers, small businesses can protect their valuable data, mitigate risks, and ensure long-term success. Prioritizing CRM security is an investment in your business’s future, safeguarding your reputation and fostering lasting customer relationships. The journey towards a secure CRM environment is ongoing, requiring continuous vigilance, adaptation, and a commitment to protecting your most valuable asset: your customer data.