Small Business CRM Cost Guide: Find the Perfect CRM Without Breaking the Bank

Small Business CRM Cost Guide: Navigating the CRM Landscape Without Overspending
Running a small business is a whirlwind of activity. You’re juggling customer interactions, sales pipelines, marketing campaigns, and a whole host of other responsibilities. In the midst of this chaos, a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system can be your saving grace. But with so many CRM options available, figuring out the cost can feel like navigating a minefield. This comprehensive guide will break down everything you need to know about small business CRM costs, helping you find the perfect solution without blowing your budget. We’ll explore pricing models, features, hidden costs, and how to make an informed decision that aligns with your business needs.
What is a CRM and Why Does Your Small Business Need One?
Before we dive into the financials, let’s quickly recap what a CRM is and why it’s essential for small businesses. A CRM is essentially a centralized hub for all your customer-related information. It helps you manage interactions, track leads, automate tasks, and ultimately, build stronger customer relationships. Think of it as your digital assistant, keeping track of everything from initial contact to post-sale support.
Here’s a glimpse of the benefits a CRM can bring to your small business:
- Improved Customer Relationships: CRM systems provide a 360-degree view of your customers, allowing you to personalize interactions and provide better service.
- Increased Sales: By streamlining the sales process and providing valuable insights, CRM systems can help you close more deals.
- Enhanced Efficiency: CRM automates repetitive tasks, freeing up your time to focus on more strategic activities.
- Better Data Analysis: CRM systems provide valuable data on customer behavior, sales trends, and marketing performance, enabling you to make data-driven decisions.
- Improved Collaboration: CRM systems facilitate better communication and collaboration between team members, ensuring everyone is on the same page.
Understanding CRM Pricing Models
CRM pricing can be complex, with various models available. Understanding these models is crucial to accurately assess the total cost of ownership. Here’s a breakdown of the most common pricing models:
1. Per-User, Per-Month Pricing
This is the most common pricing model. You pay a monthly fee for each user who has access to the CRM. The price per user can vary significantly depending on the features included and the vendor. This model is often scalable, allowing you to easily add or remove users as your business grows.
Pros:
- Predictable costs
- Easy to scale
- Often includes a range of features
Cons:
- Can be expensive if you have a large team
- You pay for users who may not actively use the system
2. Tiered Pricing
Tiered pricing offers different plans with varying features and user limits. Each tier comes with a different price point. This model allows you to choose a plan that best suits your needs and budget. Typically, the higher the tier, the more features and users are included.
Pros:
- Offers flexibility and choice
- Allows you to scale features as your business grows
- Can be cost-effective for businesses with specific needs
Cons:
- Can be confusing to compare different plans
- May require upgrading to a higher tier as your business grows
3. Usage-Based Pricing
With usage-based pricing, you pay based on the amount of resources you consume, such as the number of contacts, emails sent, or storage used. This model is often used for CRM systems with extensive marketing automation features.
Pros:
- Cost-effective for businesses with fluctuating needs
- You only pay for what you use
Cons:
- Can be difficult to predict costs
- May become expensive if usage increases unexpectedly
4. Freemium Pricing
Freemium models offer a basic version of the CRM for free, with limited features and user limits. You can then upgrade to a paid plan for more advanced features and increased capacity. This is a great way to test out a CRM before committing to a paid subscription.
Pros:
- Free to start
- Allows you to test the CRM before paying
- Can be a good option for very small businesses
Cons:
- Limited features in the free version
- May require upgrading to a paid plan as your business grows
5. On-Premise Pricing
This model involves purchasing a license for the CRM software and installing it on your own servers. You typically pay a one-time license fee and ongoing maintenance costs. This option gives you more control over your data and customization options, but it also requires more technical expertise and upfront investment.
Pros:
- More control over data and customization
- Potentially lower long-term costs for very large businesses
Cons:
- High upfront costs
- Requires technical expertise to manage
- Ongoing maintenance and support costs
Breaking Down the Costs: What to Expect
Now that we’ve covered the pricing models, let’s delve into the specific costs associated with CRM systems. These costs can be broadly categorized into the following:
1. Software Subscription Fees
This is the most obvious cost and often the most significant. It’s the recurring fee you pay to access the CRM software. As mentioned earlier, this is typically charged on a per-user, per-month basis, but it can also be tiered or usage-based.
Factors that influence subscription fees include:
- Number of Users: The more users you have, the higher the cost.
- Features: More advanced features, such as marketing automation, sales forecasting, and advanced reporting, will typically increase the price.
- Vendor: Different CRM vendors have different pricing structures and price points.
- Contract Length: Some vendors offer discounts for annual or multi-year contracts.
2. Implementation Costs
Implementing a CRM system involves setting up the software, configuring it to your specific needs, and importing your existing data. Implementation costs can vary significantly depending on the complexity of your business and the CRM system you choose.
These costs can include:
- Setup Fees: Some vendors charge a one-time setup fee to get you up and running.
- Data Migration: Importing your existing customer data into the CRM can be time-consuming and may require professional assistance.
- Customization: Customizing the CRM to fit your specific business processes may require development work.
- Training: Training your team on how to use the CRM is essential for successful adoption.
3. Ongoing Maintenance and Support Costs
Once your CRM is up and running, you’ll need to budget for ongoing maintenance and support. These costs can include:
- Support Fees: Many vendors offer different levels of support, from basic email support to premium phone support.
- Updates and Upgrades: CRM vendors regularly release updates and upgrades to improve the software and add new features.
- Integration Costs: Integrating your CRM with other business applications, such as your email marketing platform or accounting software, may incur additional costs.
- IT Support: If you’re using an on-premise CRM, you’ll need to budget for IT support to maintain the servers and infrastructure.
4. Hidden Costs to Watch Out For
Beyond the obvious costs, there are some hidden costs that can catch you off guard. Being aware of these can help you avoid budget surprises.
- Data Storage Limits: Some CRM systems have data storage limits. If you exceed these limits, you may be charged extra.
- API Usage Fees: If you integrate your CRM with other applications, you may be charged for API usage.
- Add-ons and Integrations: Certain features or integrations may require additional subscriptions or fees.
- Training and Documentation: While some vendors include training, others may charge extra for it. Make sure to factor in the cost of training your team.
- Downtime: Although rare, downtime can impact your business. Factor in the potential cost of lost productivity.
Choosing the Right CRM for Your Small Business: Key Considerations
Choosing the right CRM is a crucial decision that can significantly impact your business’s success. Here are some key considerations to help you make the right choice:
1. Define Your Needs and Goals
Before you start comparing CRM systems, take the time to define your needs and goals. What do you want to achieve with a CRM? What are your pain points? What features are essential for your business? Knowing your requirements will help you narrow down your options and choose a CRM that fits your specific needs.
Consider these questions:
- What are your current customer management processes?
- What data do you need to track?
- What are your sales and marketing goals?
- What is your budget?
- How many users will need access to the CRM?
2. Assess Your Budget
Determine your budget and stick to it. Consider all the costs involved, including subscription fees, implementation costs, and ongoing maintenance. Don’t be tempted to overspend on features you don’t need. Focus on finding a CRM that meets your core requirements within your budget.
When assessing your budget, consider:
- Your monthly or annual budget for the CRM.
- Any one-time setup or implementation fees.
- Costs for training and support.
- Potential costs for add-ons or integrations.
3. Research Different CRM Vendors
Once you have a clear understanding of your needs and budget, start researching different CRM vendors. Compare their features, pricing, and reviews. Look for vendors that offer a free trial or a free plan so you can test the software before committing to a paid subscription.
Consider these factors when researching vendors:
- Features: Does the CRM offer the features you need, such as contact management, sales automation, marketing automation, and reporting?
- Pricing: Does the pricing model fit your budget and business needs?
- Ease of Use: Is the CRM easy to use and navigate?
- Integrations: Does the CRM integrate with other business applications you use, such as your email marketing platform and accounting software?
- Customer Support: Does the vendor offer good customer support?
- Reviews: Read reviews from other small businesses to get an idea of their experiences with the CRM.
4. Consider Scalability
Choose a CRM that can scale with your business. As your business grows, you’ll need a CRM that can accommodate more users, more data, and more features. Make sure the CRM you choose offers the flexibility to upgrade to higher tiers or add more users as needed.
5. Prioritize User-Friendliness
A CRM is only effective if your team actually uses it. Choose a CRM that is easy to use and navigate. The user interface should be intuitive and user-friendly. If the CRM is too complex, your team may be reluctant to use it, and you won’t realize the full benefits.
6. Evaluate Integration Capabilities
Consider how well the CRM integrates with other business applications you use. Integration capabilities can streamline your workflow and improve efficiency. Look for a CRM that integrates with your email marketing platform, accounting software, and other essential tools.
7. Data Security and Privacy
Data security and privacy are paramount. Choose a CRM that has robust security measures in place to protect your customer data. Look for vendors that comply with industry standards and regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA.
Top CRM Systems for Small Businesses: A Quick Overview
Here’s a glimpse at some popular CRM systems suitable for small businesses. Remember, the best choice depends on your specific needs and budget. This is not an exhaustive list, but it provides a starting point for your research.
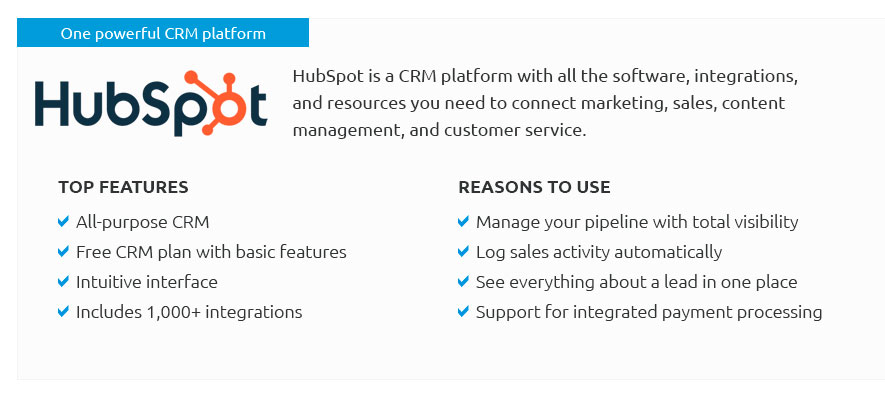
1. HubSpot CRM
HubSpot CRM is a popular choice for small businesses due to its free plan and user-friendly interface. It offers a range of features, including contact management, sales automation, and marketing tools. HubSpot’s pricing is based on a tiered system, with more advanced features available in the paid plans.
Pros:
- Free plan available
- User-friendly interface
- Comprehensive features
- Excellent for marketing automation
Cons:
- Limited features in the free plan
- Can be expensive for advanced features
2. Zoho CRM
Zoho CRM is a feature-rich CRM system that offers a range of plans, including a free plan for up to three users. It’s a good option for businesses that need a comprehensive CRM solution at a reasonable price. Zoho CRM offers a wide range of integrations with other Zoho apps and third-party applications.
Pros:
- Free plan available
- Feature-rich
- Competitive pricing
- Strong integration capabilities
Cons:
- Interface can be overwhelming for some users
- Customer support can be improved
3. Freshsales
Freshsales is a sales-focused CRM system that is designed to help businesses close more deals. It offers features such as lead scoring, sales automation, and built-in phone and email integration. Freshsales offers a free plan and paid plans that are competitively priced.
Pros:
- Sales-focused features
- User-friendly interface
- Competitive pricing
- Excellent customer support
Cons:
- Marketing automation features are limited
- Can be less flexible than other CRM systems
4. Pipedrive
Pipedrive is a sales-focused CRM system that is designed to help salespeople manage their sales pipeline and close deals. It offers a visual interface and a user-friendly experience. Pipedrive is known for its focus on sales and its ease of use.
Pros:
- User-friendly interface
- Visual sales pipeline
- Excellent for sales teams
- Easy to learn and use
Cons:
- Limited features for marketing automation
- Can be more expensive than other CRM systems
5. Agile CRM
Agile CRM is an all-in-one CRM system that offers a range of features, including sales automation, marketing automation, and help desk. It offers a free plan and paid plans that are competitively priced. Agile CRM is a good option for businesses that need a comprehensive CRM solution at an affordable price.
Pros:
- All-in-one features
- Affordable pricing
- Good for small businesses
- Marketing automation capabilities
Cons:
- Interface can be less intuitive than other CRM systems
- Customer support can be slow
Tips for Reducing CRM Costs
While CRM systems are an investment, there are ways to minimize costs without sacrificing functionality. Here are some tips to help you save money:
- Start with a Free Plan: If possible, start with a free plan to test the CRM and see if it meets your needs.
- Choose the Right Plan: Carefully evaluate your needs and choose a plan that includes only the features you need. Don’t overspend on features you won’t use.
- Negotiate Pricing: Don’t be afraid to negotiate pricing with the vendor, especially if you’re signing up for an annual or multi-year contract.
- Take Advantage of Discounts: Look for discounts, such as discounts for non-profits or educational institutions.
- Train Your Team Effectively: Proper training can reduce the need for costly support and help you get the most out of your CRM.
- Optimize Your Data: Clean up your data and remove any unnecessary contacts to reduce storage costs.
- Explore Open-Source Options: Consider open-source CRM systems if you have the technical expertise to manage them.
- Integrate Wisely: Only integrate the applications you truly need to avoid unnecessary integration costs.
The Bottom Line: Making the Smart CRM Investment
Choosing the right CRM for your small business is a significant decision, and the cost is a crucial factor. By understanding the different pricing models, breaking down the costs, and carefully considering your needs and budget, you can find a CRM solution that helps you build stronger customer relationships, increase sales, and streamline your operations without breaking the bank. Remember to prioritize your needs, research your options, and choose a CRM that aligns with your long-term goals. The right CRM is an investment that can pay dividends for years to come.
Don’t be afraid to experiment, read reviews, and take advantage of free trials. The perfect CRM is out there, waiting to help your small business thrive. By taking the time to understand the costs and benefits, you can make a smart investment that will propel your business forward.