Fortifying Your Fortress: A Comprehensive Guide to CRM Security for Small Businesses
Introduction: The Unseen Threat to Your Small Business Fortress
In today’s digital landscape, the lifeblood of any business, especially a small one, is its data. Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems have become indispensable, acting as the central nervous system for managing interactions, sales, and customer information. But with this increased reliance comes a significant responsibility: safeguarding that data. The threat landscape is vast and ever-evolving, with cybercriminals constantly seeking vulnerabilities to exploit. For small businesses, the consequences of a data breach can be devastating, potentially leading to financial ruin, reputational damage, and loss of customer trust. This comprehensive guide will delve into the crucial aspects of CRM security for small businesses, equipping you with the knowledge and strategies to build a robust defense against cyber threats.
Understanding the Stakes: Why CRM Security Matters for Small Businesses
Before we delve into the specifics, let’s underscore the importance of CRM security. Why should a small business owner prioritize this? The answer lies in the potential ramifications of a security breach:
- Financial Loss: Data breaches can lead to significant financial burdens, including fines for non-compliance with data privacy regulations (like GDPR or CCPA), the cost of investigating and remediating the breach, legal fees, and potential lawsuits.
- Reputational Damage: A security breach can severely tarnish your business’s reputation. Customers may lose trust in your ability to protect their sensitive information, leading to a decline in sales and customer loyalty. Negative press and social media backlash can further exacerbate the damage.
- Operational Disruption: Breaches can disrupt your business operations, leading to downtime, lost productivity, and the need to rebuild systems. This can be particularly damaging for small businesses that rely on streamlined operations.
- Loss of Competitive Advantage: Losing access to your CRM data can cripple your sales and marketing efforts, hindering your ability to understand your customers, personalize interactions, and effectively target your audience.
- Legal and Regulatory Consequences: Depending on the nature of the data compromised, you may face legal action and regulatory penalties, particularly if you fail to comply with data protection laws.
In short, CRM security is not just a technical issue; it’s a fundamental business imperative. It’s about protecting your assets, your reputation, and your future.
Key Security Threats Facing Small Businesses Using CRM Systems
Small businesses are often targeted by cybercriminals because they are perceived as having weaker security measures compared to larger corporations. Here are some of the most common security threats that small businesses using CRM systems face:
- Phishing Attacks: Phishing is a social engineering tactic where attackers use deceptive emails, messages, or websites to trick users into revealing sensitive information, such as login credentials or financial details. Phishing attacks are highly effective because they exploit human vulnerabilities.
- Malware Infections: Malware, including viruses, Trojans, and ransomware, can infect your systems through various means, such as malicious attachments, infected websites, or compromised software. Malware can steal data, disrupt operations, and hold your data hostage.
- Ransomware Attacks: Ransomware is a particularly devastating type of malware that encrypts your data and demands a ransom payment in exchange for the decryption key. Small businesses are often targeted because they may not have the resources to recover from a ransomware attack.
- Insider Threats: Insider threats can come from current or former employees, contractors, or anyone with authorized access to your CRM system. These individuals may intentionally or unintentionally compromise your data, either through malicious actions or negligence.
- Weak Passwords and Poor Password Management: Using weak passwords or reusing passwords across multiple accounts makes it easier for attackers to gain access to your CRM system. Poor password management practices, such as storing passwords in plain text or failing to enforce strong password policies, further increase the risk.
- Unsecured Networks: Using unsecured Wi-Fi networks or failing to properly secure your network infrastructure can expose your CRM data to eavesdropping and unauthorized access.
- Lack of Data Encryption: If your CRM data is not encrypted, it is vulnerable to interception and theft, both in transit and at rest.
- Software Vulnerabilities: CRM systems, like all software, can have vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit. Failing to update your CRM software regularly can leave you exposed to known vulnerabilities.
- Social Engineering: Attackers may use social engineering techniques, such as impersonation or pretexting, to trick your employees into divulging sensitive information or granting unauthorized access to your CRM system.
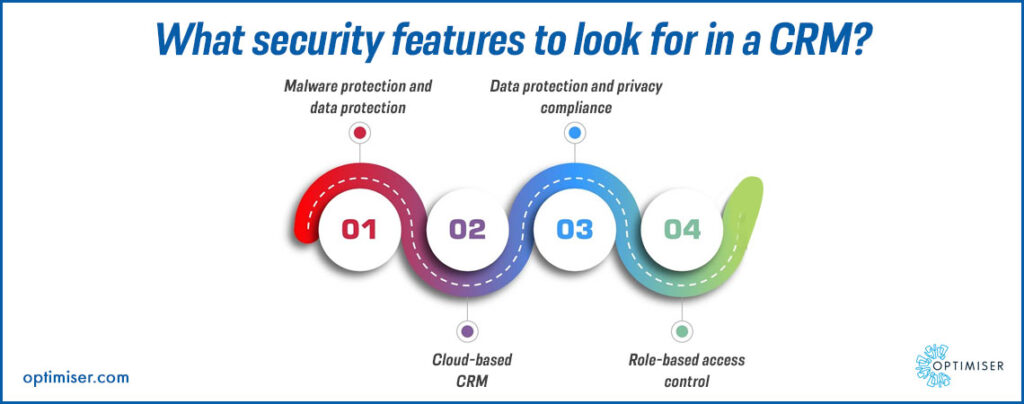
Building a Secure CRM Environment: Best Practices for Small Businesses
Implementing a robust security strategy is crucial for protecting your CRM system and the sensitive data it contains. Here are some best practices that small businesses should follow:
1. Implement Strong Password Policies and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Password Policies:
- Enforce strong password requirements, including a minimum length (e.g., 12 characters), a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters.
- Prohibit the use of common passwords, dictionary words, and easily guessable information.
- Require regular password changes (e.g., every 90 days).
- Educate employees on the importance of strong passwords and password security best practices.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA):
- Enable MFA on all CRM user accounts. MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide a second form of verification, such as a code from a mobile app or a security key, in addition to their password. This makes it significantly harder for attackers to gain unauthorized access, even if they have stolen a user’s password.
2. Control User Access and Permissions
Principle of Least Privilege:
- Grant users only the minimum level of access necessary to perform their job duties. Avoid giving users excessive permissions that could allow them to access sensitive data they don’t need.
- Regularly review user access and permissions to ensure they are still appropriate.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC):
- Use RBAC to assign users to specific roles with predefined permissions. This simplifies access management and helps ensure consistency.
Regular Audits:
- Conduct regular audits of user access and permissions to identify and address any potential security risks.
3. Secure Your Network and Devices
Firewalls:
- Use a firewall to protect your network from unauthorized access. Configure the firewall to block all unnecessary incoming and outgoing traffic.
Network Segmentation:
- Segment your network to isolate your CRM system from other parts of your network. This limits the impact of a security breach.
Wireless Security:
- Use a strong password for your Wi-Fi network and encrypt your wireless traffic using WPA2 or WPA3.
- Consider using a guest network for visitors to isolate their devices from your internal network.
Device Security:
- Ensure that all devices used to access your CRM system (e.g., laptops, smartphones, tablets) are secured with strong passwords, encryption, and up-to-date security software.
- Implement mobile device management (MDM) solutions to manage and secure mobile devices.
4. Encrypt Your Data
Encryption at Rest:
- Encrypt your CRM data at rest, meaning the data stored on your servers and databases. This protects your data if your systems are compromised.
Encryption in Transit:
- Encrypt your data in transit, meaning the data transmitted between your users, your CRM system, and other systems. Use HTTPS (SSL/TLS) to encrypt web traffic.
5. Implement Data Backup and Disaster Recovery Plans
Regular Backups:
- Implement a regular data backup schedule, backing up your CRM data frequently (e.g., daily or even more frequently, depending on your needs).
- Store backups in a secure, off-site location to protect against data loss due to a disaster or security breach.
Disaster Recovery Plan:
- Develop a disaster recovery plan that outlines the steps you will take to restore your CRM system and data in the event of a disaster, such as a natural disaster, a security breach, or a system failure.
- Test your disaster recovery plan regularly to ensure it works effectively.
6. Train Your Employees on Security Best Practices
Security Awareness Training:
- Provide regular security awareness training to all employees, covering topics such as phishing, social engineering, password security, data privacy, and incident response.
- Conduct simulated phishing exercises to test employee awareness and identify areas for improvement.
Company Policies:
- Establish clear company policies on data security, acceptable use of company resources, and incident reporting.
- Ensure that all employees understand and adhere to these policies.
7. Regularly Update and Patch Your CRM System and Software
Software Updates:
- Keep your CRM software and all related software (e.g., operating systems, web browsers, plugins) up-to-date with the latest security patches.
- Enable automatic updates whenever possible.
Vulnerability Scanning:
- Use vulnerability scanning tools to identify and address security vulnerabilities in your systems.
8. Monitor Your CRM System for Suspicious Activity
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM):
- Implement a SIEM solution to collect and analyze security logs from your CRM system and other systems. This can help you detect and respond to security incidents in a timely manner.
Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS):
- Use IDS/IPS to monitor your network traffic for malicious activity and automatically block suspicious traffic.
Regular Log Review:
- Regularly review your CRM system logs to identify any unusual activity, such as unauthorized access attempts or data modification.
9. Consider Using a CRM Provider with Robust Security Features
Security Certifications:
- Choose a CRM provider that has earned industry-recognized security certifications, such as SOC 2 or ISO 27001.
Security Features:
- Look for a CRM provider that offers robust security features, such as encryption, multi-factor authentication, access controls, and data backup and recovery.
Data Privacy Compliance:
- Ensure that your CRM provider complies with relevant data privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA.
10. Develop an Incident Response Plan
Incident Response Plan:
- Develop a comprehensive incident response plan that outlines the steps you will take in the event of a security breach or other security incident.
- The plan should include procedures for containment, eradication, recovery, and post-incident analysis.
Regular Drills:
- Conduct regular incident response drills to test your plan and ensure that your team is prepared to respond effectively.
Choosing the Right CRM: Security Considerations in the Selection Process
When selecting a CRM system, security should be a primary consideration. Here’s how to evaluate the security posture of different CRM providers:
- Security Features: Evaluate the security features offered by each provider, such as encryption, multi-factor authentication, access controls, and data backup and recovery.
- Security Certifications: Look for providers that have earned industry-recognized security certifications, such as SOC 2 or ISO 27001. These certifications demonstrate that the provider has implemented robust security controls.
- Data Privacy Compliance: Ensure that the provider complies with relevant data privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA.
- Vendor Reputation: Research the provider’s reputation for security and data protection. Read reviews and case studies to assess their track record.
- Data Location: Consider where the provider stores your data. If you are subject to data privacy regulations, you may need to ensure that your data is stored in a compliant location.
- Support and Training: Assess the provider’s support and training resources for security best practices.
- Pricing: Compare the cost of different CRM systems, taking into account the security features and other factors.
Conducting a Security Risk Assessment
A security risk assessment is a crucial step in identifying and mitigating security risks. Here’s how to conduct a risk assessment:
- Identify Assets: Identify all of your CRM-related assets, including your CRM system, data, devices, and network infrastructure.
- Identify Threats: Identify potential threats to your assets, such as phishing attacks, malware infections, and insider threats.
- Assess Vulnerabilities: Assess the vulnerabilities of your assets, such as weak passwords, outdated software, and lack of encryption.
- Analyze Risks: Analyze the risks associated with each threat and vulnerability, considering the likelihood of the threat occurring and the potential impact.
- Prioritize Risks: Prioritize risks based on their likelihood and impact.
- Develop Mitigation Strategies: Develop mitigation strategies to reduce the risks, such as implementing strong password policies, enabling multi-factor authentication, and encrypting your data.
- Implement Mitigation Strategies: Implement the mitigation strategies.
- Monitor and Review: Monitor your security controls and review your risk assessment regularly to ensure they are effective.
The Role of Third-Party Integrations in CRM Security
Many small businesses integrate their CRM systems with other third-party applications, such as marketing automation tools, email marketing platforms, and e-commerce platforms. While these integrations can enhance functionality and streamline workflows, they can also introduce new security risks.
Here’s how to manage the security risks associated with third-party integrations:
- Vet Third-Party Providers: Before integrating with a third-party application, thoroughly vet the provider’s security practices. Review their security policies, certifications, and track record.
- Limit Data Sharing: Only share the minimum amount of data necessary with third-party applications.
- Monitor Integrations: Regularly monitor your integrations for any unusual activity or security issues.
- Review Access Permissions: Regularly review the access permissions granted to third-party applications.
- Implement API Security: Secure your APIs to prevent unauthorized access to your CRM data.
Staying Compliant: Data Privacy Regulations and CRM Security
Small businesses that handle customer data must comply with data privacy regulations, such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act). These regulations impose specific requirements for protecting customer data, including:
- Data Minimization: Only collect and retain the minimum amount of data necessary.
- Data Security: Implement appropriate security measures to protect customer data.
- Data Subject Rights: Respect data subject rights, such as the right to access, rectify, and erase personal data.
- Transparency: Be transparent about how you collect, use, and share customer data.
- Data Breach Notification: Notify data protection authorities and affected individuals in the event of a data breach.
Failure to comply with these regulations can result in significant fines and reputational damage. Ensure that your CRM system and security practices comply with all applicable data privacy regulations.
The Human Element: The Importance of Security Awareness Training
No matter how robust your technical security measures are, they are only as effective as the people who use them. Human error is a leading cause of data breaches. Security awareness training is essential for educating employees about security risks and best practices. Here’s what effective security awareness training should include:
- Phishing Awareness: Teach employees how to identify and avoid phishing attacks.
- Password Security: Emphasize the importance of strong passwords and password security best practices.
- Social Engineering Awareness: Educate employees about social engineering tactics and how to avoid falling victim to them.
- Data Privacy: Explain data privacy regulations and the importance of protecting customer data.
- Incident Reporting: Provide clear procedures for reporting security incidents.
Regular security awareness training, combined with simulated phishing exercises, can significantly reduce the risk of human error and improve your overall security posture.
Incident Response: Preparing for the Inevitable
Despite your best efforts, a security incident may occur. Having a well-defined incident response plan is crucial for minimizing the damage and recovering quickly. Your incident response plan should include:
- Preparation: Establish a team, define roles, and create procedures.
- Identification: Detect and confirm the security incident.
- Containment: Limit the damage by isolating affected systems.
- Eradication: Remove the cause of the incident.
- Recovery: Restore affected systems and data.
- Post-Incident Activity: Analyze the incident, learn from it, and implement preventative measures.
Test your incident response plan regularly through drills to ensure it is effective.
The Future of CRM Security: Emerging Trends
The threat landscape is constantly evolving, and so are the security technologies and practices used to combat them. Here are some emerging trends in CRM security:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML are being used to detect and respond to security threats in real-time.
- Zero Trust Security: Zero trust security is a security model that assumes no user or device is trustworthy and requires verification before granting access to resources.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain technology can be used to secure CRM data and improve data privacy.
- Automated Security: Automation is being used to streamline security tasks, such as vulnerability scanning and incident response.
Staying informed about these trends can help you proactively protect your CRM system.
Conclusion: Building a Resilient CRM Security Strategy
Securing your CRM system is an ongoing process, not a one-time fix. By implementing the best practices outlined in this guide, you can significantly reduce your risk of a data breach and protect your business’s valuable data. Remember that a strong security posture involves a combination of technical measures, employee training, and ongoing monitoring. By prioritizing CRM security, you’re not just protecting your data; you’re safeguarding your business’s future. Embrace a proactive approach, stay informed about emerging threats, and continuously improve your security practices. Your customers, your employees, and your business will thank you for it.