Small Business CRM Features: The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Right Software
Small Business CRM Features: The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Right Software
Running a small business is a wild ride. You’re juggling a million things at once – from product development and marketing to sales and customer service. In the midst of all this chaos, keeping track of your customers can feel like herding cats. That’s where a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system comes in. It’s your digital headquarters for all things customer-related, a central hub for managing interactions, streamlining processes, and ultimately, boosting your bottom line.
But with so many CRM solutions on the market, each boasting a dazzling array of features, how do you choose the right one for your small business? This comprehensive guide will break down the essential CRM features, explain why they matter, and help you make an informed decision that empowers your team and drives success. We’ll delve into the core functionalities, explore advanced capabilities, and provide practical tips for implementation.
What is a CRM System?
Before we dive into features, let’s clarify what a CRM system actually is. At its core, a CRM is a technology that helps businesses manage and analyze customer interactions and data throughout the customer lifecycle. It’s more than just a contact database; it’s a strategic tool that helps you understand your customers better, personalize your interactions, and build lasting relationships.
Think of it as a central repository for all your customer information: contact details, purchase history, communication logs, and more. This data is then used to improve customer service, automate marketing efforts, and ultimately, increase sales. CRM systems are designed to help you:
- Organize Customer Data: Store and manage all customer information in a centralized location.
- Improve Communication: Track and manage all interactions with customers, including emails, calls, and meetings.
- Automate Tasks: Automate repetitive tasks like email marketing and lead nurturing.
- Increase Sales: Identify and nurture leads, track sales progress, and close deals more effectively.
- Enhance Customer Service: Provide personalized and efficient customer support.
- Analyze Data: Generate reports and dashboards to gain insights into customer behavior and business performance.
Essential CRM Features for Small Businesses
While the CRM landscape is vast, some features are non-negotiable for small businesses. These core functionalities form the foundation of a successful CRM strategy:
1. Contact Management
This is the heart of any CRM. Contact management allows you to store, organize, and manage all your customer and prospect information in one place. Key features include:
- Contact Database: A central repository for all contact details, including names, titles, phone numbers, email addresses, and physical addresses.
- Segmentation: Ability to group contacts based on various criteria, such as demographics, purchase history, or engagement level. This allows you to tailor your marketing and sales efforts.
- Custom Fields: The flexibility to add custom fields to capture specific information relevant to your business, such as industry, interests, or preferred communication methods.
- Import/Export: The ability to easily import and export contact data from spreadsheets or other systems.
- Deduplication: Automatic detection and merging of duplicate contact records to maintain data accuracy.
Effective contact management is the cornerstone of building strong customer relationships. By having all your contact information readily available and organized, you can personalize your interactions and provide a better customer experience.
2. Lead Management
Lead management is the process of tracking and nurturing potential customers through the sales funnel. A good CRM system should provide features that help you capture, qualify, and convert leads into paying customers. Key features include:
- Lead Capture Forms: Integration with website forms to automatically capture lead information.
- Lead Scoring: Assigning points to leads based on their behavior and demographics to prioritize the most promising prospects.
- Lead Segmentation: Grouping leads based on their characteristics and behavior to tailor your sales and marketing efforts.
- Lead Assignment: Automatically assigning leads to the appropriate sales representatives.
- Lead Nurturing: Automated email campaigns and workflows to engage and educate leads.
Lead management helps you streamline your sales process, identify qualified leads, and convert them into customers more efficiently. By automating lead nurturing, you can stay top-of-mind and guide prospects through the sales funnel.
3. Sales Automation
Sales automation streamlines repetitive tasks and frees up your sales team to focus on closing deals. Key features include:
- Workflow Automation: Automating repetitive tasks like sending follow-up emails, updating contact information, and creating tasks.
- Email Templates: Pre-written email templates for common sales scenarios, such as follow-ups, meeting confirmations, and proposals.
- Sales Pipeline Management: Visual representation of your sales pipeline, allowing you to track deals and identify bottlenecks.
- Deal Tracking: Tracking the progress of each deal, including stage, value, and close date.
- Reporting and Analytics: Generating reports on sales performance, including sales volume, conversion rates, and average deal size.
Sales automation increases efficiency, reduces manual errors, and allows your sales team to spend more time selling. By automating routine tasks, you can accelerate the sales cycle and close more deals.
4. Email Integration
Seamless email integration is crucial for managing customer communication. A CRM should integrate with your existing email provider (e.g., Gmail, Outlook) and provide features like:
- Email Tracking: Tracking whether emails have been opened and clicked.
- Email Templates: Pre-written email templates for various communication scenarios.
- Email Automation: Automated email workflows for lead nurturing, customer onboarding, and follow-up.
- Two-Way Sync: Synchronizing emails between your CRM and your email provider.
- Email Archiving: Automatically archiving emails related to specific contacts and deals.
Email integration allows you to track and manage all customer communication in one place, ensuring that your team is always on the same page and that no important emails are missed.
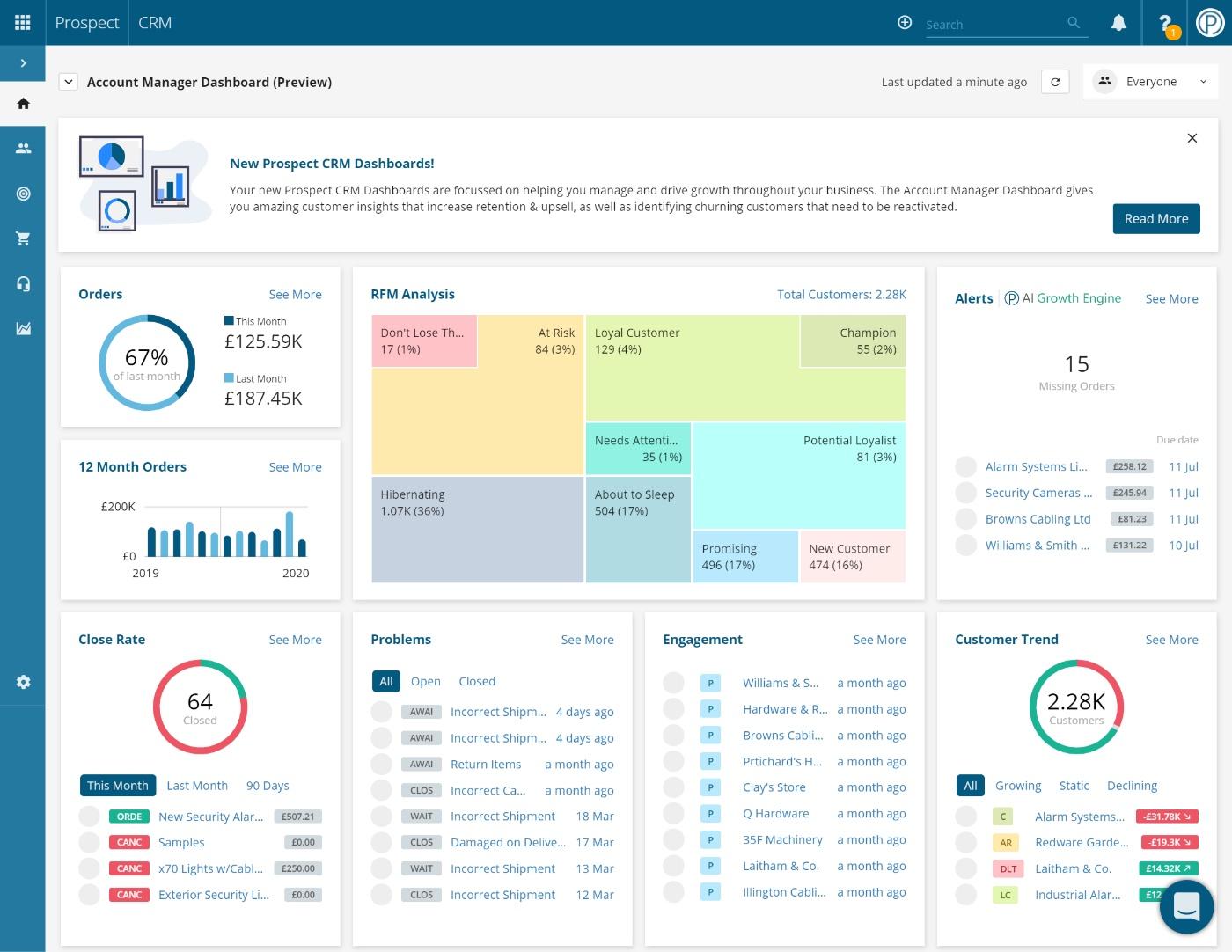
5. Reporting and Analytics
Data is king, and a good CRM provides robust reporting and analytics capabilities to help you track your performance, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions. Key features include:
- Customizable Dashboards: Creating dashboards that display key metrics and insights.
- Pre-built Reports: Accessing pre-built reports on sales performance, customer activity, and marketing effectiveness.
- Custom Report Builder: Creating custom reports to analyze specific data points.
- Data Visualization: Using charts and graphs to visualize data and identify trends.
- Sales Forecasting: Forecasting future sales based on historical data and current pipeline activity.
Reporting and analytics provide valuable insights into your business performance, allowing you to identify areas for improvement and make informed decisions. By tracking key metrics, you can measure your progress and optimize your strategies.
6. Mobile Access
In today’s fast-paced world, your team needs access to customer information on the go. A CRM with mobile access allows your team to:
- Access Contact Information: View contact details, notes, and communication history from their mobile devices.
- Update Records: Add new contacts, update existing records, and log activities.
- Manage Deals: Track the progress of deals and update deal stages.
- Receive Notifications: Receive real-time notifications about important activities.
- Access Reports: View key reports and dashboards on their mobile devices.
Mobile access empowers your team to stay connected and productive, even when they’re away from the office. This is particularly important for sales teams who spend a significant amount of time on the road.
7. Integrations
Your CRM shouldn’t exist in a vacuum. It needs to integrate with other tools you use, such as:
- Email Marketing Platforms: (e.g., Mailchimp, Constant Contact) to synchronize contact lists and automate email campaigns.
- Accounting Software: (e.g., QuickBooks, Xero) to track invoices, payments, and financial data.
- Social Media Platforms: (e.g., Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn) to monitor social media activity and engage with customers.
- Website Forms: To automatically capture leads from your website.
- Help Desk Software: (e.g., Zendesk, Freshdesk) to manage customer support tickets.
Integrations allow your CRM to seamlessly exchange data with other systems, streamlining your workflows and providing a holistic view of your customer data.
Advanced CRM Features to Consider
Once you’ve mastered the essential features, you might want to explore more advanced capabilities to further optimize your CRM strategy:
1. Marketing Automation
Marketing automation goes beyond basic email marketing and allows you to automate a wide range of marketing tasks, such as:
- Email Marketing Campaigns: Creating and sending automated email campaigns based on customer behavior and demographics.
- Lead Nurturing Workflows: Automating lead nurturing sequences to guide prospects through the sales funnel.
- Behavioral Targeting: Targeting customers based on their website activity, purchase history, and other behaviors.
- Social Media Automation: Scheduling and publishing social media posts.
- Personalization: Personalizing email content and website content based on customer data.
Marketing automation helps you nurture leads, improve customer engagement, and drive more sales.
2. Sales Forecasting
Sales forecasting uses historical data and current pipeline activity to predict future sales. This allows you to:
- Predict Revenue: Forecast future revenue with greater accuracy.
- Allocate Resources: Allocate resources effectively based on projected sales.
- Identify Opportunities: Identify potential sales opportunities and areas for improvement.
- Set Realistic Goals: Set realistic sales goals based on historical data and market trends.
Sales forecasting provides valuable insights into your sales performance and helps you make data-driven decisions.
3. Customer Service Automation
Customer service automation helps you streamline your customer support processes and improve customer satisfaction. Features include:
- Help Desk Integration: Integrating with help desk software to manage customer support tickets.
- Self-Service Portals: Providing customers with self-service portals where they can find answers to their questions.
- Chatbots: Using chatbots to provide instant customer support.
- Automated Ticket Routing: Automatically routing customer support tickets to the appropriate team members.
Customer service automation improves efficiency, reduces response times, and enhances the customer experience.
4. Customization
The ability to customize your CRM to fit your specific business needs is crucial. Features include:
- Custom Fields: Adding custom fields to capture specific information relevant to your business.
- Custom Reports: Creating custom reports to analyze specific data points.
- Workflow Customization: Customizing workflows to automate specific tasks.
- User Roles and Permissions: Defining user roles and permissions to control access to data and features.
Customization allows you to tailor your CRM to your unique business processes and requirements.
5. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML are transforming the CRM landscape, offering powerful capabilities such as:
- Lead Scoring: Using AI to score leads based on their likelihood to convert.
- Predictive Analytics: Predicting customer behavior and identifying potential sales opportunities.
- Sentiment Analysis: Analyzing customer feedback to understand their sentiment.
- Chatbots: Using AI-powered chatbots to provide more intelligent customer support.
AI and ML can provide valuable insights, automate tasks, and improve the customer experience.
Choosing the Right CRM for Your Small Business
Selecting the right CRM is a critical decision. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you choose the best solution for your small business:
1. Define Your Needs
Before you start evaluating CRM systems, take some time to define your specific needs and goals. Consider the following questions:
- What are your current challenges? What problems are you trying to solve with a CRM?
- What are your sales processes? How do you currently manage leads, track deals, and close sales?
- What are your marketing goals? How do you plan to nurture leads and engage with customers?
- What are your customer service processes? How do you currently provide customer support?
- What are your reporting needs? What metrics do you need to track to measure your performance?
- How many users will need access to the CRM? This will affect the pricing and features you need.
- What integrations do you need? What other systems do you need to integrate with your CRM?
Answering these questions will help you create a clear picture of your requirements and narrow down your options.
2. Research CRM Providers
Once you know your needs, start researching CRM providers. Here are some popular options for small businesses:
- Zoho CRM: A popular and affordable CRM with a wide range of features.
- HubSpot CRM: A free CRM with powerful features for sales and marketing.
- Salesforce Sales Cloud: A comprehensive CRM with advanced features for larger businesses.
- Pipedrive: A sales-focused CRM with a user-friendly interface.
- Freshsales: A sales CRM with integrated phone and email.
- Insightly: A CRM designed for small businesses and project management.
- Agile CRM: An all-in-one CRM with sales, marketing, and service features.
Read reviews, compare features, and consider the pricing of each provider.
3. Evaluate Features
Compare the features of each CRM provider against your needs. Make sure the CRM offers the essential features you need, such as contact management, lead management, sales automation, and email integration. Consider the advanced features that could benefit your business, such as marketing automation and sales forecasting.
4. Consider Ease of Use
The CRM should be easy to use and intuitive. A complex CRM can be difficult to implement and may not be adopted by your team. Look for a CRM with a user-friendly interface, clear navigation, and helpful tutorials.
5. Evaluate Integrations
Make sure the CRM integrates with the other tools you use, such as your email marketing platform, accounting software, and website forms. Integrations will streamline your workflows and save you time.
6. Consider Pricing
CRM pricing varies widely. Consider your budget and choose a CRM that offers the features you need at a price you can afford. Some CRMs offer free plans with limited features, while others offer paid plans with more advanced features. Pay attention to the pricing structure (e.g., per-user, per-month) and the total cost of ownership.
7. Try a Free Trial or Demo
Many CRM providers offer free trials or demos. Take advantage of these to test the CRM and see if it’s a good fit for your business. This will allow you to experience the features firsthand and evaluate the user interface.
8. Get Training and Support
Make sure the CRM provider offers adequate training and support. You’ll need training to implement the CRM and support to troubleshoot any issues. Look for a provider that offers documentation, tutorials, and customer support.
9. Plan for Implementation
Implementing a CRM takes time and effort. Plan for the implementation process, including data migration, user training, and system configuration. Consider hiring a consultant to help you with the implementation.
10. Review and Optimize
Once you’ve implemented your CRM, regularly review your processes and optimize your CRM strategy. Monitor your performance, identify areas for improvement, and make adjustments as needed.
Benefits of Using a CRM
Investing in a CRM system offers a wealth of benefits for small businesses:
- Improved Customer Relationships: By centralizing customer data and providing a 360-degree view of your customers, CRMs help you build stronger relationships.
- Increased Sales: CRMs streamline the sales process, automate tasks, and help you close more deals.
- Enhanced Customer Service: CRMs provide your customer service team with the tools they need to provide personalized and efficient support.
- Increased Efficiency: CRMs automate repetitive tasks, freeing up your team to focus on more important activities.
- Improved Data Analysis: CRMs provide powerful reporting and analytics capabilities, allowing you to track your performance and make data-driven decisions.
- Better Team Collaboration: CRMs centralize information and facilitate communication, improving collaboration among your team members.
- Increased Productivity: CRMs streamline workflows and automate tasks, increasing productivity across your organization.
- Reduced Costs: CRMs automate tasks, reduce errors, and improve efficiency, which can lead to significant cost savings.
- Scalability: CRMs are scalable, so they can grow with your business.
- Competitive Advantage: By using a CRM, you can gain a competitive advantage by providing a better customer experience and improving your sales and marketing effectiveness.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Implementing a CRM
While a CRM can be a game-changer for your small business, it’s important to avoid common pitfalls during implementation:
- Choosing the Wrong CRM: Selecting a CRM that doesn’t meet your specific needs and goals can lead to wasted time and money.
- Not Defining Your Needs: Failing to define your needs and goals before selecting a CRM can lead to choosing a system that doesn’t meet your requirements.
- Not Involving Your Team: Failing to involve your team in the selection and implementation process can lead to resistance and lack of adoption.
- Not Training Your Team: Failing to provide adequate training can lead to users not understanding how to use the CRM effectively.
- Not Migrating Data Properly: Improper data migration can lead to data loss and inaccuracies.
- Not Integrating with Other Systems: Failing to integrate your CRM with other systems can lead to data silos and inefficiencies.
- Not Customizing the CRM: Failing to customize the CRM to fit your specific business needs can lead to inefficiencies.
- Not Monitoring Your Performance: Failing to monitor your performance and make adjustments as needed can lead to wasted resources.
- Not Having a Clear Implementation Plan: Lack of a clear implementation plan can lead to delays and frustrations.
- Giving Up Too Soon: CRM implementation takes time and effort. Don’t give up too soon.
Conclusion
Choosing the right CRM is a crucial investment for any small business looking to grow and thrive. By understanding the essential features, carefully evaluating your needs, and following the steps outlined in this guide, you can select a CRM that empowers your team, streamlines your processes, and drives success. Remember to focus on building strong customer relationships, automating your workflows, and making data-driven decisions. With the right CRM in place, you’ll be well-equipped to navigate the challenges of running a small business and achieve your goals.