Small Business CRM Security in 2025: Protecting Your Data in a Changing Landscape
Small Business CRM Security in 2025: Protecting Your Data in a Changing Landscape
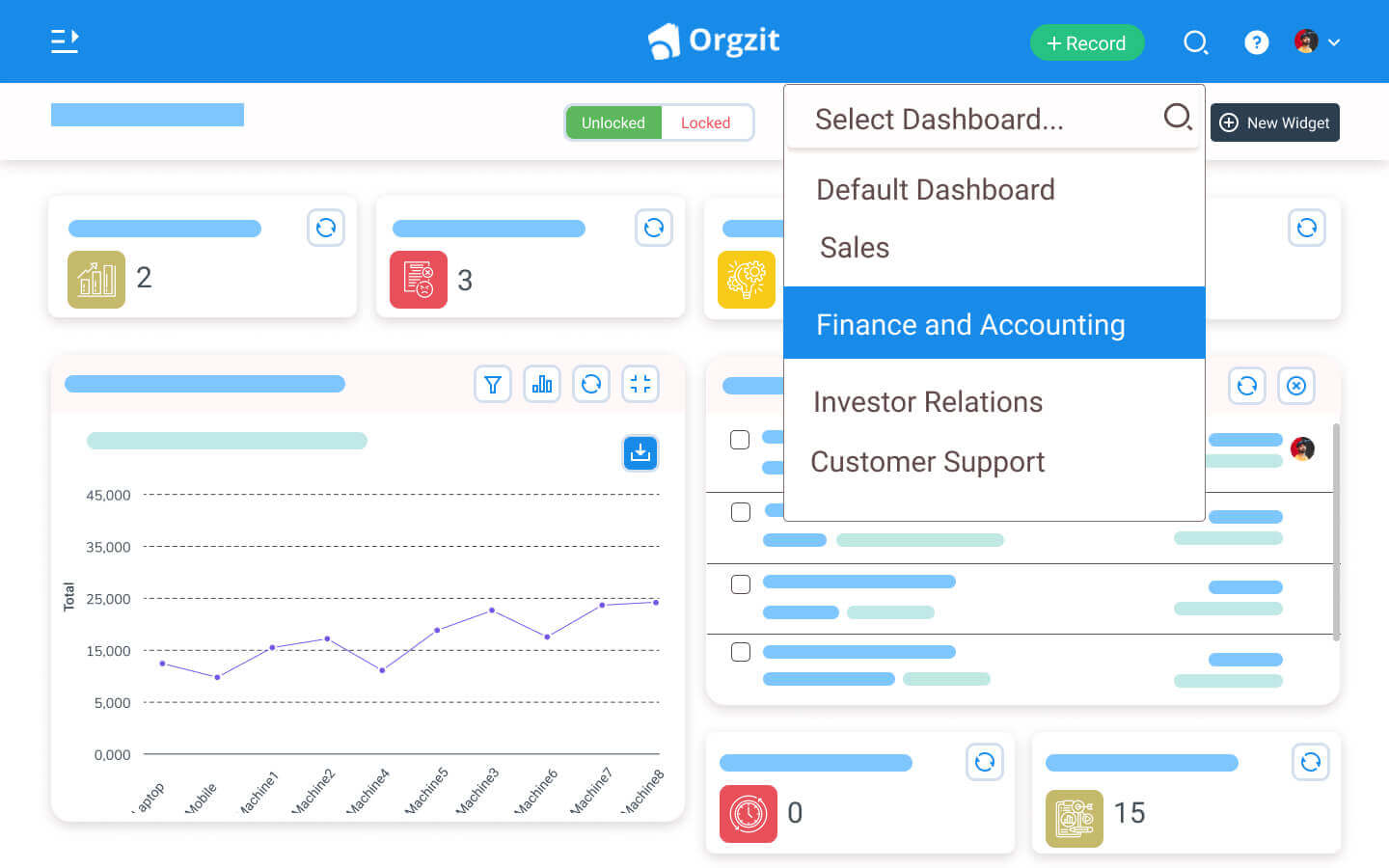
The world of small business is constantly evolving, and with it, the threats to your valuable data. Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems have become indispensable tools for businesses of all sizes, providing a central hub for managing customer interactions, sales pipelines, and marketing campaigns. However, as CRM systems become more integral, they also become prime targets for cyberattacks. This comprehensive guide delves into the crucial aspects of small business CRM security in 2025, equipping you with the knowledge and strategies to safeguard your data and navigate the evolving threat landscape.
The Growing Importance of CRM Security
In today’s digital age, data is the lifeblood of any business. Your CRM system holds a treasure trove of sensitive information, including customer contact details, purchase history, financial data, and more. A security breach can have devastating consequences, including financial losses, reputational damage, legal liabilities, and loss of customer trust. Furthermore, in 2025, with the increasing sophistication of cyberattacks and the rise of data privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA, the stakes are higher than ever.
Why Small Businesses Are Prime Targets
Small businesses often lack the resources and expertise of larger corporations, making them more vulnerable to cyberattacks. They may not have dedicated IT security teams or the budget for advanced security solutions. Moreover, small businesses are often seen as easier targets by cybercriminals, who may believe they are less likely to have robust security measures in place. The lack of awareness and training among employees can also contribute to a higher risk of breaches.
Key Threats to CRM Security in 2025
The threat landscape is constantly changing, and new vulnerabilities emerge regularly. Staying informed about the latest threats is crucial for effective security. Here are some of the most significant threats to CRM security in 2025:
1. Phishing Attacks
Phishing remains one of the most prevalent and effective attack vectors. Cybercriminals use deceptive emails, messages, and websites to trick employees into revealing sensitive information, such as usernames, passwords, and financial details. In 2025, phishing attacks are becoming increasingly sophisticated, with attackers using social engineering techniques and personalized attacks to bypass security measures. They may impersonate trusted sources, such as colleagues, vendors, or even the CRM provider itself.
2. Malware and Ransomware
Malware, including viruses, Trojans, and spyware, can infect CRM systems and steal data or disrupt operations. Ransomware, a particularly insidious form of malware, encrypts data and demands a ransom payment for its release. The rise of ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) has made ransomware attacks more accessible to cybercriminals. In 2025, ransomware attacks are becoming more targeted, with attackers focusing on businesses with valuable data and the ability to pay large ransoms.
3. Insider Threats
Insider threats, whether malicious or unintentional, pose a significant risk to CRM security. Malicious insiders may intentionally steal data or sabotage systems, while unintentional threats can arise from employee negligence, such as clicking on phishing links or using weak passwords. With the increasing use of remote work and the proliferation of mobile devices, the risk of insider threats is growing.
4. Data Breaches
Data breaches, whether caused by hacking, malware, or insider threats, can result in the exposure of sensitive customer data. Data breaches can have severe consequences, including financial losses, reputational damage, and legal liabilities. In 2025, data breaches are becoming more frequent and sophisticated, with attackers using advanced techniques to bypass security measures.
5. Weak Passwords and Authentication
Weak passwords and inadequate authentication methods are a common point of entry for cybercriminals. Many users still rely on easily guessable passwords or reuse passwords across multiple accounts. In 2025, with the increasing sophistication of cyberattacks, it is essential to implement strong password policies, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and other authentication methods to protect your CRM system.
6. Vulnerabilities in CRM Software
CRM software, like any software, can have vulnerabilities that cybercriminals can exploit. These vulnerabilities can be caused by coding errors, design flaws, or outdated software versions. It is essential to keep your CRM software up to date with the latest security patches and updates to mitigate these risks.
Essential Security Measures for Small Business CRMs in 2025
Protecting your CRM system requires a multi-layered approach that addresses various threats and vulnerabilities. Here are some essential security measures for small businesses in 2025:
1. Strong Password Policies and Management
Implement strong password policies that require users to create complex passwords that are at least 12 characters long and include a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Enforce regular password changes and prohibit password reuse. Consider using a password manager to securely store and manage passwords.
2. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Implement MFA, which requires users to verify their identity using multiple factors, such as a password and a one-time code sent to their mobile device. MFA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, even if a password is compromised.
3. Regular Security Audits and Assessments
Conduct regular security audits and assessments to identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in your CRM system and IT infrastructure. This can involve penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, and code reviews. Use the results to improve your security posture.
4. Data Encryption
Encrypt sensitive data, both at rest and in transit, to protect it from unauthorized access. Data at rest encryption protects data stored on servers and devices, while data in transit encryption protects data transmitted over networks. Encryption ensures that even if data is intercepted, it will be unreadable without the decryption key.
5. Access Controls and Permissions
Implement strict access controls and permissions to limit access to sensitive data. Grant users only the minimum necessary access to perform their job duties. Regularly review and update access controls to ensure they remain appropriate.
6. Security Awareness Training
Provide regular security awareness training to all employees to educate them about the latest threats and best practices for protecting data. Training should cover topics such as phishing, malware, password security, and social engineering. Conduct simulated phishing attacks to test employee awareness.
7. Data Backup and Disaster Recovery
Implement a robust data backup and disaster recovery plan to ensure that you can recover your data in the event of a security breach or other disaster. Back up your CRM data regularly, both on-site and off-site. Test your backup and recovery procedures regularly.
8. CRM Software Updates and Patches
Keep your CRM software up to date with the latest security patches and updates. Software vendors regularly release updates to address vulnerabilities and improve security. Regularly check for updates and apply them promptly.
9. Network Security Measures
Implement network security measures, such as firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, and anti-malware software, to protect your CRM system from external threats. Regularly monitor your network for suspicious activity.
10. Incident Response Plan
Develop an incident response plan to outline the steps you will take in the event of a security breach. The plan should include procedures for identifying, containing, and recovering from the breach. Regularly test and update your incident response plan.
11. Choose a Secure CRM Provider
If you are using a cloud-based CRM, choose a reputable provider with a strong track record of security. Research the provider’s security certifications, data protection policies, and incident response procedures. Ensure that the provider complies with relevant data privacy regulations.
12. Endpoint Protection
Protect the devices that access your CRM system, such as laptops, smartphones, and tablets, with endpoint protection software. This software should include anti-malware, firewall, and intrusion detection capabilities. Regularly update the software and scan devices for threats.
13. Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
Implement DLP solutions to prevent sensitive data from leaving your organization’s control. DLP solutions can monitor and control data movement, detect data leaks, and block unauthorized data transfers. This is especially important with the rise of remote work.
14. Regular Monitoring and Logging
Monitor your CRM system and network for suspicious activity. Review logs regularly to identify potential security incidents. Implement security information and event management (SIEM) systems to automate log analysis and threat detection.
The Role of Emerging Technologies in CRM Security
The future of CRM security will be shaped by emerging technologies. Here are some of the key technologies that will play a significant role in 2025:
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML can be used to automate security tasks, detect threats, and improve incident response. AI-powered security solutions can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and anomalies that may indicate a security breach. ML can be used to train security systems to recognize and respond to new threats automatically.
2. Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology can be used to secure CRM data by creating a tamper-proof record of all transactions and interactions. Blockchain can also be used to improve data privacy and control, allowing customers to have more control over their data.
3. Zero Trust Security Model
The Zero Trust security model assumes that no user or device is inherently trustworthy. This model requires all users and devices to be authenticated and authorized before accessing resources. Zero Trust can help to prevent unauthorized access and limit the impact of security breaches.
4. Biometric Authentication
Biometric authentication, such as fingerprint scanning and facial recognition, can be used to enhance security and improve user experience. Biometric authentication is more secure than traditional password-based authentication and can help to prevent unauthorized access.
Staying Ahead of the Curve: Best Practices for 2025
In the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats, it’s crucial to adopt a proactive approach to CRM security. Here are some best practices to keep your small business protected:
1. Stay Informed
Keep abreast of the latest security threats, vulnerabilities, and best practices. Subscribe to security blogs, newsletters, and industry publications. Attend security conferences and webinars. Stay informed about data privacy regulations and compliance requirements.
2. Prioritize Risk Assessment
Regularly assess your security risks and vulnerabilities. Identify the most critical assets and the threats that pose the greatest risk. Prioritize security measures based on your risk assessment.
3. Foster a Security-Conscious Culture
Create a security-conscious culture within your organization. Train employees on security best practices and make them aware of the importance of protecting data. Encourage employees to report suspicious activity.
4. Review and Update Your Security Plan Regularly
Your security plan is not a set-it-and-forget-it document. Review and update it regularly to reflect changes in your business, the threat landscape, and data privacy regulations. Test your security plan regularly.
5. Partner with Security Experts
Consider partnering with security experts, such as cybersecurity consultants or managed security service providers (MSSPs), to help you implement and manage your security program. These experts can provide valuable insights and expertise.
6. Embrace Automation
Automate security tasks, such as vulnerability scanning, patch management, and incident response, to improve efficiency and reduce the risk of human error. Leverage AI and ML-powered security solutions to automate threat detection and response.
7. Practice the Principle of Least Privilege
Grant users only the minimum necessary access to perform their job duties. This principle helps to limit the impact of security breaches and prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data.
8. Regularly Review and Update Your Vendor Contracts
Ensure that your vendors comply with your security policies and data privacy regulations. Regularly review and update your vendor contracts to reflect changes in your security requirements.
9. Plan for the Worst
Even with the best security measures in place, security breaches can still happen. Develop a comprehensive incident response plan that outlines the steps you will take in the event of a security breach. Regularly test and update your incident response plan.
Conclusion: Securing Your CRM for a Secure Future
CRM security is not a one-time task; it’s an ongoing process. By implementing the security measures and best practices outlined in this guide, small businesses can protect their valuable data, maintain customer trust, and ensure their long-term success. Staying informed, proactive, and adaptable is key to navigating the evolving threat landscape and securing your CRM system in 2025 and beyond. The future is digital, and with the right security measures in place, your small business can thrive in this new era.