Boost Your Small Business Sales: A Comprehensive Guide to CRM Systems

Introduction: Leveling the Playing Field with CRM
In the dynamic world of small businesses, staying ahead of the competition demands more than just a great product or service. It requires a deep understanding of your customers, efficient management of your sales pipeline, and the ability to nurture relationships that drive growth. This is where a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system steps in as a game-changer. CRM isn’t just for the big corporations anymore; it’s an essential tool for small businesses looking to thrive.
This comprehensive guide delves into the world of CRM for small business sales, exploring its benefits, features, implementation strategies, and how to choose the right system for your specific needs. We’ll cut through the jargon and present the information in a clear, actionable way, empowering you to transform your sales process and achieve sustainable success.
What is CRM and Why Does Your Small Business Need It?
CRM, at its core, is a system for managing your interactions with current and potential customers. It’s a centralized hub that stores all customer-related data, providing a 360-degree view of each customer’s journey. This includes contact information, communication history, purchase history, and any other relevant details.
But why is this so crucial for small businesses? Here’s why:
- Improved Customer Relationships: CRM helps you personalize interactions, understand customer needs, and provide exceptional service, leading to increased customer loyalty.
- Enhanced Sales Efficiency: By automating tasks, streamlining workflows, and providing sales teams with the right information, CRM boosts productivity and allows them to focus on closing deals.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: CRM provides valuable insights into your sales performance, customer behavior, and market trends, enabling you to make informed decisions and optimize your strategies.
- Increased Revenue: By improving sales efficiency, customer retention, and lead conversion rates, CRM ultimately contributes to increased revenue and profitability.
- Better Organization: CRM systems eliminate the chaos of scattered spreadsheets and disorganized contact lists, ensuring that everyone on your team has access to the same, up-to-date information.
In essence, CRM empowers small businesses to operate with the efficiency and customer focus of larger organizations, without the associated costs. It’s about working smarter, not harder.
Key Features of a CRM System for Small Business Sales
When choosing a CRM system, it’s crucial to understand the core features that will directly impact your sales performance. Here are some essential features to look for:
Contact Management
This is the foundation of any CRM. It allows you to store and organize all your contact information, including names, phone numbers, email addresses, and other relevant details. Good contact management features should include:
- Contact Segmentation: The ability to group contacts based on various criteria (e.g., industry, location, purchase history).
- Lead Scoring: Assigning points to leads based on their engagement and behavior, allowing you to prioritize the most promising prospects.
- Automated Data Entry: Integration with other tools to automatically capture contact information, saving time and reducing manual errors.
Sales Automation
Sales automation streamlines your sales process, freeing up your team to focus on more strategic activities. Key sales automation features include:
- Workflow Automation: Automating repetitive tasks, such as sending follow-up emails, creating tasks, and updating deal stages.
- Lead Routing: Automatically assigning leads to the appropriate sales representatives based on predefined rules.
- Email Tracking: Monitoring email opens, clicks, and replies to gauge engagement and personalize follow-ups.
Sales Pipeline Management
A well-designed sales pipeline allows you to track the progress of your deals, identify bottlenecks, and forecast revenue. Key features include:
- Deal Tracking: Visualizing the sales process, from lead to closed deal.
- Stage Customization: Customizing the sales stages to align with your specific sales process.
- Reporting and Analytics: Generating reports on sales performance, deal velocity, and other key metrics.
Reporting and Analytics
Data is your most valuable asset. Robust reporting and analytics features allow you to gain insights into your sales performance and make data-driven decisions. Look for features such as:
- Customizable Dashboards: Displaying key metrics and KPIs in a clear and concise format.
- Sales Forecasting: Predicting future revenue based on current sales pipeline activity.
- Performance Tracking: Monitoring individual and team performance to identify areas for improvement.
Integration Capabilities
Your CRM should seamlessly integrate with other tools you use, such as email marketing platforms, accounting software, and social media. This ensures that data flows smoothly between systems, eliminating data silos and improving efficiency. Consider the integrations offered with:
- Email Marketing Platforms: Syncing contact data and tracking email campaigns.
- Accounting Software: Integrating sales data with financial records.
- Social Media: Monitoring social media activity and engaging with customers.
Mobile Accessibility
In today’s fast-paced world, your sales team needs access to customer data and CRM functionality on the go. A mobile-friendly CRM allows them to:
- Access customer information from anywhere.
- Update deals and tasks on the go.
- Stay connected with customers, regardless of location.
Choosing the Right CRM for Your Small Business
Selecting the right CRM is a crucial decision that can significantly impact your business’s success. With so many options available, it’s important to carefully evaluate your needs and choose a system that aligns with your specific requirements. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you make the right choice:
1. Define Your Needs and Goals
Before you start researching CRM systems, take the time to define your needs and goals. Consider the following questions:
- What are your primary sales goals? (e.g., increase leads, improve conversion rates, boost customer retention)
- What are the biggest challenges in your current sales process?
- What features are essential for your business?
- What is your budget?
- How many users will need access to the CRM?
Answering these questions will help you narrow down your options and choose a system that meets your specific requirements.
2. Research CRM Vendors
Once you have a clear understanding of your needs, start researching CRM vendors. There are numerous options available, ranging from basic, affordable solutions to more comprehensive, enterprise-level systems. Some popular CRM vendors for small businesses include:
- HubSpot CRM: A free, user-friendly CRM with a wide range of features.
- Zoho CRM: A comprehensive and affordable CRM with a variety of integrations.
- Salesforce Sales Cloud: A powerful and customizable CRM, suitable for businesses of all sizes.
- Pipedrive: A sales-focused CRM with a visual pipeline and intuitive interface.
- Freshsales: An AI-powered CRM with features like lead scoring and sales automation.
Read reviews, compare features, and consider your budget when evaluating different vendors.
3. Evaluate Features and Functionality
Once you’ve narrowed down your list of potential vendors, carefully evaluate their features and functionality. Make sure the system offers the features you need, such as contact management, sales automation, sales pipeline management, reporting and analytics, and integration capabilities. Consider the following:
- Ease of Use: Is the system user-friendly and easy to navigate?
- Customization Options: Can you customize the system to align with your specific sales process?
- Scalability: Can the system scale as your business grows?
- Customer Support: Does the vendor offer adequate customer support?
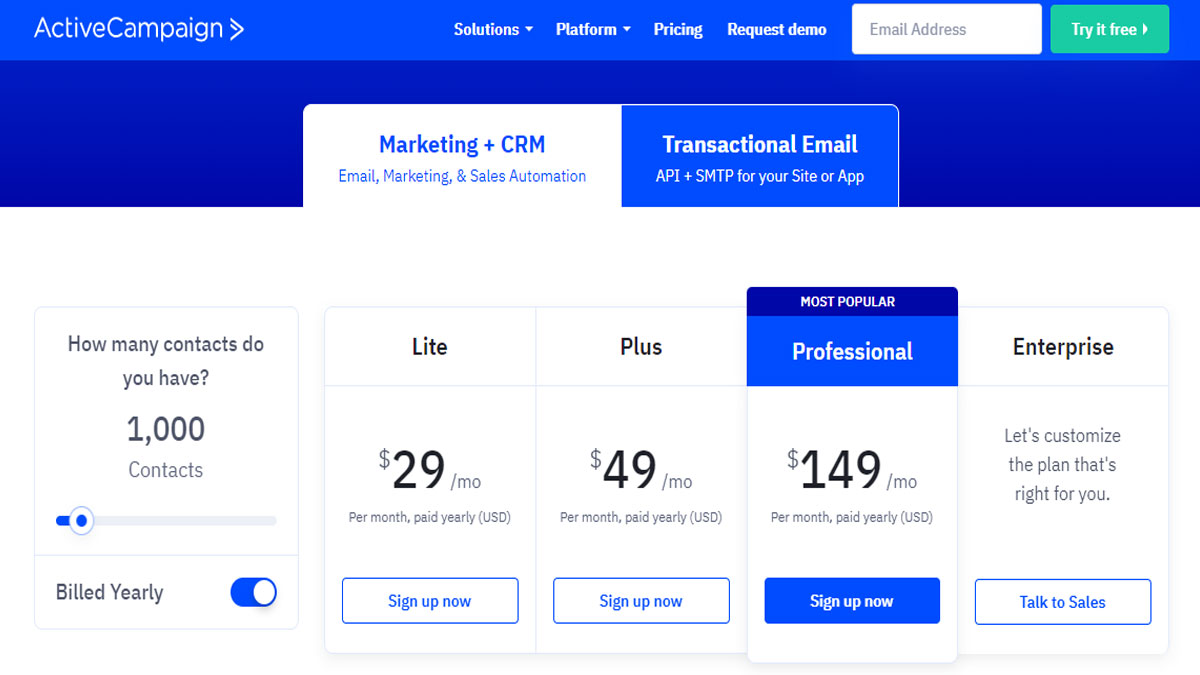
4. Consider Pricing and Implementation Costs
CRM systems vary in price, ranging from free options to monthly subscription fees. Consider your budget and the value you’ll receive from the system. Also, factor in the implementation costs, such as data migration and training. Some vendors offer free trials, which can be a great way to test the system before committing to a subscription.
5. Test the System with a Free Trial
Before making a final decision, take advantage of free trials offered by CRM vendors. This will allow you to test the system, explore its features, and determine if it’s the right fit for your business. During the trial, pay attention to:
- Ease of use: How easy is it to navigate the interface and use the system’s features?
- Performance: Does the system perform smoothly and efficiently?
- Integration capabilities: Does the system integrate with your existing tools?
- Customer Support: How responsive and helpful is the vendor’s customer support?
6. Plan for Implementation and Training
Once you’ve chosen a CRM system, develop a detailed implementation plan. This should include:
- Data Migration: Transferring your existing customer data into the new CRM.
- System Configuration: Customizing the system to align with your sales process.
- User Training: Training your sales team on how to use the system effectively.
Proper training is essential for ensuring that your team adopts the new CRM and utilizes its features to their full potential.
Implementing a CRM System: A Step-by-Step Guide
Implementing a CRM system can seem daunting, but with a well-defined plan, you can ensure a smooth and successful transition. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you get started:
1. Planning and Preparation
Before you begin, take the time to plan and prepare for the implementation process. This includes:
- Defining your goals and objectives: What do you hope to achieve with the CRM?
- Identifying key stakeholders: Who will be involved in the implementation process?
- Creating a project timeline: Set realistic deadlines for each stage of the implementation.
- Assigning roles and responsibilities: Clearly define who is responsible for each task.
Proper planning will help you avoid common pitfalls and ensure a successful implementation.
2. Data Migration
Data migration is a critical step in the implementation process. You’ll need to transfer your existing customer data into the new CRM. This can involve:
- Cleaning and organizing your data: Removing duplicates, correcting errors, and standardizing data formats.
- Importing your data into the CRM: Using the CRM’s import tools to transfer your data.
- Verifying the data: Checking to ensure that all data has been imported correctly.
Accurate data migration is essential for ensuring that your CRM is populated with the information you need to succeed.
3. System Configuration
Once your data has been migrated, you’ll need to configure the CRM to align with your specific sales process. This includes:
- Customizing the sales pipeline: Defining your sales stages and configuring the pipeline view.
- Setting up user roles and permissions: Granting access to the appropriate features and data to each user.
- Configuring integrations: Connecting the CRM to your other tools, such as email marketing platforms and accounting software.
Proper configuration will ensure that the CRM is tailored to your business needs.
4. User Training
User training is essential for ensuring that your team adopts the new CRM and utilizes its features to their full potential. Provide comprehensive training on:
- How to use the CRM: Covering all the key features and functionalities.
- Best practices for data entry: Ensuring that data is entered accurately and consistently.
- How to use the CRM to support their sales activities: Showing how the CRM can help them close deals and achieve their goals.
Offer ongoing support and training to ensure that users continue to utilize the system effectively.
5. Testing and Refinement
Before launching the CRM, test it thoroughly to identify and resolve any issues. This includes:
- Testing the features: Ensuring that all features are working correctly.
- Testing the integrations: Verifying that data is flowing smoothly between systems.
- Gathering user feedback: Getting feedback from your team on their experience with the system.
Based on the feedback, refine the system to optimize its performance and usability.
6. Launch and Ongoing Support
Once you’ve completed the testing and refinement phase, launch the CRM and start using it to manage your sales process. Provide ongoing support to your team, including:
- Troubleshooting technical issues: Addressing any technical problems that arise.
- Providing ongoing training: Offering additional training as needed.
- Monitoring performance: Tracking the CRM’s performance and making adjustments as necessary.
Continuous improvement is key to maximizing the value of your CRM system.
Maximizing CRM Adoption and User Engagement
Implementing a CRM system is only the first step. To truly reap the benefits, you need to ensure that your team actively uses the system and embraces it as an essential tool. Here are some strategies to maximize CRM adoption and user engagement:
1. Communicate the Benefits
Clearly communicate the benefits of the CRM to your team. Explain how it will help them:
- Save time and increase productivity.
- Improve customer relationships.
- Close more deals.
- Achieve their sales goals.
Highlighting the advantages will motivate your team to embrace the new system.
2. Provide Adequate Training and Support
Ensure that your team receives comprehensive training on how to use the CRM. Offer ongoing support and answer any questions they may have. Make sure users feel comfortable using the system.
3. Make it Easy to Use
Choose a CRM system that is user-friendly and easy to navigate. Customize the system to align with your team’s workflows. Simplify the data entry process by integrating with other tools and automating tasks.
4. Lead by Example
Lead by example. Use the CRM yourself and demonstrate its value to your team. Share success stories and highlight how the CRM is helping you achieve your sales goals.
5. Encourage Feedback and Collaboration
Encourage your team to provide feedback on the CRM. Use their feedback to improve the system and make it more user-friendly. Foster a collaborative environment where users can share tips and best practices.
6. Monitor Usage and Provide Incentives
Monitor CRM usage and identify areas where users may be struggling. Provide incentives for consistent CRM usage. Recognize and reward users who are actively using the system and achieving positive results.
Measuring the ROI of Your CRM System
To justify the investment in a CRM system, it’s important to measure its return on investment (ROI). Here are some key metrics to track:
- Sales Revenue: Track the increase in sales revenue after implementing the CRM.
- Lead Conversion Rate: Monitor the percentage of leads that convert into customers.
- Sales Cycle Length: Measure the time it takes to close a deal.
- Customer Retention Rate: Track the percentage of customers who remain loyal to your business.
- Customer Lifetime Value: Assess the total revenue generated by a customer over their relationship with your business.
- Sales Productivity: Measure the number of deals closed per sales representative.
By tracking these metrics, you can demonstrate the value of your CRM system and make data-driven decisions to optimize your sales strategies.
Conclusion: Embracing CRM for Small Business Success
In today’s competitive landscape, a CRM system is no longer a luxury for small businesses; it’s a necessity. By implementing a CRM, you can improve customer relationships, enhance sales efficiency, make data-driven decisions, and ultimately, drive revenue growth. Choosing the right CRM, implementing it effectively, and maximizing user adoption are crucial steps to ensure your success.
By following the guidance in this comprehensive guide, you can confidently embark on your CRM journey and transform your sales process. Embrace the power of CRM and unlock the potential for sustainable growth in your small business. Remember, the key to success is to choose the right CRM, implement it effectively, and commit to continuous improvement. The future of your sales success is in your hands!