Small Business CRM Setup: Your Ultimate Guide to Customer Relationship Management

Small Business CRM Setup: Your Ultimate Guide to Customer Relationship Management
Starting a small business is an exciting journey, filled with the thrill of innovation and the promise of growth. But as your business blossoms, so does the complexity of managing your customer relationships. That’s where a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system comes in. Setting up a CRM might seem daunting, but trust me, it’s a game-changer. This comprehensive guide will walk you through every step of the small business CRM setup process, helping you choose the right system, implement it effectively, and reap the rewards of stronger customer relationships and improved business efficiency.
Why Your Small Business Needs a CRM
Before diving into the setup, let’s understand why a CRM is so crucial for small businesses. In the early days, you might be able to keep track of everything in your head or a simple spreadsheet. But as your customer base grows, this approach becomes unsustainable. Here’s why a CRM is essential:
- Centralized Customer Data: A CRM consolidates all your customer information – contact details, purchase history, communication logs, and more – in one place. No more scattered spreadsheets or lost emails!
- Improved Customer Relationships: With a 360-degree view of each customer, you can personalize interactions, understand their needs better, and provide exceptional customer service.
- Enhanced Sales Efficiency: CRM systems automate sales processes, track leads, and manage the sales pipeline, allowing your sales team to focus on closing deals.
- Better Marketing Campaigns: CRM data provides valuable insights into customer behavior, enabling you to create targeted marketing campaigns that resonate with your audience.
- Increased Productivity: Automating tasks and streamlining workflows frees up your team’s time, allowing them to focus on more strategic activities.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: CRM systems generate reports and analytics that provide valuable insights into your business performance, helping you make informed decisions.
In essence, a CRM empowers you to build stronger customer relationships, drive sales, and optimize your business operations. It’s not just a luxury; it’s a necessity for sustainable growth.
Choosing the Right CRM for Your Small Business
The market is flooded with CRM solutions, each with its own features, pricing, and target audience. Choosing the right one for your small business is crucial. Here’s how to navigate the selection process:
1. Assess Your Needs
Before you even look at CRM options, take a step back and define your specific needs and goals. Ask yourself:
- What are your primary business objectives? (e.g., increase sales, improve customer service, streamline marketing)
- What are your biggest pain points in managing customer relationships?
- What features are essential for your business? (e.g., contact management, sales pipeline, email marketing integration)
- How many users will need access to the CRM?
- What is your budget?
Answering these questions will give you a clear understanding of what you need from a CRM and will help you narrow down your choices.
2. Research CRM Options
Once you know your needs, it’s time to research the available CRM solutions. Consider these popular options:
- HubSpot CRM: Free CRM with robust features, ideal for small businesses. Excellent for sales and marketing.
- Zoho CRM: Affordable and customizable, suitable for various business sizes.
- Salesforce Sales Cloud: Powerful and feature-rich, but can be complex and expensive for very small businesses.
- Pipedrive: Focuses on sales pipeline management, user-friendly interface.
- Freshsales: Intuitive and offers features for sales and customer support.
- Monday.com: While not solely a CRM, Monday.com is a highly customizable work OS that can be adapted for CRM purposes, especially for project management and team collaboration.
Read reviews, compare features, and consider factors like ease of use, integration capabilities, and customer support.
3. Consider Pricing and Features
CRM pricing varies widely, from free options to enterprise-level subscriptions. Consider your budget and the features you need. Don’t overspend on features you won’t use. Most CRM providers offer different pricing tiers, so choose the plan that best fits your needs and budget. Look for features like:
- Contact management
- Sales pipeline management
- Lead tracking
- Email marketing integration
- Reporting and analytics
- Mobile access
- Integration with other business tools (e.g., accounting software, email marketing platforms)
4. Evaluate Ease of Use and Implementation
A CRM is only valuable if your team actually uses it. Choose a system that is user-friendly and easy to navigate. Consider the learning curve and the level of technical expertise required for setup and maintenance. Look for CRM systems that offer:
- Intuitive interface
- Drag-and-drop functionality
- Tutorials and training resources
- Responsive customer support
5. Prioritize Integration Capabilities
Your CRM should integrate with other tools you use, such as your email marketing platform, accounting software, and social media channels. This integration will streamline your workflows and ensure data consistency across your business.
6. Take Advantage of Free Trials and Demos
Most CRM providers offer free trials or demos. Take advantage of these opportunities to test the system and see if it’s the right fit for your business. This allows you to explore the features, evaluate the user interface, and get a feel for the overall user experience before committing to a subscription.
7. Check for Scalability
Choose a CRM that can scale with your business. As your business grows, you’ll need a CRM that can handle more data, more users, and more complex workflows. Ensure that the CRM you choose can accommodate your future needs.
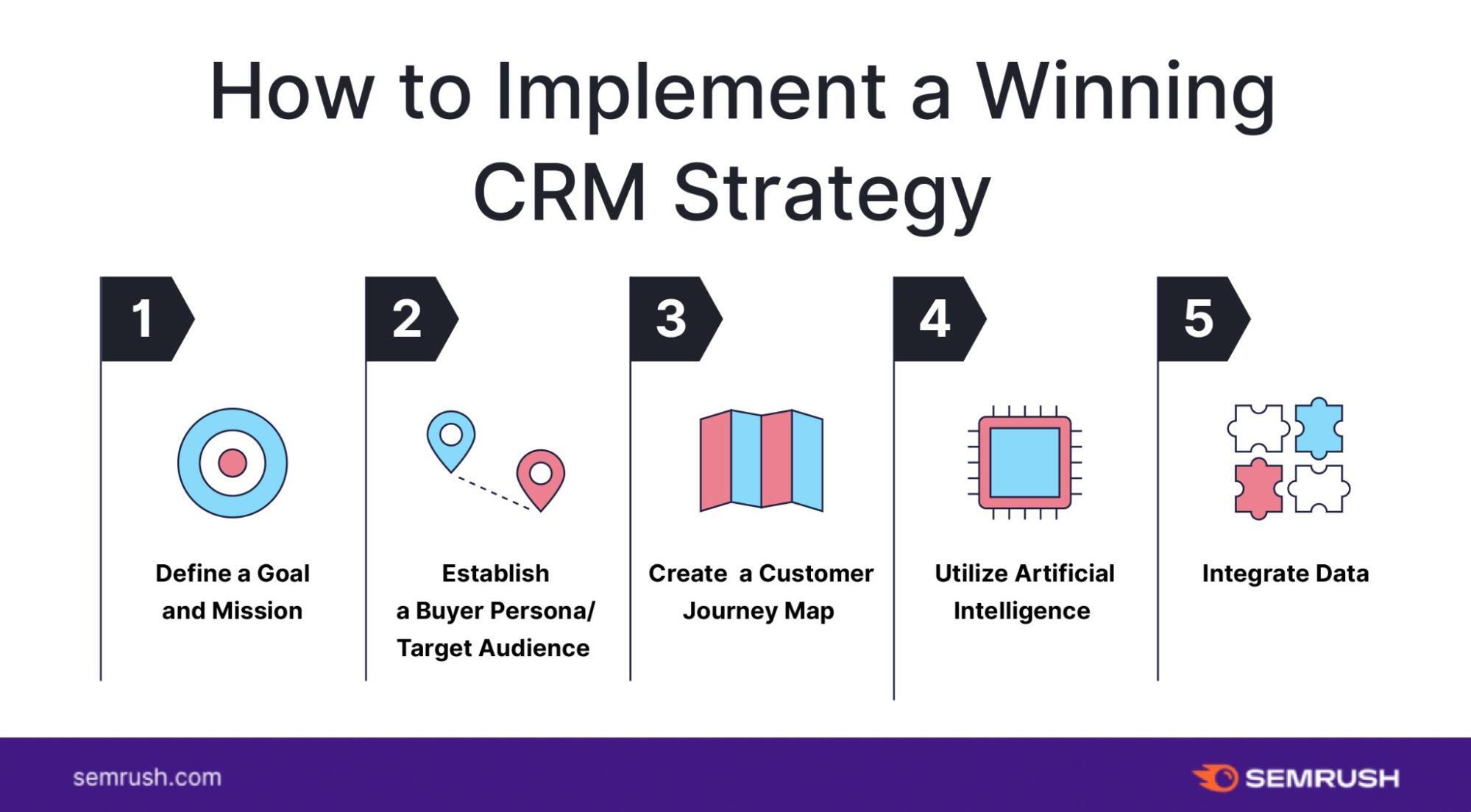
Step-by-Step Guide to Setting Up Your Small Business CRM
Once you’ve chosen your CRM, it’s time to set it up. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you get started:
1. Planning and Preparation
Before you start setting up your CRM, take some time to plan. This will save you time and effort in the long run. Consider these steps:
- Define Your Goals: What do you want to achieve with your CRM? (e.g., increase sales, improve customer satisfaction)
- Identify Key Data Fields: What information do you need to capture about your customers? (e.g., name, contact details, purchase history)
- Map Your Sales Process: How does a lead become a customer? (This will help you set up your sales pipeline.)
- Decide on User Roles and Permissions: Who will have access to the CRM, and what can they do?
- Prepare Your Data: Gather your existing customer data from spreadsheets, email contacts, and other sources. Clean and organize the data to ensure accuracy.
2. Account Creation and Initial Setup
The first step is to create an account with your chosen CRM provider. Follow the provider’s instructions to set up your account. This typically involves:
- Creating an Account: Provide your business information and create a username and password.
- Setting Up Your Profile: Add your company logo, contact information, and other relevant details.
- Configuring User Accounts: Create user accounts for each member of your team who will be using the CRM. Assign roles and permissions to control access to data and features.
3. Data Import and Organization
Once your account is set up, it’s time to import your customer data. Most CRM systems allow you to import data from spreadsheets, CSV files, or other sources. Follow these steps:
- Prepare Your Data: Ensure your data is clean, organized, and formatted correctly.
- Choose the Import Method: Select the appropriate import method for your data source.
- Map Data Fields: Match the fields in your data source to the corresponding fields in the CRM.
- Import Your Data: Upload your data and review it for accuracy.
- Organize Your Data: Use tags, segments, or other organizational tools to categorize your customers.
4. Customization and Configuration
CRM systems are highly customizable. Take advantage of this to tailor the system to your specific business needs. This includes:
- Customizing Fields: Add custom fields to capture specific data points relevant to your business.
- Configuring Sales Pipelines: Define your sales stages and create a sales pipeline that reflects your sales process.
- Setting Up Workflows and Automations: Automate repetitive tasks, such as sending follow-up emails or creating tasks.
- Integrating with Other Tools: Connect your CRM with other tools you use, such as your email marketing platform and accounting software.
5. Training and Onboarding
Successful CRM implementation requires proper training and onboarding. Ensure that your team understands how to use the CRM and how it fits into their daily workflows. This includes:
- Providing Training: Offer training sessions, tutorials, and documentation to help your team learn how to use the CRM.
- Creating User Guides: Develop user guides and cheat sheets to help your team quickly find information and complete tasks.
- Encouraging Adoption: Encourage your team to use the CRM by highlighting its benefits and providing support.
- Providing Ongoing Support: Offer ongoing support and training to help your team stay up-to-date with the latest features and best practices.
6. Testing and Refinement
Before fully launching your CRM, test it thoroughly. This includes:
- Testing Functionality: Ensure that all features are working as expected.
- Testing Integrations: Verify that your CRM is properly integrated with other tools.
- Gathering Feedback: Get feedback from your team on the user experience and make adjustments as needed.
- Refining Workflows: Optimize your workflows to ensure efficiency and effectiveness.
7. Launch and Ongoing Management
Once you’re confident that your CRM is set up correctly, launch it and start using it to manage your customer relationships. Ongoing management is essential for maximizing the value of your CRM. This includes:
- Monitoring Data Quality: Regularly review your data and ensure its accuracy.
- Analyzing Reports and Analytics: Use the CRM’s reporting features to track your progress and identify areas for improvement.
- Making Adjustments: Continuously refine your CRM setup based on your business needs and the feedback you receive.
- Providing Ongoing Training: Keep your team up-to-date with the latest features and best practices.
- Staying Updated: CRM systems are constantly evolving. Stay informed about new features and updates to maximize your investment.
Tips for Successful CRM Implementation
Setting up a CRM is a significant undertaking. Here are some tips to help you ensure a successful implementation:
- Start Small: Don’t try to implement everything at once. Start with the core features and gradually add more functionality as your team becomes comfortable.
- Get Buy-In from Your Team: Involve your team in the selection and implementation process. This will increase their buy-in and make them more likely to use the CRM.
- Provide Clear Instructions and Training: Make sure your team understands how to use the CRM and how it fits into their daily workflows.
- Communicate Regularly: Keep your team informed about the progress of the implementation and any changes that are made.
- Be Patient: CRM implementation takes time. Don’t get discouraged if you don’t see results immediately.
- Seek External Help if Needed: Consider hiring a consultant or CRM specialist to help you with the implementation process.
- Regularly Review and Optimize: CRM implementation is not a one-time event. Continuously review your setup and make adjustments as needed.
- Focus on Data Quality: Garbage in, garbage out. The accuracy of your data is critical for the success of your CRM.
- Prioritize User Experience: Make sure the CRM is easy to use and intuitive. A clunky interface will lead to low adoption rates.
- Measure Your Results: Track key metrics to measure the success of your CRM implementation. This will help you identify areas for improvement.
Maximizing Your CRM Investment: Beyond the Basics
Once your CRM is set up and running, don’t stop there. There are many ways to maximize your investment and leverage your CRM for even greater success. Here are some advanced strategies:
1. Leverage Automation
CRM systems excel at automation. Explore advanced automation features to streamline your workflows and save time. Automate tasks such as:
- Lead Qualification: Automatically score leads based on their behavior and demographics.
- Email Marketing: Send automated email sequences based on customer behavior or purchase history.
- Task Creation: Automatically create tasks for your team based on specific triggers.
- Data Entry: Automate data entry tasks, such as updating contact information or creating new deals.
2. Integrate with Marketing Automation Tools
Integrate your CRM with marketing automation tools to create more sophisticated marketing campaigns. This will allow you to:
- Personalize Your Messaging: Tailor your marketing messages to each customer based on their behavior and demographics.
- Automate Your Marketing Funnel: Guide leads through your sales funnel with automated email sequences and targeted content.
- Track Your ROI: Measure the effectiveness of your marketing campaigns and optimize your spend.
3. Use CRM for Customer Service
CRM systems can also be used to improve customer service. Use your CRM to:
- Track Customer Interactions: Keep a record of all customer interactions, including emails, phone calls, and support tickets.
- Provide Personalized Support: Access customer data to provide personalized support and resolve issues quickly.
- Manage Support Tickets: Track and manage support tickets to ensure that all customer issues are resolved efficiently.
4. Analyze Your Data and Make Data-Driven Decisions
CRM systems generate a wealth of data. Use this data to gain insights into your business performance and make data-driven decisions. Analyze data such as:
- Sales Performance: Track your sales pipeline, identify top-performing sales reps, and measure your conversion rates.
- Customer Behavior: Analyze customer behavior to understand their needs and preferences.
- Marketing Campaign Effectiveness: Measure the effectiveness of your marketing campaigns and optimize your spend.
5. Train Your Team on Advanced Features
Invest in ongoing training for your team to ensure they are using the CRM to its full potential. Train them on advanced features such as:
- Workflow Automation: Teach your team how to create and manage automated workflows.
- Reporting and Analytics: Train your team how to use the CRM’s reporting features to generate valuable insights.
- Advanced Segmentation: Teach your team how to segment customers based on their behavior and demographics.
Overcoming Common CRM Implementation Challenges
While the benefits of a CRM are undeniable, the implementation process can present challenges. Here are some common obstacles and how to overcome them:
1. Data Migration Issues
Migrating data from existing systems can be complex. To avoid problems:
- Clean Your Data: Before importing, clean and standardize your data to ensure accuracy.
- Map Fields Carefully: Carefully map fields from your old system to the new CRM.
- Test the Import: Test the import process with a small sample of data before importing the entire dataset.
- Consider External Help: If you’re struggling, consider hiring a data migration specialist.
2. User Adoption Issues
Getting your team to use the CRM can be a challenge. To improve adoption:
- Provide Training: Offer comprehensive training on how to use the CRM.
- Highlight the Benefits: Clearly communicate the benefits of using the CRM to your team.
- Make it Easy to Use: Choose a user-friendly CRM and customize it to meet your team’s needs.
- Lead by Example: Encourage managers to use the CRM and set a good example for the team.
3. Integration Problems
Integrating the CRM with other systems can be difficult. To minimize problems:
- Plan Ahead: Before choosing a CRM, make sure it integrates with the other systems you use.
- Test Integrations: Thoroughly test all integrations to ensure they are working correctly.
- Seek Technical Support: If you encounter problems, contact the CRM provider’s technical support team.
4. Lack of Clear Goals
Without clear goals, it’s difficult to measure the success of your CRM implementation. To avoid this problem:
- Define Your Goals: Before implementing the CRM, define your goals and objectives.
- Track Key Metrics: Track key metrics to measure your progress toward your goals.
- Regularly Review Your Goals: Regularly review your goals and make adjustments as needed.
5. Budget Constraints
CRM systems can be expensive. To manage your budget:
- Choose a Cost-Effective Solution: There are many affordable CRM options available.
- Start with a Free Trial: Before committing to a paid plan, try a free trial to see if the CRM meets your needs.
- Consider a Phased Implementation: Implement the CRM in phases to spread out the costs.
The Future of CRM for Small Businesses
The world of CRM is constantly evolving, with new technologies and features emerging all the time. Here’s what the future holds for small business CRM:
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML are already transforming CRM, and their impact will only grow. Expect to see:
- Predictive Analytics: CRM systems will use AI to predict customer behavior and identify future opportunities.
- Intelligent Automation: AI will automate more tasks, such as lead scoring, email personalization, and customer support.
- Personalized Customer Experiences: AI will enable businesses to deliver highly personalized customer experiences.
2. Enhanced Integration
CRM systems will continue to integrate with other business tools, such as:
- Social Media: CRM systems will integrate more seamlessly with social media platforms to enable businesses to engage with customers on social media.
- E-commerce Platforms: CRM systems will integrate with e-commerce platforms to provide a unified view of customer data.
- Communication Tools: CRM systems will integrate with communication tools, such as video conferencing and chat, to improve communication and collaboration.
3. Mobile-First Approach
Mobile access will become even more important. Expect to see:
- Mobile-Optimized CRM: CRM systems will be designed with a mobile-first approach, making them easy to use on smartphones and tablets.
- Mobile CRM Apps: CRM providers will offer mobile apps that provide access to all the features of the CRM.
- Location-Based Services: CRM systems will integrate with location-based services to provide insights into customer behavior and enable businesses to target customers based on their location.
4. Focus on Customer Experience
Customer experience will be at the forefront of CRM. Expect to see:
- Personalized Customer Journeys: CRM systems will enable businesses to create personalized customer journeys that guide customers through the sales process.
- Proactive Customer Service: CRM systems will enable businesses to proactively identify and address customer issues.
- Omnichannel Communication: CRM systems will support omnichannel communication, allowing businesses to communicate with customers across multiple channels, such as email, phone, and chat.
Conclusion: Embrace CRM for Small Business Success
Setting up a CRM for your small business is a smart move. It equips you with the tools you need to build stronger customer relationships, boost sales, and streamline your operations. While the initial setup might require some effort, the long-term benefits are well worth it. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can choose the right CRM, implement it effectively, and unlock the potential for sustainable growth. Embrace the power of CRM, and watch your small business thrive!