Small Business CRM Implementation: A Step-by-Step Guide to Boost Customer Relationships and Sales

Small Business CRM Implementation: A Step-by-Step Guide to Boost Customer Relationships and Sales
Embarking on the journey of implementing a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system can feel like a daunting task for small businesses. However, the benefits – enhanced customer relationships, streamlined sales processes, and ultimately, increased revenue – are well worth the effort. This comprehensive guide provides a step-by-step approach to CRM implementation, specifically tailored for small businesses, ensuring a smooth transition and successful adoption. We’ll delve into everything from selecting the right CRM to training your team and optimizing your system for peak performance. Get ready to transform how you interact with your customers and drive your business forward!
Chapter 1: Understanding the Importance of CRM for Small Businesses
Before diving into the ‘how,’ let’s address the ‘why.’ Why is CRM so crucial for small businesses? The answer lies in the core of any successful enterprise: building and nurturing strong customer relationships. In today’s competitive landscape, simply having a great product or service isn’t enough. You need to understand your customers, anticipate their needs, and provide exceptional experiences. CRM empowers you to do just that.
1.1 The Benefits of CRM
Implementing a CRM offers a multitude of advantages:
- Improved Customer Relationships: CRM centralizes customer data, providing a 360-degree view of each customer. This allows you to personalize interactions, address concerns promptly, and build stronger, more loyal relationships.
- Enhanced Sales Process: CRM automates many sales tasks, such as lead generation, contact management, and follow-up reminders. This frees up your sales team to focus on closing deals and driving revenue.
- Increased Efficiency: CRM streamlines workflows and eliminates manual processes, saving time and reducing the risk of errors.
- Better Data Analysis: CRM provides valuable insights into customer behavior, sales performance, and marketing effectiveness. This data allows you to make informed decisions and optimize your strategies.
- Improved Communication: CRM facilitates seamless communication across departments, ensuring everyone is on the same page regarding customer interactions.
- Scalability: CRM systems are designed to grow with your business. As your company expands, your CRM can adapt to handle increased data volume and user needs.
1.2 Common Challenges Faced by Small Businesses
While the benefits of CRM are undeniable, small businesses often face specific challenges when implementing these systems:
- Budget Constraints: The cost of CRM software can be a barrier for some small businesses.
- Lack of Technical Expertise: Many small businesses lack dedicated IT staff to manage and maintain a CRM system.
- Time Constraints: Implementing a CRM requires time for planning, data migration, training, and ongoing maintenance.
- Employee Resistance: Some employees may resist adopting a new system, especially if they are accustomed to existing processes.
This guide will address these challenges and provide practical solutions to ensure a successful CRM implementation.
Chapter 2: Choosing the Right CRM System for Your Small Business
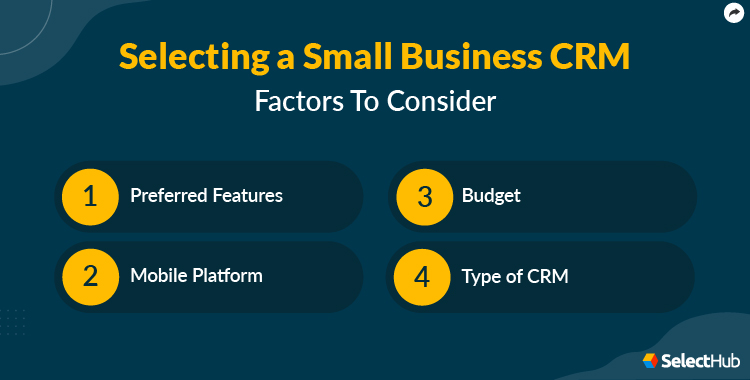
Selecting the right CRM is a critical first step. There’s a vast array of options available, each with its own features, pricing, and target audience. Choosing the wrong system can lead to frustration, wasted resources, and a failed implementation. Here’s how to choose the perfect fit:
2.1 Define Your Needs and Goals
Before you even look at software, take the time to understand your specific needs and goals. What problems are you trying to solve? What do you hope to achieve with a CRM? Consider the following:
- Customer Relationship Goals: Do you want to improve customer service, personalize interactions, or increase customer loyalty?
- Sales Process Goals: Do you want to automate lead generation, improve sales forecasting, or track sales performance?
- Marketing Goals: Do you want to manage email campaigns, track marketing ROI, or segment your customer base?
- Team Needs: What features and functionalities do your sales, marketing, and customer service teams need?
- Budget: How much are you willing to spend on software, implementation, and ongoing maintenance?
Document your needs and goals. This will serve as a roadmap for your selection process.
2.2 Research CRM Software Options
Once you have a clear understanding of your needs, it’s time to research the available CRM solutions. Consider the following factors:
- Features: Does the software offer the features you need, such as contact management, sales automation, email marketing, and reporting?
- Ease of Use: Is the software user-friendly and intuitive? A complex system will be difficult for your team to adopt.
- Integration: Does the software integrate with your existing tools, such as email, accounting software, and marketing automation platforms?
- Pricing: Does the pricing model fit your budget? Consider the cost of software, implementation, and ongoing maintenance.
- Scalability: Can the software scale to meet your needs as your business grows?
- Customer Support: Does the vendor offer reliable customer support?
- Reviews and Ratings: Read reviews from other small businesses to get insights into the software’s strengths and weaknesses.
Some popular CRM options for small businesses include:
- Zoho CRM: A comprehensive and affordable CRM with a wide range of features.
- HubSpot CRM: A free CRM with powerful marketing and sales tools.
- Salesforce Sales Cloud: A robust CRM with advanced features, suitable for growing businesses.
- Pipedrive: A sales-focused CRM with a user-friendly interface.
- Freshsales: A sales CRM with built-in phone and email features.
2.3 Request Demos and Trials
Narrow down your options to a few top contenders and request demos or free trials. This will allow you to:
- Get a Hands-On Experience: Test the software’s features and functionality firsthand.
- Evaluate the User Interface: See how easy it is to navigate and use the software.
- Assess the Customer Support: Contact the vendor’s support team to gauge their responsiveness and helpfulness.
- Ask Specific Questions: Address any questions or concerns you have about the software.
2.4 Make Your Decision
After evaluating the demos and trials, make your final decision. Choose the CRM that best meets your needs, goals, and budget. Don’t be afraid to start small and scale up as your business grows.
Chapter 3: Planning Your CRM Implementation
With your CRM selected, it’s time to plan your implementation. A well-defined plan will ensure a smooth transition and minimize disruptions.
3.1 Define Your Implementation Scope
Determine the scope of your implementation. What features will you implement initially? What data will you migrate? Start with the core features and data that are essential for your business. You can always add more features and data later.
3.2 Assemble Your Implementation Team
Form a dedicated implementation team, including representatives from sales, marketing, customer service, and IT (if available). Assign roles and responsibilities, such as project manager, data migration specialist, and training coordinator.
3.3 Data Migration Strategy
Develop a data migration strategy. This involves identifying the data you need to migrate, cleaning and organizing the data, and importing it into the CRM. Consider the following:
- Data Sources: Identify all data sources, such as spreadsheets, databases, and existing CRM systems.
- Data Cleaning: Clean and standardize your data to ensure accuracy and consistency. This may involve removing duplicates, correcting errors, and formatting data.
- Data Mapping: Map your data fields to the corresponding fields in the CRM.
- Data Import: Import your data into the CRM. Most CRM systems offer data import tools or integrations with data migration services.
3.4 Customize Your CRM
Customize your CRM to meet your specific business needs. This may involve:
- Configuring Settings: Configure the CRM’s settings, such as user roles, security settings, and notification preferences.
- Creating Custom Fields: Create custom fields to store unique data that is relevant to your business.
- Designing Workflows: Design workflows to automate tasks, such as lead assignment, follow-up reminders, and email campaigns.
- Integrating with Other Tools: Integrate your CRM with other tools, such as email, accounting software, and marketing automation platforms.
3.5 Develop a Training Plan
Develop a comprehensive training plan to ensure that your team is comfortable using the CRM. This should include:
- Training Materials: Create training materials, such as user manuals, video tutorials, and quick reference guides.
- Training Sessions: Conduct training sessions for your team, covering the CRM’s features, functionality, and best practices.
- Ongoing Support: Provide ongoing support to your team, such as answering questions, troubleshooting issues, and providing refresher training.
3.6 Set a Timeline and Budget
Establish a realistic timeline and budget for your implementation. This will help you track progress and stay on schedule. Consider the following:
- Implementation Phases: Break down the implementation into phases, such as planning, data migration, customization, and training.
- Milestones: Set milestones for each phase to track progress.
- Budget Allocation: Allocate your budget for software, implementation services, training, and ongoing maintenance.
Chapter 4: Implementing Your CRM: Step-by-Step Guide
Now for the exciting part – the actual implementation! Follow these steps to bring your CRM to life:
4.1 Data Preparation and Migration
Careful data preparation is the foundation for a successful CRM. Follow these steps:
- Data Audit: Review your existing customer data. Identify duplicates, inaccuracies, and outdated information.
- Data Cleaning: Clean your data. Standardize formats, correct errors, and remove irrelevant information.
- Data Formatting: Format your data to match the CRM’s requirements.
- Data Import: Import your data into the CRM using the tools provided. Test the import with a small sample before importing the entire dataset.
4.2 CRM Customization
Tailor your CRM to fit your unique business needs:
- User Roles and Permissions: Define user roles and assign permissions to control access to data and features.
- Custom Fields: Create custom fields to capture specific data relevant to your business.
- Workflow Automation: Set up automated workflows for tasks like lead assignment, follow-up emails, and task creation.
- Integrations: Connect your CRM with other tools like email marketing platforms, accounting software, and social media accounts.
4.3 User Training and Adoption
Successful CRM adoption depends on effective training and support:
- Training Sessions: Conduct training sessions for all users. Cover essential features, best practices, and how to use the CRM in their daily tasks.
- Documentation: Provide user manuals, quick reference guides, and video tutorials.
- Ongoing Support: Offer ongoing support through FAQs, help desk, and internal champions.
- Encourage Adoption: Promote the benefits of the CRM and encourage users to embrace the new system. Address any concerns or resistance promptly.
4.4 Testing and Go-Live
Before launching the CRM to your entire team, thorough testing is crucial:
- Test Data: Test the CRM with sample data to ensure everything works as expected.
- User Acceptance Testing (UAT): Involve key users in testing the system. Gather feedback and make any necessary adjustments.
- Go-Live Strategy: Plan your go-live strategy. Consider a phased rollout or a ‘big bang’ approach, depending on your needs.
- Monitor and Support: After go-live, monitor the system closely. Provide immediate support to users and address any issues that arise.
4.5 Ongoing Maintenance and Optimization
CRM implementation is not a one-time event. Continuous maintenance and optimization are essential for long-term success:
- Regular Data Updates: Keep your data clean and up-to-date by regularly reviewing and updating it.
- Performance Monitoring: Monitor the CRM’s performance and address any slowdowns or issues.
- User Feedback: Gather feedback from users and make adjustments to the system as needed.
- Feature Updates: Stay informed about new features and updates and implement them to improve the CRM’s functionality.
Chapter 5: Training Your Team for CRM Success
Your team’s ability to effectively use the CRM is directly proportional to your CRM’s success. Proper training is non-negotiable. Let’s explore how to train your team for optimal CRM utilization.
5.1 Develop a Training Plan
A structured training plan is the cornerstone of successful CRM adoption. Your plan should include:
- Training Objectives: Clearly define what you want your team to learn.
- Target Audience: Tailor the training to the specific roles and responsibilities of each team member.
- Training Methods: Use a combination of methods, such as in-person training, online tutorials, and hands-on exercises.
- Training Schedule: Schedule training sessions at convenient times and ensure adequate time for practice and questions.
- Training Materials: Develop user manuals, quick reference guides, and video tutorials.
5.2 Training Content
Your training content should cover the following key areas:
- CRM Overview: Introduce the CRM and its benefits. Explain how it will help them in their daily tasks.
- Navigation: Teach users how to navigate the CRM, find information, and use the main features.
- Data Entry: Provide detailed instructions on how to enter data accurately and efficiently.
- Workflow Automation: Explain how to use automated workflows to save time and improve productivity.
- Reporting and Analytics: Show users how to generate reports and analyze data to make informed decisions.
- Best Practices: Share best practices for using the CRM effectively, such as how to manage contacts, track leads, and follow up with customers.
5.3 Training Delivery Methods
Choose the training methods that best suit your team’s learning styles and preferences:
- In-Person Training: Conduct in-person training sessions for a more interactive and personalized learning experience.
- Online Tutorials: Create video tutorials and online courses that users can access at their own pace.
- Hands-On Exercises: Provide hands-on exercises and real-world scenarios to allow users to practice using the CRM.
- Mentoring: Pair experienced users with new users to provide ongoing support and guidance.
- Train-the-Trainer: Identify internal champions who can train other team members and provide ongoing support.
5.4 Post-Training Support
Training doesn’t end with the initial sessions. Ongoing support is essential for ensuring continued CRM success:
- FAQ: Create a frequently asked questions (FAQ) document to answer common questions.
- Help Desk: Set up a help desk or support channel to address user issues.
- Regular Check-ins: Conduct regular check-ins with users to gather feedback and provide ongoing support.
- Refresher Training: Provide refresher training sessions to reinforce key concepts and introduce new features.
- User Groups: Create user groups where team members can share tips, best practices, and ask questions.
5.5 Measuring Training Effectiveness
Evaluate the effectiveness of your training program:
- User Surveys: Collect feedback from users through surveys to assess their understanding and satisfaction with the training.
- Performance Metrics: Track key performance indicators (KPIs), such as data entry accuracy, CRM usage, and sales performance, to measure the impact of the training.
- Feedback Loop: Use the feedback to improve your training program and ensure it meets the needs of your team.
Chapter 6: Maximizing CRM Adoption and Usage
Even with the right CRM and training, achieving full adoption can be a challenge. Here’s how to ensure your team embraces the new system and maximizes its value:
6.1 Communicate the Benefits
Clearly communicate the benefits of using the CRM to your team. Highlight how it will:
- Make Their Jobs Easier: Show them how the CRM will automate tasks, save time, and improve efficiency.
- Improve Customer Relationships: Explain how the CRM will help them build stronger relationships with customers.
- Enhance Sales Performance: Demonstrate how the CRM will help them close more deals and increase their sales.
- Provide Valuable Insights: Show them how the CRM will give them access to valuable data and insights to make informed decisions.
6.2 Lead by Example
Management support is crucial for CRM adoption. Leaders should:
- Use the CRM Themselves: Demonstrate their commitment to the CRM by using it in their daily tasks.
- Encourage Adoption: Encourage team members to use the CRM and provide positive reinforcement.
- Address Resistance: Address any resistance to the CRM and provide support to those who are struggling.
6.3 Make it Easy to Use
A user-friendly CRM is essential for adoption. Ensure that:
- The System is Intuitive: The CRM should be easy to navigate and use.
- Training is Comprehensive: Provide thorough training to ensure that all users know how to use the CRM effectively.
- Support is Readily Available: Offer ongoing support to address any issues or questions.
6.4 Incentivize Usage
Consider incentivizing CRM usage to encourage adoption:
- Set Goals: Set goals for CRM usage, such as the number of contacts added, the number of leads tracked, or the number of tasks completed.
- Reward Success: Reward team members who achieve their CRM usage goals.
- Recognize Top Performers: Recognize and reward team members who are using the CRM effectively.
6.5 Provide Ongoing Feedback
Regular feedback is essential for continuous improvement:
- Gather Feedback: Gather feedback from users about their experience with the CRM.
- Make Adjustments: Make adjustments to the system based on user feedback.
- Communicate Updates: Communicate any updates or changes to the CRM to the team.
Chapter 7: CRM Best Practices for Small Businesses
To truly leverage your CRM, adopting best practices is key. These practices will help you optimize your system and achieve the desired results.
7.1 Data Hygiene
Maintaining clean and accurate data is paramount. Implement the following practices:
- Regular Data Cleansing: Schedule regular data cleansing sessions to remove duplicates, correct errors, and update outdated information.
- Data Validation: Implement data validation rules to ensure that data is entered correctly.
- Standardized Data Entry: Establish standardized data entry procedures to maintain consistency.
7.2 Contact Management
Effective contact management is at the heart of CRM. Follow these best practices:
- Centralized Contact Database: Ensure all customer data is stored in a centralized database.
- Complete Contact Profiles: Capture comprehensive information about each contact, including contact details, interactions, and preferences.
- Segmentation: Segment your contacts based on demographics, behavior, and other relevant criteria.
7.3 Sales Process Automation
Streamline your sales process for increased efficiency:
- Lead Management: Automate lead capture, qualification, and assignment.
- Sales Pipeline Management: Visualize your sales pipeline and track the progress of each deal.
- Automated Follow-Ups: Set up automated follow-up reminders and email sequences.
7.4 Customer Service Excellence
Provide exceptional customer service with these strategies:
- Customer Support Tickets: Use the CRM to manage customer support tickets and track issue resolution.
- Personalized Interactions: Personalize your interactions with customers based on their history and preferences.
- Proactive Communication: Proactively communicate with customers to address their needs and provide updates.
7.5 Reporting and Analytics
Leverage the power of data to make informed decisions:
- Track Key Metrics: Track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as sales revenue, customer satisfaction, and marketing ROI.
- Generate Reports: Generate regular reports to analyze your performance and identify areas for improvement.
- Use Data to Drive Decisions: Use data to make informed decisions about your sales, marketing, and customer service strategies.
Chapter 8: Measuring the ROI of Your CRM
Demonstrating the value of your CRM is important for justifying the investment and ensuring continued support. Here’s how to measure your CRM’s ROI:
8.1 Define Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Identify the specific metrics that are most important to your business. These KPIs will help you track your progress and measure the impact of your CRM. Examples include:
- Sales Revenue: Track the increase in sales revenue after CRM implementation.
- Sales Cycle Length: Measure the reduction in the sales cycle length.
- Lead Conversion Rate: Track the increase in lead conversion rates.
- Customer Retention Rate: Measure the improvement in customer retention rates.
- Customer Satisfaction: Track customer satisfaction scores.
- Marketing ROI: Measure the return on investment for your marketing campaigns.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): Determine if your cost to acquire new customers has decreased.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV): Analyze if the lifetime value of your customers has increased.
- Employee Productivity: Measure any increase in employee productivity.
8.2 Track Your KPIs
Regularly track your KPIs to monitor your progress and identify areas for improvement. Use the CRM’s reporting and analytics features to track these metrics.
8.3 Analyze the Results
Analyze the results of your KPI tracking to determine the impact of your CRM. Compare your performance before and after implementation to assess the improvements.
8.4 Calculate Your ROI
Calculate your ROI by comparing the benefits of your CRM implementation to the costs. This will demonstrate the value of your investment.
ROI = (Benefits – Costs) / Costs
8.5 Communicate Your Success
Share your ROI results with stakeholders to demonstrate the value of your CRM and justify continued investment. Use the data to inform future decisions and optimize your CRM strategy.
Chapter 9: Troubleshooting Common CRM Issues
Even with careful planning and implementation, you may encounter issues. Here’s how to troubleshoot common problems:
9.1 Data Import Problems
If you experience data import issues, consider these steps:
- Check Data Formatting: Ensure your data is formatted correctly for the CRM.
- Review Error Messages: Carefully review any error messages generated during the import process.
- Test with a Sample: Test the import with a small sample of data before importing the entire dataset.
- Contact Support: Contact the CRM vendor’s support team for assistance.
9.2 User Adoption Challenges
If your team is not adopting the CRM, take the following steps:
- Provide Additional Training: Offer additional training to address any knowledge gaps.
- Address Concerns: Address any concerns or resistance to the CRM.
- Lead by Example: Encourage management to use the CRM and demonstrate its value.
- Incentivize Usage: Consider incentivizing CRM usage to encourage adoption.
9.3 Performance Issues
If you experience performance issues, consider these actions:
- Optimize Data: Optimize your data by removing duplicates and correcting errors.
- Review Integrations: Review any integrations with other tools that may be slowing down the system.
- Contact Support: Contact the CRM vendor’s support team for assistance.
9.4 Integration Problems
If you encounter integration problems, try these troubleshooting steps:
- Verify Credentials: Verify your integration credentials.
- Check Compatibility: Ensure that the CRM and the integrated tool are compatible.
- Test the Integration: Test the integration to ensure that data is flowing correctly.
- Contact Support: Contact the CRM vendor’s support team or the support team for the integrated tool.
Chapter 10: The Future of CRM for Small Businesses
The CRM landscape is constantly evolving. Staying informed about the latest trends will help you leverage the power of CRM to its fullest potential.
10.1 Emerging Trends
Keep an eye on these trends:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI-powered CRM features, such as chatbots, predictive analytics, and automated data entry, are becoming more prevalent.
- Mobile CRM: Mobile CRM solutions are becoming increasingly important, allowing users to access CRM data on the go.
- Personalization: CRM systems are becoming more sophisticated in their ability to personalize interactions with customers.
- Integration with Social Media: CRM systems are increasingly integrating with social media platforms.
- Focus on Customer Experience: CRM is evolving to prioritize the customer experience, with a focus on building long-term relationships.
10.2 Staying Ahead
To stay ahead of the curve, consider these strategies:
- Stay Informed: Stay informed about the latest CRM trends by reading industry publications, attending webinars, and attending conferences.
- Evaluate Your CRM Regularly: Regularly evaluate your CRM to ensure it meets your current needs and is aligned with your business goals.
- Embrace New Technologies: Embrace new technologies, such as AI and mobile CRM, to improve your CRM’s functionality.
- Adapt Your Strategy: Adapt your CRM strategy as the landscape evolves.
Implementing a CRM system is a significant investment, but the potential rewards for small businesses are substantial. By following this comprehensive guide, you can navigate the implementation process successfully, build stronger customer relationships, streamline your sales processes, and achieve sustainable growth. Remember that CRM is not just about technology; it’s about fostering a customer-centric culture within your organization. Embrace the journey, and watch your business thrive!