Small Business CRM Implementation Guide: Your Roadmap to Customer Relationship Success
Introduction: Why Your Small Business Needs a CRM
Running a small business is a whirlwind. You’re juggling a million things – from product development and marketing to sales and customer service. In the midst of all this, it’s easy for customer relationships to fall by the wayside. That’s where a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system comes in. Think of it as your central hub for all things customer-related.
A CRM isn’t just for the big guys. In fact, it can be even more crucial for small businesses. Why? Because every customer interaction matters. Every lost lead hurts. A CRM empowers you to:
- Organize Customer Data: Say goodbye to spreadsheets and scattered notes. A CRM centralizes all customer information in one place.
- Improve Communication: Track interactions, personalize your messaging, and ensure no customer falls through the cracks.
- Boost Sales: Identify and nurture leads, automate sales processes, and close more deals.
- Enhance Customer Service: Provide faster, more efficient support and build stronger customer loyalty.
- Gain Valuable Insights: Analyze customer data to understand their behavior, preferences, and needs.
This guide will walk you through everything you need to know to implement a CRM in your small business, from choosing the right system to training your team and maximizing its impact. We’ll cover the essential steps, best practices, and potential pitfalls to help you achieve customer relationship success.
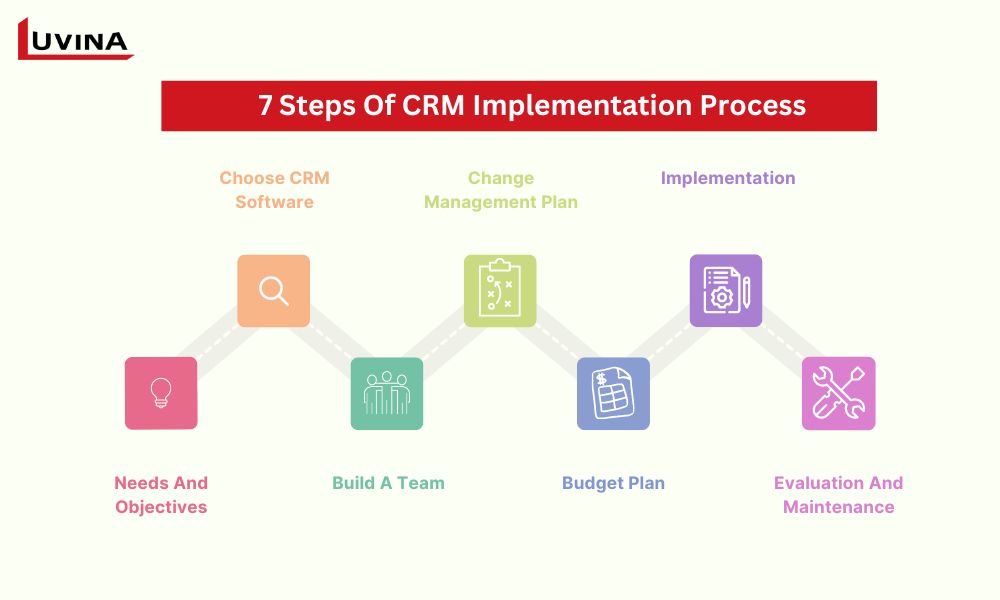
Step 1: Assessing Your Needs and Goals Before CRM Implementation
Before you dive headfirst into choosing a CRM, you need to take a step back and assess your specific needs and goals. This crucial first step ensures you select a system that aligns with your business objectives and avoids costly mistakes down the line.
Identify Your Pain Points
What challenges are you currently facing in managing your customer relationships? Are you struggling with:
- Lost Leads? Are potential customers slipping through the cracks?
- Inefficient Communication? Are you wasting time searching for information or sending repetitive emails?
- Poor Customer Service? Are you receiving complaints about slow response times or a lack of personalized attention?
- Disorganized Data? Is customer information scattered across multiple spreadsheets, emails, and notebooks?
- Lack of Sales Visibility? Do you struggle to track your sales pipeline and forecast revenue?
Make a list of your biggest pain points. These will serve as a roadmap when evaluating CRM features and functionality.
Define Your Goals
What do you hope to achieve by implementing a CRM? Be specific and measurable. Some common goals include:
- Increase Sales: By X% within Y months.
- Improve Customer Retention: Reduce customer churn by X% within Y months.
- Reduce Customer Service Response Time: Decrease average response time by X%.
- Improve Lead Conversion Rates: Increase lead conversion rates by X%.
- Enhance Customer Satisfaction: Increase customer satisfaction scores by X%.
Having clear goals will help you justify the investment in a CRM and measure its success.
Analyze Your Current Processes
How do you currently manage customer interactions? Map out your existing processes, including:
- Lead Generation: How do you attract and capture leads?
- Sales Process: What steps do you take to convert leads into customers?
- Customer Service: How do you handle customer inquiries and support requests?
- Marketing Efforts: How do you nurture leads and engage with customers?
Understanding your current processes will help you identify areas where a CRM can streamline workflows and improve efficiency.
Consider Your Budget
CRM systems vary widely in price. Determine a realistic budget, considering:
- Subscription Fees: Recurring costs for the CRM software itself.
- Implementation Costs: Potential costs for setup, data migration, and customization.
- Training Costs: Costs for training your team on how to use the CRM.
- Ongoing Support: Costs for technical support and maintenance.
Research different CRM pricing models and choose a system that fits your budget and offers the features you need.
Step 2: Choosing the Right CRM for Your Small Business
Selecting the right CRM is critical to its success. With so many options available, the decision can feel overwhelming. Here’s how to narrow down your choices and find the perfect fit for your small business.
CRM Types and Features
CRMs come in various forms, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Consider these types:
- Cloud-Based CRM: Hosted on the vendor’s servers, offering accessibility from anywhere with an internet connection. Generally easier to implement and maintain.
- On-Premise CRM: Installed on your own servers, providing greater control over data and security. Requires more technical expertise and upfront investment.
- Open-Source CRM: Customizable and often free, but requires technical skills for setup and maintenance.
Key features to look for include:
- Contact Management: Centralized storage of customer information.
- Lead Management: Tools for capturing, tracking, and nurturing leads.
- Sales Automation: Features for automating sales tasks, such as email campaigns and follow-ups.
- Marketing Automation: Tools for creating and managing marketing campaigns.
- Customer Service: Features for managing customer inquiries, support tickets, and knowledge bases.
- Reporting and Analytics: Dashboards and reports to track key metrics and gain insights.
- Integration: Ability to integrate with other business tools, such as email marketing platforms, accounting software, and social media.
- Mobile Access: Access to the CRM on mobile devices.
Research and Evaluate CRM Providers
Once you have a clear understanding of your needs and desired features, it’s time to research potential CRM providers. Consider these factors:
- Reputation and Reviews: Read online reviews and case studies to assess the provider’s reputation and customer satisfaction.
- Pricing and Plans: Compare pricing plans and features to find the best value for your budget.
- Scalability: Choose a CRM that can grow with your business.
- Ease of Use: Select a system that is user-friendly and easy to learn.
- Support and Training: Ensure the provider offers adequate support and training resources.
- Free Trials or Demos: Take advantage of free trials or demos to test the system before committing.
- Security and Compliance: Verify the provider’s security measures and compliance with relevant regulations (e.g., GDPR, CCPA).
Some popular CRM options for small businesses include:
- HubSpot CRM: Free CRM with powerful features for sales and marketing.
- Zoho CRM: Feature-rich CRM with affordable pricing plans.
- Salesforce Essentials: Scaled-down version of Salesforce, designed for small businesses.
- Pipedrive: Sales-focused CRM with a user-friendly interface.
- Freshsales: Sales CRM with built-in phone and email features.
Prioritize Your Must-Have Features
Create a list of the features that are essential for your business. This will help you narrow down your choices and prioritize the systems that best meet your needs. Don’t get caught up in features you don’t need.
Consider Integrations
Think about the other tools you use in your business, such as email marketing platforms, accounting software, and social media channels. Ensure the CRM you choose integrates seamlessly with these tools to streamline your workflows and avoid data silos.
Step 3: Planning Your CRM Implementation
With your CRM chosen, it’s time to develop a detailed implementation plan. A well-defined plan minimizes disruptions and ensures a smooth transition.
Project Scope and Timeline
Define the scope of your CRM implementation. What features will you implement initially? What data will you migrate? Establish a realistic timeline, breaking down the project into manageable phases.
Data Migration Strategy
Plan how you will migrate your existing customer data into the CRM. This may involve:
- Data Cleanup: Remove duplicate entries, correct errors, and standardize formatting.
- Data Mapping: Map your existing data fields to the corresponding fields in the CRM.
- Data Import: Import your data into the CRM using CSV files or other import tools.
- Data Validation: Verify the accuracy of the imported data.
Consider using a data migration tool or seeking assistance from the CRM provider or a consultant.
Customization and Configuration
Customize the CRM to fit your specific business needs. This may involve:
- Adding Custom Fields: Create fields to capture specific customer data that is relevant to your business.
- Configuring Workflows: Automate tasks, such as lead assignment, email follow-ups, and task creation.
- Setting Up User Roles and Permissions: Define user roles and permissions to control access to data and features.
- Designing Reports and Dashboards: Create reports and dashboards to track key metrics and gain insights.
Team Roles and Responsibilities
Assign roles and responsibilities to your team members. Who will be responsible for data entry? Who will be the CRM administrator? Clearly define each person’s role to avoid confusion and ensure accountability.
Communication Plan
Communicate regularly with your team throughout the implementation process. Keep them informed of progress, address any concerns, and provide updates on training and new features.
Step 4: Data Migration and System Setup
Now comes the hands-on work of migrating your data and setting up your CRM. This phase requires careful planning and execution to ensure a successful implementation.
Data Import and Validation
Follow your data migration plan to import your customer data into the CRM. Once the data is imported, validate its accuracy. Check for any errors or inconsistencies. Ensure all the necessary data has been successfully transferred.
Customization and Configuration (Continued)
Continue customizing and configuring the CRM based on your plan. This includes:
- Setting up User Accounts: Create user accounts for each team member and assign appropriate roles and permissions.
- Configuring Email Integration: Connect your email accounts to the CRM to track email communication and automate email campaigns.
- Setting up Integrations with Other Tools: Integrate the CRM with other business tools, such as email marketing platforms, accounting software, and social media channels.
- Testing the System: Thoroughly test all the features and functionalities of the CRM to ensure they are working correctly.
User Training
Provide comprehensive training to your team on how to use the CRM. Training should cover:
- Basic Navigation: How to navigate the CRM and find the information they need.
- Data Entry: How to enter and update customer data.
- Using Key Features: How to use the core features of the CRM, such as lead management, sales automation, and customer service tools.
- Reporting and Analytics: How to generate reports and interpret data.
- Best Practices: Best practices for using the CRM effectively.
Offer different training methods, such as online tutorials, in-person training sessions, and user manuals. Encourage hands-on practice and provide ongoing support.
Step 5: Training and Onboarding Your Team
Training your team is a crucial part of CRM implementation. Without proper training, your team won’t be able to use the CRM effectively, and you won’t realize its full potential.
Develop a Training Plan
Create a detailed training plan that outlines the training objectives, the content to be covered, the training methods to be used, and the schedule. Tailor the training plan to the specific needs of your team and the features of your CRM.
Training Methods
Use a variety of training methods to cater to different learning styles. Consider:
- Online Tutorials: Self-paced video tutorials that cover the basics of the CRM.
- In-Person Training Sessions: Hands-on training sessions led by a trainer or CRM expert.
- User Manuals and Documentation: Comprehensive documentation that provides detailed instructions on how to use the CRM.
- On-the-Job Training: Practical training where team members learn by doing.
Training Content
The training content should cover all the essential features of the CRM, including:
- Basic Navigation: How to log in, navigate the interface, and find information.
- Data Entry: How to create, update, and manage customer records.
- Lead Management: How to capture, track, and nurture leads.
- Sales Automation: How to automate sales tasks, such as email campaigns and follow-ups.
- Customer Service: How to manage customer inquiries and support tickets.
- Reporting and Analytics: How to generate reports and interpret data.
- Best Practices: Best practices for using the CRM effectively.
Provide Ongoing Support
Provide ongoing support to your team after the initial training. This includes:
- Help Desk: Create a help desk or designate a point of contact for team members to ask questions and get assistance.
- FAQ Section: Develop a frequently asked questions (FAQ) section to address common questions and issues.
- Ongoing Training: Provide ongoing training on new features and updates.
- Regular Check-Ins: Conduct regular check-ins with your team to assess their progress and provide support.
Monitor Usage and Adoption
Monitor the usage and adoption of the CRM by your team. Track key metrics, such as the number of logins, the amount of data entered, and the use of key features. Identify any team members who are struggling to use the CRM and provide additional support.
Step 6: Launch and Go-Live
The launch phase marks the official go-live of your new CRM. A well-executed launch minimizes disruption and ensures a smooth transition for your team.
Communication and Announcement
Announce the launch of the CRM to your team. Clearly communicate the benefits of the new system and how it will improve their work. Provide a timeline for the go-live and any relevant deadlines.
Data Migration Completion
Ensure that all data migration is complete and that all the necessary data has been successfully transferred into the CRM. Verify that the data is accurate and consistent.
System Testing and Final Checks
Before going live, conduct final checks to ensure everything is working correctly. Test all the features and functionalities of the CRM. Verify that all integrations are working as expected.
Go-Live Support
Provide support to your team during the initial go-live period. Be available to answer questions and troubleshoot any issues that may arise. Assign a dedicated support team or person to assist your team.
Monitor Performance
Monitor the performance of the CRM after the launch. Track key metrics, such as user adoption, data entry accuracy, and system performance. Identify any issues and address them promptly.
Step 7: Maximizing CRM Adoption and Usage
The initial implementation is just the beginning. To realize the full benefits of your CRM, you need to ensure your team actively uses the system and leverages its features. Here’s how to maximize CRM adoption and usage:
Promote the Benefits
Regularly communicate the benefits of using the CRM to your team. Highlight how it can improve their productivity, make their jobs easier, and help them achieve their goals. Share success stories and examples of how the CRM has helped other team members.
Lead by Example
Lead by example. Demonstrate your own commitment to using the CRM. Regularly enter data, update records, and utilize the CRM’s features. This will encourage your team to do the same.
Make it Easy to Use
Ensure the CRM is easy to use and accessible to your team. Provide clear instructions, training, and ongoing support. Customize the CRM to meet the specific needs of your team and streamline their workflows.
Incentivize Usage
Incentivize CRM usage. Recognize and reward team members who actively use the CRM and achieve positive results. This could include bonuses, promotions, or other forms of recognition.
Regularly Review and Optimize
Regularly review your CRM usage and identify areas for improvement. Seek feedback from your team and make adjustments as needed. Optimize the CRM to ensure it is meeting the evolving needs of your business.
Integrate CRM into Daily Workflows
Integrate the CRM into your team’s daily workflows. Make it an essential part of their routine. Encourage them to use the CRM for all customer interactions, from lead generation to customer service.
Step 8: Measuring Success and Ongoing Optimization
Implementing a CRM is an ongoing process. To ensure its continued success, you need to measure its impact and make adjustments as needed. Here’s how to measure success and optimize your CRM for the long term.
Define Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Identify the key performance indicators (KPIs) that are most important to your business. These KPIs will help you measure the impact of your CRM on your business goals. Some common KPIs include:
- Sales Growth: Track the increase in sales revenue.
- Lead Conversion Rates: Measure the percentage of leads that convert into customers.
- Customer Retention Rate: Track the percentage of customers who stay with your business.
- Customer Satisfaction: Measure customer satisfaction scores.
- Customer Service Response Time: Track the average time it takes to respond to customer inquiries.
- Sales Cycle Length: Measure the average time it takes to close a deal.
- Marketing ROI: Track the return on investment for your marketing campaigns.
Track and Analyze Data
Regularly track and analyze your KPIs. Use the CRM’s reporting and analytics features to generate reports and gain insights. Identify trends and patterns in your data.
Review and Iterate
Regularly review your CRM usage and performance. Identify areas for improvement and make adjustments as needed. Seek feedback from your team and use their insights to optimize the CRM. Iterate on your processes and strategies to maximize the value of your CRM.
Ongoing Training and Support
Provide ongoing training and support to your team. Stay up-to-date on the latest CRM features and best practices. Ensure your team has the knowledge and skills they need to use the CRM effectively.
Regular System Audits
Conduct regular system audits to ensure your CRM is functioning properly and that your data is secure. Review your security settings and data backup procedures.
Stay Up-to-Date
The CRM landscape is constantly evolving. Stay up-to-date on the latest CRM trends and technologies. Evaluate new features and integrations and consider adopting them to improve your CRM’s capabilities.
Conclusion: The Long-Term Benefits of CRM for Small Businesses
Implementing a CRM is a significant investment, but the long-term benefits for small businesses are undeniable. By following this guide, you can successfully implement a CRM and unlock its potential to transform your customer relationships. Embrace the power of a CRM, and watch your small business thrive.
Here’s a recap of the key benefits:
- Improved Customer Relationships: Build stronger relationships with your customers by providing personalized experiences and proactive support.
- Increased Sales: Generate more leads, close more deals, and increase your sales revenue.
- Enhanced Customer Service: Provide faster, more efficient support and improve customer satisfaction.
- Increased Efficiency: Streamline your workflows and automate repetitive tasks.
- Improved Data Insights: Gain valuable insights into your customer behavior and preferences.
- Better Collaboration: Improve collaboration and communication among your team members.
- Scalability: Scale your business more effectively as your customer base grows.
The journey of CRM implementation is a continuous one. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you’ll be well on your way to building a customer-centric business that thrives in today’s competitive market. Remember to adapt and optimize your CRM strategy over time to meet the evolving needs of your business and your customers.