Running a small business is a whirlwind. You’re juggling everything from product development and marketing to customer service and, of course, keeping the finances in order. In the midst of this chaos, the right tools can be a lifesaver. A Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system is one such tool. But before you dive in, you need to understand something crucial: the small business CRM cost. This guide is your comprehensive compass, navigating the often-murky waters of CRM pricing to help you find the perfect fit without breaking the bank.
We’ll delve deep into the various pricing models, the factors that influence cost, and, most importantly, how to determine the true value of a CRM system for your specific business needs. Forget the generic, one-size-fits-all approach. We’re here to equip you with the knowledge to make an informed decision, ensuring your CRM investment pays off handsomely.
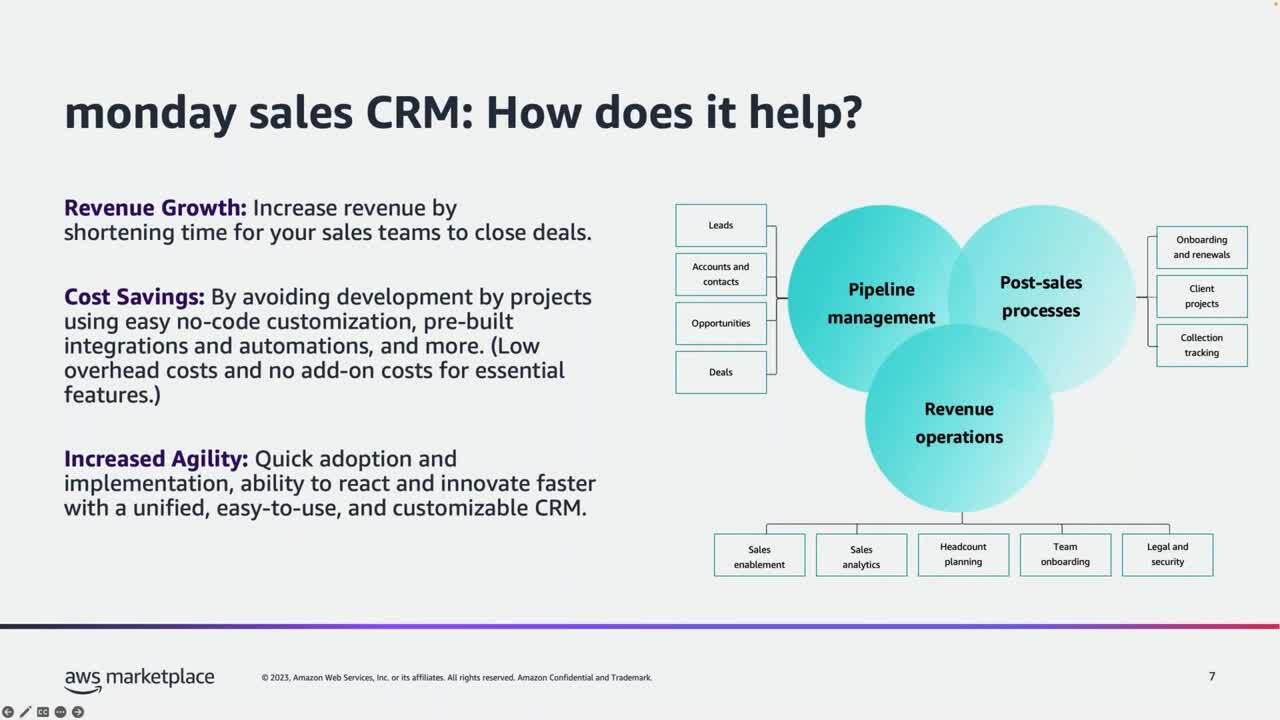
Why a CRM Matters for Small Businesses
Before we dissect the numbers, let’s quickly recap why a CRM is so vital for small businesses. Think of it as the central nervous system of your customer interactions. It’s where you store, organize, and analyze all your customer data, from initial contact to post-sale support.
- Improved Customer Relationships: A CRM helps you understand your customers better. You’ll know their preferences, purchase history, and communication patterns, enabling you to personalize interactions and build stronger relationships.
- Enhanced Sales Efficiency: CRM automates repetitive tasks, such as data entry and follow-up emails, freeing up your sales team to focus on what they do best: closing deals.
- Better Marketing ROI: With a CRM, you can segment your audience and tailor your marketing campaigns for maximum impact. You’ll target the right customers with the right message at the right time.
- Streamlined Customer Service: A CRM provides a centralized hub for all customer inquiries, ensuring consistent and efficient support.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: CRM systems generate valuable insights into your sales pipeline, customer behavior, and overall business performance, allowing you to make informed decisions.
In essence, a CRM empowers you to work smarter, not harder, leading to increased sales, improved customer satisfaction, and ultimately, sustainable growth. Now, let’s get down to the nitty-gritty of the small business CRM cost.
Understanding CRM Pricing Models
The CRM landscape is diverse, and so are the pricing models. Here’s a breakdown of the most common approaches:
1. Per-User, Per-Month Subscriptions
This is the most prevalent pricing model, particularly for cloud-based CRM systems. You pay a monthly fee for each user who accesses the system. The cost varies based on the features included and the vendor. This model is often the most predictable, allowing you to easily scale up or down as your team grows or shrinks.
Pros:
- Predictable costs
- Easy scalability
- Often includes updates and support
Cons:
- Costs can add up quickly as your team grows
- May not be the most cost-effective option if only a few users need access
2. Tiered Pricing
Many CRM providers offer tiered pricing plans, with different levels of features and functionality at varying price points. Typically, the more you pay, the more features you unlock. This allows you to choose a plan that aligns with your specific needs and budget.
Pros:
- Flexibility to choose a plan that suits your needs
- Can start with a basic plan and upgrade as needed
Cons:
- May need to upgrade to a more expensive plan to access essential features
- Can be challenging to compare plans and determine the best value
3. Usage-Based Pricing
Some CRM systems, particularly those with advanced features like email marketing or SMS messaging, charge based on usage. This means you pay for the number of emails sent, SMS messages delivered, or other specific actions. This model can be beneficial if you have fluctuating usage patterns.
Pros:
- Pay only for what you use
- Can be cost-effective for businesses with infrequent usage
Cons:
- Costs can be unpredictable
- Difficult to budget accurately
4. On-Premise CRM (Less Common for Small Businesses)
With on-premise CRM, you purchase a license to install the software on your own servers. This model typically involves a significant upfront investment and ongoing costs for maintenance, IT support, and potential hardware upgrades. While it offers more control, it’s often less appealing to small businesses due to the high initial investment and the need for in-house technical expertise.
Pros:
- More control over data and security
- Potentially lower long-term costs for large businesses
Cons:
- High upfront costs
- Requires in-house IT expertise
- Ongoing maintenance and upgrade costs
5. Free CRM Options
Several CRM providers offer free versions of their software, often with limited features and user capacity. These can be a great starting point for very small businesses or those with basic CRM needs. However, be aware of limitations and potential upgrade costs down the line.
Pros:
- No initial cost
- Great for testing the waters
Cons:
- Limited features
- May have user restrictions
- Potential for upgrade costs
Factors Influencing Small Business CRM Costs
The price of a CRM isn’t just a flat fee. Several factors contribute to the overall small business CRM cost. Understanding these will help you make a more informed decision:
- Number of Users: As mentioned earlier, the number of users is a primary driver of cost, particularly with per-user pricing models.
- Features and Functionality: More advanced features, such as marketing automation, sales forecasting, and advanced reporting, often come with a higher price tag.
- Storage and Data Limits: Some CRM providers limit the amount of data you can store. If you anticipate needing significant storage, factor this into your cost analysis.
- Integrations: CRM systems often integrate with other business tools, such as email marketing platforms, accounting software, and e-commerce platforms. Integrations can sometimes incur additional costs.
- Customer Support: The level of customer support offered can impact the price. Premium support options, with dedicated account managers or priority response times, usually cost more.
- Training and Onboarding: Implementing a new CRM requires training for your team. Some vendors offer training as part of their packages, while others charge extra.
- Customization: If you require extensive customization to tailor the CRM to your specific business processes, expect additional costs.
- Implementation Services: For more complex CRM implementations, you might need professional implementation services, which can add to the overall cost.
- Contract Length: Some vendors offer discounts for longer-term contracts.
Estimating the True Cost of a Small Business CRM
Calculating the true small business CRM cost involves more than just looking at the monthly or annual fee. Consider these additional expenses:
- Implementation Costs: This includes the time and resources needed to set up the CRM, migrate your data, and train your team.
- Ongoing Maintenance Costs: These encompass any fees for updates, upgrades, and ongoing support.
- Opportunity Cost: This is the cost of the time your team spends learning and using the new CRM.
- Hidden Costs: Be aware of potential hidden costs, such as extra fees for exceeding data limits or using certain features.
To get a realistic estimate, follow these steps:
- Define Your Needs: Clearly outline your business requirements and the features you need in a CRM.
- Research Different Providers: Compare pricing plans, features, and customer reviews from various CRM providers.
- Request Quotes: Get detailed quotes from potential vendors, including all associated costs.
- Calculate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Factor in all the expenses mentioned above to get a complete picture of the cost.
- Consider the Return on Investment (ROI): Evaluate the potential benefits of the CRM, such as increased sales, improved customer satisfaction, and reduced operational costs, to determine its value.
Popular CRM Systems for Small Businesses and Their Estimated Costs
Let’s look at some popular CRM systems and their typical pricing. Please note that prices are subject to change, so always check the vendor’s website for the most up-to-date information.
1. HubSpot CRM
HubSpot offers a free CRM with unlimited users and a range of basic features. Paid plans start at around $45 per month and scale up based on features and the number of contacts. It’s a popular choice for its ease of use and robust free offering.
Estimated Cost: Free – $3,200+/month (depending on features and contacts)
2. Zoho CRM
Zoho CRM provides a comprehensive suite of features, with a free plan for up to three users. Paid plans start around $14 per user per month, offering various features and integrations. Zoho is known for its affordability and extensive customization options.
Estimated Cost: Free – $52+ per user/month
3. Freshsales (Freshworks CRM)
Freshsales is a sales-focused CRM with a user-friendly interface. It offers a free plan and paid plans starting around $15 per user per month. It’s well-suited for businesses that prioritize sales automation and lead management.
Estimated Cost: Free – $79+ per user/month
4. Pipedrive
Pipedrive is a sales-focused CRM known for its visual pipeline management. It’s designed to be intuitive and easy to use. Pricing starts around $14.90 per user per month. It’s a great choice for sales teams looking for a clear and organized pipeline view.
Estimated Cost: $14.90 – $99+ per user/month
5. Salesforce Sales Cloud Essentials
Salesforce is a well-established CRM provider, and its Sales Cloud Essentials plan is designed for small businesses. While it’s more expensive than some other options, it offers a robust feature set and scalability. Pricing starts around $25 per user per month.
Estimated Cost: $25 – $300+ per user/month
Important Note: The prices listed above are approximate and can vary depending on the specific plan, contract length, and any add-ons you choose. Always check the vendor’s website for the latest pricing and feature details.
Finding the Right CRM for Your Budget
Choosing the right CRM is about more than just the lowest price. It’s about finding the system that provides the best value for your specific needs. Here’s how to approach the decision-making process:
- Assess Your Requirements: Clearly define your business goals, sales processes, and customer service needs. What features are essential, and what are nice-to-haves?
- Set a Budget: Determine a realistic budget that considers both the upfront and ongoing costs.
- Research and Compare Options: Explore different CRM providers and compare their pricing plans, features, and customer reviews.
- Take Advantage of Free Trials: Most CRM providers offer free trials, allowing you to test the software and see if it’s a good fit.
- Read Reviews and Case Studies: Learn from the experiences of other small businesses.
- Consider Scalability: Choose a CRM that can grow with your business.
- Factor in Ease of Use: A CRM that’s difficult to use won’t be adopted by your team, regardless of its price.
- Prioritize Integrations: Ensure the CRM integrates with your existing tools.
- Don’t Be Afraid to Negotiate: Some vendors are willing to negotiate pricing, especially for longer-term contracts.
- Regularly Evaluate Your CRM: Periodically review your CRM usage and costs to ensure it’s still meeting your needs and delivering value.
Making the Most of Your CRM Investment
Once you’ve chosen a CRM, the work doesn’t stop there. To maximize your investment, consider these best practices:
- Implement Properly: Ensure a smooth implementation process, including data migration, user training, and system configuration.
- Train Your Team: Provide comprehensive training to ensure your team understands how to use the CRM effectively.
- Clean and Organize Your Data: Maintain accurate and up-to-date customer data.
- Use the CRM Consistently: Encourage your team to use the CRM daily to track leads, manage deals, and communicate with customers.
- Automate Tasks: Leverage the CRM’s automation features to streamline your workflows and save time.
- Track Key Metrics: Monitor your CRM’s performance by tracking key metrics, such as sales conversion rates, customer satisfaction, and lead generation.
- Regularly Review and Optimize: Periodically review your CRM usage and make adjustments as needed to improve its effectiveness.
- Seek Ongoing Support: Take advantage of the vendor’s support resources to address any issues or questions.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice for Your Business
The small business CRM cost is an important consideration, but it shouldn’t be the only factor driving your decision. By understanding the different pricing models, the factors that influence cost, and the true value of a CRM for your business, you can make an informed choice that will set you up for success. Remember to prioritize your business needs, research your options thoroughly, and choose a CRM that aligns with your budget and goals. With the right CRM in place, your small business can build stronger customer relationships, streamline its operations, and achieve sustainable growth.
Don’t be afraid to invest in a CRM. It’s an investment in your future. With careful planning and execution, you can find a CRM that fits your budget and helps you take your small business to the next level. Good luck!