Securing Your Small Business: A Deep Dive into CRM Security and Protecting Customer Data
Introduction: The Critical Role of CRM Security for Small Businesses
In today’s digital landscape, small businesses are increasingly reliant on Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems. These systems are the backbone of customer interactions, sales processes, and marketing efforts. However, with the convenience and efficiency that CRM offers comes the critical responsibility of safeguarding sensitive customer data. For a small business, a data breach can be devastating, leading to financial losses, reputational damage, and a loss of customer trust. This article delves into the intricacies of CRM security for small businesses, providing a comprehensive guide to understanding the threats, implementing robust security measures, and ensuring the long-term protection of your valuable customer information.
This isn’t just about ticking boxes; it’s about building a resilient business that customers can trust. We’ll explore the various facets of CRM security, from choosing the right CRM provider to establishing internal security protocols and staying ahead of evolving cyber threats. We’ll also look at real-world examples and best practices to help you navigate the complex world of data protection and maintain a secure and thriving business.
Understanding the Security Risks: What Small Businesses Face
Before diving into solutions, it’s crucial to understand the potential threats that small businesses face regarding CRM security. The reality is, small businesses are often targeted because they may lack the robust security infrastructure of larger corporations. Cybercriminals see them as easier targets, and the consequences can be severe.
Common Threats:
- Data Breaches: This is the most significant risk. A data breach occurs when sensitive customer information, such as names, addresses, credit card details, and purchase history, is stolen or exposed. This can happen through various means, including hacking, malware, phishing, and insider threats.
- Ransomware Attacks: Cybercriminals encrypt a business’s data and demand a ransom for its release. This can cripple operations and lead to significant financial losses. CRM data is often a prime target in ransomware attacks.
- Phishing Attacks: Cybercriminals use deceptive emails or websites to trick employees into revealing sensitive information, such as login credentials. This can give attackers access to the CRM system and customer data.
- Insider Threats: This involves malicious actions by employees, contractors, or other individuals with access to the CRM system. This could involve data theft, sabotage, or unauthorized access.
- Malware Infections: Malware, such as viruses and Trojans, can infect a business’s systems and steal data, monitor activity, or disrupt operations.
- Weak Passwords and Poor Access Controls: Using weak passwords or failing to implement proper access controls makes it easier for attackers to gain unauthorized access to the CRM system.
- Lack of Data Encryption: Without encryption, data is vulnerable to interception and theft, both while in transit and at rest.
These threats can lead to a range of negative consequences, including:
- Financial Losses: Costs associated with data breaches include investigation, notification of affected customers, legal fees, fines, and remediation efforts.
- Reputational Damage: A data breach can severely damage a business’s reputation, leading to a loss of customer trust and a decline in sales.
- Legal and Regulatory Consequences: Businesses are often subject to data privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA, and can face fines and legal action for failing to protect customer data.
- Operational Disruptions: A data breach can disrupt business operations, leading to downtime, lost productivity, and delays in providing services to customers.
Choosing a Secure CRM Provider: Key Considerations
The foundation of your CRM security lies in selecting a provider that prioritizes data protection. Not all CRM platforms are created equal, and some offer more robust security features than others. Here’s what to consider when choosing a CRM for your small business:
Security Features:
- Data Encryption: The CRM provider should encrypt data both in transit (e.g., when data is being transmitted between your computer and the CRM server) and at rest (e.g., when data is stored on the CRM server). This is a fundamental security measure.
- Access Controls and Permissions: The platform should allow you to define granular access controls, restricting access to sensitive data based on user roles and responsibilities.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to verify their identity through multiple methods, such as a password and a code sent to their mobile device.
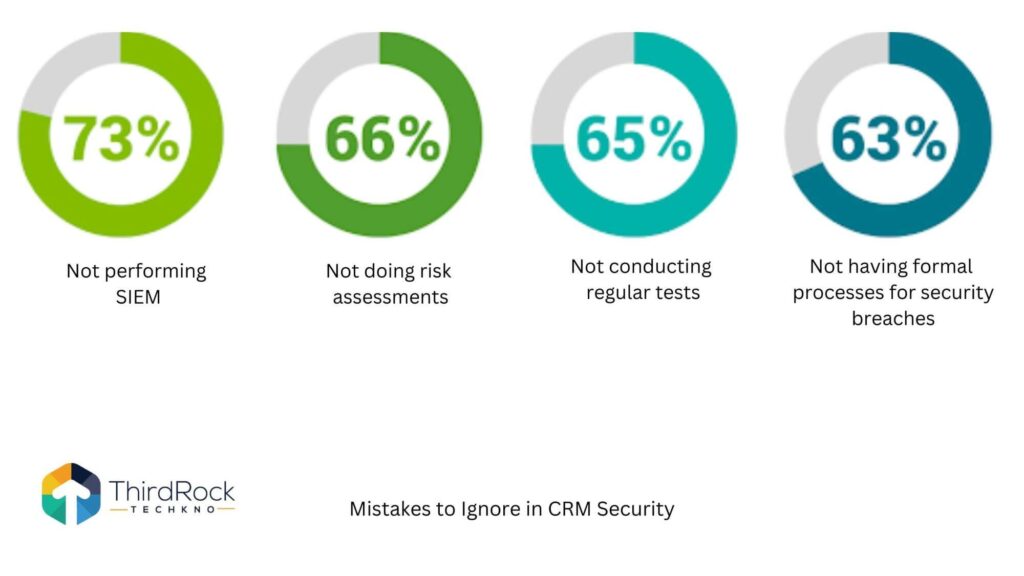
- Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing: The CRM provider should conduct regular security audits and penetration testing to identify and address vulnerabilities in their systems.
- Compliance Certifications: Look for CRM providers that comply with industry-recognized security standards, such as ISO 27001 and SOC 2.
- Data Backup and Recovery: The provider should offer regular data backups and a reliable data recovery plan in case of a data breach or system failure.
- Security Incident Response Plan: A well-defined incident response plan outlines the steps the provider will take in the event of a security breach.
Provider Reputation and Track Record:
- Research the provider’s security track record. Have they experienced any data breaches? How have they responded to security incidents?
- Read customer reviews and testimonials. Pay attention to any mentions of security concerns or issues.
- Check the provider’s website for information about their security practices. Look for a dedicated security page or documentation outlining their security measures.
- Contact the provider and ask specific questions about their security features and practices. Don’t hesitate to ask for clarification or more details.
Data Residency and Location:
- Consider where the CRM provider stores its data. Data residency regulations may apply, depending on your industry and location. Make sure the provider complies with relevant regulations.
- Choose a provider with data centers in secure locations. Data centers should have robust physical security measures, such as surveillance, access controls, and environmental controls.
Scalability and Future-Proofing:
- Choose a CRM that can scale with your business. As your business grows, you’ll need a CRM that can handle increasing amounts of data and user activity.
- Consider the provider’s commitment to security updates and improvements. The security landscape is constantly evolving, so the provider should be proactive in addressing new threats and vulnerabilities.
Implementing Internal Security Measures: Best Practices for Small Businesses
Choosing a secure CRM provider is only the first step. You also need to implement internal security measures to protect your CRM data. Here are some best practices:
Password Management:
- Enforce strong password policies. Require employees to use strong, unique passwords that are at least 12 characters long and include a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Regularly change passwords. Require employees to change their passwords every 90 days or less.
- Use a password manager. Encourage employees to use a password manager to securely store and manage their passwords.
- Train employees on password security best practices. Educate employees about the risks of using weak passwords, reusing passwords, and sharing passwords.
Access Control and User Permissions:
- Implement the principle of least privilege. Grant employees only the minimum access necessary to perform their job duties.
- Regularly review user permissions. Revoke access for employees who no longer need it or who have left the company.
- Use role-based access control (RBAC). Define user roles based on job functions and assign permissions to those roles.
- Monitor user activity. Regularly review user activity logs to detect any suspicious activity or unauthorized access attempts.
Employee Training and Awareness:
- Provide regular security awareness training. Educate employees about the latest security threats, such as phishing, social engineering, and malware.
- Conduct phishing simulations. Test employees’ ability to identify and avoid phishing attacks.
- Establish a clear security policy. Communicate your security policies to employees and ensure they understand their responsibilities.
- Encourage employees to report security incidents. Create a culture where employees feel comfortable reporting suspicious activity or security concerns.
Data Backup and Disaster Recovery:
- Implement a regular data backup schedule. Back up your CRM data regularly, ideally daily.
- Store backups in a secure location. Store backups offsite or in the cloud to protect them from physical damage or loss.
- Test your data recovery plan regularly. Ensure that you can successfully restore your CRM data in the event of a data breach or system failure.
- Document your data backup and recovery procedures. Create clear and concise documentation that outlines your backup and recovery processes.
Network Security:
- Use a firewall. A firewall helps protect your network from unauthorized access.
- Keep your software up to date. Regularly update your operating systems, software, and security patches to address known vulnerabilities.
- Use a secure Wi-Fi network. Protect your Wi-Fi network with a strong password and encryption.
- Segment your network. Separate your CRM system from other parts of your network to limit the impact of a potential breach.
- Consider using a VPN (Virtual Private Network) for remote access. A VPN encrypts your internet traffic and protects it from eavesdropping.
Endpoint Security:
- Install and maintain antivirus and anti-malware software. Regularly scan your devices for malware and viruses.
- Enable device encryption. Encrypt your laptops, tablets, and smartphones to protect your data in case of loss or theft.
- Implement mobile device management (MDM). Use MDM to manage and secure mobile devices that access your CRM data.
- Control access to USB drives and other removable media. Prevent employees from using unauthorized devices that could introduce malware.
Incident Response Plan:
- Develop a detailed incident response plan. This plan should outline the steps you will take in the event of a security breach or other security incident.
- Identify key personnel. Assign roles and responsibilities to individuals who will be involved in the incident response process.
- Establish communication protocols. Define how you will communicate with employees, customers, and other stakeholders in the event of a security incident.
- Practice your incident response plan. Regularly conduct drills to test your plan and ensure that your team is prepared to respond to a security incident.
Staying Ahead of the Curve: Proactive Security Measures
CRM security is not a one-time effort; it’s an ongoing process. To stay ahead of evolving threats, small businesses need to be proactive in their security efforts. Here are some proactive measures to consider:
Regular Security Audits and Vulnerability Assessments:
- Conduct regular security audits. Hire a third-party security expert to assess your CRM system and identify any vulnerabilities.
- Perform vulnerability assessments. Regularly scan your systems for known vulnerabilities and patch them promptly.
- Conduct penetration testing. Simulate a real-world attack to identify weaknesses in your security defenses.
Threat Intelligence and Monitoring:
- Stay informed about the latest security threats. Subscribe to security blogs, newsletters, and industry publications to stay up-to-date on the latest threats and vulnerabilities.
- Implement security monitoring tools. Use security information and event management (SIEM) tools to monitor your systems for suspicious activity.
- Monitor your CRM system for unusual activity. Look for unusual login attempts, data access patterns, or system behavior.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP):
- Implement DLP policies. Use DLP tools to prevent sensitive data from leaving your organization.
- Monitor data transfers. Track data transfers to and from your CRM system to identify any unauthorized activity.
- Encrypt sensitive data. Encrypt sensitive data at rest and in transit to protect it from unauthorized access.
Compliance and Regulatory Awareness:
- Stay informed about relevant data privacy regulations. Understand the data privacy regulations that apply to your business, such as GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA.
- Implement the necessary security measures to comply with those regulations. Ensure that your CRM system and security practices meet the requirements of these regulations.
- Regularly review your compliance posture. Conduct regular audits to ensure that you are meeting your compliance obligations.
The Human Element: Training and Culture of Security
While technical measures are essential, the human element is often the weakest link in the security chain. Investing in employee training and fostering a culture of security can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches. Here’s how:
Security Awareness Training:
- Provide regular security awareness training. Educate employees about the latest security threats, such as phishing, social engineering, and malware.
- Use interactive training methods. Make training engaging and memorable by using interactive methods, such as quizzes, simulations, and real-world examples.
- Tailor training to different roles. Customize training content to address the specific security risks faced by different roles within your organization.
- Provide ongoing training. Security threats are constantly evolving, so provide ongoing training to keep employees up-to-date on the latest threats and best practices.
Cultivating a Security-Conscious Culture:
- Promote a culture of security. Encourage employees to take ownership of security and to report any suspicious activity or security concerns.
- Lead by example. Senior management should demonstrate a commitment to security and set a positive example for employees.
- Recognize and reward good security practices. Acknowledge and reward employees who demonstrate a commitment to security.
- Make security a part of your company’s values. Integrate security into your company’s mission statement and values.
Fostering Open Communication:
- Encourage employees to report security incidents. Create a culture where employees feel comfortable reporting security incidents without fear of reprisal.
- Provide clear reporting channels. Establish clear channels for employees to report security incidents or concerns.
- Investigate all reported incidents thoroughly. Take all reported incidents seriously and investigate them thoroughly.
- Provide feedback to employees. Let employees know the outcome of investigations and any actions taken.
Conclusion: Building a Secure Future for Your Small Business
CRM security is not a destination; it’s a journey. By understanding the risks, choosing the right CRM provider, implementing internal security measures, staying proactive, and investing in employee training, small businesses can significantly reduce their risk of data breaches and protect their valuable customer data. Remember, it’s an ongoing process. Continuously assess your security posture, adapt to new threats, and foster a culture of security throughout your organization. By prioritizing CRM security, you can build a secure and thriving business that customers can trust.
Securing your CRM system is an investment in your business’s future. It’s about protecting your customers, safeguarding your reputation, and ensuring the long-term success of your small business. The time and effort you invest in CRM security today will pay dividends in the form of increased customer trust, reduced financial risks, and a more resilient business overall. Start today, and build a secure future.