Unlocking Engineering Success: The Best CRM Systems for Small Engineering Firms

Unlocking Engineering Success: The Best CRM Systems for Small Engineering Firms
In the fast-paced world of engineering, where precision and efficiency are paramount, managing client relationships effectively is crucial for success. Small engineering firms, in particular, often face the challenge of juggling multiple projects, clients, and administrative tasks. This is where a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system becomes an invaluable asset. This article delves into the best CRM systems tailored for small engineering businesses, exploring their features, benefits, and how they can streamline operations, boost productivity, and drive growth. We’ll navigate the complexities of choosing the right CRM, ensuring your firm not only survives but thrives in a competitive landscape.
Why a CRM is Essential for Small Engineering Firms
Before diving into specific CRM solutions, let’s understand why a CRM is so vital for small engineering firms. Unlike larger corporations with dedicated departments, small firms often have limited resources. A CRM acts as a centralized hub for all client-related information, eliminating the need for scattered spreadsheets, email threads, and manual data entry. This centralized approach offers several key advantages:
- Improved Client Communication: A CRM tracks all interactions with clients, including emails, phone calls, meetings, and project updates. This ensures that everyone on the team is on the same page, providing a consistent and professional experience for clients.
- Enhanced Project Management: Many CRM systems offer project management features, allowing engineers to track project progress, deadlines, and budgets. This integrated approach streamlines workflows and helps avoid costly delays.
- Increased Sales and Revenue: By tracking leads, managing sales pipelines, and automating follow-ups, a CRM helps small firms convert leads into paying clients and identify opportunities for upselling and cross-selling.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: A CRM provides valuable insights into client behavior, project performance, and sales trends. This data empowers engineering firms to make informed decisions and optimize their strategies.
- Time Savings and Efficiency: Automating repetitive tasks, such as data entry and email follow-ups, frees up engineers to focus on their core responsibilities, such as designing and engineering.
Key Features to Look for in a CRM for Small Engineering Firms
Choosing the right CRM is a critical decision. Here are some essential features to consider when evaluating CRM systems for your small engineering firm:
1. Contact Management
At the heart of any CRM is contact management. Ensure the system allows you to store and organize client information, including contact details, company information, project history, and communication logs. The best CRMs offer:
- Customizable Fields: The ability to add custom fields to store specific information relevant to your engineering projects.
- Segmentation: The ability to segment contacts based on various criteria, such as industry, project type, or client value.
- Import/Export Capabilities: Easy import and export of contact data from spreadsheets or other systems.
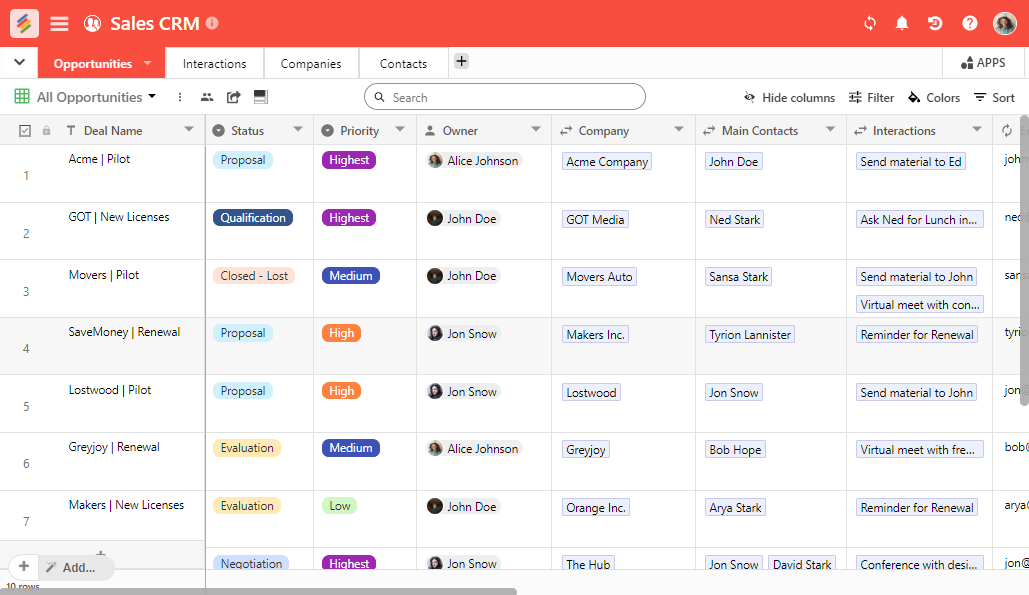
2. Sales Pipeline Management
A robust sales pipeline is essential for converting leads into clients. Look for a CRM that allows you to:
- Track Leads: Capture and track leads from various sources, such as website forms, email campaigns, and referrals.
- Manage Opportunities: Create and manage sales opportunities, including stages, estimated value, and close dates.
- Automate Follow-ups: Set up automated email sequences and reminders to nurture leads and move them through the sales pipeline.
3. Project Management Integration
For engineering firms, project management integration is a must-have. The ideal CRM should:
- Allow Project Tracking: Track project progress, deadlines, and budgets within the CRM.
- Facilitate Task Management: Assign tasks to team members, set deadlines, and track progress.
- Enable Document Management: Store and share project-related documents securely within the CRM.
4. Reporting and Analytics
Data is king. A good CRM provides comprehensive reporting and analytics to help you understand your business performance. Look for features such as:
- Sales Reports: Track sales performance, revenue, and conversion rates.
- Project Performance Reports: Analyze project profitability, timelines, and resource utilization.
- Customizable Dashboards: Create custom dashboards to visualize key metrics and track progress towards goals.
5. Integration Capabilities
Your CRM should integrate with other tools you use, such as:
- Email Marketing Platforms: Integrate with platforms like Mailchimp or Constant Contact to send targeted email campaigns.
- Accounting Software: Integrate with accounting software like QuickBooks or Xero to track invoices and payments.
- Project Management Software: Integrate with project management tools like Asana or Trello for seamless workflow.
6. Mobile Accessibility
Engineers are often on the go, so a mobile-friendly CRM is essential. Look for a CRM that offers a mobile app or a responsive web design that allows you to access your data and manage your clients from anywhere.
7. User-Friendliness and Ease of Use
A CRM is only useful if your team actually uses it. Choose a system that is intuitive, easy to navigate, and requires minimal training. Consider the following:
- User Interface: A clean and user-friendly interface is crucial.
- Training and Support: Look for a CRM provider that offers comprehensive training and support resources.
- Scalability: Choose a CRM that can grow with your business.
Top CRM Systems for Small Engineering Firms
Now, let’s explore some of the best CRM systems specifically designed or well-suited for small engineering firms:
1. HubSpot CRM
Overview: HubSpot CRM is a popular choice for small businesses due to its user-friendly interface and generous free plan. While it might lack some advanced features found in paid options, its simplicity and ease of use make it a great starting point for engineering firms new to CRM.
Key Features for Engineers:
- Free CRM: A robust free plan with unlimited users, contacts, and storage.
- Contact Management: Centralized contact database with detailed information.
- Sales Pipeline: Basic sales pipeline management to track deals.
- Email Integration: Integrates with email providers for tracking email activity.
- Reporting: Basic reporting on sales and marketing performance.
Pros:
- Free and easy to use.
- Excellent customer support.
- Integrates with other HubSpot tools (Marketing Hub, Sales Hub).
Cons:
- Limited features in the free plan.
- Not specifically tailored for engineering project management.
2. Zoho CRM
Overview: Zoho CRM is a comprehensive CRM solution that offers a wide range of features at a competitive price. It is a good fit for small engineering firms seeking a powerful, yet affordable, CRM.
Key Features for Engineers:
- Contact Management: Detailed contact management with custom fields.
- Sales Force Automation: Robust sales pipeline management, lead scoring, and workflow automation.
- Project Management Integration: Integrates with Zoho Projects for project tracking.
- Reporting and Analytics: Advanced reporting and analytics with customizable dashboards.
- Customization: Highly customizable to fit specific engineering workflows.
Pros:
- Feature-rich and affordable.
- Strong customization options.
- Integrates with other Zoho apps (Zoho Projects, Zoho Books).
Cons:
- Can be complex to set up and learn.
- The interface, while improved, can still feel a bit cluttered.
3. Pipedrive
Overview: Pipedrive is a sales-focused CRM known for its intuitive interface and visual sales pipeline. It’s an excellent choice for engineering firms that prioritize sales efficiency and want a CRM that’s easy to use.
Key Features for Engineers:
- Visual Sales Pipeline: Highly visual and intuitive sales pipeline management.
- Deal Tracking: Track deals through various stages with clear visual indicators.
- Activity Tracking: Track all sales activities, including calls, emails, and meetings.
- Automation: Automate repetitive tasks to save time.
- Reporting: Basic reporting on sales performance.
Pros:
- User-friendly and easy to learn.
- Excellent sales pipeline visualization.
- Strong focus on sales productivity.
Cons:
- Limited project management features.
- Less customizable than other options.
4. Monday.com
Overview: While not a dedicated CRM, monday.com is a highly versatile work operating system that can be customized to function as a powerful CRM. It’s an excellent option for engineering firms that want a flexible and visually appealing solution.
Key Features for Engineers (as a CRM):
- Customizable Boards: Create custom boards to manage contacts, deals, projects, and tasks.
- Workflow Automation: Automate repetitive tasks to streamline workflows.
- Project Management Capabilities: Manage projects and track progress.
- Collaboration: Collaborate with team members in real-time.
- Integrations: Integrates with various apps, including email and calendar.
Pros:
- Highly customizable and flexible.
- Visually appealing and easy to use.
- Strong project management capabilities.
Cons:
- Not a dedicated CRM, so some CRM-specific features may be missing.
- Can be more expensive than other options, depending on usage.
5. Agile CRM
Overview: Agile CRM is a comprehensive CRM solution designed for small businesses, offering sales, marketing, and service automation features. It’s a good option for engineering firms looking for an all-in-one solution.
Key Features for Engineers:
- Contact Management: Centralized contact database with detailed information.
- Sales Automation: Sales pipeline management, lead scoring, and workflow automation.
- Marketing Automation: Email marketing, social media integration, and landing page creation.
- Helpdesk: Integrated helpdesk for customer support.
- Reporting: Reporting on sales, marketing, and customer service performance.
Pros:
- All-in-one solution with sales, marketing, and customer service features.
- Affordable pricing.
- User-friendly interface.
Cons:
- Project management features are limited.
- Customer support can be inconsistent.
Choosing the Right CRM: A Step-by-Step Guide
Choosing the right CRM is a significant investment, so it’s crucial to take a strategic approach. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you make the right decision:
1. Define Your Needs and Goals
Before you start evaluating CRM systems, take the time to clearly define your needs and goals. Ask yourself:
- What are your current pain points in managing client relationships, sales, and projects?
- What are your key objectives for implementing a CRM? (e.g., increase sales, improve client communication, streamline project management)
- What specific features are essential for your engineering firm?
- How many users will need access to the CRM?
- What is your budget?
2. Research and Evaluate CRM Systems
Once you know your needs, research different CRM systems. Consider the following:
- Features: Does the CRM offer the features you need, such as contact management, sales pipeline management, project management integration, and reporting?
- Ease of Use: Is the CRM user-friendly and easy to navigate?
- Integrations: Does the CRM integrate with other tools you use, such as email marketing platforms, accounting software, and project management software?
- Pricing: Is the pricing model affordable and scalable for your business?
- Reviews and Ratings: Read reviews and ratings from other engineering firms to get insights into the CRM’s performance and customer satisfaction.
- Free Trials: Take advantage of free trials to test out different CRM systems and see how they work for your firm.
3. Consider Your Budget
CRM pricing varies widely. Consider both the initial costs and the ongoing costs, such as:
- Subscription Fees: Most CRMs use a subscription model, with pricing based on the number of users and features.
- Implementation Costs: Some CRMs require professional implementation, which can add to the cost.
- Training Costs: Factor in the cost of training your team on how to use the CRM.
- Ongoing Support Costs: Consider the cost of ongoing support and maintenance.
4. Prioritize Scalability
Choose a CRM that can grow with your business. As your firm expands, you’ll need a CRM that can handle more users, more data, and more complex workflows. Look for a CRM that offers:
- Scalable Pricing: Pricing plans that allow you to add users and features as needed.
- Data Storage Capacity: Sufficient data storage capacity to accommodate your growing client base and project data.
- Customization Options: The ability to customize the CRM to meet your evolving needs.
5. Implement and Train Your Team
Once you’ve chosen a CRM, the next step is implementation. This involves:
- Data Migration: Transferring your existing client data from spreadsheets or other systems into the CRM.
- Customization: Configuring the CRM to meet your specific needs, such as adding custom fields and setting up workflows.
- Training: Training your team on how to use the CRM. Provide comprehensive training and ongoing support to ensure that everyone is comfortable using the system.
- Testing: Test the CRM thoroughly to ensure that it’s working correctly.
6. Monitor and Optimize
After implementation, it’s essential to monitor your CRM’s performance and make adjustments as needed. Regularly review your CRM data to identify areas for improvement. Track key metrics, such as sales conversion rates, project completion times, and client satisfaction. Use this data to optimize your CRM usage and improve your business performance.
Best Practices for CRM Implementation in Engineering Firms
To maximize the benefits of your CRM, follow these best practices:
- Get Buy-In from Your Team: Involve your team in the decision-making process and provide adequate training to ensure that everyone understands the value of the CRM and how to use it effectively.
- Clean Up Your Data: Before importing your data into the CRM, clean it up to ensure accuracy and consistency.
- Establish Clear Processes: Define clear processes for using the CRM, such as how to enter data, manage leads, and track projects.
- Automate Tasks: Use automation features to streamline repetitive tasks, such as data entry and email follow-ups.
- Regularly Review and Update Data: Keep your CRM data up-to-date by regularly reviewing and updating client information, project progress, and sales opportunities.
- Use Reporting and Analytics: Leverage the CRM’s reporting and analytics features to gain insights into your business performance and make data-driven decisions.
- Integrate with Other Tools: Integrate your CRM with other tools you use, such as email marketing platforms, accounting software, and project management software.
- Provide Ongoing Training and Support: Provide ongoing training and support to your team to ensure that they are using the CRM effectively.
The Future of CRM in Engineering
The future of CRM in engineering is likely to be shaped by several key trends:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI will play an increasingly important role in CRM, automating tasks, providing insights, and personalizing client interactions.
- Mobile CRM: Mobile CRM will become even more important, allowing engineers to access their data and manage their clients from anywhere.
- Integration with IoT: CRM systems will integrate with the Internet of Things (IoT) to collect data from connected devices and provide real-time insights.
- Focus on Customer Experience: CRM systems will focus on providing exceptional customer experiences, with features such as personalized communication and proactive support.
Conclusion: Empowering Engineering Success with the Right CRM
Selecting and implementing the right CRM system is a strategic move for small engineering firms. By centralizing client data, streamlining workflows, and gaining valuable insights, a CRM empowers engineering firms to build stronger client relationships, improve project management, and drive sustainable growth. By carefully considering your needs, researching the available options, and following best practices for implementation and optimization, your firm can harness the power of CRM to achieve its full potential. The journey to engineering success starts with the right tools, and a well-chosen CRM is undoubtedly a cornerstone of that journey.