Small Business CRM Cost: A Comprehensive Guide to Budgeting and Finding the Best Value
Running a small business is a whirlwind of activity. You’re juggling everything from product development and marketing to customer service and finances. Amidst this chaos, one tool can be a game-changer: a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system. But the question of small business CRM cost often looms large. Is it worth the investment? And if so, how much should you expect to pay?
This comprehensive guide will delve deep into the world of CRM costs for small businesses. We’ll explore the various pricing models, features that impact cost, and strategies for finding the best value for your money. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of how to budget for a CRM and choose the right solution to help your business thrive.
Understanding the Value of a CRM for Small Businesses
Before we dive into the specifics of cost, let’s briefly touch upon why a CRM is so crucial for small businesses. A CRM isn’t just a fancy address book; it’s a central hub for managing all your customer interactions and data. This includes:
- Contact Management: Storing and organizing customer information, including contact details, communication history, and purchase history.
- Sales Automation: Streamlining your sales process, from lead generation and qualification to closing deals.
- Marketing Automation: Automating marketing tasks, such as email campaigns and social media posting, to nurture leads and drive conversions.
- Customer Service: Providing excellent customer service by tracking support requests, resolving issues efficiently, and building strong customer relationships.
- Reporting and Analytics: Gaining valuable insights into your sales, marketing, and customer service performance.
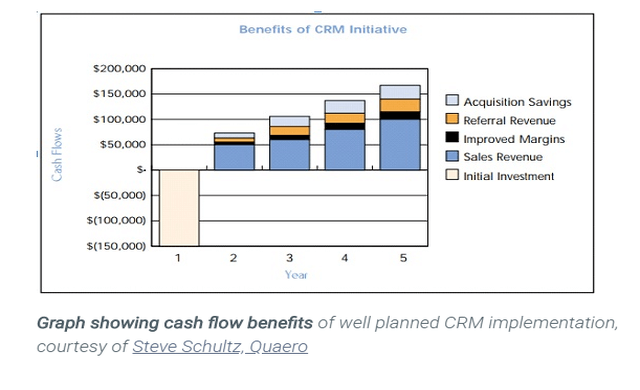
By implementing a CRM, small businesses can experience numerous benefits, including:
- Increased Sales: By streamlining the sales process and improving lead management.
- Improved Customer Retention: By providing personalized customer experiences and proactive support.
- Enhanced Productivity: By automating tasks and freeing up employees to focus on more strategic initiatives.
- Better Decision-Making: By providing data-driven insights into your business performance.
The benefits of a CRM are clear, but the question remains: how much does it cost?
Breaking Down Small Business CRM Cost: Pricing Models Explained
CRM systems offer a variety of pricing models, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these models is crucial for budgeting and choosing the right CRM for your needs.
1. Subscription-Based (SaaS) Pricing
This is the most common pricing model for CRM systems. With SaaS (Software as a Service), you pay a recurring fee, typically monthly or annually, to access the CRM software. The fee is usually based on the number of users, the features included, and the level of support provided. This model offers several advantages:
- Predictable Costs: You know exactly how much you’ll be paying each month or year.
- Scalability: You can easily add or remove users as your business grows or shrinks.
- Reduced Upfront Investment: You don’t need to purchase expensive hardware or software licenses.
- Automatic Updates: The CRM provider handles all software updates and maintenance.
However, SaaS pricing can also have some drawbacks:
- Recurring Costs: You’ll need to pay for the CRM as long as you use it.
- Feature Limitations: Some features may only be available at higher pricing tiers.
- Vendor Lock-in: Switching CRM providers can be complex and time-consuming.
2. Per-User Pricing
This is a common sub-category of SaaS pricing. You pay a fixed fee per user per month or year. This model is straightforward and easy to understand. It’s ideal for businesses with a consistent number of users and predictable CRM usage.
3. Tiered Pricing
Many CRM providers offer tiered pricing plans, with different features and user limits at each tier. The price increases as you move up the tiers. This model allows you to choose a plan that aligns with your specific needs and budget. Be sure to carefully compare the features offered at each tier to ensure you’re getting the best value.
4. Usage-Based Pricing
Some CRM providers charge based on usage, such as the number of contacts stored, emails sent, or data storage used. This model can be cost-effective for businesses with fluctuating needs. However, it can also be unpredictable, as your costs may vary from month to month.
5. On-Premise Pricing
This model involves purchasing a software license and installing the CRM on your own servers. You are responsible for all hardware, software, and maintenance costs. This model offers more control over your data and customization options but requires a significant upfront investment and ongoing IT expertise. This model is less common for small businesses due to the high initial cost and ongoing maintenance requirements.
6. Free CRM Options
Some CRM providers offer free versions of their software, typically with limited features and user limits. These free options can be a good starting point for small businesses with basic CRM needs. However, you may need to upgrade to a paid plan as your business grows.
Factors Influencing Small Business CRM Cost
Several factors can influence the overall cost of a CRM system. Understanding these factors will help you make informed decisions and find a solution that fits your budget.
1. Number of Users
The number of users is often the most significant factor influencing CRM cost, especially with subscription-based pricing. Most CRM providers charge per user, so the more users you have, the higher your monthly or annual fees will be. Consider how many employees will need access to the CRM and choose a plan that accommodates your current and future needs.
2. Features and Functionality
The features and functionality offered by a CRM system directly impact its cost. More advanced features, such as sales automation, marketing automation, and advanced reporting, typically come at a higher price. Assess your business’s needs and choose a CRM with the features you need, but avoid paying for features you won’t use.
3. Storage and Data Limits
Some CRM providers limit the amount of data you can store, such as the number of contacts, files, or emails. Exceeding these limits may result in additional charges. Consider your data storage needs and choose a CRM with sufficient storage capacity.
4. Support and Training
The level of support and training provided by the CRM provider can also impact the cost. Some providers offer premium support options, such as dedicated account managers and priority support, at an additional cost. Training can help your team effectively use the CRM and maximize its benefits. Factor in the cost of support and training when evaluating CRM options.
5. Integrations
CRM systems often integrate with other business tools, such as email marketing platforms, accounting software, and e-commerce platforms. The cost of integrations can vary depending on the complexity of the integration and the provider’s pricing model. Consider the integrations you need and factor in the associated costs.
6. Customization
Some CRM systems offer extensive customization options, allowing you to tailor the software to your specific needs. However, customization can be time-consuming and expensive, especially if you need to hire a developer. Assess your customization needs and factor in the associated costs.
7. Implementation Costs
Implementing a CRM system involves setting up the software, migrating your data, and training your team. These tasks can require time and resources. Some CRM providers offer implementation services, which can add to the overall cost. Consider the implementation costs when choosing a CRM system.
Budgeting for a Small Business CRM: A Step-by-Step Guide
Creating a realistic budget is essential for choosing the right CRM and avoiding unexpected costs. Follow these steps to create a budget for your small business CRM:
1. Assess Your Needs
Before you start budgeting, assess your business’s specific needs. What are your goals for implementing a CRM? What features do you need? How many users will need access to the CRM? Answering these questions will help you narrow down your options and determine the features and functionality you need.
2. Research CRM Providers
Research different CRM providers and compare their pricing models, features, and functionality. Read reviews, compare pricing plans, and request quotes from multiple providers. Look for providers that offer free trials or demos to test their software.
3. Determine Your Budget Range
Based on your research, determine a realistic budget range for your CRM. Consider both the initial costs and the ongoing costs, such as monthly or annual subscription fees. Factor in the cost of support, training, and integrations.
4. Prioritize Features
Prioritize the features you need and identify the “must-have” features versus the “nice-to-have” features. This will help you choose a CRM that meets your needs without overspending.
5. Consider Hidden Costs
Be aware of potential hidden costs, such as implementation fees, data migration costs, and the cost of integrations. Factor these costs into your budget.
6. Review and Adjust
Review your budget regularly and adjust it as needed. As your business grows, your CRM needs may change, and you may need to upgrade to a more expensive plan. Be prepared to adjust your budget as needed.
Finding the Best Value: Tips for Saving Money on CRM
Finding the best value for your money is crucial when choosing a CRM. Here are some tips to help you save money on CRM costs:
1. Start Small
If you’re just starting out, consider starting with a free or low-cost CRM plan. This will allow you to test the software and see if it meets your needs before committing to a more expensive plan. You can always upgrade as your business grows.
2. Negotiate Pricing
Don’t be afraid to negotiate pricing with CRM providers. You may be able to get a discount, especially if you’re signing up for an annual plan or purchasing multiple licenses. Ask about any special offers or promotions.
3. Choose the Right Plan
Carefully evaluate the different pricing plans offered by CRM providers and choose the plan that best fits your needs and budget. Don’t pay for features you won’t use.
4. Leverage Free Trials and Demos
Take advantage of free trials and demos to test different CRM systems before making a decision. This will allow you to see how the software works and determine if it’s a good fit for your business.
5. Utilize Free Resources
Many CRM providers offer free resources, such as tutorials, webinars, and knowledge bases. Utilize these resources to learn how to use the software effectively and minimize your training costs.
6. Consider Open-Source Options
Open-source CRM systems are available for free, but they often require technical expertise to set up and maintain. If you have the technical skills or can hire someone to manage the system, open-source options can be a cost-effective solution.
7. Consolidate Your Tools
Choose a CRM that integrates with your existing business tools to avoid paying for multiple software solutions. Consolidating your tools can save you money and streamline your workflow.
8. Look for Bundled Deals
Some CRM providers offer bundled deals that include other business tools, such as email marketing software or project management software. These bundled deals can be a cost-effective way to get all the tools you need.
Top CRM Systems for Small Businesses (and their approximate costs)
Here’s a brief overview of some popular CRM systems for small businesses and their general cost structures. Keep in mind that pricing can change, so always check the provider’s website for the most up-to-date information.
- HubSpot CRM: HubSpot offers a free CRM that’s a great starting point for small businesses. Paid plans offer more features and start at around $45 per month (billed annually).
- Zoho CRM: Zoho CRM has a free plan for up to 3 users. Paid plans start around $14 per user per month (billed annually).
- Freshsales: Freshsales offers a free plan for a limited number of users. Paid plans start around $15 per user per month (billed annually).
- Pipedrive: Pipedrive focuses on sales and offers plans starting at around $14.90 per user per month (billed annually).
- Salesforce Essentials: Salesforce Essentials is designed for small businesses and starts around $25 per user per month (billed annually).
Note: The costs listed above are approximate and may vary depending on the provider and the specific features you choose. Always check the provider’s website for the most up-to-date pricing information.
Conclusion: Making the Right CRM Investment for Your Business
Choosing a CRM system is a significant decision for any small business, and understanding the small business CRM cost is a crucial part of that decision. By understanding the different pricing models, factors influencing cost, and strategies for finding the best value, you can make an informed decision and choose a CRM that helps your business succeed.
Remember to:
- Assess your business needs and goals.
- Research different CRM providers and compare their pricing and features.
- Create a realistic budget and stick to it.
- Prioritize the features you need.
- Take advantage of free trials and demos.
With careful planning and research, you can find a CRM that helps you manage your customer relationships, streamline your sales process, and drive business growth without breaking the bank. Investing in the right CRM is an investment in the future of your small business.
Ultimately, the best CRM is the one that meets your specific needs and fits within your budget. Don’t be afraid to take your time, do your research, and choose the solution that empowers your business to thrive. Good luck!