Small Business CRM Costs: A Comprehensive Guide to Finding the Right Fit and Budget

Small Business CRM Costs: Navigating the Landscape
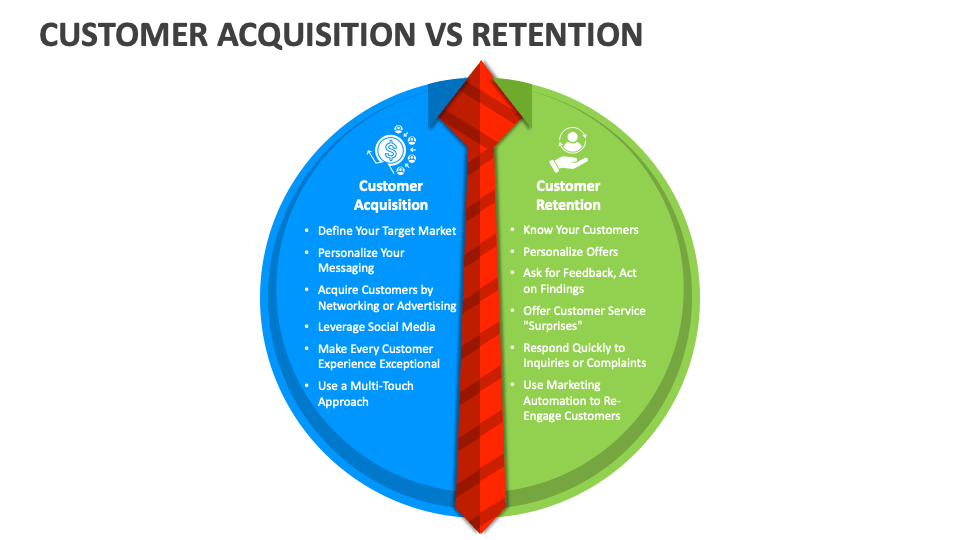
Starting a small business is an exciting journey. You’re the captain of your own ship, charting a course to success. But as your business grows, so does the complexity of managing customer relationships. That’s where a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system comes in. However, the phrase ‘CRM cost’ can send shivers down the spine of any small business owner. It’s a valid concern, but it shouldn’t be a deterrent. This comprehensive guide will demystify the costs associated with CRM systems, helping you find the perfect fit for your business and budget.
What is a CRM, and Why Do You Need One?
Before we dive into the nitty-gritty of CRM costs, let’s quickly recap what a CRM actually does. At its core, a CRM is a software solution designed to manage and analyze all your interactions with current and potential customers. Think of it as your central hub for all customer-related information. It’s where you store contact details, track communication, manage sales pipelines, and analyze customer behavior. Essentially, a CRM helps you:
- Improve Customer Relationships: By providing a 360-degree view of your customers, you can personalize interactions and build stronger relationships.
- Increase Sales: CRM systems help you streamline your sales process, identify leads, and close deals more efficiently.
- Enhance Customer Service: With easy access to customer information and history, your support team can provide faster and more effective assistance.
- Boost Productivity: Automate tasks, reduce manual data entry, and free up your team to focus on more strategic initiatives.
- Make Data-Driven Decisions: CRM systems provide valuable insights into customer behavior, sales performance, and marketing effectiveness, allowing you to make informed decisions.
In short, a CRM is a powerful tool that can help small businesses grow and thrive. Now, let’s get to the heart of the matter: the cost.
Understanding the Different CRM Cost Models
The cost of a CRM system isn’t a one-size-fits-all equation. It varies widely depending on several factors, including the type of system, the features you need, and the size of your business. Here’s a breakdown of the common cost models:
1. Subscription-Based (SaaS) CRM
This is the most popular cost model, especially for small businesses. SaaS (Software as a Service) CRM systems are cloud-based, meaning you access them over the internet. You pay a recurring fee, typically monthly or annually, to use the software. The fee is usually based on the number of users or the features you need.
- Pros:
- Lower upfront costs: No need to invest in expensive hardware or IT infrastructure.
- Scalability: Easily add or remove users as your business grows or shrinks.
- Automatic updates: The vendor handles software updates and maintenance.
- Accessibility: Access your CRM from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Cons:
- Recurring costs: You’ll be paying for the software as long as you use it.
- Limited customization: You may have less control over the software’s features and functionality compared to on-premise solutions.
- Vendor lock-in: Switching CRM providers can be a complex process.
2. On-Premise CRM
With an on-premise CRM, you purchase a license and install the software on your own servers. This gives you more control over your data and the system’s functionality. However, it also comes with higher upfront costs and ongoing maintenance responsibilities.
- Pros:
- Greater control: You have full control over your data and the system’s configuration.
- Customization: You can customize the software to meet your specific needs.
- Data security: You control the security of your data, which may be important for businesses with sensitive information.
- Cons:
- High upfront costs: You’ll need to purchase licenses, hardware, and potentially hire IT staff.
- Ongoing maintenance: You’re responsible for software updates, security, and server maintenance.
- Scalability challenges: Scaling the system can be more complex and expensive.
3. Hybrid CRM
A hybrid CRM combines elements of both SaaS and on-premise solutions. You might use a cloud-based CRM for some functions and an on-premise system for others. This offers a balance between flexibility, control, and cost.
- Pros:
- Flexibility: You can choose the best approach for each part of your business.
- Data control: You can keep sensitive data on-premise while using cloud-based features for other functions.
- Cons:
- Complexity: Managing both cloud and on-premise systems can be more complex.
- Integration challenges: Integrating the two systems can require technical expertise.
Breaking Down the Costs: What to Expect
Now, let’s delve into the specific costs you can expect when implementing a CRM system. Remember, these are estimates, and the actual costs will vary depending on your chosen CRM provider, the features you need, and the size of your business.
1. Subscription Fees
As mentioned earlier, subscription fees are the primary cost for SaaS CRM systems. These fees are typically charged per user, per month, or per year. The price can range from free (for very basic CRM solutions) to several hundred dollars per user, per month, for more feature-rich platforms. Factors that influence subscription fees include:
- Number of users: The more users you have, the higher the subscription cost.
- Features: Basic plans usually offer limited features, while premium plans include advanced features like marketing automation, sales forecasting, and advanced reporting.
- Storage: Some CRM providers charge extra for storage space.
- Support: The level of support you receive can also affect the price.
When evaluating subscription fees, carefully assess your needs and choose a plan that provides the features you require without paying for unnecessary extras. Consider the long-term cost and whether the features justify the expense.
2. Implementation Costs
Implementing a CRM system involves setting up the software, migrating your data, and training your team. Implementation costs can vary widely depending on the complexity of the system and the level of support you need. These costs can include:
- Data migration: Transferring your existing customer data from spreadsheets, databases, or other systems to the CRM. This can be time-consuming and may require specialized tools or services.
- Customization: Adapting the CRM to meet your specific business needs. This may involve configuring workflows, creating custom fields, and integrating with other systems.
- Training: Providing training to your team on how to use the CRM. This can involve online tutorials, in-person training sessions, or a combination of both.
- Consulting fees: Hiring a CRM consultant to help with the implementation process. Consultants can provide expert advice, streamline the implementation process, and ensure that you get the most out of your CRM.
To minimize implementation costs, consider the following tips:
- Choose a CRM that’s easy to implement: Look for a CRM with a user-friendly interface and intuitive setup process.
- Plan your implementation carefully: Define your goals, identify your requirements, and create a detailed implementation plan.
- Use online resources: Take advantage of online tutorials, documentation, and support forums.
- Consider phased implementation: Implement the CRM in phases, starting with the most critical features and gradually adding more functionality.
3. Ongoing Costs
In addition to subscription fees and implementation costs, there are ongoing costs associated with using a CRM system. These costs can include:
- Maintenance and support: The CRM provider may charge fees for ongoing maintenance, support, and updates.
- Integrations: Integrating the CRM with other systems, such as your email marketing platform or accounting software, may involve additional costs.
- Add-ons: Some CRM systems offer add-ons or plugins that provide additional functionality. These add-ons may come with a separate fee.
- Hardware costs (for on-premise systems): If you’re using an on-premise CRM, you’ll need to budget for hardware maintenance, upgrades, and replacements.
When evaluating ongoing costs, consider the long-term implications. Factor in the cost of maintenance, support, integrations, and any potential add-ons. Choose a CRM that offers a balance between functionality and affordability.
Free CRM Options: Are They Right for You?
For small businesses on a tight budget, free CRM options can be tempting. These systems typically offer basic features and are a good starting point for businesses that are new to CRM. However, it’s important to understand the limitations of free CRM systems.
- Limited features: Free CRM systems usually offer a limited set of features compared to paid plans.
- Storage restrictions: You may have limited storage space for your data.
- User limitations: Free plans often restrict the number of users you can have.
- Support limitations: Free plans may offer limited or no support.
- Branding: Some free CRM systems include their branding in your interface.
While free CRM systems can be a good option for very small businesses or startups with basic needs, they may not be suitable for businesses that require advanced features, extensive storage, or dedicated support. As your business grows, you’ll likely need to upgrade to a paid plan.
Tips for Reducing CRM Costs
Implementing a CRM system doesn’t have to break the bank. Here are some tips for reducing CRM costs:
- Start small: Begin with a basic plan and add features as your needs evolve.
- Choose a cloud-based CRM: Cloud-based CRM systems typically have lower upfront costs than on-premise solutions.
- Negotiate pricing: Don’t be afraid to negotiate with CRM providers, especially if you’re committing to a long-term contract.
- Take advantage of free trials: Test out different CRM systems before committing to a paid plan.
- Use free resources: Utilize online tutorials, documentation, and support forums to minimize your reliance on paid support.
- Implement the CRM yourself: If you have the technical expertise, consider implementing the CRM yourself to save on consulting fees.
- Optimize your data: Regularly clean up your data to reduce storage costs.
- Focus on essential features: Prioritize the features that are most important to your business and avoid paying for unnecessary extras.
Choosing the Right CRM: Key Considerations
Choosing the right CRM system is crucial for the success of your business. Here are some key considerations to keep in mind:
- Your business needs: Identify your specific requirements, such as sales automation, marketing automation, customer service, or reporting.
- Your budget: Determine how much you’re willing to spend on a CRM system.
- The size of your business: Choose a CRM that’s appropriate for the size of your business.
- Ease of use: Select a CRM with a user-friendly interface and intuitive features.
- Scalability: Choose a CRM that can grow with your business.
- Integration capabilities: Ensure that the CRM integrates with your existing systems, such as your email marketing platform, accounting software, and website.
- Support and training: Look for a CRM provider that offers adequate support and training resources.
- Reviews and ratings: Research different CRM systems and read reviews from other users.
By carefully considering these factors, you can choose a CRM system that meets your business needs and fits your budget.
Top CRM Systems for Small Businesses
Here are some of the top CRM systems for small businesses, categorized by price point and features:
Budget-Friendly Options
- Zoho CRM: Offers a free plan for up to three users and affordable paid plans with a wide range of features.
- HubSpot CRM: Provides a free CRM with unlimited users and a robust set of features. Paid plans offer advanced marketing, sales, and service tools.
- Bitrix24: Offers a free plan with a generous user limit and a variety of features. Paid plans offer more advanced functionality.
Mid-Range Options
- Pipedrive: A sales-focused CRM that’s easy to use and offers a range of features for managing sales pipelines.
- Freshsales: A CRM designed for sales teams, with features like lead scoring, sales automation, and phone integration.
- Insightly: A CRM that’s suitable for small to medium-sized businesses, with features for sales, marketing, and project management.
Premium Options
- Salesforce Sales Cloud: A powerful CRM platform with a wide range of features and customization options.
- Microsoft Dynamics 365: A comprehensive CRM and ERP platform that integrates with other Microsoft products.
- Oracle NetSuite CRM: A cloud-based CRM that’s suitable for businesses of all sizes.
Remember to research each CRM system and compare its features, pricing, and reviews to determine which one is the best fit for your business.
The Bottom Line: Investing in Your Future
Implementing a CRM system is an investment in your business’s future. While the initial cost may seem daunting, the benefits of improved customer relationships, increased sales, and enhanced productivity far outweigh the expense. By understanding the different cost models, carefully evaluating your needs, and following the tips outlined in this guide, you can find a CRM system that fits your budget and helps you achieve your business goals. Don’t let the fear of CRM cost hold you back. Embrace the power of CRM and watch your small business thrive!
Choosing a CRM is a significant decision, but it’s an investment that can pay off handsomely. Take your time, do your research, and select a system that aligns with your business goals and financial constraints. Remember, the right CRM can be a game-changer, helping you build stronger customer relationships, streamline your sales process, and drive sustainable growth.